Efficacy of Metformin as Adjuvant Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Treatment Schedule
2.3. Follow-Up Parameters
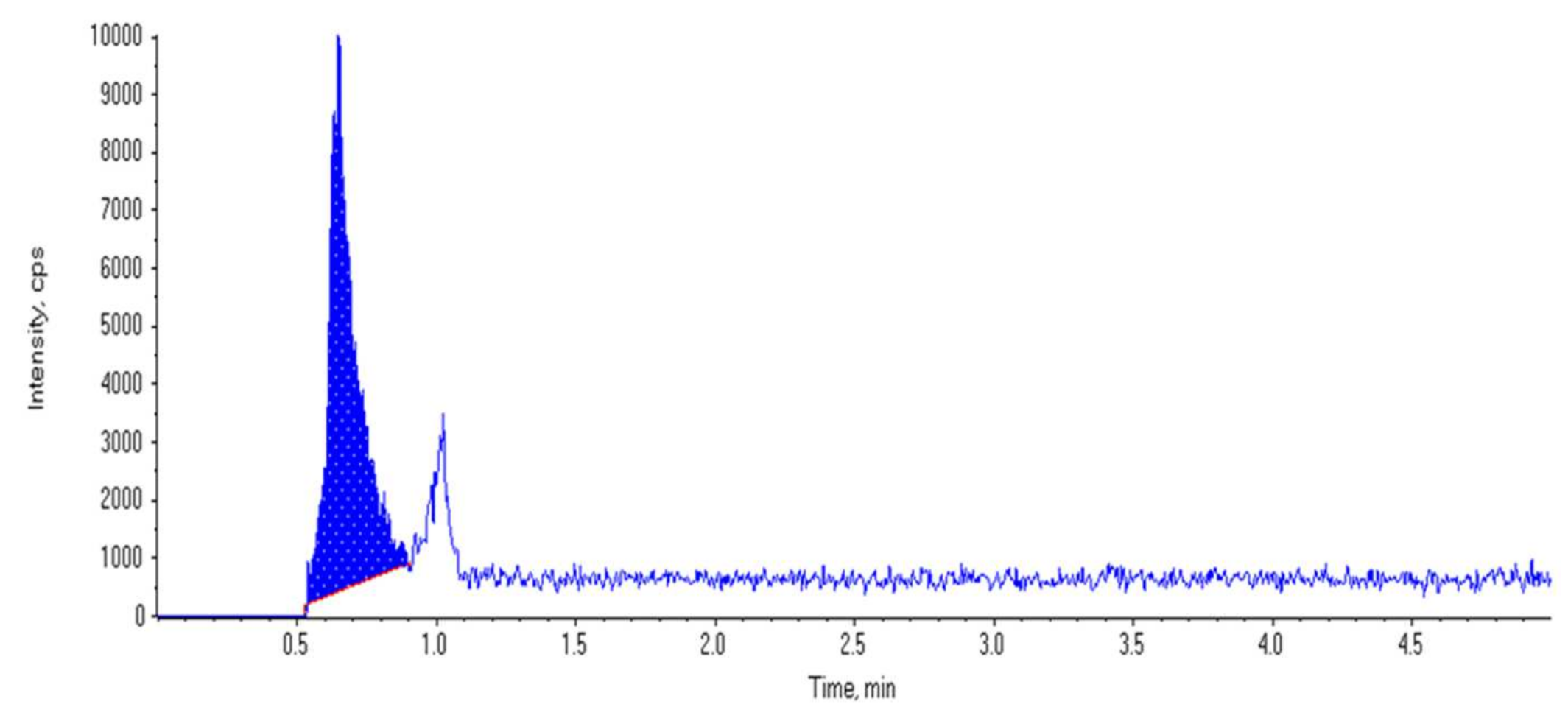
2.3.1. Blood Samples Collection
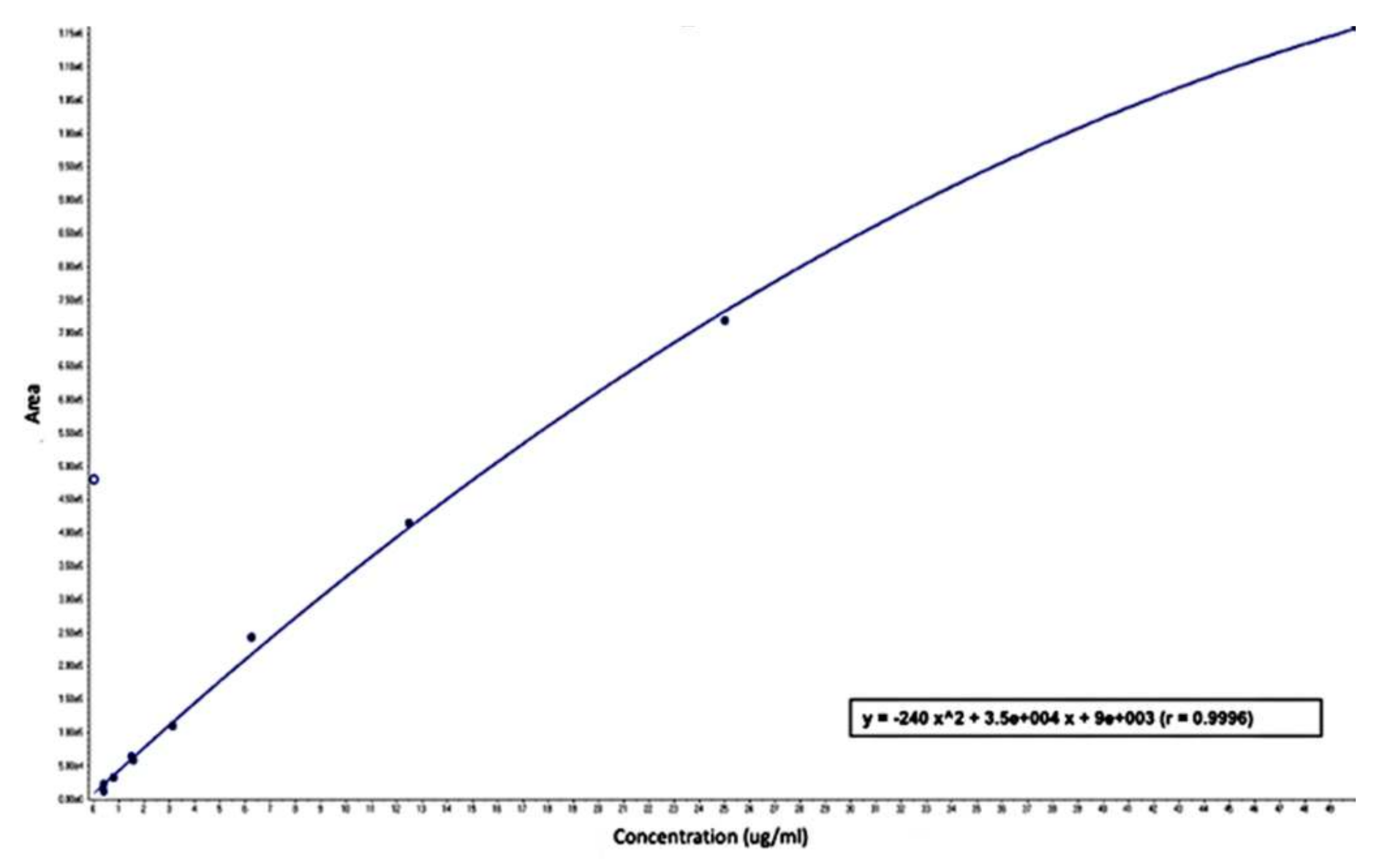
2.3.2. Assessment Method
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Response Rate (RR)
3.3. Toxicity Profile of Metformin
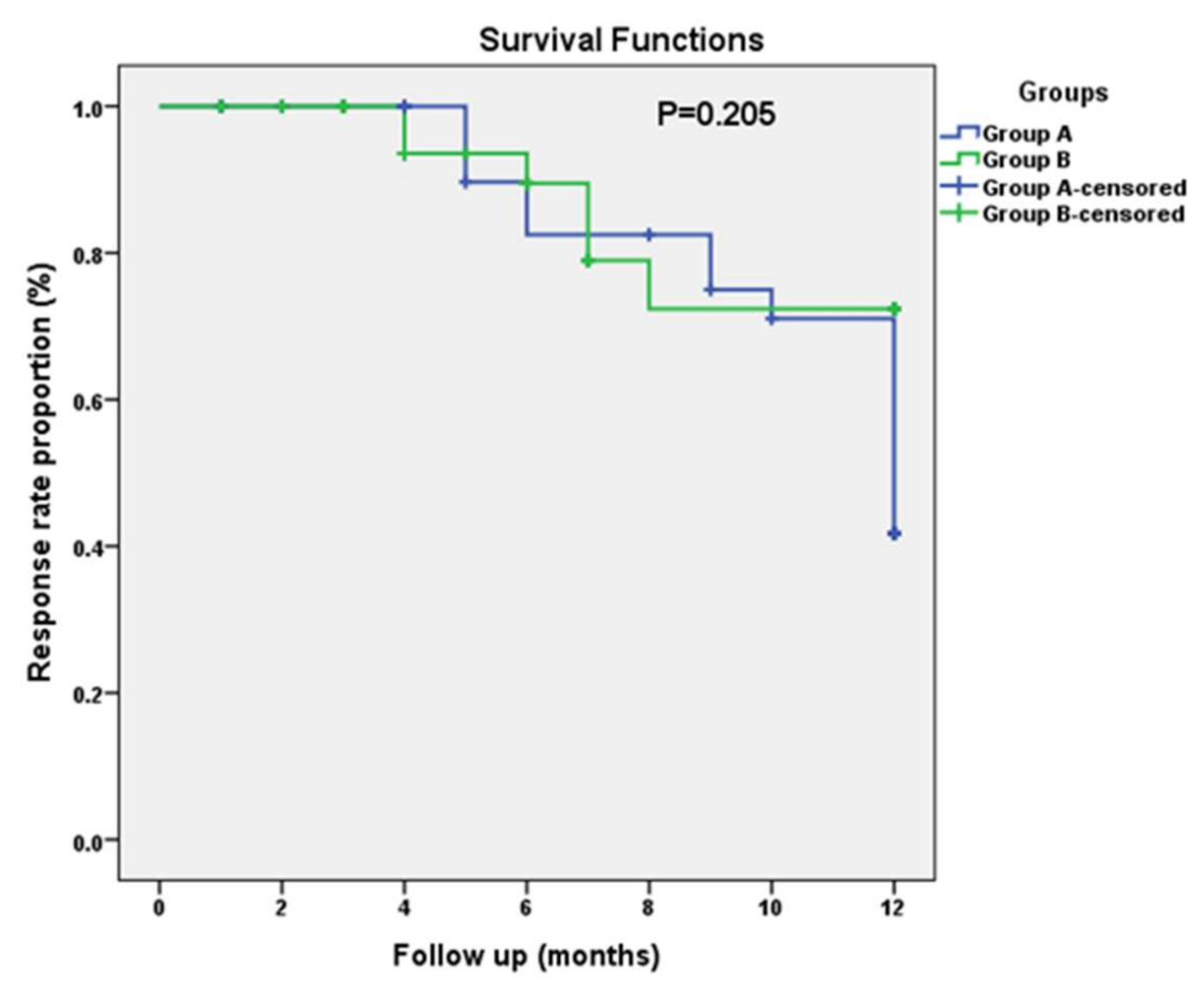
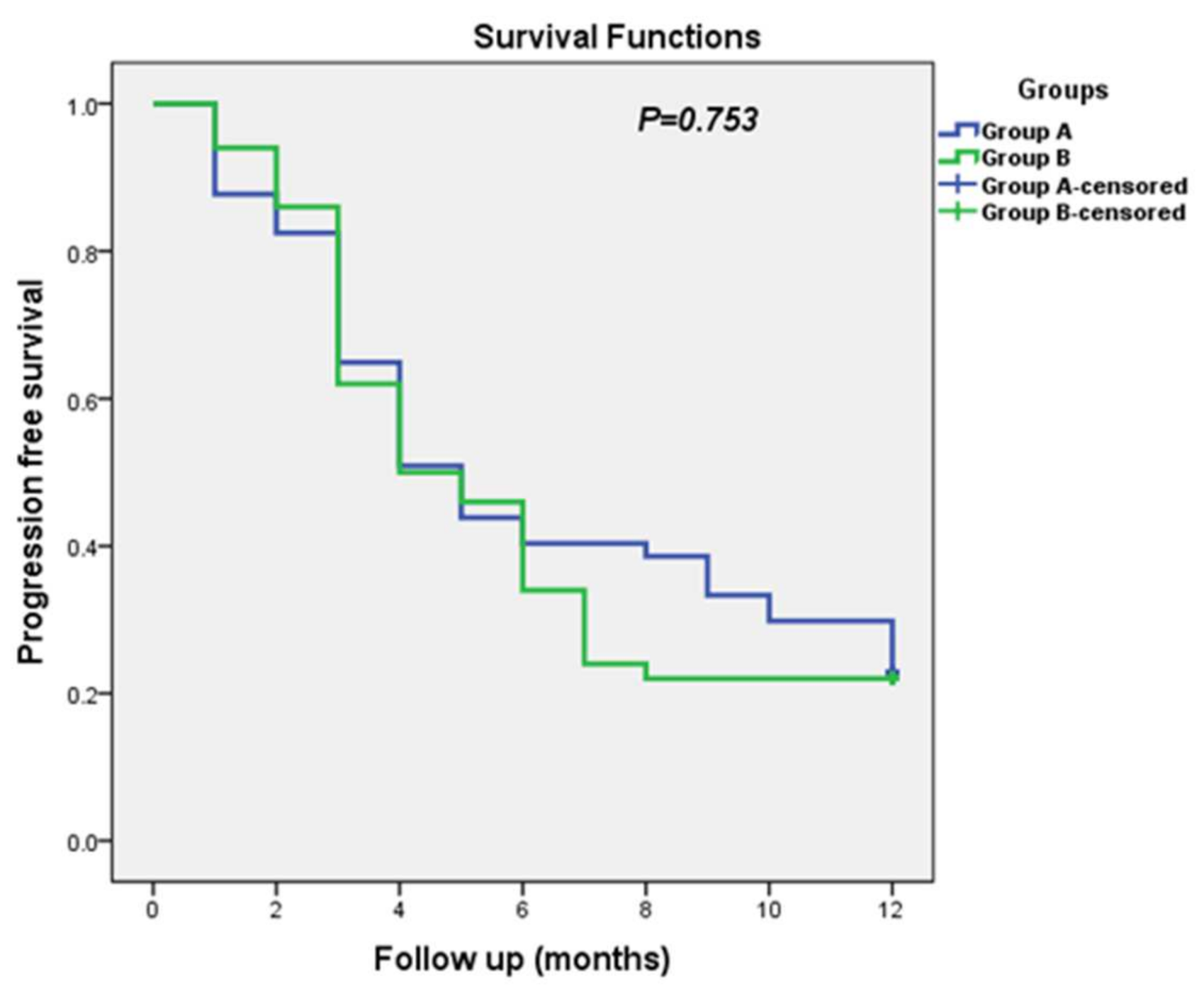
3.4. Progression-Free Survival (PFS)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, N.; Salama, A.; Badawy, O.; Khorshed, E.; Mohamed, G.; Ibrahim, M.; Abdelazim, H. Cancer Pathology Registry 2000–2011; National Cancer Institute Cairo University: Cairo, Egypt, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Kavehie, B. Survival Rates for Breast Cancer in Iranian Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, H. Future treatment strategies for metastatic breast cancer: Curable or incurable? Breast Cancer 2011, 19, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkus, E.; Łacko, A. Metastatic Breast Cancer: Prognosis, Diagnosis and Oncological Management. In Breast Cancer Management for Surgeons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 579–594. [Google Scholar]
- Pollak, M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat. Cancer 2008, 8, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, D.B. Insulin and cancer. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, M.M.; Yuen, J.S.; Protheroe, A.S.; Pollak, M.; Macaulay, V.M. The Type 1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6364–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A. The Role of Insulin Receptor Isoforms and Hybrid Insulin/IGF-I Receptors in Human Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, H.A.; Bahl, A.; Holly, J.M.P.; Perks, C.M. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer: A role for insulin-like growth factor i and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 3? Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2015, 7, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Saraei, P.; Asadi, I.; Kakar, M.A.; Moradi-Kor, N. The beneficial effects of metformin on cancer prevention and therapy: A comprehensive review of recent advances. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3295–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Luo, J.; Yu, T.; Zhou, L.; Lv, H.; Shang, P. Anticancer mechanisms of metformin: A review of the current evidence. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourelis, T.V.; Siegel, R.D. Metformin and cancer: New applications for an old drug. Med. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillane, S.; Bennett, K.; Sharp, L.; Barron, T.I. A Cohort Study of Metformin Exposure and Survival in Patients with Stage I–III Colorectal CancerMetformin and Stage I–III Colorectal Cancer Survival. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From Mechanisms of Action to Therapies. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muaddi, H.; Chowdhury, S.; Vellanki, R.; Zamiara, P.; Koritzinsky, M. Contributions of AMPK and p53 dependent signaling to radiation response in the presence of metformin. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoria, M.J.; Patel, H.; Boros, L.G.; Meuillet, E.J. Metformin and pancreatic cancer metabolism. In Pancreatic Cancer-Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Novel Approaches to Early Detection and Treatment; IntechOpen: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfstein, R.; Friedman, Y.; Attias-Geva, Z.; Fishman, A.; Bruchim, I.; Werner, H. Metformin Downregulates the Insulin/IGF-I Signaling Pathway and Inhibits Different Uterine Serous Carcinoma (USC) Cells Proliferation and Migration in p53-Dependent or -Independent Manners. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasznicki, J.; Sliwinska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Metformin in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zi, F.; Zi, H.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Shi, Q.; Cai, Z. Metformin and cancer: An existing drug for cancer prevention and therapy (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2017, 15, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Metformin: A Therapeutic Opportunity in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morio, K.; Kurata, Y.; Kawaguchi-Sakita, N.; Shiroshita, A.; Kataoka, Y. Efficacy of Metformin in Patients With Breast Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy or Endocrine Therapy: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2022, 56, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, J. The addition of metformin to systemic anticancer therapy in advanced or metastatic cancers: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, K.; Maurer, M.; Lee, S.M.; Crew, K.D.; Trivedi, M.S.; Accordino, M.K.; Hershman, D.L.; Kalinsky, K. Phase 1 Study of Erlotinib and Metformin in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.; Elshahed, M.S.; Nasr, T.; Aboutaleb, N.; Zakaria, O. Novel LC–MS/MS method for analysis of metformin and canagliflozin in human plasma: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, I.; Lohmann, A.E.; Ennis, M.; Dowling, R.J.O.; Elser, D.C.; Potvin, K.R.; Haq, R.; Hamm, C.; Chang, M.C.; Stambolic, V.; et al. A phase II randomized clinical trial of the effect of metformin versus placebo on progression-free survival in women with metastatic breast cancer receiving standard chemotherapy. Breast 2019, 48, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanni, O.; Amadori, D.; de Censi, A.; Rocca, A.; Freschi, A.; Bologna, A.; Gianni, L.; Rosetti, F.; Amaducci, L.; Cavanna, L.; et al. Metformin plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in the first-line treatment of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. MYME Randomized Phase 2 Clin. Trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 174, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.; Ennis, M.; Cescon, D.W.; Elser, C.; Haq, R.; Hamm, C.M.; Lohmann, A.E.; Pimentel, I.; Chang, M.C.; Dowling, R.J.; et al. Abstract P1-16-03: Phase II randomized clinical trial (RCT) of metformin (MET) vs placebo (PLAC) in combination with chemotherapy (CXT) in refractory locally advanced (LABC) or metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Cancer Res. 2019, 79 (Suppl. 4), P1-16-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qu, B.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Gao, P.; Shi, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z. The potential adjunctive benefit of adding metformin to standard treatment in inoperable cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, H.; Hassan, A.; Elberry, A.A. Metformin as an Adjuvant Treatment in Non-Diabetic Metastatic Breast Cancer. Bahrain Med. Bull. 2021, 43, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-C.; Li, G.-Y.; Wang, B.; Han, S.-X.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Y.-N.; Shen, Y.-W.; Zhou, C.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.-Y.; et al. Metformin inhibits metastatic breast cancer progression and improves chemosensitivity by inducing vessel normalization via PDGF-B downregulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannella, V.E.; Pra, A.D.; Muaddi, H.; McKee, T.D.; Stapleton, S.; Sykes, J.; Glicksman, R.; Chaib, S.; Zamiara, P.; Milosevic, M.; et al. Reprogramming metabolism with metformin improves tumor oxygenation and radiotherapy response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6741–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, R.U.; Parker, S.J.; Eichner, L.J.; Kolar, M.J.; Wallace, M.; Brun, S.N.; Lombardo, P.S.; van Nostrand, J.L.; Hutchins, A.; Vera, L.; et al. Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer in preclinical models. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.W.; Lee, H.; Dings, R.P.M.; Williams, B.; Powers, J.; Santos, T.D.; Choi, B.; Park, H.J. Metformin kills and radiosensitizes cancer cells and preferentially kills cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Fan, J.; Wu, K.; Guan, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Hsieh, J.; He, D.; et al. Metformin sensitizes prostate cancer cells to radiation through EGFR/p-DNA-PKCS In vitro and In vivo. Radiat. Res. 2014, 181, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnoli, C.; Pasanisi, P.; Abbà, C.; Ambroggio, S.; Biglia, N.; Brucato, T.; Colombero, R.; Danese, S.; Donadio, M.; Venturelli, E.; et al. Effect of different doses of metformin on serum testosterone and insulin in non-diabetic women with breast cancer: A randomized study. Clin. Breast Cancer 2012, 12, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.J.; Hellberg, K.; Turner, M.; Talbott, G.; Kolar, M.J.; Ross, D.S.; Hoxhaj, G.; Saghatelian, A.; Shaw, R.J.; Manning, B.D. Metformin inhibits hepatic mTORC1 signaling via dose-dependent mechanisms involving AMPK and the TSC complex. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Kuppusamy, G. Metformin in breast cancer: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Meuter, A.; Thapa, P.; Langstraat, C.; Giri, S.; Chien, J.; Rattan, R.; Cliby, W.; Shridhar, V. Metformin intake is associated with better survival in ovarian cancer: A case-control study. Cancer 2013, 119, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.B.A.; Gomes, M.B. Metformin: An old but still the best treatment for type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
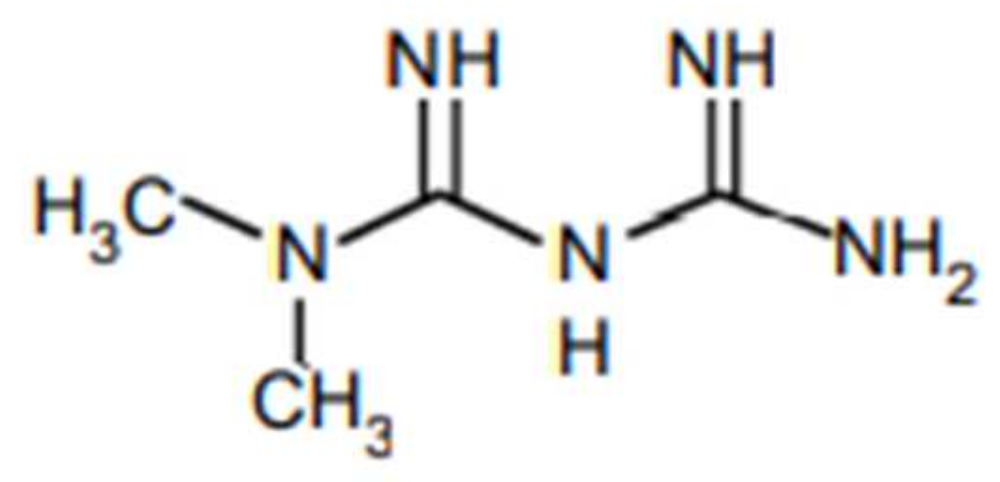
| Variable Name | Group A (CTH + M), n = 57 | Group B (CTH Alone), n = 50 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), Mean ± SD | 49.56 ± 12.53 | 48.40 ± 12.61 | 0.634 * | |||
| Median (range) | 50 (26–75) | 47.5 (27–83) | ||||
| Pathology | (IDC) | 56 | (98.2) | 47 | (94.0) | 0.338 ** |
| (ILC) | 1 | (1.8) | 3 | (6.0) | ||
| Grade | Grade 2 | 55 | (96.5) | 46 | (92.0) | 0.415 *** |
| Grade 3 | 2 | (3.5) | 4 | (8.0) | ||
| Menopausal status | Pre-menopausal | 24 | (42.1) | 29 | (58.0) | 0.101 ** |
| Post-menopausal | 33 | (57.9) | 21 | (42.0) | ||
| (BMI) | <25 | 15 | (26.3) | 21 | (42.0) | 0.058 ** |
| ≥25–<30 | 23 | (40.4) | 10 | (20.0) | ||
| ≥30 | 19 | (33.3) | 19 | (38.0) | ||
| (ER) | Negative | 17 | (29.8) | 19 | (38.0) | 0.372 ** |
| Positive | 40 | (70.2) | 31 | (62.0) | ||
| (PR) | Negative | 25 | (43.9) | 20 | (40.0) | 0.687 ** |
| Positive | 32 | (56.1) | 30 | (60.0) | ||
| Her2neu | Negative | 30 | (52.6) | 30 | (60.0) | 0.444 ** |
| Positive | 27 | (47.4) | 20 | (40.0) | ||
| Luminal A | No | 33 | (57.9) | 26 | (52.0) | 0.541 ** |
| Yes | 24 | (42.1) | 24 | (48.0) | ||
| Luminal B | No | 40 | (70.2) | 41 | (82.0) | 0.155 ** |
| Yes | 17 | (29.8) | 9 | (18.0) | ||
| Her2neu overexpression | No | 47 | (82.5) | 39 | (78.0) | 0.563 ** |
| Yes | 10 | (17.5) | 11 | (22.0) | ||
| Triple negative | No | 51 | (89.5) | 45 | (90.0) | 0.929 *** |
| Yes | 6 | (10.5) | 5 | (10.0) | ||
| CEA, Median (range) | 16.2 (0.5–142.0) | 28.3 (1.9–06.0) | 0.154 **** | |||
| CA 15-3, Median (range) | 39.4 (7.1–241.8) | 28.9 (4.3–413.7) | 0.562 **** | |||
| Variable Name | Group A (CTH + M), n = 57 | Group B (CTH + P), n = 50 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site of Mets | Visceral | 34 | (59.6) | 25 | (50.0) | 0.317 # |
| Non-visceral | 23 | (40.0) | 25 | (50.0) | ||
| No. of Mets | 1 | 14 | (24.6) | 23 | (46.0) | 0.067 # |
| 2 | 30 | (52.6) | 17 | (34.0) | ||
| >2 | 13 | (22.8) | 10 | (20.0) | ||
| Variable Name | Group A (CTH + M), n = 51 | Group B (CTH Alone), n = 47 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response | (RD) | 15 | (29.4) | 6 | (12.8) | 0.068 # |
| (SD) | 23 | (45.1) | 20 | (42.6) | ||
| (PD) | 13 | (25.5) | 21 | (44.7) | ||
| Variable Name | Mean ± SD | p-Value # | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response | RD | 2.41 ± 0.52 | 0.284 |
| SD | 2.13 ± 0.59 | ||
| PD | 2.11 ± 0.63 | ||
| Adverse Events | N | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 21 | (36.8) |
| 19 | (33.3) |
| 14 | (24.6) |
| 14 | (24.6) |
| 10 | (17.5) |
| 10 | (17.5) |
| 8 | (14.0) |
| 7 | (12.3) |
| 7 | (12.3) |
| 6 | (10.5) |
| 5 | (8.8) |
| 5 | (8.8) |
| 5 | (8.8) |
| 0 | (0.0) |
| Side Effects | Metformin Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | p-Value # | ||
| Heartburn | No | 2.19 ± 0.58 | 0.692 |
| Yes | 2.09 ± 0.53 | ||
| Abdominal pain | No | 2.19 ± 0.58 | 0.703 |
| Yes | 2.14 ± 0.57 | ||
| Physical weakness | No | 2.19 ± 0.58 | 0.634 |
| Yes | 1.97 ± 0.33 | ||
| Flatulence | No | 2.19 ± 0.57 | 0.502 |
| Yes | 2.00 ± 0.61 | ||
| Muscle pain | No | 2.16 ± 0.56 | 0.655 |
| Yes | 2.26 ± 0.71 | ||
| URTI | No | 2.16 ± 0.59 | 0.384 |
| Yes | 2.31 ± 0.42 | ||
| Hypoglycemia | No | 2.17 ± 0.57 | - |
| Yes | - | ||
| Diarrhea | No | 2.23 ± 0.58 | 0.290 |
| Yes | 2.06 ± 0.55 | ||
| Weight loss | No | 2.17 ± 0.56 | 0.881 |
| Yes | 2.19 ± 0.64 | ||
| Headache | No | 2.16 ± 0.55 | 1 |
| Yes | 2.22 ± 0.73 | ||
| Unpleasant taste | No | 2.19 ± 0.58 | 0.576 |
| Yes | 2.05 ± 0.50 | ||
| Nausea and vomiting | No | 2.17 ± 0.62 | 0.813 |
| Yes | 2.18 ± 0.42 | ||
| Dyspnea | No | 2.16 ± 0.59 | 0.637 |
| Yes | 2.21 ± 0.43 | ||
| Anorexia | No | 2.20 ± 0.62 | 0.835 |
| Yes | 2.08 ± 0.38 | ||
| Item | Median | Log Rank (Mantel–Cox) p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
| Group A (CTH + Metformin) | 5.000 | 0.624 | 3.776 | 6.224 | |
| Group B (CTH + Placebo) | 4.000 | 0.758 | 2.515 | 5.485 | 0.753 |
| Overall | 5.000 | 0.514 | 3.992 | 6.008 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Essa, N.M.; Salem, H.F.; Elgendy, M.O.; Gabr, A.; Omran, M.M.; Hassan, N.A.; Tashkandi, H.M.; Harakeh, S.; Boshra, M.S. Efficacy of Metformin as Adjuvant Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195505
Essa NM, Salem HF, Elgendy MO, Gabr A, Omran MM, Hassan NA, Tashkandi HM, Harakeh S, Boshra MS. Efficacy of Metformin as Adjuvant Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195505
Chicago/Turabian StyleEssa, Nourhan M., Heba F. Salem, Marwa O. Elgendy, A. Gabr, Mervat M. Omran, Nivin A. Hassan, Hanaa M. Tashkandi, Steve Harakeh, and Marian S. Boshra. 2022. "Efficacy of Metformin as Adjuvant Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195505
APA StyleEssa, N. M., Salem, H. F., Elgendy, M. O., Gabr, A., Omran, M. M., Hassan, N. A., Tashkandi, H. M., Harakeh, S., & Boshra, M. S. (2022). Efficacy of Metformin as Adjuvant Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195505






