Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic continues to have an impact on geriatric patients worldwide since geriatrics itself is an age group with a high risk due to declined physiological function and many comorbidities, especially for those who undergo surgery. In this study, we determine the association between perioperative factors with 30-day mortality and a survival rate of geriatric patients undergoing surgery during COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted at 14 central hospitals in Indonesia. The recorded variables were perioperative factors, 30-day mortality, and survival rate. Analyses of associations between variables and 30-day mortality were performed using univariate/multivariable logistic regression, and survival rates were determined with Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Results: We analyzed 1621 elderly patients. The total number of patients who survived within 30 days of observation was 4.3%. Several perioperative factors were associated with 30-day mortality (p < 0.05) is COVID-19 (OR, 4.34; 95% CI, 1.04–18.07; p = 0.04), CCI > 3 ( odds ratio [OR], 2.33; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.03–5.26; p = 0.04), emergency surgery (OR, 3.70; 95% CI, 1.96–7.00; p ≤ 0.01), postoperative ICU care (OR, 2.70; 95% CI, 1.32–5.53; p = 0.01), and adverse events (AEs) in the ICU (OR, 3.43; 95% CI, 1.32–8.96; p = 0.01). Aligned with these findings, COVID-19, CCI > 3, and comorbidities have a log-rank p < 0.05. The six comorbidities that have log-rank p < 0.05 are moderate-to-severe renal disease (log-rank p ≤ 0.01), cerebrovascular disease (log-rank p ≤ 0.01), diabetes with chronic complications (log-rank p = 0.03), metastatic solid tumor (log-rank p = 0.02), dementia (log-rank p ≤ 0.01), and rheumatology disease (log-rank p = 0.03). Conclusions: Having at least one of these conditions, such as COVID-19, comorbidities, emergency surgery, postoperative ICU care, or an AE in the ICU were associated with increased mortality in geriatric patients undergoing surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic.
1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has created a healthcare crisis in the world. Due to a large number of COVID-19 cases, many hospitals shifted to serve COVID-19 patients compared to those without. Consequently, the number of surgeries performed dropped globally by about 25 million elective surgeries in early 2020 [1]. This also had an impact on geriatric patients’ surgical services. Geriatric patients have decreased physiological function (e.g., diminished cognitive function, decreased cardiac output, increased mean arterial pressure, decreased arterial oxyhemoglobin, and lowered glomerular filtration rate) and have many comorbidities (e.g., cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, or cancer). This alone puts geriatric patients at risk of undergoing surgery [2]. Undergoing surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic also has a high risk. Patients may not be infected with COVID-19 at the initial admission, but the patients may be exposed during treatment. Having COVID-19 may increase mortality and decreased survival rate. The combination of those worsens the outcome of surgical and anesthesia services in geriatric patients [1,3].
The research included 1128 patients from 235 hospitals in Europe, Africa, Asia, and North America, showing high mortality rate (23.8%) in patients COVID-19 who underwent surgery. The mortality rate of patients older than 70 years and infected with COVID-19 is high compared to people at a young age, 33.7% vs. 13.9% [4]. COVID-19 has been shown to increase the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admissions, length of stay patients in hospital, and mortality, and decrease the survival rate patients [5,6].
Many factors affect the mortality and survival of patients undergoing surgery [7], but not much is known about the factors that affect mortality and survival during COVID-19 pandemic, especially in geriatric patients. Thus, it is important to know how perioperative factors impact the mortality and survival rates of geriatric patients undergoing surgery in the COVID-19 pandemic, since it may influence the decision-making and identification of patients who benefit from surgery requiring anesthesia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study is a prospective cohort study. This research was conducted in 14 teaching hospitals for Anesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Residency Education in Indonesia. The data collection was conducted for four months, including three months of data collection from February to April 2021, and we prospectively followed up for 30 days. Every collector was briefed and had standardized training before the data collection. We enrolled patients after their initial consultation with the anesthesiologist.
2.2. Sample and Population
We recruited patients who underwent surgery and required anesthesia. We included all patients aged 60 years or older who underwent surgery from all disciplines between February and April 2021. Patients willing to participate in this study with complete records of medical comorbidities were included. We excluded all patients who did not provide consent and did not complete the follow-up within the established follow-up periods.
2.3. Parameters
The variables included preoperative factors, including age, gender, BMI, comorbidities based on the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, COVID-19 status, ASA score, nonemergency and emergency surgery, and anesthesia techniques. The patients’ ages were categorized into two groups: 60–84 and ≥85 [8]. The BMI was divided into two groups: normal (18.5–24.9) and under/overweight (<18.5 or ≥25 kg/m2). The CCI score is a scoring system that is used to predict prognosis based on the comorbidities of patients. It was divided into two categories: CCI ≤ 3 and CCI > 3 [9]. The status of COVID-19 was determined using a preoperative nasopharyngeal swab (Rapid antigen or PCR SARS-CoV-2) within the period of one day before the day of surgery. The anesthesia technique was divided into two groups: nongeneral anesthesia and general anesthesia. These variables were carried out in preanesthesia assessment.
Intraoperative factors include adverse events (AEs) that occur in the operating room, such as hypotension, hemorrhage more than estimated blood volume (EBV), prolonged surgery time, oxygen saturation, anesthesia awareness, anesthesia technique conversion, and prolonged block. Postoperative factors included AE in the recovery room, postoperative ICU care, AE in the ICU, and AE inward. AEs in the recovery room were hypotension, shivering, delayed emergence, hemorrhage more than EBV, postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), pain, oxygen desaturation, and hypothermia. AEs in the ICU were prolonged length of stay in ICU, unexpected ventilation used, and nosocomial infection. AE inward are pain, hypotension, PONV, hemorrhage, and oxygen desaturation. Patients were admitted to the ICU when the patient needed intensive monitoring, cardiovascular stabilization, unstable condition, or had a risk for severe complications after surgery [10,11]. These were recorded if patients have it during surgery or/and postoperatively. See the definition in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameter definition of variables.
2.4. Outcome Measures
The output variables in this study included mortality within 30 days after surgery and survival rate. The participants were followed prospectively for 30 days, whether the participants had died or not, and the survival time was recorded.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The statistical tests were performed with the SPSS® 23 software program (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Numerical variables with a normal distribution are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) or if not normal as the median (minimum-maximum). Missing data were excluded from the analyses. Categorical variables are displayed as numbers (percentages). Next, we summarized the data in the form of tables and narratives. We determined the association between perioperative factors and mortality using chi-square tests and, if p < 0.05, the analysis was subjected to multivariable logistic regression analysis. We used Kaplan–Meier survival analysis to describe the survival rate in COVID-19, comorbidities, and CCI. If p < 0.05, it is displayed in figure form.
2.6. Ethical Feasibility
Overall, this study was approved by the local ethics committees and institutional review boards, including the Medical and Health Research Ethics Committee (MHREC), Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada—Dr. Sardjito General Hospital with approval number KE/FK/1381/EC/2020. The ethics committee waived the written informed consent from all subjects, a legal surrogate, or the parent.
3. Results
A total of 2091 patients were included in this study, and 470 patients were excluded due to incomplete data. Finally, 1621 patients were analyzed, with 1551 patients who survived (95.7%) and 70 patients who died (4.3%). The average age of the patients was 67.1 ± 6.2 years, and most were male (54%) with almost all of the patients (98.9%) being below 84 years of age. On average, the majority of the patients (60%) had normal BMI, most of the patients (90%) underwent nonemergency surgery, and most had an ASA classification of I and II, with general anesthesia being the most commonly used technique. The majority of the patients (60%) had at least one comorbidity, with as many as 95.4% with CCI ≤ 3 and most of them (99.1%) were non-COVID. The most common comorbidity was hypertension, which was found in approximately 30% of the patients (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Demographic data of geriatric patients with mortality and univariate analysis.
Based on the place where AE occurred, hypotension was observed in the intraoperative and recovery rooms (12.7% and 4.1%, respectively), a prolonged length of stay was observed in the ICU (17.2%), and pain was observed in the ward (3.7%). As many as 13% of the geriatric patients after surgery were admitted to the ICU (see Table 2).
Five variables had p < 0.05 with univariate/multivariable logistic regression analyses. These were COVID-19 (OR, 4.34; 95% CI, 1.04–18.07; p = 0.04), CCI > 3 (OR, 2.33; 95% CI, 1.03–5.26; p = 0.04), emergency surgery (OR, 3.70; 95% CI, 1.96–7.00; p ≤ 0.01), postoperative ICU care (OR, 2.70; 95% CI, 1.32–5.53; p = 0.01), and AE in the ICU (OR, 3.43; 95% CI, 1.32–8.96; p = 0.01) (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Univariate and multivariable logistic regression analysis for patient characteristics with mortality of geriatric patients undergoing surgery.
We also analyzed the survival rate with Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. The patients with COVID-19, comorbidities, CCI > 3, and any of six comorbidities had a decreasing survival rate (log-rank p < 0.05). In addition, the geriatric patients with COVID-19, comorbidities, and CCI > 3 also had a lower survival rate than those without (see Figure 1). The six comorbidities were a moderate-to-severe renal disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes with chronic complications, metastatic solid tumor, dementia, and rheumatologic disease (see Figure 2).
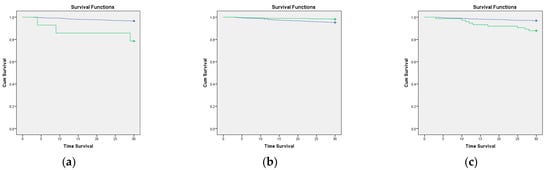
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier curve of the 30-day survival rate according to COVID-19 status, CCI score, and comorbidities. The green line is patients who have that variable, and the blue line is patients without that variable. (a) COVID-19 status (log-rank p ≤ 0.01; (b) comorbidities (log-rank p ≤ 0.01); and (c) CCI > 3 (log-rank p ≤ 0.01).
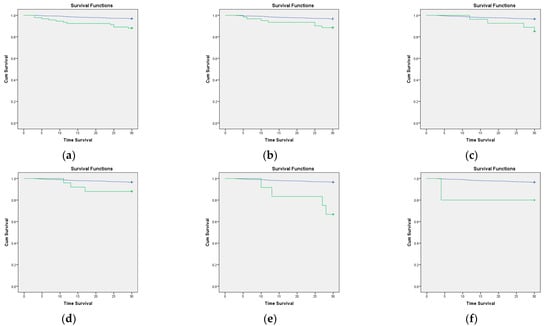
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curve of the 30-day survival rate of comorbidity in geriatric patients. The green line indicates patients with comorbidities, and the blue line indicates patients with no comorbidities. (a) Moderate-to-severe renal disease (log-rank p ≤ 0.01); (b) cerebrovascular disease (log-rank p ≤ 0.01); (c) diabetes with chronic complications (log-rank p = 0.03); (d) metastatic solid tumor (log-rank p = 0.02); (e) dementia (log-rank p ≤ 0.01), and (f) rheumatologic disease (log-rank p = 0.03).
4. Discussion
There are challenges associated with administering anesthesia to aging patients. As the number of older people increases, more surgeries will be performed. Unfortunately, the problems faced in Indonesia are exacerbated by limited healthcare facilities, and these problems were worsened in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Turrentine et al. [12] showed that geriatric patients who underwent surgery had a 28% morbidity rate and 2.3% mortality rate, which increased in people older than 80 years of age. These morbidity and mortality rates were obtained pre-COVID-19 pandemic. In Indonesia, there are no data on the 30-day mortality rate of geriatric patients undergoing surgery in the time before the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, at Hasan Sadikin General Hospital in 2017–2019, the mortality rate was 0.2% for patients of all ages [7]. In addition, we found that 4.3% of geriatric patients died within 30 days after undergoing surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic. This 30-day mortality rate is quite low compared to that in Italy, where the mortality rate is 8.13% [13]. However, we found that the proportion of mortality rate in geriatric patients with COVID-19 was higher, 26.6%, than that in Italy, 19.51% [13]. This means that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, 30-day mortality was higher when compared to prepandemic. These findings are supported by our subsequent analysis.
In our study, we found that COVID-19, a CCI score > 3, emergency surgery, postoperative ICU care, an AE in the ICU was associated with 30-day mortality in geriatric patients who received anesthesia services. This finding supports that of other studies that were focused on geriatric patients. Several risk factors are associated with postoperative mortality in geriatric patients, such as older age, sex, comorbidities, higher ASA classification, anesthesia method, longer length of stay, complications in perioperative care, ICU admission, and COVID-19 infection [13,14]. In one study in Turkey, older age, emergency surgery, several preexisting comorbidities, a longer preoperative hospital stay, postoperative complications, ICU admission, and ventilator use were associated with increased mortality in geriatric patients undergoing orthopedic surgery [15].
Geriatric patients with COVID-19 have a 4.34 times greater risk than geriatric patients without COVID-19. This is because geriatric patients are more susceptible to adverse clinical outcomes related to COVID-19 infection, and treatment in geriatric patients is more challenging since they tend to face more comorbid conditions and side effects of polypharmacotherapy [16]. In addition, one systematic review showed that COVID-19 infection increases 30-day mortality, inpatient mortality, and ICU admission among elderly hip fracture patients [5].
The CCI is associated with all-cause mortality after discharge. A high CCI score reflects that patients have more comorbidities. Initially, the CCI was used to classify comorbid conditions in patients and determine the effects of comorbidities on mortality at 1 year and 10 years [17]. At present, the CCI is used to evaluating several outcomes related to surgery or intensive care settings [18,19]. The CCI may be used to predict surgical outcomes such as 30-day mortality, 30-day readmission, 1-year mortality, complications, and failure to rescue. A higher CCI score may mean the risk of mortality increases by 16.9% at 21 months after surgery [18]. In our study, there was an association between a CCI score > 3 and 30-day mortality (p = 0.04), but interestingly, there was no association found in geriatric patients who had at least one comorbidity or no comorbidities (p = 0.33). Our finding is in line with one study in Israel that showed that a higher CCI score increased 30-day postoperative mortality in all groups of geriatric patients [20]. In addition, our findings show that, even though geriatric patients have comorbidities, the determination of the prognosis related to mortality must be seen from the existing comorbid classification, such as the CCI score. Many researchers who have used the CCI to predict postoperative mortality in the short term have used an average or categorical CCI score instead of using a single score [20,21,22,23]. The CCI score is used not only to predict the mortality risk but also to predict a prolonged length of hospital stay, and it can predict a high number of complications that may occur or patient readmission after surgery [9,18].
We found that emergency surgery has a 3.70 times greater risk for mortality than nonemergency surgery. This is because emergency admissions to the hospital may often occur during out-of-office periods, weekends, or at night, and emergency surgery may involve the risk of not having a well-defined management plan. The important consideration for emergency patients is that the intervention may not improve the patient’s condition as well as elective surgery [8].
Geriatric patients have a 2.70 times greater risk of increased mortality with postoperative ICU care. Since some surgeries are high-risk, postoperative ICU care should involve contingency planning to achieve a better postsurgical outcome. It may be necessary to admit surgical patients to the ICU admission because of known preoperative risk factors or due to unpreventable intraoperative events. In those cases, it is necessary to admit patients to the ICU for a better outcome. However, ICU patients have a high mortality rate due to critical factors, such as their condition or intraoperative/postoperative AE [8]. Geriatric patients having an AE in the ICU increase the risk of mortality by 3.43 times. Patients in the ICU also have a high risk of treatment-related injury. Having an AE during ICU care may further increase the mortality rate [8]. The occurrence of an AE is associated with an increased potential for serious problems in intensive care, a higher rate of mortality, and a prolonged length of stay.
Several factors impacted the survival rate in our study. COVID-19, comorbidities, a CCI score > 3, and six comorbidities were associated with a decreased survival rate in the Kaplan-Meier analysis. These findings align with our regression analysis that indicated that COVID-19 and a CCI score > 3 have a significant association with mortality. The six comorbidities are moderate-to-severe renal disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes with chronic complications, metastatic solid tumor, dementia, and rheumatologic disease, which are associated with lower survival rates in geriatric patients who receive anesthesia. Our finding is in line with a study in Taiwan. This study shows that having at least one of these conditions, such as congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, solid tumor metastasis, and a CCI score ≥ 3, decreases the survival rate in geriatric patients after hip surgery [24]. In addition, COVID-19 is an independent risk factor for a decreased survival rate. One of the retrospective cohort studies in Iran showed that COVID-19 decreased the survival rate in almost all patients of all ages; however, patients aged > 70 years old were the most affected group [6].
Moderate-to-severe renal disease is associated with an increased risk of death, increased cardiovascular events, and hospitalization, and it also increases the incidence of an AE after elective surgery [25]. Renal impairment in geriatric patients can lead to an increased burden of diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension, decreasing the clearance of renal excreted medication, increasing the risk of dehydration, and increasing electrolyte imbalance [26,27].
Cerebrovascular disease has the highest mortality rate and is also an important public health problem that leads to high rates of disability among elderly individuals [25]. Geriatric patients with cerebrovascular disease may have a decreased ability to perform daily living activities, an increased risk of postoperative cognitive dysfunction and delirium, and an increased sensitivity to neuraxial and regional anesthesia [26].
We found that patients with diabetes did not have a decreased survival rate, but chronic complications can decrease the survival rate. If patients have chronic complications caused by diabetes, it indicates that the patients have poor control of their blood glucose. Hyperglycemia can increase the risk of postoperative infection, leading to longer hospitalization stays, higher ICU admissions, and increased morbidity and mortality [28].
Patients with oncological disease are rarely referred for surgery due to poor outcomes and are directed to palliative care [29]. The incidence of cancer in geriatric patients is increased by 26% compared to that in younger aged patients, and cancer-related mortality increases by 15% in patients ≥ 65 years [30]. Geriatric patients who undergo surgery may have an impaired stress response, increased senescence, and decreased immunity after surgery. Therefore, we must consider the risks and benefits before planning to perform surgery in oncology patients, especially geriatric patients [23].
At present, dementia has been identified as a major challenge to health care worldwide. Anesthesia use can worsen dementia, especially Alzheimer’s disease. Volatile anesthetics such as halothane and isoflurane increase oligomerization and cytotoxicity of amyloid peptide, leading to worsening of the pathology of dementia. In addition, the use of sevoflurane and isoflurane can cause neuronal apoptosis and alpha-beta protein aggregation, increasing behavioral impairment and mortality [31].
Rheumatologic disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology. Rheumatic disorders have high variability; some develop very rapidly, while others develop chronically, causing disability. One of the rheumatologic diseases is rheumatoid arthritis. This disease is characterized by deformities, which may affect the patients’ positioning during surgery and make it difficult to access the area that requires anesthesia (especially regional anesthesia). In addition, head and neck involvement in rheumatoid arthritis can result in difficulties with impaired airways due to the complexity of several maneuvers that are necessary for tracheal intubation. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the extension of the cervical spine, temporomandibular joint, and cricoarytenoid joint involvement in preoperative assessments [32]. Patients with rheumatologic disease have a higher risk of myocardial infarction, which is similar to individuals with diabetes or a person ten years older than the age of the patients [33].
In our study, there are several limitations. First, not all the hospitals in Indonesia were involved. This study was conducted in 14 teaching hospitals which is a referral hospital, including referrals for COVID-19 patients where the cases encountered are complex. Second, although 30 days is enough to see mortality and survival rate of geriatric patients undergoing surgery, it may be necessary to see survival with longer follow-up. Third, we did not provide causes of death because death can occur from various causes and is not always directly related to the study. Fourth, AEs (such as hypoxia, hypotension, and hypothermia) were measured and recorded from the presence or absence during or after surgery and did not include more detailed data on the duration and frequency of occurrence. Lastly, although hemorrhage more than EBV was recorded as one of the AEs, we did not include blood transfusion as one of the perioperative factors that could affect the patient’s mortality and survival rate. We recommend that further research be conducted on blood transfusion as a factor that may be related to patients’ mortality and survival rate. Nevertheless, apart from the limitations mentioned above, our results may sufficiently represent the general geriatric patients who undergo surgery in Indonesia, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
5. Conclusions
The overall 30-day mortality rate of geriatric patients undergoing surgery was 4.3%. Five variables were associated with the 30-day mortality rate in geriatric patients undergoing surgery, including COVID-19 infection, a CCI score > 3, emergency surgery, postoperative ICU, and an AE in the ICU. Aligned with these findings, COVID-19, comorbidities, and a CCI score > 3 have lower survival rates.
Using a single comorbidity alone may not predict the 30-day mortality rate. Comorbidities became relevant when converted into categories using the Charlson Comorbidity Index score, which can be used to predict the 30-day mortality rate and the decrease in survival rate in geriatric patients. Based on these results, an anesthesiologist may be more aware of the perioperative factors that may affect the 30-day mortality rate in geriatric patients, such as COVID-19 infection, a CCI score > 3, undergoing emergency surgery, and admission to the ICU, especially if an AE occurs. In addition, when geriatric patients have one of these conditions, such as COVID-19 infection, a CCI score > 3, moderate-to-severe renal disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes with chronic complications, a metastatic solid tumor, dementia, or rheumatologic disease, it may decrease the survival rate of geriatric patients.
Finally, we realize that each country and each place have different perioperative risk factors for geriatric patients undergoing surgery. In addition to being useful for Indonesian local data, of course, this research can be useful when applied to populations in countries because COVID-19 affected many countries in terms of rapid transmission and high mortality rates. Additional information obtained in various countries (including our research) can improve our understanding, help us identify better treatment methods, prevent a worsening condition, and improve the prognosis of geriatric patients undergoing surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm11185292/s1, Supplementary File S1: List of collaborators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M.R., S.C., D.S., M.I.L., T.G.A.S. and H.N.; formal Analysis: N.M.R., S.C. and D.S.; investigation, D.S., M.I.L., H.N., B.W., B.P., A.P.P., I.I., N.A., K.M.S., R.A.H., Z.K.J., A.H.N., M.M. and P.P.; methodology, N.M.R., S.C. and T.G.A.S.; project administration, N.M.R., S.C., D.S. and M.I.L.; resources, D.S., M.I.L., H.N., B.W., B.P., A.P.P., I.I., N.A., K.M.S., R.A.H., Z.K.J., A.H.N., M.M. and P.P.; supervision, N.M.R., S.C. and T.G.A.S.; validation, N.M.R., S.C., D.S., M.I.L., T.G.A.S., H.N., B.W., B.P., A.P.P., I.I., N.A., K.M.S., R.A.H., Z.K.J., A.H.N., M.M. and P.P.; visualization, D.S, M.I.L. and H.N.; writing—original draft, D.S. and M.I.L.; writing—review and editing, N.M.R., S.C., D.S., M.I.L., T.G.A.S., H.N., B.W., B.P., A.P.P., I.I., N.A., K.M.S., R.A.H., Z.K.J., A.H.N., M.M. and P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Indonesian College of Anesthesiology and Intensive Therapy (KATI) and the Indonesian Society of Anesthesiologists and Intensive Therapy (PERDATIN).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the local ethics committees and institutional review boards Medical and Health Research Ethics Committee (MHREC), Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada—Dr. Sardjito General Hospital (KE/FK/1381/EC/2020). All methods were conducted following National Guidelines on ethical standards and procedures for research with a human being.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent from all participants or a legal surrogate was waived by the MHREC, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada—Dr. Sardjito General Hospital due to the observational design of this study and the provision of standards of care to all participants.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Iche Andriyani Liberty and Dhite Bayu Nugroho for their contribution in reviewing our statistics. The author also would like to thank Andre Krislee, Timor Krisna Bayu, Muhammad Imam Mulia, and other collaborators [see Supplementary File S1] for their contribution to finishing this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Koroye, O.F.; Adejumo, A.; Emile, S.H.; Ukoima, H.S.; Fente, B.G. Surgery in the COVID-19 Era: A Narrative Review. J. West Afr. Coll. Surg. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, D.J. Anaesthesia in the elderly. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 20, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.K.; Lake, R.; Englum, B.R.; Turner, D.J.; Siddiqui, T.; Mayorga-Carlin, M.; Sorkin, J.D.; Lal, B.K. Increased complications in patients who test COVID-19 positive after elective surgery and implications for pre and postoperative screening. Am. J. Surg. 2022, 223, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepogodiev, D.; Bhangu, A.; Glasbey, J.C.; Li, E.; Omar, O.M.; Simoes, J.F.; Abbott, T.E.; Alser, O.; Arnaud, A.P.; Bankhead-Kendall, B.K. Mortality and pulmonary complications in patients undergoing surgery with perioperative SARS-CoV-2 infection: An international cohort study. Lancet 2020, 396, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.K.; Varghese, P.; Panigrahi, S.; Panda, B.B.; Srinivasan, A.; Sen, R.K. Perioperative mortality and morbidity of hip fractures among COVID-19 infected and non-infected patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshrati, B.; Baradaran, H.R.; Erfanpoor, S.; Mohazzab, A.; Moradi, Y. Investigating the factors affecting the survival rate in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. Med. J. Islamic Repub. Iran 2020, 34, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrina, J.A.; Indriasari, I.; Zulfariansyah, A. Angka Kejadian serta Karakteristik Mortalitas dan Morbiditas pada Pengelolaan Anestesi Perioperatif di RSUP Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung Tahun 2017–2019. J. Anestesi Perioper. 2022, 10, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Søreide, K.; Desserud, K.F. Emergency surgery in the elderly: The balance between function, frailty, fatality and futility. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.; Yiğt, A.; Benli, A.R. The prognostic role of Charlson comorbidity index for critically ill elderly patients. Eur. Res. J. 2020, 6, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, J.; Wunsch, H. Triage of high-risk surgical patients for intensive care. Crit Care. 2011, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidet, B.; Thomas, C.; Leblanc, G.; Boumendil, A.; Pateron, D. Postoperative Admission to the Intensive Care Unit in Perioperative Care of the Elrderly; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrentine, F.E.; Wang, H.; Simpson, V.B.; Jones, R.S. Surgical risk factors, morbidity, and mortality in elderly patients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2006, 203, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doglietto, F.; Vezzoli, M.; Gheza, F.; Lussardi, G.L.; Domenicucci, M.; Vecchiarelli, L.; Zanin, L.; Saraceno, G.; Signorini, L.; Panciani, P.P. Factors associated with surgical mortality and complications among patients with and without coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA Surg. 2020, 155, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Meng, L.-Z.; Wang, T.-L. Geriatric anesthesia-related morbidity and mortality in China: Current status and trend. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükosman, G.; Öztoprak, H.; Öztürk, T.; Ayoğlu, H. Factors associated with postoperative mortality in geriatric orthopedic surgery: A retrospective analysis of single center data. Anestezi Derg. 2019, 27, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, F.; Corbi, G.; Mazzeo, G.; Boccia, M.; Aronne, L.; D’Agnano, V.; Komici, K.; Mazzarella, G.; Parrella, R.; Bianco, A. COVID-19 and the elderly: Insights into pathogenesis and clinical decision-making. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbian, F.; De Giorgi, A.; Ferro, S.; Lacavalla, D.; Andreotti, D.; Ascanelli, S.; Volpato, S.; Occhionorelli, S. Post-Operative All-Cause Mortality in Elderly Patients Undergoing Abdominal Emergency Surgery: Role of Charlson Comorbidity Index. Healthcare 2021, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraccaro, P.; Kontopantelis, E.; Sperrin, M.; Peek, N.; Mallen, C.; Urban, P.; Buchan, I.E.; Mamas, M.A. Predicting mortality from change-over-time in the Charlson Comorbidity Index: A retrospective cohort study in a data-intensive UK health system. Medicine 2016, 95, e4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laor, A.; Tal, S.; Guller, V.; Zbar, A.P.; Mavor, E. The Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) as a mortality predictor after surgery in elderly patients. Am. Surg. 2016, 82, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.; Kwon, J.-H.; Oh, A.R.; Gook, J.; Yang, K.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, K.; Sung, J.D.; Ahn, J. The Charlson Comorbidity Index is associated with risk of 30-day mortality in patients with myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, L.L.; Kashiwagi, D.T.; Burton, M.C.; Cha, S.; Varkey, P. The Charlson Comorbidity Index Score as a predictor of 30-day mortality after hip fracture surgery. Am. J. Med. Qual. 2011, 26, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowdley, G.C.; Merchant, N.; Richardson, J.P.; Somerville, J.; Gorospe, M.; Cunningham, S.C. Cancer surgery in the elderly. Sci. World J. 2012, 14, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-C.; Chou, M.-Y.; Liang, C.-K.; Lin, Y.-T.; Ku, Y.-C.; Wang, R.-H. Factors affecting one-year mortality of elderly patients after surgery for hip fracture. Int. J. Gerontol. 2016, 10, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chu, C.-L.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Chou, W.-H.; Chang, P.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Yeh, H.-M. Leading comorbidity associated with 30-day post-anesthetic mortality in geriatric surgical patients in Taiwan: A retrospective study from the health insurance data. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.T.; Hemati, K.; Donovan, A.L. Geriatric physiology and the frailty syndrome. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.; Gooneratne, M.; Partridge, J. Preoperative assessment of the older patient. BJA Educ. 2021, 21, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Min, L.; Mody, L. Perioperative glucose control and infection risk in older surgical patients. Curr. Geriatr. Rep. 2014, 3, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiner, S.; Westlake, B.; Dutton, R.P. Patterns of surgical care and complications in elderly adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancik, R. Population aging and cancer: A cross-national concern. Cancer J. 2005, 11, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Berger, M.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; Seitz, D.P. General anesthetic and the risk of dementia in elderly patients: Current insights. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1619. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, E.M.; Goodman, S.; Tanaka, P.P. Anesthesia and rheumatoid arthritis. Rev. Bras. Anestesiol. 2011, 61, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krause, M.L.; Matteson, E.L. Perioperative management of the patient with rheumatoid arthritis. World J. Orthop. 2014, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).