Psychiatric Comorbidity and Emotional Dysregulation in Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants Selection
2.2. Psychological Status Measurement
2.3. Covariate Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
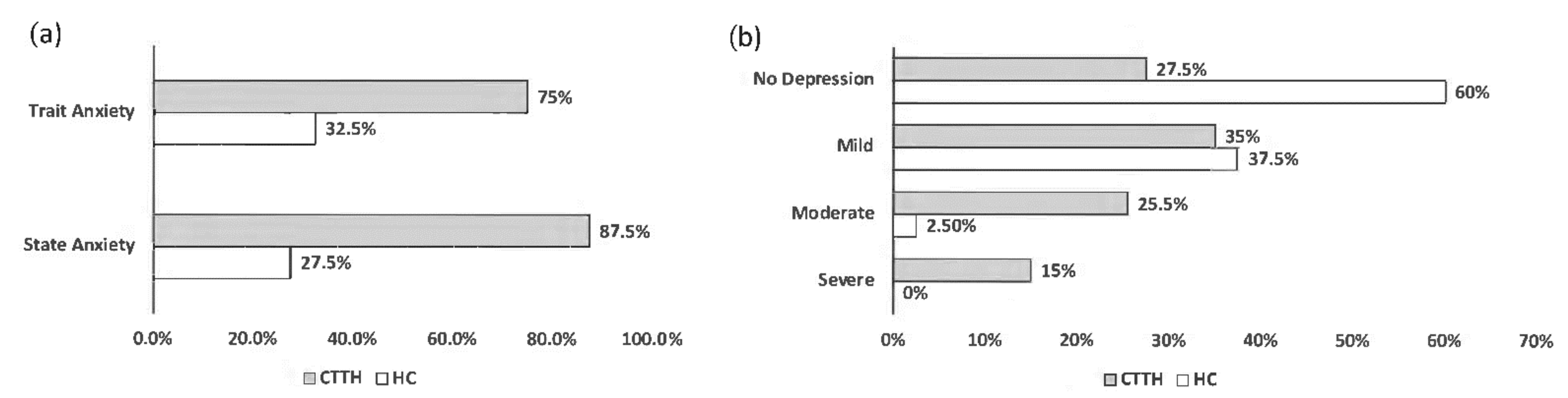
3.2. Psychopathological Characteristics of the Participants
3.3. Socio-Demographic Characteristics Associated with Psychological Status
3.4. Association between CTTH and Psychological Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, L.; Jensen, R. Tension-type headache: The most common, but also the most neglected, headache disorder. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, M.; Gustavsson, A.; Stovner, L.J.; Steiner, T.J.; Barré, J.; Katsarava, Z.; Lainez, J.M.; Lampl, C.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Rastenyte, D.; et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: The Eurolight project. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, D. Tension type headache. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2012, 15, S83–S88. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, V.P.; Ellard, D.R.; Griffiths, F.E.; Kamal, A.; Underwood, M.; Taylor, S.J.C. The lived experience of chronic headache: A systematic review and synthesis of the qualitative literature. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e019929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.J.; Antonac, F.; Jensen, R.; Lainez, M.J.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Valade, D. Recommendations for headache service organization and delivery in Europe. J. Headache Pain 2011, 12, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñacoba-Puente, C.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; González-Gutierrez, J.L.; Miangolarra-Page, J.C.; Pareja, J.A. Interaction between anxiety, depression, quality of life and clinical parameters in chronic tension-type headache. Eur. J. Pain 2008, 12, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebenholzer, K.; Lechner, A.; Broessner, G.; Lampl, C.; Luthringshausen, G.; Wuschitz, A.; Obmann, S.M.; Berek, K.; Wöber, C. Impact of depression and anxiety on burden and management of episodic and chronic headaches—A cross-sectional multicentre study in eight Austrian headache centres. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongini, F.; Rota, E.; Deregibus, A.; Ferrero, L.; Migliaretti, G.; Cavallo, F.; Mongini, T.; Novello, A. Accompanying symptoms and psychiatric comorbidity in migraine and tension-type headache patients. J. Psychosom. Res. 2006, 61, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Holroyd, K.A.; Stensland, M.; Lipchik, G.L.; Hill, K.R.; O’Donnell, F.S.; Cordingley, G. Psychosocial correlates and impact of chronic tension-type headaches. Headache 2000, 40, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.J.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, K.I.K.; Yun, C.H.; Chu, M.K. Anxiety and Depression in Tension-Type Headache: A Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghi, E.; Bussone, G.; D’Amico, D.; Cortelli, P.; Cevoli, S.; Manzoni, G.C.; Torelli, P.; Tonini, M.C.; Allais, G.; De Simone, R.; et al. Headache, anxiety and depressive disorders: The HADAS study. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwart, J.A.; Dyb, G.; Hagen, K.; Ødegård, K.J.; Dahl, A.A.; Bovim, G.; Stovner, L.J. Depression and anxiety disorders associated with headache frequency. The Nord-Trøndelag Health Study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2003, 10, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatchel, R.J.; Peng, Y.B.; Peters, M.L.; Fuchs, P.N.; Turk, D.C. The biopsychosocial approach to chronic pain: Scientific advances and future directions. Psychol. Bull. 2007, 133, 581–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Europea de Salud en España. 2020. Available online: https://www.ine.es/prensa/eese_2020.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Hu, T.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Mistry, R.; Ran, G.; Wang, X. Relation between emotion regulation and mental health: A meta-analysis review. Psychol. Rep. 2014, 114, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, K.I.; Yun, C.H.; Chu, M.K. Insomnia in tension-type headache: A population-based study. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, R.E.; Joormann, J.; Eugène, F.; Dennis, E.L.; Gotlib, I.H. Neural correlates of rumination in depression. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 10, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuen Yee Lo, B.; Lau, S.; Cheung, S.H.; Allen, N.B. The impact of rumination on internal attention switching. Cogn. Emot. 2012, 26, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratian, A.; Amjadi, M.M.; Ghandehari, K.; Hatamian, H.; Kiani, S.; Habibi, M.; Aghababaei, Z.; Ataei, M. Emotion Regulation Difficulties and Repetitive Negative Thinking in Patients with Tension Headaches and Migraine. Casp. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 6, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Pulvers, K.; Hood, A. The role of positive traits and pain catastrophizing in pain perception. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory-II; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, J.; Perdigón, A.L.; Vázquez, C. The Spanish adaptation of Beck’s Depression Inventory–II (BDI–II): 2. Psychometric properties in the general population. Clínica Y Salud 2003, 14, 249–280. [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger, C.; Gorsuch, R.; Lushene, R. STAI Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Consulting Psychologist Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger, C.; Gorsuch, R.; Lushene, R. Cuestionario de Ansiedad Estado-Rasgo. Manual, 4th ed.; TEA Ediciones SA: Madrid, Spain, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, J.J.; John, O.P. Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 85, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabello, R.; Salguero, J.M.; Fernández-Berrocal, P.; Gross, J.J. A Spanish adaptation of the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2013, 29, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandín, B.; Chorot, P.; Lostao, L.; Joiner, T.E.; Santed, M.A.; Valiente, R.M. Escalas PANAS de Afecto Positivo y Negativo: Validación factorial y convergencia estructural. Psicothema 1999, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heckman, B.D.; Holroyd, K.A. Tension-type headache and psychiatric comorbidity. Curr. Sci. Inc. 2006, 10, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, B.; Kora, K.; Ozyalçín, S.; Alçalar, N.; Ozdemir, O.; Yücel, A. Depression, automatic thoughts, alexithymia, and assertiveness in patients with tension-type headache. Headache 2002, 42, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koechlin, H.; Coakley, R.; Schechtery, N.; Werner, C.; Kossowsky, J. The role of emotion regulation in chronic pain: A systematic literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2018, 107, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomons, T.V.; Nusslock, R.; Detloff, A.; Johnstone, T.; Davidson, R.J. Neural emotion regulation circuitry underlying anxiolytic effects of perceived control over pain. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2015, 27, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Desarrollo y validación de medidas breves de afecto positivo y negativo: Las escalas PANAS. Rev. Pers. Y Psicol. Soc. 1988, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.J. Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: Divergent consequences for experience, expression, and physiology. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 74, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T.; Keogh, E.; French, C.C.; Davis, R. Anxiety sensitivity and pain: Generalisability across noxious stimuli. Pain 2008, 134, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve, M.R.; Camacho, L. Anxiety sensitivity, body vigilance and fear of pain. Behav. Res. Ther. 2008, 46, 715–727. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, N.; Tan, G.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J. Triggers of migraine and tension-type headache in China: A clinic-based survey. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.; DeFife, J.A.; Guarnaccia, C.; Phifer, J.; Fani, N.; Ressler, K.J.; Westen, D. Emotion dysregulation and negative affect: Association with psychiatric symptoms. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, J.R.; Lake, A.E. Borderline Personality Disorder and the Chronic Headache Patient: Review and Management Recommendations. Headache 2008, 42, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.; Gross, R.T.; Vargovichb, A.M. Difficulties in emotion regulation and chronic pain-related disability and opioid misuse. Addict. Behav. 2018, 87, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, A.; Stang, P.; Gutterman, D.L.; Cady, R.; Markley, H.; Weeks, R.; Saiers, J.; Fox, A.W. Analgesic rebound headache in clinical practice: Data from a physician survey. Headache 1996, 36, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.N.; Lake, A.E. 3rd. Clinical aspects of medication overuse headaches. Headache 2014, 54, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnider, P.; Aull, S.; Feucht, M.; Mraz, M.; Travniczek, A.; Zeiler, K.; Wessely, P. Use and abuse of analgesics in tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 1994, 14, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauser, J.W.; Nelson, C.I.; Gross, R.T.; Vargovich, A.M. Pain Experiences and Their Relation to Opioid Misuse Risk and Emotion Dysregulation. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 7234625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.B.; Japuntich, S.J.; Hogle, J.M.; McCarthy, D.E.; Curtin, J.J. Pharmacologic and Behavioral Withdrawal from Addictive Drugs. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 15, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Le Moal, M. Drug abuse: Hedonic homeostatic dysregulation. Science 1997, 278, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.K.; Kwon, D.R. Efficacy of cranial microcurrent stimulation in patients with tension-type headache: A prospective, randomised, double-blinded, sham-controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2021, 75, e14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumplido-Trasmonte, C.; Fernández-González, P.; Alguacil-Diego, I.M.; Molina-Rueda, F. Manual therapy in adults with tension-type headache: A systematic review. Terapia manual en adultos con cefalea tensional: Revisión sistemática. Neurologia 2021, 36, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Florencio, L.L.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Arias-Buría, J.L. Clinical Reasoning Behind Non-Pharmacological Interventions for the Management of Headaches: A Narrative Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, E.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, S. Efficacy of psychological treatment for headache disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, B.; Rao, A. Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin in Tension-Type Headaches: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Pain Pr. 2019, 19, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditi, D.; Robinson, M.E.; Litwins, N. Effects of coping statements on experimental pain in chronic pain patients. J. Pain Res. 2009, 2, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thorn, B.E.; Pence, L.B.; Ward, L.C.; Kilgo, G.; Clements, K.L.; Cross, T.H.; Davis, A.M.; Tsui, P.W. A randomized clinical trial of targeted cognitive behavioral treatment to reduce catastrophizing in chronic headache sufferers. J. Pain 2007, 8, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, A. Cognitive reappraisal. In Process Based CBT. The Science and Core Clinical Competencies of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Hayes, S.C., Hofmann, S.G., Eds.; New Harbinger Publications, Inc: Oakland, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Gopichandran, L.; Srivastsava, A.K.; Vanamail, P.; Kanniammal, C.; Valli, G.; Mahendra, J.; Dhandapani, M. Relaxation and Deep Breathing Exercise on Pain, Disability, and Sleep Among Patients with Chronic Tension-Type Headache. Holist. Nurs. Pract. 2021. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | CTTH | HC | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 40 | 40 | |
| Age (years) | 50.6 (10.5) | 40.6 (10.5) | <0.001 a |
| Sex (% women) | 87.5 | 67.5 | 0.059 c |
| Smoking (%) | 10.0 | 17.5 | 0.518 c |
| Background (% urban) | 75.0 | 82.5 | 0.586 c |
| Low socio-economic status (%) | 30.0 | 22.5 | 0.612 c |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 26.9 (4.4) | 23.0 (2.2) | <0.001 b |
| Physical activity (%) | 17.5 | 52.5 | 0.002 c |
| Tertiary education (%) | 15.0 | 70.0 | <0.001 c |
| Dietary intake | |||
| Alcohol (%) | 2.5 | 22.5 | 0.014 c |
| Coffee or tea (%) | 30.0 | 60.0 | 0.013 c |
| Psychological Variables | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socio-Demographic Variables | Depression | State Anxiety | Trait Anxiety | Cognitive Reappraisal | Expressive Suppression | |||||
| Adjusted Mean | p b | Adjusted Mean | p b | Adjusted Mean | pb | Adjusted Mean | p b | Adjusted Mean | p b | |
| Sex c | ||||||||||
| Men (n = 18) | 12.0 | 0.915 | 23.2 | 0.138 | 24.4 | 0.785 | 4.2 | 0.560 | 4.8 | <0.001 |
| Women (n = 62) | 11.8 | 29.4 | 25.3 | 4.4 | 3.3 | |||||
| Background | ||||||||||
| Urban (n = 17) | 11.6 | 0.629 | 27.7 | 0.726 | 24.1 | 0.162 | 4.5 | 0.203 | 3.5 | 0.421 |
| Rural (n = 63) | 12.8 | 29.2 | 28.7 | 4.0 | 3.8 | |||||
| Tertiary education | ||||||||||
| Yes (n = 34) | 7.6 | 0.001 | 20.8 | 0.001 | 21.5 | 0.037 | 4.5 | 0.708 | 3.1 | 0.011 |
| No (n = 46) | 14.9 | 33.3 | 27.7 | 4.3 | 4.0 | |||||
| Low socio-economic status | ||||||||||
| Yes (n = 21) | 15.7 | 0.019 | 33.5 | 0.053 | 28.5 | 0.129 | 4.1 | 0.257 | 4.4 | 0.001 |
| No (n = 59) | 10.4 | 26.0 | 23.9 | 4.5 | 3.3 | |||||
| Physical activity | ||||||||||
| Yes (n = 28) | 9.2 | 0.069 | 23.3 | 0.054 | 21.4 | 0.051 | 5.1 | 0.001 | 3.2 | 0.079 |
| No (n = 52) | 13.2 | 30.5 | 27.1 | 4.0 | 3.8 | |||||
| Smoking | ||||||||||
| Yes (n = 11) | 11.9 | 0.980 | 28.2 | 0.967 | 23.7 | 0.672 | 5.0 | 0.132 | 4.0 | 0.312 |
| No (n = 69) | 11.8 | 28.0 | 25.3 | 4.3 | 3.5 | |||||
| Alcohol intake | ||||||||||
| Yes (n = 10) | 11.3 | 0.841 | 28.3 | 0.631 | 21.0 | 0.252 | 4.4 | 0.982 | 3.6 | 0.914 |
| No (n = 70) | 11.9 | 25.8 | 25.7 | 4.4 | 3.6 | |||||
| Coffee or Tea intake | ||||||||||
| Yes (n = 36) | 8.8 | 0.007 | 22.2 | 0.002 | 22.2 | 0.055 | 4.5 | 0.447 | 3.4 | 0.219 |
| No (n = 44) | 14.3 | 32.8 | 27.5 | 4.3 | 3.8 | |||||
| Age (years) | 0.129 d | 0.152 e | −0.112 d | 0.464 e | 0.222 d | 0.065 e | −0.007 d | 0.618 e | 0.049 d | 0.001 e |
| Body Mass Index (Kg/m2) | 1.089 f | <0.001 e | 0.901 f | 0.059 e | 1.136 f | 0.002 e | −0.108 f | 0.015 e | 0.086 f | 0.053 e |
| Psychological Variables | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socio-Demographic Variables | State Positive Affect | Trait Positive Affect | State Negative Affect | Trait Negative Affect | ||||
| Adjusted Mean a | p b | Adjusted Mean a | p b | Adjusted Mean a | p b | Adjusted Mean a | p b | |
| Sex c | ||||||||
| Men (n = 18) | 28.4 | 0.999 | 29.6 | 0.337 | 20.0 | 0.339 | 20.7 | 0.617 |
| Women (n = 62) | 28.4 | 31.6 | 22.2 | 19.8 | ||||
| Background | ||||||||
| Urban (n = 17) | 29.0 | 0.157 | 32.0 | 0.034 | 21.5 | 0.669 | 19.9 | 0.818 |
| Rural (n = 63) | 26.0 | 27.8 | 22.5 | 20.3 | ||||
| Tertiary education | ||||||||
| Yes (n= 34) | 32.4 | <0.001 | 33.3 | 0.039 | 17.8 | 0.001 | 18.4 | 0.109 |
| No (n = 46) | 25.4 | 29.5 | 24.6 | 21.1 | ||||
| Low socio-economic status | ||||||||
| Yes (n = 21) | 24.0 | 0.003 | 29.2 | 0.167 | 25.2 | 0.027 | 20.5 | 0.644 |
| No (n = 59) | 29.9 | 31.8 | 20.5 | 19.8 | ||||
| Physical activity | ||||||||
| Yes (n = 28) | 32.2 | 0.002 | 33.4 | 0.048 | 19.3 | 0.065 | 19.8 | 0.909 |
| No (n = 52) | 26.3 | 29.9 | 23.1 | 20.0 | ||||
| Smoking | ||||||||
| Yes (n = 11) | 25.9 | 0.264 | 32.2 | 0.616 | 22.0 | 0.916 | 21.2 | 0.498 |
| No (n = 69) | 28.8 | 31.0 | 21.7 | 19.8 | ||||
| Alcohol intake | ||||||||
| Yes (n = 10) | 29.4 | 0.656 | 33.0 | 0.385 | 21.2 | 0.842 | 20.1 | 0.956 |
| No (n = 70) | 28.2 | 30.9 | 21.8 | 19.9 | ||||
| Coffee or Tea intake | ||||||||
| Yes (n = 36) | 30.4 | 0.049 | 31.4 | 0.798 | 18.6 | 0.003 | 18.3 | 0.049 |
| No (n = 44) | 26.7 | 30.9 | 24.3 | 21.3 | ||||
| Age (years) | −0.126 d | 0.114 e | −0.091 d | 0.217 e | 0.045 d | 0.592 e | −0.010 d | 0.881 e |
| Body Mass Index (Kg/m2) | −0.309 f | 0.215 e | −0.373 f | 0.106 e | 0.619 f | 0.018 e | 0.626 f | 0.002 e |
| Dependent Variable | Non-Standardized Regression Coefficient for CTTH (95% Confidence Interval) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Depression b | 5.46 (1.04, 9.88) | 0.016 |
| State Anxiety b | 12.77 (4.99, 20.56) | 0.002 |
| Trait Anxiety b,c | 8.79 (2.29, 15.30) | 0.009 |
| Cognitive Reappraisal c,d | −0.69 (−1.51, 0.13) | 0.098 |
| Expressive Suppression b | 0.02 (−0.77, 0.81) | 0.962 |
| State Positive Affect b,c | −3.82 (−8.02, 0.37) | 0.074 |
| Trait Positive Affect b,c | −2.56 (−6.82, 1.69) | 0.234 |
| State Negative Affect b | 5.26 (0.88, 9.64) | 0.019 |
| Trait Negative Affect | 1.90 (−1.83, 5.64) | 0.312 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Godoy, R.; Romero-Godoy, S.R.; Romero-Acebal, M.; Gutiérrez-Bedmar, M. Psychiatric Comorbidity and Emotional Dysregulation in Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175090
Romero-Godoy R, Romero-Godoy SR, Romero-Acebal M, Gutiérrez-Bedmar M. Psychiatric Comorbidity and Emotional Dysregulation in Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175090
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Godoy, Rosalinda, Sara Raquel Romero-Godoy, Manuel Romero-Acebal, and Mario Gutiérrez-Bedmar. 2022. "Psychiatric Comorbidity and Emotional Dysregulation in Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175090
APA StyleRomero-Godoy, R., Romero-Godoy, S. R., Romero-Acebal, M., & Gutiérrez-Bedmar, M. (2022). Psychiatric Comorbidity and Emotional Dysregulation in Chronic Tension-Type Headache: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175090






