Comprehensive Approaches to Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly on the Disease Time-Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prevalence
3. Mechanism
3.1. Cough Reflex Sensitivity
3.2. Swallowing Reflex
3.3. Lacunar Infarction and the Upper Respiratory Protective Reflexes
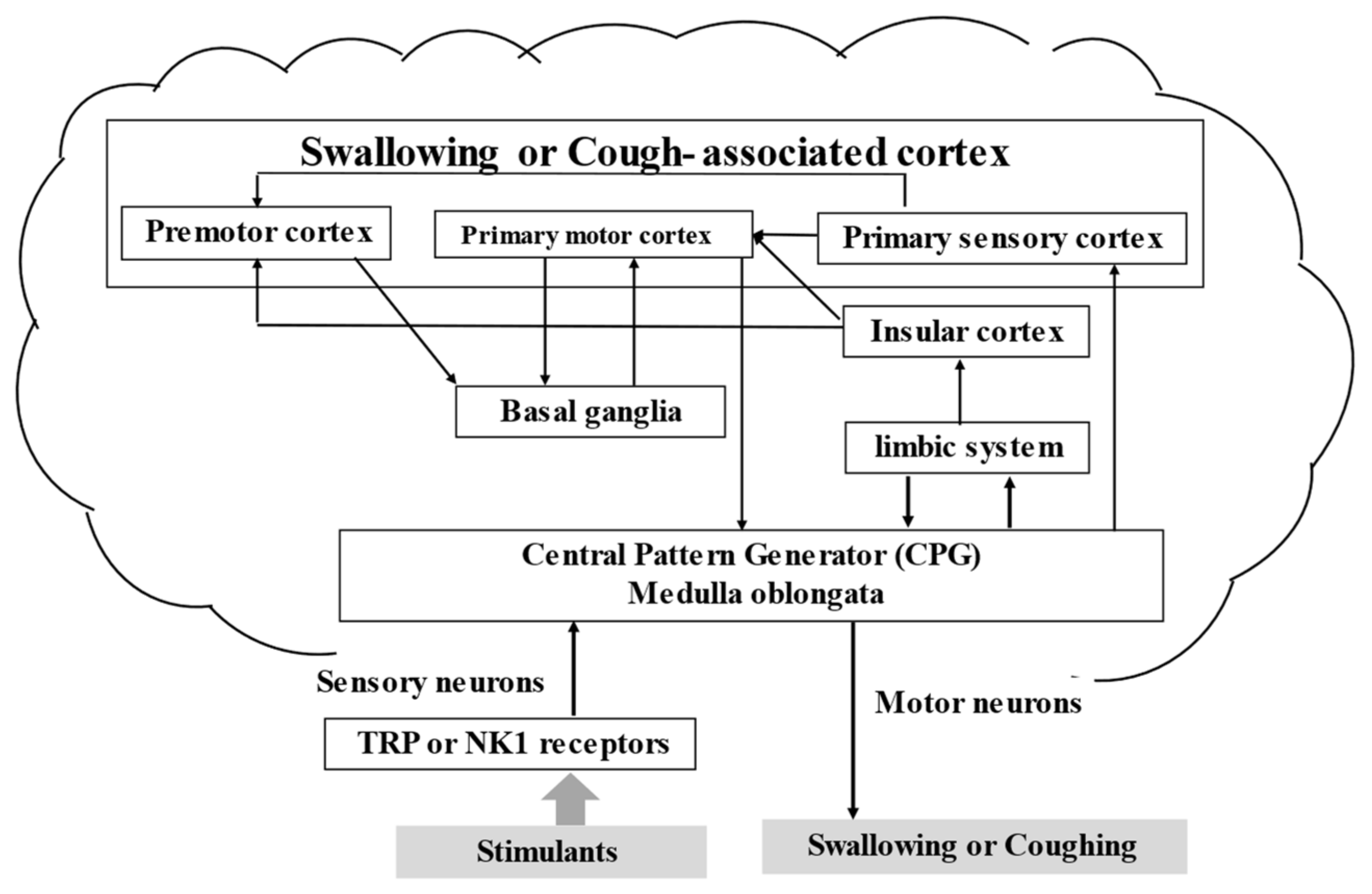
3.4. Brain and Swallowing
3.5. Breathing and Swallowing
3.6. Comorbidities Modifying the Development of Pneumonia
3.7. Pneumonia-Associated Sarcopenia
3.8. End-of-Life in Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia
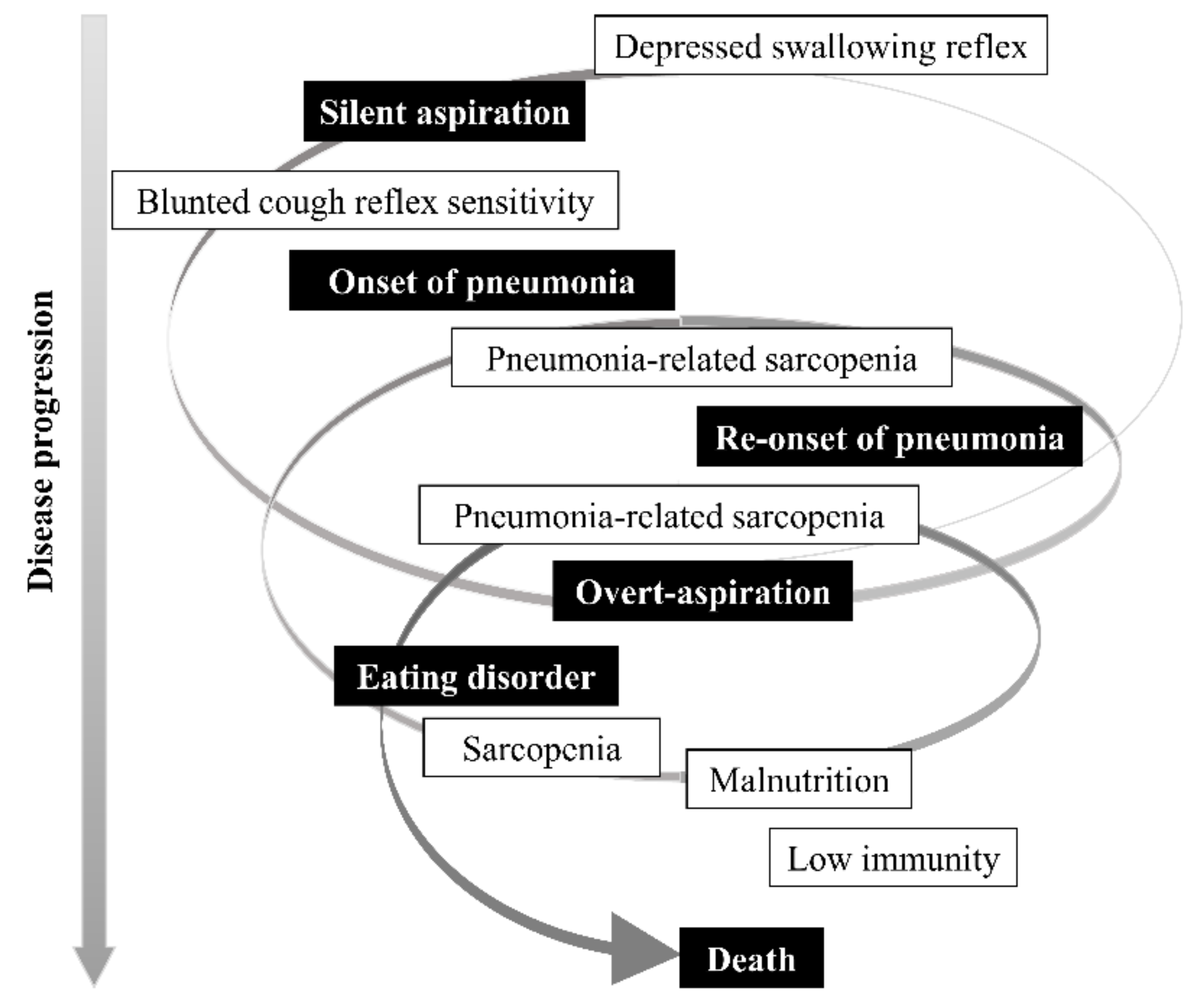
3.9. Pathophysiological Time-Axis of Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia
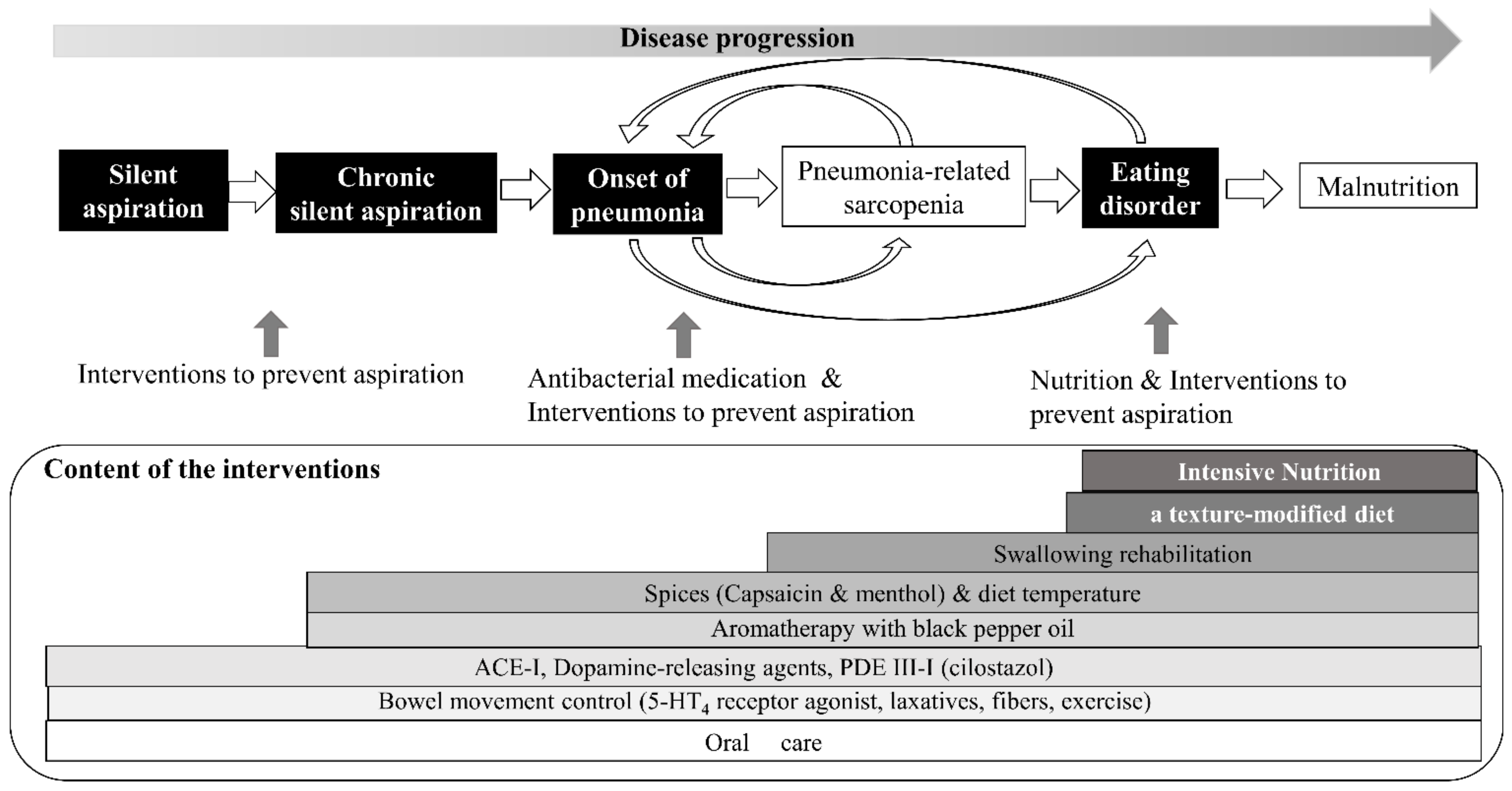
4. Comprehensive Preventive Approach
4.1. Pharmacological Preventive Approach
4.1.1. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
4.1.2. Dopamine-Release-Stimulating Agent
4.1.3. Combination of Dopamine-Release-Stimulating Agent and ACE Inhibitor
4.1.4. Phosphodiesterase-III Inhibitors
4.1.5. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 Receptor Agonist
4.2. Non-Pharmacological Approach: How to Prevent Aspiration at Home
4.2.1. Physical Properties of the Meal
4.2.2. Stimulation of Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Receptor
4.2.2.1. Temperature of the Meal
4.2.2.2. Spices
4.2.3. Aromatherapy
4.2.4. Nutrition
4.2.5. Swallowing Rehabilitation
4.2.6. Oral Care
4.2.7. Sitting and Holding Position after Meals
4.2.8. Bowel Movement Control
4.3. Strategies for Preventing Aspiration Pneumonia
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanspa, M.J.; Barbara, E.J.; Brown, S.M.; Dean, N.C. Mortality, morbidity, and disease severity of patients with aspiration pneumonia. J. Hosp. Med. 1996, 8, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/itiran/index.html (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Marik, P.E. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, W.B.; Yu, W.; Summe, J.P. Epidemiologic trends in the hospitalization of elderly Medicare patients for pneumonia, 1991–1998. Am. J. Public Health 2001, 91, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Teramoto, S.; Fukuchi, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Sato, K.; Sekizawa, M.K.T.; Japanese Study Group on Aspiration Pulmonary Disease. High incidence of aspiration pneumonia in community- and hospital-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients: A multicenter, prospective study in Japan. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaya, M.; Yanai, M.; Ohrui, T.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Interventions to prevent pneumonia among older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecci, A.; Giuliani, S.; Tramontana, M.; Carini, F.; Maggi, C.A. Peripheral actions of tachykinins. Neuropeptides 2000, 34, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutolo, D.; Bongianni, F.; Fontana, G.A.; Pantaleo, T. The role of excitatory amino acids and substance P in the mediation of the cough reflex within the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rabbit. Brain Res. Bull. 2007, 74, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutolo, D.; Bongianni, F.; Cinelli, E.; Pantaleo, T. Role of excitatory amino acids in the mediation of tracheobronchial cough induced by citric acid inhalation in the rabbit. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, S.B.; Mori, N.; Canning, B.J. Synergistic interactions between airway afferent nerve subtypes regulating the cough reflex in guinea pigs. J. Physiol. 2005, 569, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Ohrui, T.; Nakazawa, H.; Sasaki, H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and danazol increase sensitivity of cough reflex in female guinea pigs. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizawa, K.; Jia, Y.X.; Ebihara, T.; Hirose, Y.; Hirayama, Y.; Sasaki, H. Role of substance P in cough. Pulm. Pharmacol. 1996, 9, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope-Gill, B.D.M.; Hilldrup, S.; Davies, C.; Newton, R.P.; Harrison, N.K. A study of the cough reflex in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir Crit Care Med. 2003, 168, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizawa, K.; Ujiie, Y.; Itabashi, S.; Sasaki, H.; Takishima, T. Lack of cough reflex in aspiration pneumonia. Lancet 1990, 335, 1228–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajoh, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Matsui, T.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Relation between incidence of pneumonia and protective reflexes in post-stroke patients with oral or tube feeding. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 247, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Sasaki, H. Capsaicin and swallowing reflex. Lancet 1993, 341, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, H.; Sekizawa, K.; Ujiie, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Takishima, T. Risk of aspiration pneumonia in the elderly. Chest 1993, 103, 1636–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakagawa, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Arai, H.; Kikuchi, R.; Manabe, K.; Sasaki, H. High incidence of pneumonia in elderly patients with basal ganglia infarction. Arch. Intern. Med. 1997, 157, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.X.; Sekizawa, K.; Ohrui, T.; Nakayama, K.; Sasaki, H. Dopamine D1 receptor antagonist inhibits swallowing reflex in guinea pigs. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, R76–R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Maruyama, M.; Ebihara, T.; Matsui, T.; Nemoto, M.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H.; Yanai, K. Aspiration pneumonia and insular hypoperfusion in patients with cerebrovascular disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, I.A.; Robbins, J. Normal swallowing and functional magnetic resonance imaging: A systematic review. Dysphagia 2007, 22, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Asada, Y.; Ito, J.; Hayashi, K.; Inoue, H.; Kitano, H. Activation of cerebellum and basal ganglia on volitional swallowing detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Dysphagia 2003, 18, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.; Rothwell, J.C.; Aziz, Q.; Singh, K.D.; Thompson, D.G. Long-term reorganization of human motor cortex driven by short-term sensory stimulation. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.M.; Garcia, A.J.; Baertsch, N.A.; Pollak, J.; Bloom, J.C.; Wei, A.D.; Rai, K.G.; Ramirez, J.M. A novel excitatory network for the control of breathing. Nature 2016, 536, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, N.; Oku, Y.; Nagami, S.; Yamagata, Y.; Kayashita, J.; Ishikawa, A.; Domen, K.; Takahashi, R. Inappropriate timing of swallow in the respiratory cycle causes breathing-swallowing discoordination. Front. Physiol. 2017, 22, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marumo, K.; Homma, S.; Fukuchi, Y. Postgastrectomy aspiration pneumonia. Chest 1995, 107, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, T.; Ebihara, S.; Ida, S.; Ohrui, T.; Yasuda, H.; Sasaki, H.; Arai, H. Acid and swallowing reflex. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2007, 7, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Sasaki, H. Constipation and aspiration pneumonia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12, 570–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, T. Serum substance P levels in patients with chronic schizophrenia treated with typical or atypical antipsychotics. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, S.J.; LaSalvia, M.T.; Naidus, E.; Rothberg, M.B.; Zhou, W.; Gurwitz, J.H.; Marcantonio, E.R. Antipsychotics and the risk of aspiration pneumonia in individuals hospitalized for nonpsychiatric conditions: A cohort study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 2580–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, E.; Hirai, T.; Seki, T. Assessment of aspiration pneumonia using the anticholinergic risk scale. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchina, S.; Doros, G.; Modak, J.; Helenius, J.; Aycock, D.M.; Kumar, S. Acid-suppressive medications and risk of pneumonia in acute stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 400, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranberg, A.; Samuelsson, C.; Klarin, B. Disturbance in the oropharyngeal microbiota in relation to antibiotic and proton pump inhibitor medication and length of hospital stay. APMIS 2021, 129, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Roubenoff, R.; Mayer, J.; Nair, K.S. Sarcopenia. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2001, 137, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, C.; Lemaire, C.; Li, T.; Kimoff, R.J.; Petrof, B.J. Autophagy-associated atrophy and metabolic remodeling of the mouse diaphragm after short-term intermittent hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2015, 24, e0131068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuna-Venegas, S.; Aliaga-Vega, R.; Maguiña, J.L.; Parodi, J.F.; Runzer-Colmenares, F.M. Risk of community-acquired pneumonia in older adults with sarcopenia of a hospital from Callao, Peru 2010–2015. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 82, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, T.; Liang, F.; Li, T.; Danialou, G.; Shoelson, S.E.; Petrof, B.J. Muscle-specific inhibition of the classical nuclear factor-κB pathway is protective against diaphragmatic weakness in murine endotoxemia. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, e501–e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looijaard, W.G.P.M.; Dekker, I.M.; Beishuizen, A.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M.; Weijs, P.J.M. Early high protein intake and mortality in critically ill ICU patients with low skeletal muscle area and density. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Ebihara, S.; Mori, T.; Izumi, S.; Ebihara, T. Association between sarcopenia and pneumonia in older people. Rev. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Suzukamo, Y.; Miyatake, M.; Komatsu, R.; Yaekashiwa, M.; Nihei, M.; Izumi, S.; Ebihara, T. Respiratory muscle weakness as a risk factor for pneumonia in older people. Gerontology 2021, 67, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozu, H.; Higashijima, M.; Koga, T. Association of sarcopenia with swallowing problems, related to nutrition and activities of daily living of elderly individuals. J. Phys. Sci. 2015, 27, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Hirano, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Sakai, K.; Kim, H.; Katakura, A. Relationship between chewing ability and sarcopenia in Japanese community-dwelling older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2015, 15, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kuroda, R. Relationship between thinness and swallowing function in Japanese older adults: Implications for sarcopenic dysphagia. J. Am. Geriatr Soc. 2012, 60, 1785–1786, Erratum in: J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, N.; Mori, T.; Fujishima, I.; Wakabayashi, H.; Itoda, M.; Kunieda, K.; Shigematsu, T.; Nishioka, S.; Tohara, H.; Yamada, M.; et al. Ultrasonography to measure swallowing muscle mass and quality in older patients with sarcopenic dysphagia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Akagi, J. Decreased tongue pressure is associated with sarcopenia and sarcopenic dysphagia in the elderly. Dysphagia 2015, 30, 80–87, Erratum in: Dysphagia 2015, 30, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Kozaki, K. Prognostic factors of 90-day mortality in older people with healthcare-associated pneumonia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Ebihara, T.; Kozaki, K. The association between eating difficulties and biliary sludge in the gallbladder in older adults with advanced dementia, at end of life. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicpinigaitis, P.V. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced cough: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2006, 129, 169S–173S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaki, M.; Ichinose, M.; Miura, M.; Hirayama, Y.; Kageyama, N.; Yamauchi, H.; Shirato, K. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor-induced cough and substance P. Thorax 1996, 51, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Sekizawa, K.; Sasaki, H. ACE inhibitor and swallowing reflex. Chest 1998, 113, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizawa, K.; Matsui, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakayama, K.; Sasaki, H. ACE inhibitors and pneumonia. Lancet 1998, 352, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Ohrui, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Yoshimi, N.; Matsuoka, H.; Sasaki, H. ACE inhibitors and protection against pneumonia in elderly patients with stroke. Neurology 2005, 64, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Wada, H.; Sekizawa, K.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Amantadine and pneumonia. Lancet 1999, 353, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, A.; Ebihara, S.; Yasuda, H.; Takashi, O.; Sasaki, T.; Sasaki, H. A combinatorial therapy for pneumonia in elderly people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Maki, Y.; Maki, Y. Tube feeding can be discontinued by taking dopamine agonists and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in the advanced stages of dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 2035–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaya, M.; Yanai, M.; Ohrui, T.; Arai, H.; Sekizawa, K.; Sasaki, H. Antithrombotic therapy for prevention of pneumonia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netsu, S.; Mizuma, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Yutani, S.; Nagata, E.; Takizawaet, S. Cilostazol is effective to prevent stroke-associated pneumonia in patients receiving tube feeding. Dysphagia 2018, 33, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, A.; Maeshima, S.; Tanahashi, N. Efficacy of cilostazol in preventing aspiration pneumonia in acute cerebral infarction. J. Stroke Cereb. Dis. 2013, 22, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Ohrui, T.; Ebihara, T.; Ebihara, S.; Sasaki, H.; Arai, H. Mosapride citrate prolongs survival in stroke patients with gastrostomy. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatori, K.; Yoshida, R.; Horai, A.; Satake, S.; Ose, T.; Kitajima, N.; Yoneda, S.; Adachi, K.; Amano, Y.; Kinoshita, Y. Therapeutic effects of mosapride citrate and lansoprazole for prevention of aspiration pneumonia in patients receiving gastrostomy feeding. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlet, S.; Choi, J.; Zormeier, M.; Shamsa, F.; Stachler, R.; Muz, J.; Jones, L. Normal adult swallowing of liquid and viscous material: Scintigraphic data on bolus transit and oropharyngeal residues. Dysphagia 1996, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.M.; Kjaersgaard, A.; Hansen, T.; Poulsen, I. Systematic review and evidence-based recommendations on texture modified foods and thickened liquids for adults (above 17 years) with oropharyngeal dysphagia—An updated clinical guideline. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watando, A.; Ebihara, S.; Ebihara, T.; Okazaki, T.; Takahashi, H.; Asada, M.; Sasaki, H. Effect of temperature on swallowing reflex in elderly patients with aspiration pneumonia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 2143–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, T.; Ebihara, S.; Watando, A.; Okazaki, T.; Asada, M.; Ohrui, T.; Yamaya, M.; Arai, H. Effects of menthol on the triggering of the swallowing reflex in elderly patients with dysphagia. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Kozaki, K.; Ebihara, S. Medical aromatherapy in geriatric syndrome. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2021, 21, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaya, M.; Kawakami, G.; Momma, H.; Yamada, A.; Itoh, J.; Ichinose, M. Effects of Nutritional Treatment on the Frequency of Pneumonia in Bedridden Patients Receiving Oral Care. Intern. Med. 2020, 59, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Ohrui, T.; Matsui, T.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Folate deficiency and risk of pneumonia in older people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, Y.; Yamaya, M.; Nakajoh, K.; Matsui, T.; Yanai, M.; Sasaki, H. Prognosis of elderly patients with dysphagia in Japan. Gerontology 2000, 46, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, Y.; Nakagawa-Satoh, T.; Ohrui, T.; Fujii, M.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Survival period after tube feeding in bedridden older patients. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balou, M.; Herzberg, E.G.; Kamelhar, D.; Molfenter, S.M. An intensive swallowing exercise protocol for improving swallowing physiology in older adults with radiographically confirmed dysphagia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 11, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnaby, G.; Hankey, G.J.; Pizzi, J. Behavioural intervention for dysphagia in acute stroke: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, P.M.; Lee, H.S.; Everton, L.F. Swallowing therapy for dysphagia in acute and subacute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, CD000323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, T.; Yoshida, M.; Ohrui, T.; Mukaiyama, H.; Okamoto, H.; Hoshiba, K.; Ihara, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Ariumi, S.; Morita, T.; et al. Oral Care Working Group. Oral care reduces pneumonia in older patients in nursing homes. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, A.; Ebihara, T.; Ebihara, S.; Fuji, H.; Sasaki, H. Daily oral care and risk factors for pneumonia among elderly nursing home patients. JAMA 2001, 286, 2235–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watando, A.; Ebihara, S.; Ebihara, T.; Okazaki, T.; Takahashi, H.; Asada, M.; Sasaki, H. Daily oral care and cough reflex sensitivity in elderly nursing home patients. Chest 2004, 126, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, A.; Terekhin, P.; Kemppainen, P.; Dörfler, A.; Forster, C. The representation of experimental tooth pain from upper and lower jaws in the human trigeminal pathway. Pain 2010, 149, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Tomioka, M.; Shimazaki, Y.; Matsuyama, M.; Koyano, K.; Matsuda, K.; Yamashita, Y. Microfloral characterization of the tongue coating and associated risk for pneumonia-related health problems in institutionalized older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, E.; Maejima, I. The effects of moisturizing gel to prevent dry mouth in patients with cerebrovascular disease. Nihon. Ronen Igakkai. Zasshi. 2008, 45, 196–201. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Torres, A.; Serra-Batlles, J.; Ros, E.; Piera, C.; de la Bellacasa, J.P.; Cobos, A.; Lomeña, F.; Rodríguez-Roisin, R. Pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents in patients receiving mechanical ventilation: The effect of body position. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 116, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco-Levi, M.; Torres, A.; Ferrer, M.; Piera, C.; el-Ebiary, M.; de la Bellacasa, J.P.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Semi-recumbent position protects from pulmonary aspiration but not completely from gastroesophageal reflux in mechanically ventilated patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Crehuet, R.; Díaz-Molina, C.; de Irala, J.; Martínez-Concha, D.; Salcedo-Leal, I.; Masa-Calles, J. Nosocomial infection in an intensive-care unit: Identification of risk factors. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1997, 18, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Yamaya, M.; Ohrui, T.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Sitting position to prevent aspiration in bed-bound patients. Gerontology 2002, 48, 194–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drakulovic, M.B.; Torres, A.; Bauer, T.T.; Nicolas, J.M.; Nogué, S.; Ferrer, M. Supine body position as a risk factor for nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients: A randomized trial. Lancet 1999, 354, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiatsou, E.; Kostanti, E.; Svarna, E.; Kitsakos, A.; Koulouras, V.; Efremidis, S.C.; Nakos, G. Prone position augments recruitment and prevents alveolar overinflation in acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, A.T.; Marsland, B.J. Microbes, metabolites, and the gut-lung axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, T.; Ebihara, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Asada, M.; Yamanda, S.; Arai, H. Intensive stepwise method for oral intake using a combination of transient receptor potential stimulation and olfactory stimulation inhibits the incidence of pneumonia in dysphagic older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Before Eating |
|---|
|
| Meals |
|
| After Eating |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebihara, T. Comprehensive Approaches to Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly on the Disease Time-Axis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185323
Ebihara T. Comprehensive Approaches to Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly on the Disease Time-Axis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185323
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbihara, Takae. 2022. "Comprehensive Approaches to Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly on the Disease Time-Axis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185323
APA StyleEbihara, T. (2022). Comprehensive Approaches to Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly on the Disease Time-Axis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5323. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185323




