Reliability of a New Indentometer Device for Measuring Myofascial Tissue Stiffness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Ethics
2.2. Participants
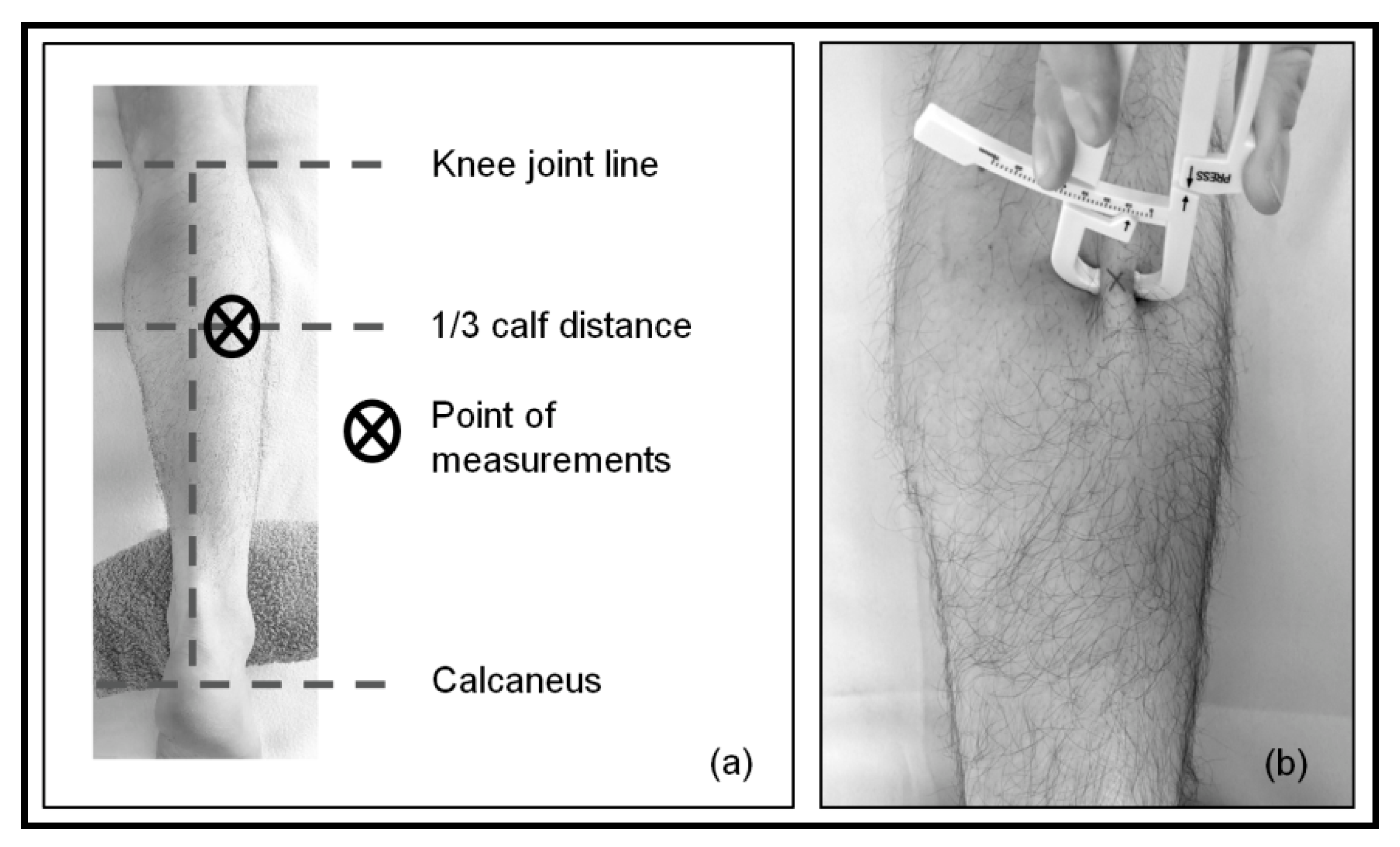
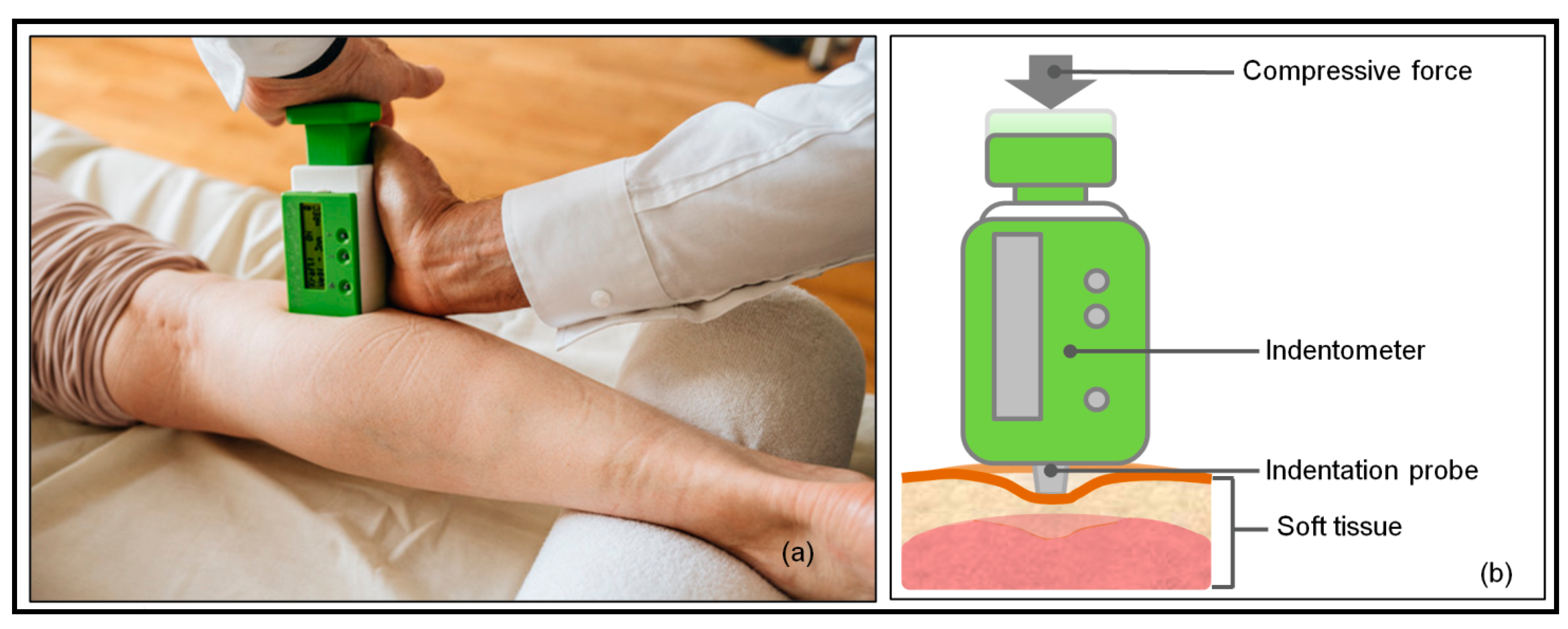
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Group Characteristics
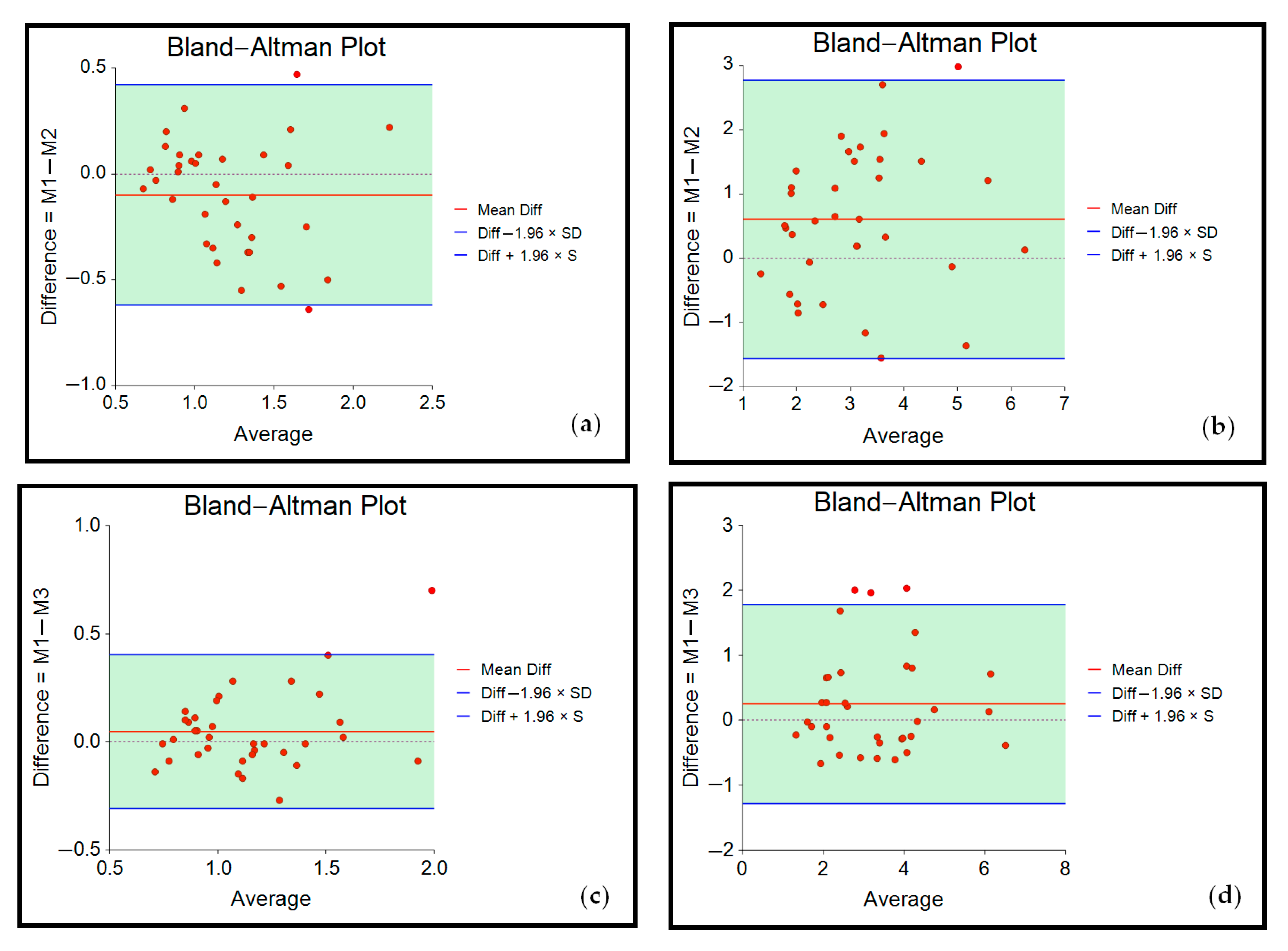
3.2. Reliability
3.3. Correlation between Skinfold Thickness, Anthropometric Data and Tissue Stiffness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischer, A.A. Tissue Compliance Meter for Objective, Quantitative Documentation of Soft Tissue Consistency and Pathology. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1987, 68, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al Mayah, A. Biomechanics of Soft Tissues: Principles and Application; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-351-13582-5. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart, E. Stiffness—An Unknown World of Mechanical Science? Injury 2000, 31 (Suppl. 2), S-B14-23. [Google Scholar]
- Arokoski, J.P.A.; Surakka, J.; Ojala, T.; Kolari, P.; Jurvelin, J.S. Feasibility of the Use of a Novel Soft Tissue Stiffness Meter. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, J.; Vogt, L.; Pfarr, T.; Banzer, W. Reliability and Validity of a Semi-Electronic Tissue Compliance Meter to Assess Muscle Stiffness. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2018, 31, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, F.; Ebihara, S.; Akiyama, M.; Horikawa, M. Pericranial Muscle Hardness in Tension-Type Headache. A Non-Invasive Measurement Method and Its Clinical Application. Brain 1995, 118 Pt 2, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, M.; Bendtsen, L.; Jensen, R.; Olesen, J. Muscle Hardness in Patients with Chronic Tension-Type Headache: Relation to Actual Headache State. Pain 1999, 79, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Kulig, K. Tendinopathy Alters Mechanical and Material Properties of the Achilles Tendon. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.-H.; Jian, D.-W.; Wang, T.-G.; Wang, Y.-C. Neck Muscle Stiffness Quantified by Sonoelastography Is Correlated with Body Mass Index and Chronic Neck Pain Symptoms. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Kulig, K. The Neuromechanical Adaptations to Achilles Tendinosis. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 3373–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugailly, P.-M.; Coucke, A.; Salem, W.; Feipel, V. Assessment of Cervical Stiffness in Axial Rotation among Chronic Neck Pain Patients: A Trial in the Framework of a Non-Manipulative Osteopathic Management. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 53, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleip, R.; Gabbiani, G.; Wilke, J.; Naylor, I.; Hinz, B.; Zorn, A.; Jäger, H.; Breul, R.; Schreiner, S.; Klingler, W. Fascia Is Able to Actively Contract and May Thereby Influence Musculoskeletal Dynamics: A Histochemical and Mechanographic Investigation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, J.R.; MacIntosh, B.R. Changes in Achilles Tendon Stiffness and Energy Cost Following a Prolonged Run in Trained Distance Runners. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumke, C.L.; Pfaffenroth, C.M.; McBride, J.M.; McCauley, G.O. Relationship between Muscle Strength, Power and Stiffness and Running Economy in Trained Male Runners. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojsen-Møller, J.; Magnusson, S.P.; Rasmussen, L.R.; Kjaer, M.; Aagaard, P. Muscle Performance during Maximal Isometric and Dynamic Contractions Is Influenced by the Stiffness of the Tendinous Structures. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Yata, H.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Effects of Isometric Squat Training on the Tendon Stiffness and Jump Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 96, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasi, M.; Sisti, D.; Amatori, S.; Andreazza, M.; Benelli, P.; Sestili, P.; Rocchi, M.B.L.; Calavalle, A.R. Muscular Viscoelastic Characteristics of Athletes Participating in the European Master Indoor Athletics Championship. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Koppenhaver, S.L.; MacDonald, C.W.; Herrera, J.M.; Streuli, J.; Visco, Z.L.; Wildermuth, N.; Albin, S.R. Normative Parameters of Gastrocnemius Muscle Stiffness and Associations with Patient Characteristics and Function. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2021, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.P.; Connolly, D.A.; Eston, R.G.; Kremenic, I.J.; Nicholas, S.J.; Gleim, G.W. The Role of Passive Muscle Stiffness in Symptoms of Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. Am. J. Sports Med. 1999, 27, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafazzoli, F.; Lamontagne, M. Mechanical Behaviour of Hamstring Muscles in Low-Back Pain Patients and Control Subjects. Clin. Biomech. 1996, 11, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrysomallis, C. Injury Incidence, Risk Factors and Prevention in Australian Rules Football. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleip, R.; Bartsch, K. (Second) Mechanical Assessment. In Fascia in Sport and Movement; Handspring Publishing Limited: Pencaitland, UK, 2021; p. 599. ISBN 978-1-912085-77-4. [Google Scholar]
- Aarrestad, D.D.; Williams, M.D.; Fehrer, S.C.; Mikhailenok, E.; Leonard, C.T. Intra- and Interrater Reliabilities of the Myotonometer When Assessing the Spastic Condition of Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2004, 19, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, C.T.; Deshner, W.P.; Romo, J.W.; Suoja, E.S.; Fehrer, S.C.; Mikhailenok, E.L. Myotonometer Intra- and Interrater Reliabilities11A Commercial Party with a Direct Financial Interest in the Results of the Research Supporting This Article Has Conferred or Will Confer a Financial Benefit upon One or More of the Authors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamukoff, D.N.; Bell, S.E.; Ryan, E.D.; Blackburn, J.T. The Myotonometer: Not a Valid Measurement Tool for Active Hamstring Musculotendinous Stiffness. J. Sport Rehabil. 2016, 25, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyapong-Badu, S.; Aird, L.; Bailey, L.; Mooney, K.; Mullix, J.; Warner, M.; Samuel, D.; Stokes, M. Interrater Reliability of Muscle Tone, Stiffness and Elasticity Measurements of Rectus Femoris and Biceps Brachii in Healthy Young and Older Males. Work. Pap. Health Sci. 2013, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, M.J.; Bryant, A.L.; Bower, W.F.; Frawley, H.C. Myotonometry Reliably Measures Muscle Stiffness in the Thenar and Perineal Muscles. Physiother. Can. 2017, 69, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.A.; Yu, Q.; Mao, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, C.; Li, L. Lumbar Muscles Biomechanical Characteristics in Young People with Chronic Spinal Pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, S.; Salkın, Y. An Investigation of the Sex-Related Differences in the Stiffness of the Achilles Tendon and Gastrocnemius Muscle: Inter-Observer Reliability and Inter-Day Repeatability and the Effect of Ankle Joint Motion. Foot 2019, 41, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kett, A.R.; Sichting, F. Sedentary Behaviour at Work Increases Muscle Stiffness of the Back: Why Roller Massage Has Potential as an Active Break Intervention. Appl. Ergon. 2020, 82, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.; Graf, C.; Klingler, W.; Weber, N.; Schleip, R. The Feasibility and Impact of Instrument-Assisted Manual Therapy (IAMT) for the Lower Back on the Structural and Functional Properties of the Lumbar Area in Female Soccer Players: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study Design. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2020, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecco, C.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; Duparc, F.; De Caro, R. The Fascia: The Forgotten Structure. Ital. J. Anat. Embryol. 2011, 116, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Schleip, R.; Wilke, J.; Schreiner, S.; Wetterslev, M.; Klingler, W. Needle Biopsy-Derived Myofascial Tissue Samples Are Sufficient for Quantification of Myofibroblast Density. Clin. Anat. 2018, 31, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjaei, K.G.; Ray, J.W.; Waite, B.; Burnham, K.J. The Fascial System in Musculoskeletal Function and Myofascial Pain. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2020, 8, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, T.W. Anatomy Trains: Myofascial Meridians for Manual and Movement Therapists, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-0-7020-4654-4. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, A.T.; Nair, K.; Evans, T.; Ghandour, Y. Clinical, Biomechanical, and Physiological Translational Interpretations of Human Resting Myofascial Tone or Tension. Int. J. Ther. Massage Bodywork 2010, 3, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilke, J.; Krause, F.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W. What Is Evidence-Based About Myofascial Chains: A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, B.; Marelli, F. Emotions in Motion: Myofascial Interoception. Complement. Med. Res. 2017, 24, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, B.; Sugumar, K.; Varacallo, M. Myofascial Pain. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, H.M. Fascia Mobility, Proprioception, and Myofascial Pain. Life 2021, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Vahdatinia, R.; Humbert, S.; Stecco, A. Myofascial Injection Using Fascial Layer-Specific Hydromanipulation Technique (FLuSH) and the Delineation of Multifactorial Myofascial Pain. Medicina 2020, 56, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecco, C.; Tiengo, C.; Stecco, A.; Porzionato, A.; Macchi, V.; Stern, R.; De Caro, R. Fascia Redefined: Anatomical Features and Technical Relevance in Fascial Flap Surgery. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottner, J.; Audige, L.; Brorson, S.; Donner, A.; Gajewski, B.J.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Roberts, C.; Shoukri, M.; Streiner, D.L. Guidelines for Reporting Reliability and Agreement Studies (GRRAS) Were Proposed. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2011, 48, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdoost, H. Sampling Methods in Research Methodology; How to Choose a Sampling Technique for Research; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Corder, G.W.; Foreman, D.I. Nonparametric Statistics for Non-Statisticians: A Step-by-Step Approach; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-45461-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, S.G.; Kim, J.H. Central Limit Theorem: The Cornerstone of Modern Statistics. Korean J Anesthesiol 2017, 70, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Melick, N.; Meddeler, B.M.; Hoogeboom, T.J.; Nijhuis-van der Sanden, M.W.G.; van Cingel, R.E.H. How to Determine Leg Dominance: The Agreement between Self-Reported and Observed Performance in Healthy Adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, E. Anatomie, Physiologie: Für die Pysiotherapie: Lehrbuch für Physiotherapeuten, Masseure/medizinische Bademeister und Sportwissenschaftler; Zalpour, C., Beek, E., Van Fritsch, H., Raichle, G., Friedel, T., Schröder, E., Menche, N., Eds.; Für die Physiotherapie; 4., Überarbeitete und Ergänzte Auflage; Elsevier, Urban & Fischer: München, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-437-45304-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.M.; Pandey, K.; Lahoti, A.; Rao, P.K. Evaluation of Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Thickness at Insulin Injection Sites in Indian, Insulin Naïve, Type-2 Diabetic Adult Population. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.; Lohman, T.G.; Stewart, A.D.; Maughan, R.J.; Meyer, N.L.; Sardinha, L.B.; Kirihennedige, N.; Reguant-Closa, A.; Risoul-Salas, V.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; et al. Subcutaneous Fat Patterning in Athletes: Selection of Appropriate Sites and Standardisation of a Novel Ultrasound Measurement Technique: Ad Hoc Working Group on Body Composition, Health and Performance, under the Auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogunleye, L.I.; Oyejola, B.A.; Obisesan, K.O. Comparison of Some Common Tests for Normality. Int. J. Probab. Stat. 2018, 7, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Weiß, C. Basiswissen medizinische Statistik; Lehrbuch 7., Vollständige und Überarbeitete Auflage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-662-56588-9. [Google Scholar]
- Portney, L.G. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Evidence-Based Practice, 4th ed.; F.A. Davis: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-8036-6116-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.I. A Concordance Correlation Coefficient to Evaluate Reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, C.A.E. A Note On “A Concordance Correlation Coefficient to Evaluate Reproducibility”. Biometrics 1997, 53, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying Test-Retest Reliability Using the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwet, K.L. Intrarater Reliability. In Methods and Applications of Statistics in Clinical Trials; Balakrishnan, N., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 340–356. ISBN 978-1-118-59633-3. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, G.B. A Proposal for Strength-of-Agreement Criteria for Lin’s Concordance Correlation Coefficient; NIWA Client Report: HAM2005-062; NIWA: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljequist, D.; Elfving, B.; Skavberg Roaldsen, K. Intraclass Correlation—A Discussion and Demonstration of Basic Features. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, E.; Walsh, C.; Holmes, N.G. Examination of Quantitative Methods for Analyzing Data from Concept Inventories. Phys. Rev. Phys. Educ. Res. 2020, 16, 010141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Agreement in Method Comparison Studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyapong-Badu, S.; Warner, M.; Samuel, D.; Stokes, M. Measurement of Ageing Effects on Muscle Tone and Mechanical Properties of Rectus Femoris and Biceps Brachii in Healthy Males and Females Using a Novel Hand-Held Myometric Device. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 62, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.; Delahunt, E.; Ditroilo, M.; Lowery, M.; De Vito, G. Effects of Age and Sex on Neuromuscular-Mechanical Determinants of Muscle Strength. Age 2016, 38, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viner, A.; Lee, M.; Adams, R. Posteroanterior Stiffness in the Lumbosacral Spine. The Correlation between Adjacent Vertebral Levels. Spine 1997, 22, 2724–2729, discussion 2729–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Steven, G.P.; Crosbie, J.; Higgs, R.J. Variations in Posteroanterior Stiffness in the Thoracolumbar Spine: Preliminary Observations and Proposed Mechanisms. Phys. Ther. 1998, 78, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Miyakawa, S.; Mukai, N.; Kono, I. Measurement of Tissue Hardness for Evaluating Flexibility of the Knee Extensor Mechanism. Football Sci. 2006, 3, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich-Zwahlen, A.K.; Casartelli, N.C.; Item-Glatthorn, J.F.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Validity of Resting Myotonometric Assessment of Lower Extremity Muscles in Chronic Stroke Patients with Limited Hypertonia: A Preliminary Study. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, K.; Takahashi, H. Handheld Tissue Hardness Meters for Assessing the Mechanical Properties of Skeletal Muscle: A Feasibility Study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2016, 39, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.A.; Zhao, J.L.; Li, L.; Mao, Y.R.; Huang, D.F. Relative and Absolute Interrater Reliabilities of a Hand-Held Myotonometer to Quantify Mechanical Muscle Properties in Patients with Acute Stroke in an Inpatient Ward. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4294028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.M.; Kang, H.; An, S.; Cheong, I.; Kim, Y.; Hwang, J.H. Mechanical Properties of Muscles around the Shoulder in Breast Cancer Patients: Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability of the MyotonPRO. PM R 2020, 12, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taş, S.; Yaşar, Ü.; Kaynak, B.A. Interrater and Intrarater Reliability of a Handheld Myotonometer in Measuring Mechanical Properties of the Neck and Orofacial Muscles. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2021, 44, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Mean | SD | Med | Q1 | Q3 | p-Value (Shapiro–Wilk) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative variable | ||||||
| Age, years | 26.6 | 12.6 | 21.0 | 19.0 | 27.0 | <0.001 |
| Height, m | 1.79 | 13.4 | 74.0 | 1.75 | 1.85 | 0.11 |
| Weight, kg | 74.8 | 0.09 | 1.79 | 65.0 | 85.0 | 0.68 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.3 | 2.8 | 23.4 | 21.1 | 24.7 | 0.55 |
| Skinfold, mm | 12.6 | 4.7 | 12.0 | 8.0 | 16.0 | 0.053 |
| Quantitative variable | n | % | ||||
| Sex | Male | 24 | 69 | |||
| Female | 11 | 31 | ||||
| Dominant leg | Right | 33 | 94 | |||
| Left | 2 | 6 | ||||
| Quantitative Variable | Mean | SD | Med | p-Value (Shapiro–Wilk) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mm indentation | M1, N/mm | 1.16 | 0.36 | 1.09 | 0.004 |
| M2, N/mm | 1.26 | 0.41 | 1.26 | 0.06 | |
| M3, N/mm | 1.12 | 0.30 | 1.16 | 0.01 | |
| 10 mm indentation | M1, N/mm | 3.40 | 1.38 | 3.22 | 0.16 |
| M2, N/mm | 2.80 | 1.24 | 2.39 | 0.002 | |
| M3, N/mm | 3.16 | 1.36 | 3.05 | 0.10 | |
| Indentation Depth | M1/M2 (Inter-Rater) | M1/M3 (Intra-Rater) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lin’s CCC (95% CI) | MSE | ICC3,1 (95% CI) | p-Value | SEM | Lin’s CCC (95% CI) | MSE | ICC3,1 (95% CI) | p-Value | SEM | |
| 5 mm | 0.74 (0.55–0.85) | 0.05 | 0.74 (0.54–0.86) | <0.001 | 0.20 | 0.84 (0.71–0.91) | 0.03 | 0.84 (0.71–0.92) | <0.001 | 0.13 |
| 10 mm | 0.58 (0.34–0.75) | 1.14 | 0.59 (0.27–0.78) | <0.001 | 0.88 | 0.82 (0.68–0.91) | 0.56 | 0.83 (0.69–0.91) | <0.001 | 0.56 |
| Quantitative Variable | Indentation Depth | M1 | M2 | M3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs | p-Value | rs | p-Value | rs | p-Value | ||
| Weight | 5 mm | 0.18 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.28 |
| 10 mm | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.05 * | 0.21 | 0.23 | |
| Height | 5 mm | 0.3 | 0.82 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.13 |
| 10 mm | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 0.13 | 0.47 | |
| BMI | 5 mm | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.34 |
| 10 mm | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.44 | 0.009 * | 0.17 | 0.32 | |
| Age | 5 mm | 0.03 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.80 |
| 10 mm | 0.06 | 0.77 | 0.08 | 0.63 | −0.08 | 0.67 | |
| Gender | 5 mm | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.75 | 0.21 | 0.24 |
| 10 mm | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.09 | |
| Skinfold thickness | 5 mm | −0.12 | 0.51 | −0.11 | 0.52 | −0.14 | 0.44 |
| 10 mm | 0.001 | 0.99 | −0.04 | 0.83 | −0.06 | 0.73 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koch, V.; Wilke, J. Reliability of a New Indentometer Device for Measuring Myofascial Tissue Stiffness. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175194
Koch V, Wilke J. Reliability of a New Indentometer Device for Measuring Myofascial Tissue Stiffness. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175194
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoch, Virginija, and Jan Wilke. 2022. "Reliability of a New Indentometer Device for Measuring Myofascial Tissue Stiffness" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175194
APA StyleKoch, V., & Wilke, J. (2022). Reliability of a New Indentometer Device for Measuring Myofascial Tissue Stiffness. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5194. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175194




