Optimization of Tokuhashi Scoring System to Improve Survival Prediction in Patients with Spinal Metastases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Medical Information
2.3. Blinding
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
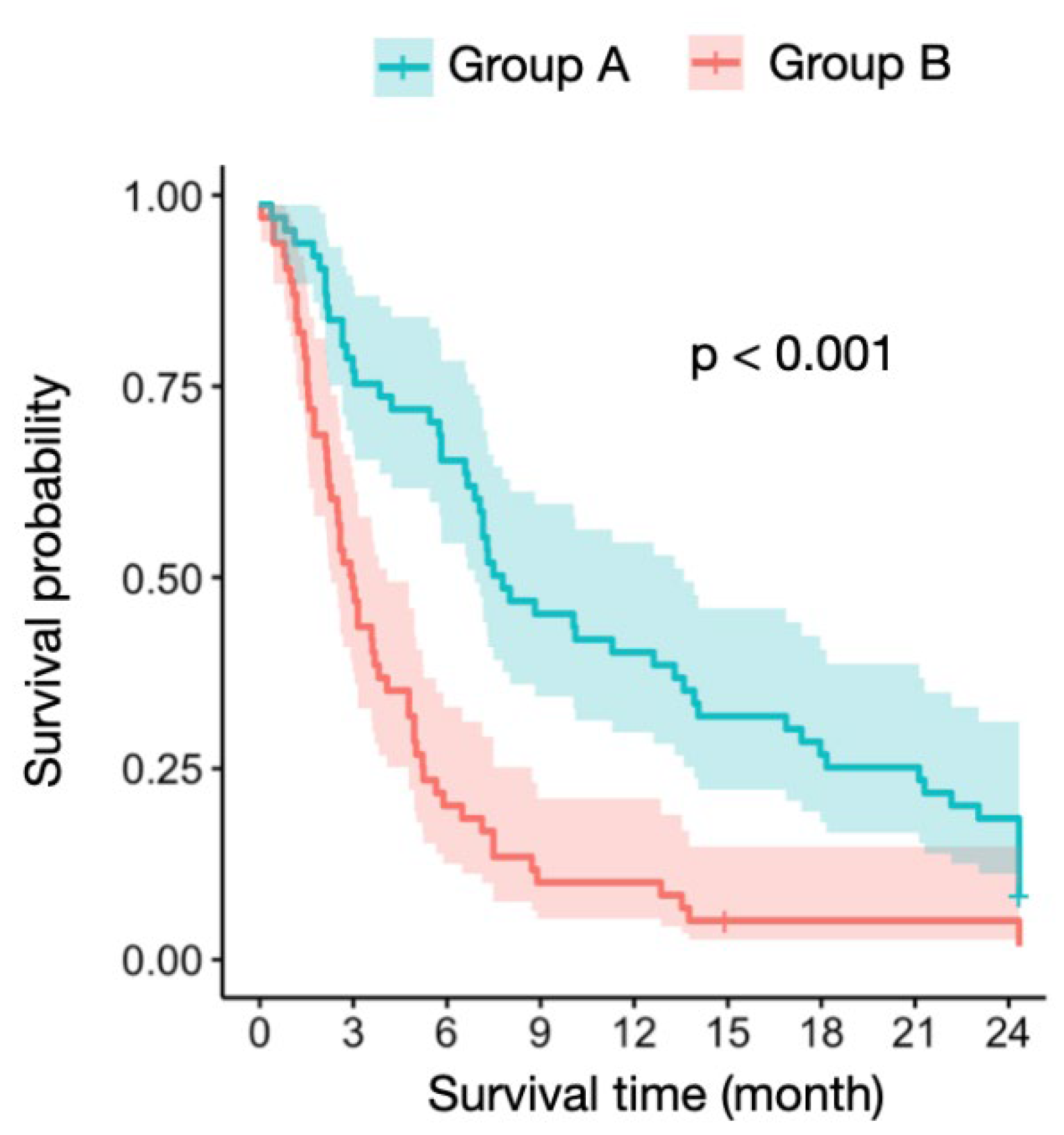
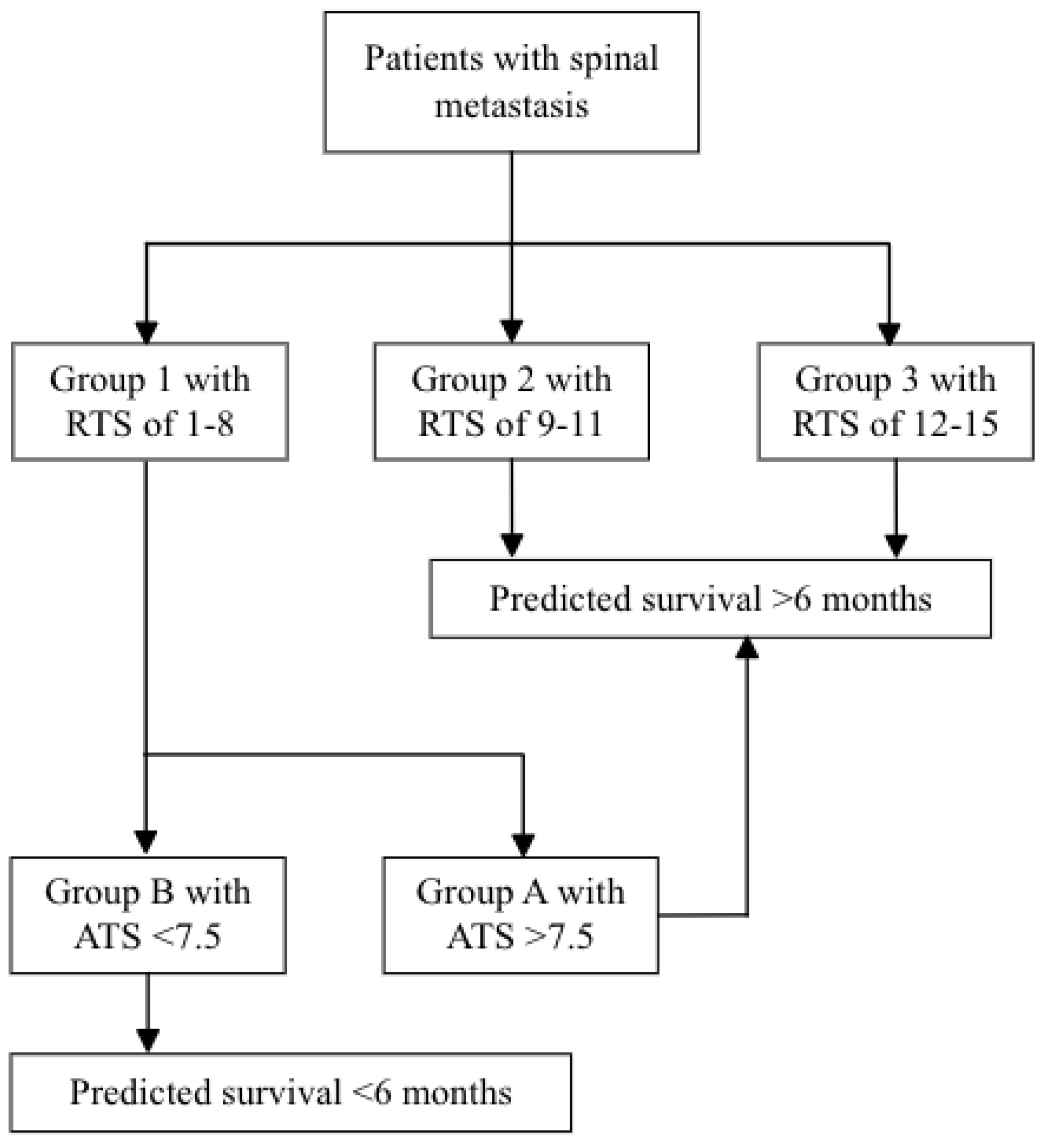
3.1. Reference Group
3.2. Factors Influencing Survival Time
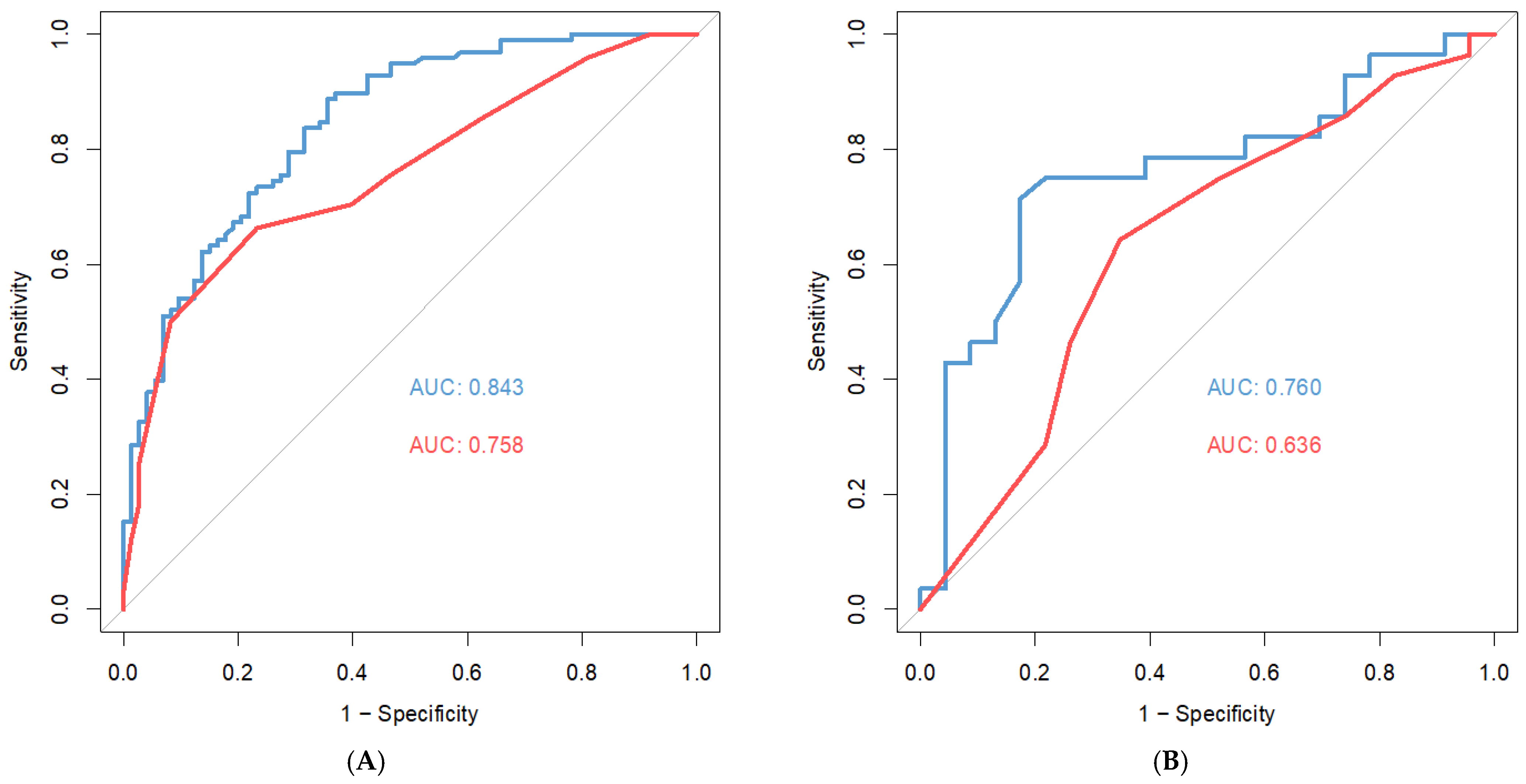
3.3. ATS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B
References
- Delank, K.S.; Wendtner, C.; Eich, H.T.; Eysel, P. The treatment of spinal metastases. Dtsch. Arzt. Int. 2011, 108, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, R.H.; van der Linden, Y.M.; van der Graaf, W.T. Spinal extradural metastasis: Review of current treatment options. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2008, 58, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, M. Spinal metastasis in the elderly. Eur. Spine J. 2003, 12 (Suppl. 2), S202–S213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, K.D. The use methylmetacrylate for vertebral body replacement and anterior stabilization of pathologic fracture dislocation of the spine due to metastatic malignant disease. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1981, 63, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, F.F.; Fouts, T.L. Metastatic cancer of unknown primary site. Cancer 1970, 26, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, J.A.; Zaveri, G.; Wai, E.; Vidmar, M.; Kreder, H.; Chow, E. A population-based study of surgery for spinal metastases. Survival rates and complications. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2003, 85, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmar, B.; Richter, M.; Cakir, B.; Muche, R.; Puhl, W.; Huch, K. The Tokuhashi score: Significant predictive value for the life expectancy of patients with breast cancer with spinal metastases. Spine 2005, 30, 2222–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wai, E.K.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Tangente, R.P.; Holden, L.; Chow, E.; Ford, M.; Yee, A. Quality of life in surgical treatment of metastatic spine disease. Spine 2003, 28, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuhashi, Y.; Matsuzaki, H.; Toriyama, S.; Kawano, H.; Ohsaka, S. Scoring system for the preoperative evaluation of metastatic spine tumor prognosis. Spine 1990, 15, 1110–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuhashi, Y.; Matsuzaki, H.; Oda, H.; Oshima, M.; Ryu, J. A revised scoring system for preoperative evaluation of metastatic spine tumor prognosis. Spine 2005, 30, 2186–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrwik, C.; Olerud, C.; Robinson, Y. Predictive Scores Underestimate Survival of Patients with Metastatic Spine Disease: A Retrospective Study of 315 Patients in Sweden. Spine 2020, 45, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Skoch, J.; Walter, C.M.; Torabi, M.; Borgstrom, M.; Baaj, A.A. The Tokuhashi score: Effectiveness and pitfalls. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quraishi, N.A.; Manoharan, S.R.; Arealis, G.; Khurana, A.; Elsayed, S.; Edwards, K.L. Accuracy of the revised Tokuhashi score in predicting survival in patients with metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC). Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22 (Suppl. 1), S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uei, H.; Tokuhashi, Y. Prognostic factors in patients with metastatic spine tumors derived from lung cancer—A novel scoring system for predicting life expectancy. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tang, X.; Yang, R.; Yan, T.; Guo, W. Modified score based on revised Tokuhashi score is needed for the determination of surgical intervention in patients with lung cancer metastases to the spine. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Meng, T.; Lin, Z.; Fan, T.; Yin, H.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, L.; et al. Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors of Pediatric Spine Tumors: A Single-Center Experience with 190 Cases Spine. Spine 2016, 41, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalita, N.; Ratanalert, S.; Kanjanapradit, K.; Chotsampancharoen, T.; Tunthanathip, T. Survival and prognostic factors in pediatric patients with medulloblastoma in Southern Thailand. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare. Statistics of Health Promotion. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/List.aspx?nodeid=1070 (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Pereira, N.; Janssen, S.; Dijk, E.; Harris, M.; Hornicek, F.; Ferrone, M.; Schwab, J. Development of a Prognostic Survival Algorithm for Patients with Metastatic Spine Disease. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2016, 98, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghori, A.; Leonard, D.; Schoenfeld, A.; Saadat, E.; Scott, N.; Ferrone, M.; Pearson, A.; Harris, M. Modeling 1-year survival after surgery on the metastatic spine. Spine J. 2015, 15, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Fourman, M.; Bongers, M.; Karhade, A.; Groot, O.; Lin, W.; Yen, H.; Huang, P.; Yang, S.; et al. International external validation of the SORG machine learning algorithms for predicting 90-day and 1-year survival of patients with spine metastases using a Taiwanese cohort. Spine J. 2021, 10, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Gao, H. Validation of a model with which to predict the survival prognosis of patients with spinal cord compression resulted from metastatic cancers. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 1924–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Au, J.S.; Thongprasert, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Khoa, M.T.; Heeroma, K.; Itoh, Y.; Cornelio, G.; Yang, P.C. A Prospective, Molecular Epidemiology Study of EGFR Mutations in Asian Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology (PIONEER). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.F.; Liu, H.P.; Li, L.H.; Ku, Y.C.; Fu, Y.N.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Lin, Y.F.; Chang, W.C.; Kuo, H.P.; et al. High Frequency of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations with Complex Patterns in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancers Related to Gefitinib Responsiveness in Taiwan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8195–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, B.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.Y.; Choi, Y.L.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. Concurrent Genetic Alterations Predict the Progression to Target Therapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, O.; Kolk, A.; Drecoll, E.; Straub, M.; Lutz, C.; Wolff, K.D.; Götz, C. EGFR and Cortactin: Markers for potential double target therapy in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4620–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.K.; Shepherd, F.A.; Feld, R.; Osoba, D.; Dang, P.; Deboer, G. VP-16 and cisplatin as first-line therapy for small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, J.L.; Carestia, L.; Daurès, J.P. Is there a case for cisplatin in the treatment of small-cell lung cancer? A meta-analysis of randomized trials of a cisplatin-containing regimen versus a regimen without this alkylating agent. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.G.; Luft, A.; Tafreshi, A.; Gumus, M.; Mazieres, J.; Hermes, B.; Cay Senler, F.; Fülöp, A.; Rodriguez-Cid, J.; Sugawara, S.; et al. Phase 3 study of carboplatin-paclitaxel/nab-paclitaxel (Chemo) with or without pembrolizumab (Pembro) for patients (Pts) with metastatic squamous (Sq) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Luft, A.V.; Szczesna, A.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Dediu, M.; Ramlau, R.; Galiulin, R.K.; Bálint, B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. Necitumumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin versus gemcitabine and cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in patients with stage IV squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (SQUIRE): An open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Cheng, A.L.; Meinhardt, G.; Nakajima, K.; De Sanctis, Y.; Llovet, J. Prognostic Factors and Predictors of Sorafenib Benefit in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Analysis of Two Phase III Studies. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.L.; Kang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Sorafenib in Patients in the Asia-Pacific Region with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Phase III Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Kudo, M.; Kawazoe, S.; Osaki, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Tamai, T.; Suzuki, T.; Hisai, T.; Hayato, S.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Lenvatinib in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srdic, D.; Plestina, S.; Sverko-Peternac, A.; Nikolac, N.; Simundic, A.M.; Samarzija, M. Cancer cachexia, sarcopenia and biochemical markers in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer-chemotherapy toxicity and prognostic value. Support Care Cancer 2016, 24, 4495–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, J.; Tschirner, A.; Haghikia, A.; Von Haehling, S.; Lal, H.; Grzesiak, A.; Kaschina, E.; Palus, S.; Pötsch, M.; Von Websky, K.; et al. Prevention of liver cancer cachexia-induced cardiac wasting and heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, H.; DeRubeis, M.B.; Burke, N.; Shannon, M.; Karsies, D.; Wolf, G.; Eisbruch, A.; Worden, F. Symptom management during and after treatment with concurrent chemoradiotherapy for oropharyngeal cancer: A review of the literature and areas for future research. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 7, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eglseer, D.; Halfens, R.J.; Lohrmann, C. Is the presence of a validated malnutrition screening tool associated with better nutritional care in hospitalized patients? Nutrition 2017, 37, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabito, E.I.; Marcadenti, A.; da Silva Fink, J.; Figueira, L.; Silva, F.M. Nutritional Risk Screening 2002, Short Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire, Malnutrition Screening Tool, and Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool Are Good Predictors of Nutrition Risk in an Emergency Service. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, J.; Teleni, L.; McKavanagh, D.; Watson, J.; McCarthy, A.L.; Isenring, E. Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment Short Form (PG-SGA SF) is a valid screening tool in chemotherapy outpatients. Support Care Cancer 2016, 24, 3883–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ræder, H.; Henriksen, C.; Bøhn, S.K.; Henriksen, H.B.; Kværner, A.S.; Rolid, K.; Paur, I.; Smeland, S.; Blomhoff, R. Agreement between PG-SGA category and fat-free mass in colorectal cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versteeg, A.L.; van Tol, F.R.; Lehr, A.M.; Oner, F.C.; Verlaan, J.J. Malnutrition in patients who underwent surgery for spinal metastases. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hunsel, F.; Van Gastel, A.; Neels, H.; Wauters, A.; Demedts, P.; Bruyland, K.; DeMeester, I.; Scharpe, S.; Janca, A.; Song, C.; et al. The Influence of Psychological Stress on Total Serum Protein and Patterns Obtained in Serum Protein Electrophoresis. Psychol. Med. 1998, 28, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Navarro, R.; Corona-Candelas, I.; Barajas-González, S.; Díaz-Flores, M.; Durán-Reyes, G. Albumin Antioxidant Response to Stress in Diabetic Nephropathy Progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, B.R.; Kaysen, G. Serum Albumin: Relationship to Inflammation and Nutrition. Semin. Dial. 2004, 17, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaysen, G.A.; Dubin, J.A.; Müller, H.G.; Rosales, L.; Levin, N.W.; Mitch, W.E. Inflammation and reduced albumin synthesis associated with stable decline in serum albumin in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.H.; Yen, H.K.; Chen, I.H.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, C.W.; Yang, J.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yen, M.H.; Yang, S.H.; Lin, W.H. Decreased psoas muscle area is a prognosticator for 90-day and 1-year survival in patients undergoing surgical treatment for spinal metastasis. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group 1 a (n = 116) | Group 2 b (n = 42) | Group 3 c (n = 13) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 58.6 (22–89) | 57.2 (19–82) | 54.5 (31–70) | 0.489 |
| 19–44 | 16 (13.8%) | 6 (14.3%) | 2 (15.4%) | |
| 45–64 | 65 (56.0%) | 25 (59.5) | 9 (69.2%) | |
| ≥65 | 35 (30.2%) | 11 (26.2%) | 2 (15.4%) | 0.847 |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 77/39 | 21/21 | 5/8 | 0.044 |
| Body measurements | ||||
| Height | 162.3 (141–184) | 161.3 (135–175) | 161.1 (151–177) | 0.772 |
| Weight | 60.6 (35–109) | 60.0 (36–96) | 60.8 (46–78) | 0.952 |
| BMI | 22.9 (15.8–38.2) | 23.1 (15.0–34.8) | 23.4 (8.5–28.6) | 0.906 |
| Adjuvant/Neoadjuvant therapy | ||||
| Chemotherapy | 91 (78.4%) | 33 (78.6%) | 13 (100%) | 0.001 |
| Target therapy | 69 (59.5%) | 27 (64.3%) | 8 (61.5%) | 0.86 |
| Hormone therapy | 7 (6%) | 9 (21.4%) | 10 (76.9%) | <0.001 |
| Primary origin | ||||
| Lung | 56 (48.3%) | 8 (19.0%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 |
| Liver | 19 (16.4%) | 5 (11.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0.257 |
| Breast | 5 (4.3%) | 7 (16.7%) | 8 (61.5%) | <0.001 |
| Prostate | 6 (5.2%) | 3 (7.1%) | 2 (15.4%) | 0.355 |
| Colorectal | 5 (4.3%) | 1 (2.4%) | 0 (0%) | <0.05 |
| Renal | 4 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | <0.05 |
| Survival | <0.001 | |||
| 6-month survival rate | 42.20% | 88.10% | 92.30% | <0.001 |
| 12-month survival rate | 24.10% | 52.30% | 84.60% | <0.001 |
| Average RTS | 5.50 (0–8) | 9.50 (9–11) | 12.30 (12–14) | <0.001 |
| Indicators | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTS | 1.41 | (1.11 to 1.83) | 0.005 |
| Chemo | 0.67 | (0.22 to 1.99) | 0.466 |
| Target | 7.08 | (2.78 to 20.10) | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.02 | (0.98 to 1.06) | 0.276 |
| Sex | 0.55 | (0.21 to 1.38) | 0.220 |
| Z-BMI | 1.89 | (1.09 to 3.39) | 0.027 |
| b = 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = 1 | 0.803 | 0.801 | 0.788 | 0.777 | 0.764 | 0.749 | 0.738 | 0.727 | 0.719 | 0.712 |
| 2 | 0.824 | 0.819 | 0.808 | 0.794 | 0.778 | 0.761 | 0.75 | 0.739 | 0.729 | 0.723 |
| 3 | 0.835 | 0.83 | 0.816 | 0/804 | 0.791 | 0.773 | 0.762 | 0.751 | 0.741 | 0.733 |
| 4 | 0.844 | 0.839 | 0.825 | 0.812 | 0.8 | 0.786 | 0.773 | 0.763 | 0.752 | 0.743 |
| 5 | 0.843 | 0.841 | 0.83 | 0.819 | 0.807 | 0.792 | 0.781 | 0.77 | 0.759 | 9.752 |
| 6 | 0.843 | 0.838 | 0.831 | 0.821 | 0.81 | 0.799 | 0.786 | 0.776 | 0.767 | 0.759 |
| 7 | 0.836 | 0.835 | 0.828 | 0.823 | 0.813 | 0.801 | 0.791 | 0.781 | 0.772 | 0.764 |
| 8 | 0.828 | 0.829 | 0.825 | 0.82 | 0.814 | 0.804 | 0.795 | 0.786 | 0.776 | 0.769 |
| 9 | 0.823 | 0.823 | 0.821 | 0.818 | 0.812 | 0.805 | 0.796 | 0.789 | 0.78 | 0.772 |
| 10 | 0.822 | 0.819 | 0.817 | 0.815 | 0.81 | 0.803 | 0.798 | 0.79 | 0.784 | 0.776 |
| Characteristic | Score |
|---|---|
| General condition | |
| Poor (10–40%) | 0 |
| Moderate (50–70%) | 1 |
| Good (80–100%) | 2 |
| Number of extraspinal metastatic foci | |
| ≥3 | 0 |
| 1–2 | 1 |
| 0 | 2 |
| Number of metastases in vertebral body | |
| ≥3 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| Metastases to major internal organ | |
| Unremovable | 0 |
| Removable | 1 |
| No metastasis | 2 |
| Primary cancer site | |
| Lung, osteosarcoma, stomach, bladder, esophagus, pancreas | 0 |
| Liver, gallbladder, unidentified | 1 |
| Others | 2 |
| Kidney, uterus | 3 |
| Rectum | 4 |
| Thyroid, prostate, breast carcinoid tumor | 5 |
| Palsy | |
| Complete (Frankel A, B) | 0 |
| Incomplete (Frankel C, D) | 1 |
| None (Frankel E) | 2 |
| Target therapy | |
| No use | 0 |
| Use | 4 |
| Z-BMI | |
| Total score > 8; Survival > 6 months. Total score < 8; Survival < 6 months. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, H.-K.; Chen, C.-W.; Lin, W.-H.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Hu, M.-H. Optimization of Tokuhashi Scoring System to Improve Survival Prediction in Patients with Spinal Metastases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185391
Yen H-K, Chen C-W, Lin W-H, Wang Z-Y, Huang C-C, Chen H-Y, Yang S-H, Hu M-H. Optimization of Tokuhashi Scoring System to Improve Survival Prediction in Patients with Spinal Metastases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185391
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Hung-Kuan, Chih-Wei Chen, Wei-Hsin Lin, Zhong-Yu Wang, Chuan-Ching Huang, Hsuan-Yu Chen, Shu-Hua Yang, and Ming-Hsiao Hu. 2022. "Optimization of Tokuhashi Scoring System to Improve Survival Prediction in Patients with Spinal Metastases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185391
APA StyleYen, H.-K., Chen, C.-W., Lin, W.-H., Wang, Z.-Y., Huang, C.-C., Chen, H.-Y., Yang, S.-H., & Hu, M.-H. (2022). Optimization of Tokuhashi Scoring System to Improve Survival Prediction in Patients with Spinal Metastases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5391. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185391






