Use of Electroneuromyography in the Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Eligibility Criteria and Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Analysis
2.4. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
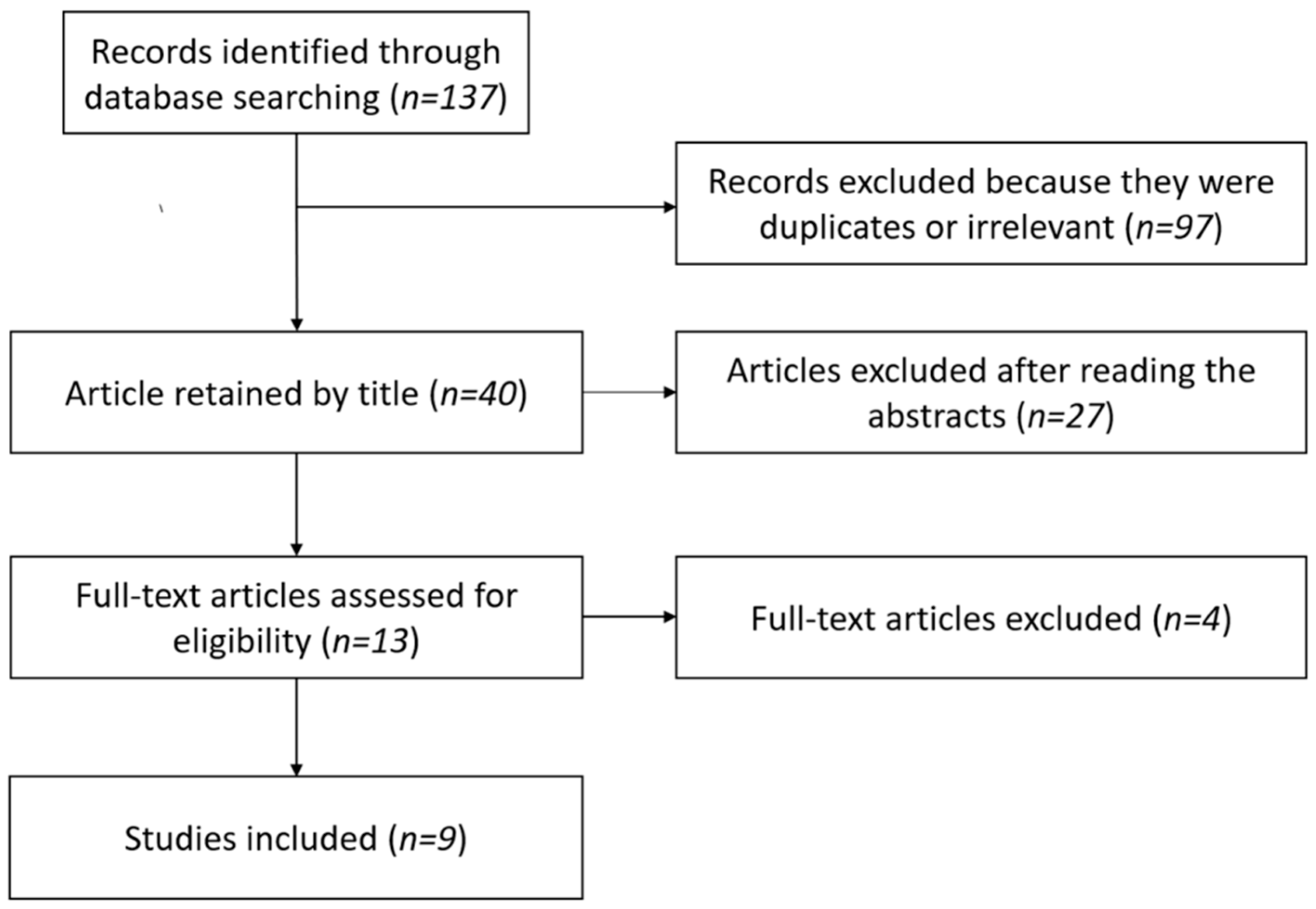
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Demographic Data
3.3. Neurological Examination
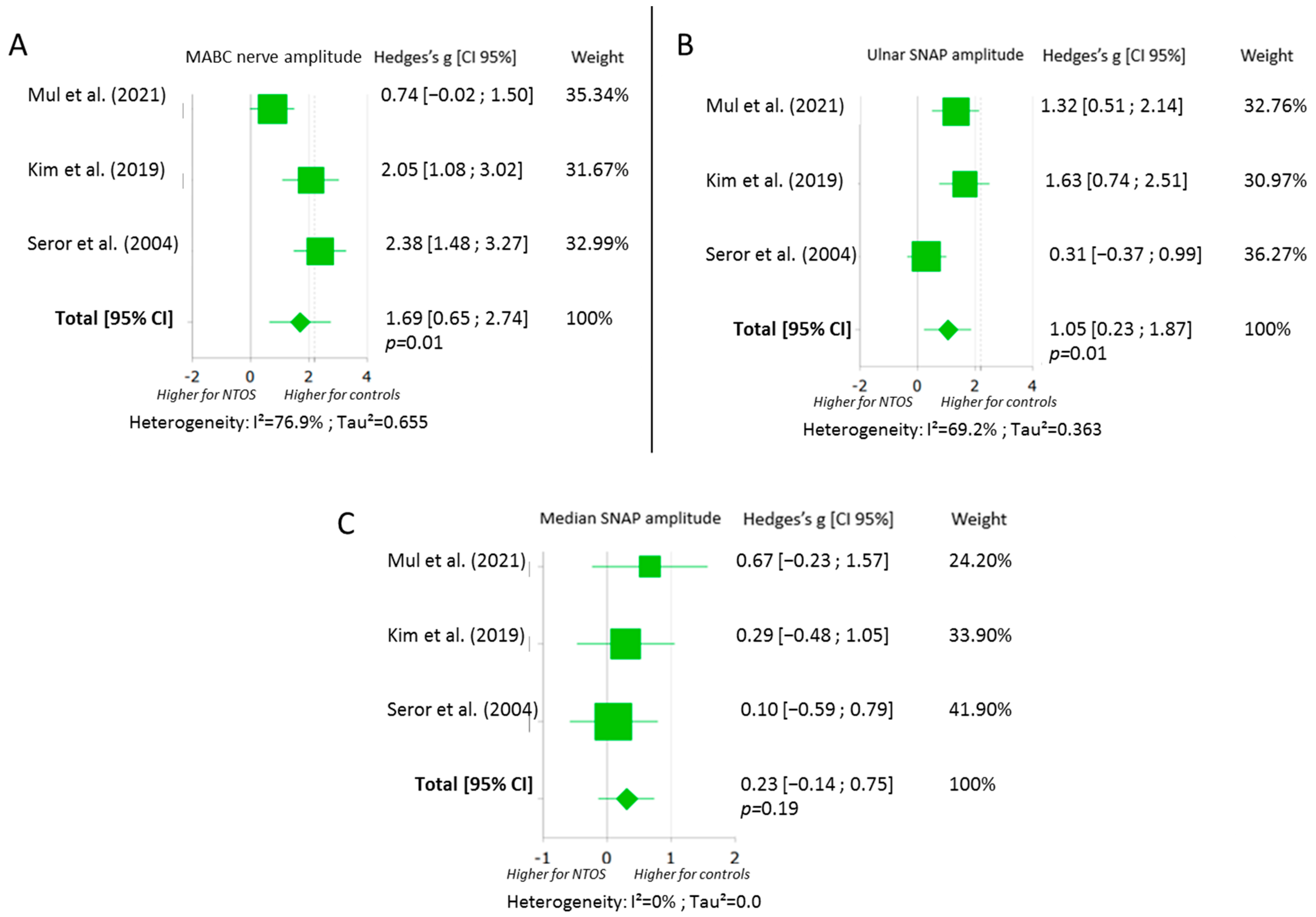
3.4. Sensory Nerve Conduction Assessment
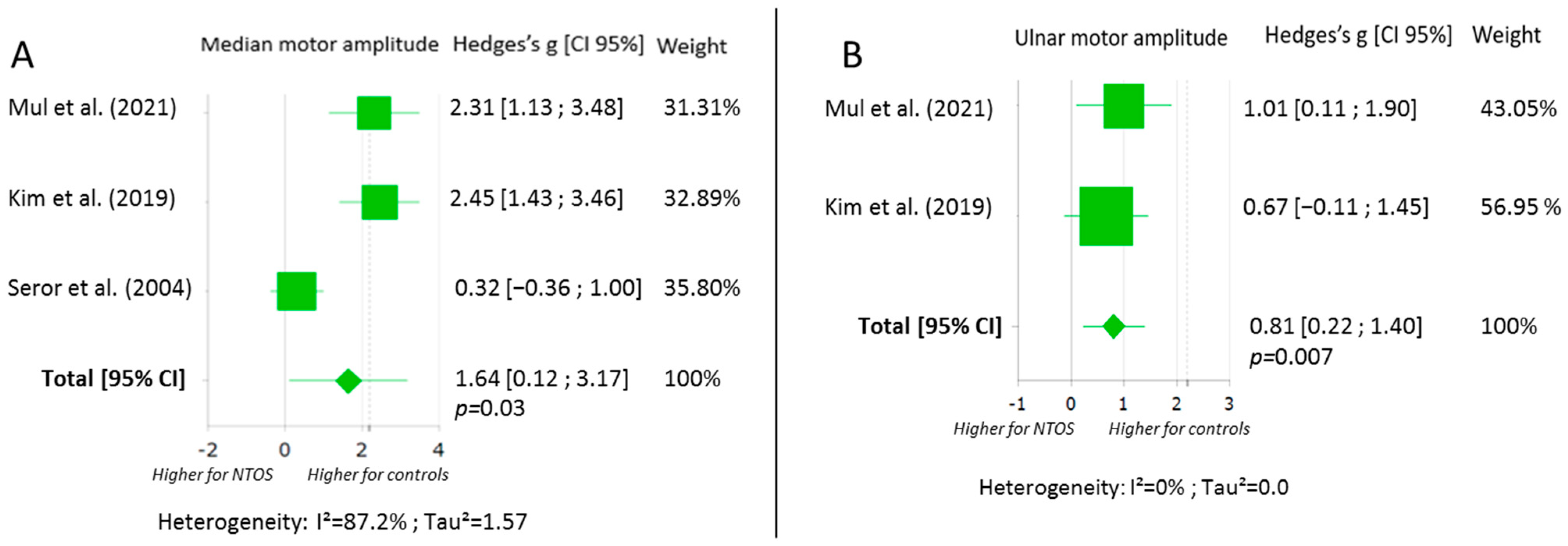
3.5. Motor Nerve Conduction Assessment
3.6. Late Responses
3.7. Needle Examination
3.8. Sensitivity to Change
3.9. NTOS Patients with No Clinical Motor Deficit
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, R.J.; Hammond, S.L.; Rao, N.M. Diagnosis of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 46, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balderman, J.; Holzem, K.; Field, B.J.; Bottros, M.M.; Abuirqeba, A.A.; Vemuri, C.; Thompson, R.W. Associations between Clinical Diagnostic Criteria and Pretreatment Patient-Reported Outcomes Measures in a Prospective Observational Cohort of Patients with Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 66, 533–544.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, C.; Natalini, L.; Romeo, A.; Tosarelli, D.; Pillastrini, P. Conservative Treatment of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. A Review of the Literature. Eur. Medicophysica 2007, 43, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.R.; Prabhakar, A.; Viswanath, O.; Urits, I.; Green, J.B.; Kendrick, J.B.; Brunk, A.J.; Eng, M.R.; Orhurhu, V.; Cornett, E.M.; et al. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Pain Ther. 2019, 8, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, P.; Pomares, G.; Menu, P.; Gadbled, G.; Dauty, M.; Fouasson-Chailloux, A. Shoulder Isokinetic Strength Deficit in Patients with Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouasson-Chailloux, A.; Daley, P.; Menu, P.; Louguet, B.; Gadbled, G.; Bouju, Y.; Abraham, P.; Dauty, M. Hand Strength Deficit in Patients with Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, K.A. Conservative Treatment of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A 2-Year Follow-Up. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1997, 78, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.W. Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: 2016 Consensus Guidelines and Other Strategies. In Thoracic Outlet Syndrome; Springer: London, UK, 2021; pp. 67–97. [Google Scholar]
- Illig, K.A.; Donahue, D.; Duncan, A.; Freischlag, J.; Gelabert, H.; Johansen, K.; Jordan, S.; Sanders, R.; Thompson, R. Reporting Standards of the Society for Vascular Surgery for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, e23–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, M.L.; Lum, Y.W. New Diagnostic and Treatment Modalities for Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouasson-Chailloux, A.; Menu, P.; Daley, P.; Gautier, G.; Gadbled, G.; Abraham, P.; Dauty, M. Subclavian Vessel Compression Assessed by Duplex Scanning in Patients with Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome and No Vascular Signs. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeteyn, J.; Pesser, N.; van Sambeek, M.R.H.M.; Thompson, R.W.; van Nuenen, B.F.L.; Teijink, J.A.W. Duplex Ultrasound Studies Are Neither Necessary or Sufficient for the Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 81, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, M.A.; Ferrante, N.D. The Thoracic Outlet Syndromes: Part 1. Overview of the Thoracic Outlet Syndromes and Review of True Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: The Thoracic Outlet Syndromes, Part 1. Muscle Nerve 2017, 55, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, B.E.; Ferrante, M.A.; Wilbourn, A.J.; Shields, R.W. Electrodiagnostic Features of True Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2014, 49, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliatt, R.W.; Le Quesne, P.M.; Logue, V.; Sumner, A.J. Wasting of the Hand Associated with a Cervical Rib or Band. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1970, 33, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Forestier, N.; Moulonguet, A.; Maisonobe, T.; Léger, J.M.; Bouche, P. True Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Electrophysiological Diagnosis in Six Cases. Muscle Nerve 1998, 21, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseff, R.; Tzvetanov, P.; Valkov, I. Utility (or Futility?) Of Electrodiagnosis in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 45, 131–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Sung, D.H. Case Report: Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome without Electrophysiologic Abnormality. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 644893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Surg. Lond. Engl. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA Group Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. Lond. Engl. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE Working Group GRADE: An Emerging Consensus on Rating Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meta-Mar Online Meta-Analysis Calculator 2022. Available online: https://www.meta-mar.com/ (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Feng, J.-T.; Zhu, Y.; Hua, X.-Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Y.-D.; Xu, J.-G.; Xu, W.-D. Diagnosing Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome with the Triple Stimulation Technique. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Martínez, A.; Arpa, J. Electrophysiological Assessment in Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 41, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.; Sung, D.H.; Kang, M.J.; Ko, M.J.; Do, J.G.; Sunwoo, H.; Kwon, T.G.; Hwang, J.M.; Park, Y. Clinical, Electrophysiological Findings in Adult Patients with Non-Traumatic Plexopathies. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 35, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tender, G.C.; Thomas, A.J.; Thomas, N.; Kline, D.G. Gilliatt-Sumner Hand Revisited: A 25-Year Experience. Neurosurgery 2004, 55, 883–890, discussion 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mul, K.; Pesser, N.; Vervaart, K.; Teijink, J.; Nuenen, B.; Alfen, N. Variability in Electrodiagnostic Findings Associated with Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2021, 65, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, B.J.; Choe, Y.H.; Yoon, Y.C.; Sung, D.H. Clinical, Electrodiagnostic and Imaging Features of True Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Experience at a Tertiary Referral Center. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 404, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgönenel, L.; Akyüz, G.; Ozgönenel, B.; Adatepe, T. Provocative F Wave in the Diagnosis of Nonspecific Neurogenic-Type Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkuş, M.; Yağmurlu, K.; Özarslan, M.; Kalani, M.Y.S. Surgical Outcomes of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Based on Electrodiagnostic Tests and QuickDASH Scores. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2018, 58, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seror, P. Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Conduction Study, a New Tool to Demonstrate Mild Lower Brachial Plexus Lesions. A Report of 16 Cases. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 2316–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machanic, B.I.; Sanders, R.J. Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Measurements to Diagnose Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 22, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillard, J.; Pérez-Cousin, M.; Hachulla, E.; Remy, J.; Hurtevent, J.F.; Vinckier, L.; Thévenon, A.; Duquesnoy, B. Diagnosing Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Contribution of Provocative Tests, Ultrasonography, Electrophysiology, and Helical Computed Tomography in 48 Patients. Joint Bone Spine 2001, 68, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.A.; Wilbourn, A.J. The Utility of Various Sensory Nerve Conduction Responses in Assessing Brachial Plexopathies. Muscle Nerve 1995, 18, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povlsen, S.; Povlsen, B. Diagnosing Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessureault-Dober, I.; Bronchti, G.; Bussières, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Clinical Tests for Neurogenic and Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Systematic Review. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 2018, 41, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Forestier, N.; Mouton, P.; Maisonobe, T.; Fournier, E.; Moulonguet, A.; Willer, J.C.; Bouche, P. True neurological thoracic outlet syndrome. Rev. Neurol. 2000, 156, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, C.H.; Park, N.S.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, M.W. Determination of an Ideal Stimulation Site of the Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve Using Ultrasound and Investigation of the Efficiency. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 38, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.I.; Lamb, C.J. Comparison of Proximal and Distal Techniques for the Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Sensory Nerve Conduction Study. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. Publ. Am. Electroencephalogr. Soc. 2020, 39, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, B.; Moghaddam, F.R.; Pajhouh, R.R. Medical Brachial Cutaneous Nerve Conduction Study. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 40, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, D.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Experimental Muscle Pain Reduces Initial Motor Unit Discharge Rates during Sustained Submaximal Contractions. J. Appl. Physiol. Bethesda Md 1985 2005, 98, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falla, D.; Lindstrøm, R.; Rechter, L.; Farina, D. Effect of Pain on the Modulation in Discharge Rate of Sternocleidomastoid Motor Units with Force Direction. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Valdes, E.; Negro, F.; Farina, D.; Falla, D. Divergent Response of Low- vs. High-Threshold Motor Units to Experimental Muscle Pain. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 2093–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, D.B. Historical Perspectives and Anatomic Considerations. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1996, 8, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B. Anatomic Issues Related to Cervical and Lumbosacral Radiculopathy. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 13, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Kumar, R.; Jain, A. Variations in Innervation of Muscles in Anterior Compartment of Arm—A Cadaveric Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2014, 8, AC01–AC03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riew, K.D. Variations in Cervical Myotomes and Dermatomes. Spine J. Off. J. N. Am. Spine Soc. 2019, 19, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katirji, M.B.; Agrawal, R.; Kantra, T.A. The Human Cervical Myotomes: An Anatomical Correlation between Electromyography and CT/Myelography. Muscle Nerve 1988, 11, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouasson-Chailloux, A.; Daley, P.; Menu, P.; Gadbled, G.; Bouju, Y.; Gautier, G.; Pomares, G.; Dauty, M. Use of Hand Hydraulic Dynamometers as an Overall Evaluation of the Upper-Limb Weakness in Patients with Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.K.; Jeyaseelan, L.; Kyriacou, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sinisi, M.; Fox, M. Diagnostic Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. J. Orthop. Surg. Hong Kong 2014, 22, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejas, C.; Rollán, C.; Michelin, G.; Nogués, M. High Resolution Neurography of the Brachial Plexus by 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Radiologia 2016, 58, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumer, P.; Kele, H.; Kretschmer, T.; Koenig, R.; Pedro, M.; Bendszus, M.; Pham, M. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome in 3T MR Neurography-Fibrous Bands Causing Discernible Lesions of the Lower Brachial Plexus. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Studies | Population | Symptomatic Limbs (n) | Mean Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | Duration of Symptoms (Months) | Diagnostic Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mul et al. (2021) [28] | Not specified | 14 | 36.4 | 2/12 | 127 | Clinical + NCS |
| Kim et al. (2019) [29] | Surgical and non-surgical | 13 | 40.3 | 3/10 | 70.6 | Clinical |
| Akkus et al. (2018) [31] | Surgical | 15 | 30.6 * | 3/12 | NA | Clinical |
| Tsao et al. (2014) [14] | Surgical | 32 | 40.7 | 2/30 | 61 | NCS |
| Ozgönenel et al. (2012) [30] | Non-surgical | 21 | 31.3 | 3/18 | 62 | Clinical |
| Machanic et al. (2008) [33] | Surgical | 41 | NA | 9/32 | NA | Clinical |
| Seror et al. (2004) [32] | Non-surgical | 16 | 43.1 | 2/14 | NA | NCS |
| Rousseff et al. (2004) [17] | Surgical | 20 | 29.5 * | 4/16 | NA | Surgical TOS |
| Gillard et al. (2001) [34] | Non-surgical | 31 | 37.1 | 5/26 | NA | Clinical + NCS + imaging |
| Studies | Design | Limitations in Study Design or Execution | Inconsistency of Results | Indirectness of Evidence | Imprecision | Quality of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mul et al. (2021) [28] | Retrospective case series | + | - | - | - | Low |
| Kim et al. (2019) [29] | Retrospective case series | + | - | - | - | Low |
| Akkus et al. (2018) [31] | Prospective case series | + | + | - | + | Very low |
| Tsao et al. (2014) [14] | Retrospective case series | + | - | - | + | Low |
| Ozgönenel et al. (2012) [30] | Prospective case series | - | - | - | - | Moderate |
| Machanic et al. (2008) [33] | Prospective case series | - | - | - | + | Low |
| Seror et al. (2004) [32] | Retrospective case series | - | - | - | - | Low |
| Rousseff et al. (2004) [17] | Retrospective case series | ++ | - | - | ++ | Low |
| Gillard et al. (2001) [34] | Prospective case series | + | - | + | ++ | Very low |
| Studies | Number of Symptomatic Limbs | Abnormal MABC Nerve Amplitude (Side-to-Side Ratio for Abnormality) | Absolute Abnormal SNAP Ulnar Amplitude (Chosen Cut-Off) | Relative Abnormal SNAP Ulnar Amplitude (Side-to-Side Ratio for Abnormality) | Abnormal CMAP Median Amplitude (APB), Absolute (Chosen Cut-Off) | Abnormal CMAP Median Amplitude (APB), Relative (Side-to-Side Ratio for Abnormality) | Abnormal CMAP Ulnar Amplitude, Absolute (Chosen Cut-Off) | Abnormal CMAP Ulnar Amplitude, Relative (Side-to-Side Ratio for Abnormality) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mul et al. (2021) [28] | 14 | 50% (2) | 79% (19.3 µV) | 71% (2) | 64% (6.2 µV) | 100% (2) * | 28% (8.4 µV) | 20% (2) ** |
| Kim et al. (2019) [29] | 13 | 92% (2) | 46% (age-stratified norms) | 58% (2) | 85% (age-stratified norms) | 75% (2) | 54% (age-stratified norms) | 8% (2) |
| Tsao et al. (2014) [14] | 32 | 95% (2) | 6% (age-stratified norms) | 78% (2) | 91% (age-stratified norms) | 97% (2) | 3.1% (age-stratified norms) | 38% (2) |
| Machanic et al. (2008) [33] | 41 | 61% (2) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Seror et al. (2004) [32] | 16 | 94% (2) | NA | NA | 0% (not mentioned) | 0% (2) | 0% (not mentioned) | 0% (not mentioned) |
| Rousseff et al. (2004) [17] | 20 | NA | 5% (criteria not mentioned) | 0% (not mentioned) | 0% (not mentioned) | 0% (not mentioned) | 0% (not mentioned) | |
| Studies | Myographies (n) | APB (Number of Evaluations) | FDI (Number of Evaluations) | ADM (Number of Evaluations) | Other (Number of Evaluations) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mul et al. (2021) [28] | 14 | 50% (9) | 86% (13) | 36% (7) | ED 29% (8), FCR 29% (7), BB 7% (3), D 0% (2), EPL 7% (2), FCU 7% (1) |
| Kim et al. (2019) [29] | 13 | 85% (13) | 69% (13) | 31% (5) | EIP 46% (9), BB 0% (10), D 0% (8), ED 15% (5), FCU 38% (12), FPL 23% (4), PSP 0% (13) |
| Tsao et al. (2014) [14] | 32 | ~50% (NA) | ~33% (NA) | ~33% (NA) | OP ~50% (NA), PSP 0% (28), Triceps 0% (31) |
| Seror et al. (2004) [32] | 16 | 25% (16) | 12% (NA) | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daley, P.; Pomares, G.; Gross, R.; Menu, P.; Dauty, M.; Fouasson-Chailloux, A. Use of Electroneuromyography in the Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175206
Daley P, Pomares G, Gross R, Menu P, Dauty M, Fouasson-Chailloux A. Use of Electroneuromyography in the Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175206
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaley, Pauline, Germain Pomares, Raphael Gross, Pierre Menu, Marc Dauty, and Alban Fouasson-Chailloux. 2022. "Use of Electroneuromyography in the Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175206
APA StyleDaley, P., Pomares, G., Gross, R., Menu, P., Dauty, M., & Fouasson-Chailloux, A. (2022). Use of Electroneuromyography in the Diagnosis of Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175206








