Diagnostic Performance of AFP, AFP-L3, or PIVKA-II for Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Analysis
Abstract
:1. Lay Summary
2. Introduction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design and Patients
3.2. Measurements of Tumor Biomarkers
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
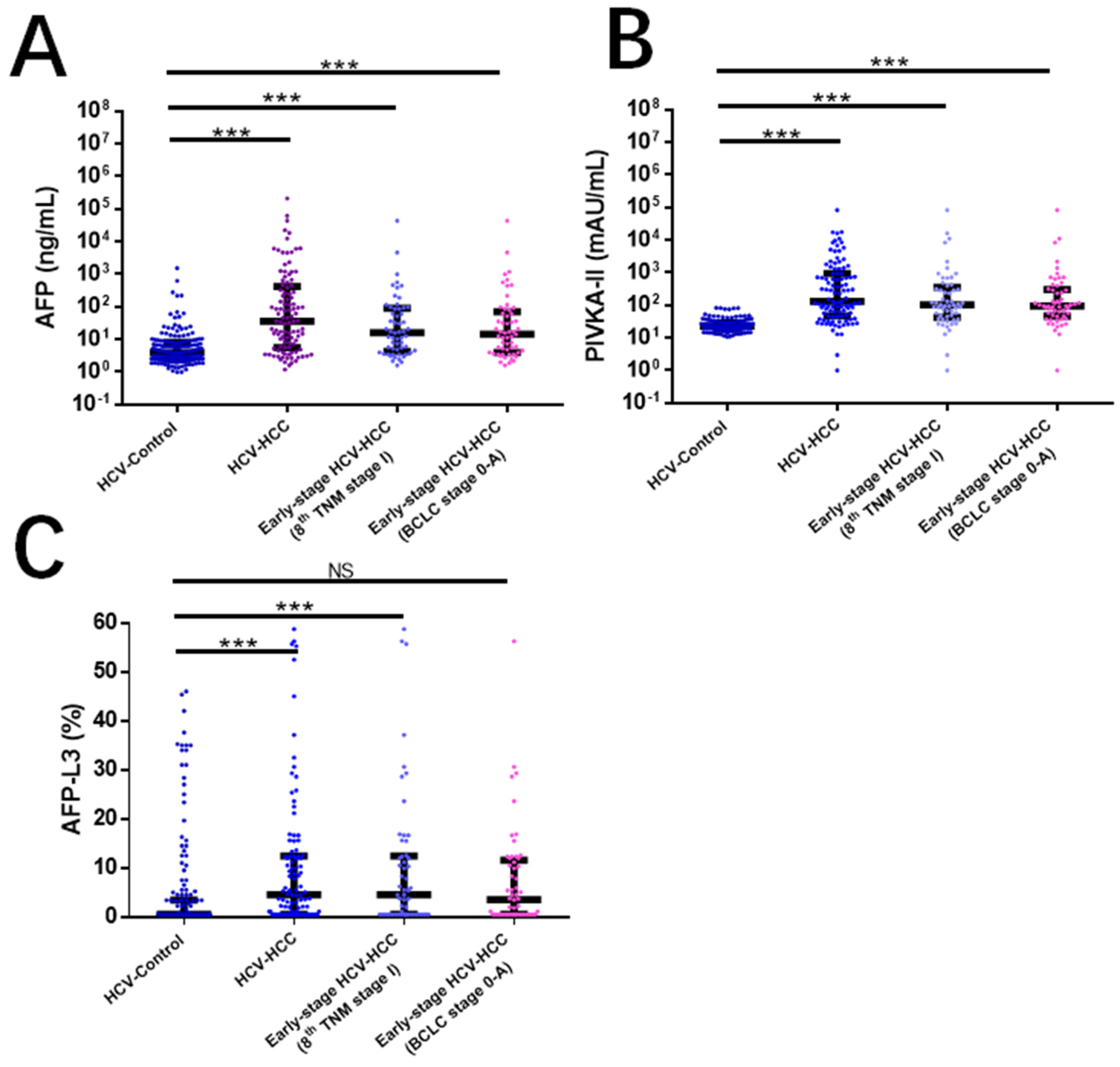
4.1. Comparisons of Clinical Characteristics between HCV-HCC and HCV Control
4.2. Comparisons of Diagnostic Performance in Detecting HCV-HCC
4.3. Comparisons of Diagnostic Performance in Patients with HCV-Cirrhosis
4.4. Comparisons of Diagnostic Performance in Detecting Early-Stage HCV-HCC
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Venook, A.P.; Papandreou, C.; Furuse, J.; de Guevara, L.L. The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist 2010, 15, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degos, F.; Christidis, C.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Farmachidi, J.-P.; Degott, C.; Guettier, C.; Trinchet, J.-C.; Beaugrand, M.; Chevret, S. Hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: Time to occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and death. Gut 2000, 47, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alazawi, W.; Cunningham, M.; Dearden, J.; Foster, G.R. Systematic review: Outcome of compensated cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis C infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshikuni, N.; Arisawa, T.; Tsutsumi, M. Hepatitis C-related liver cirrhosis—strategies for the prevention of hepatic decompensation, hepatocarcinogenesis, and mortality. World J Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2876–2887. [Google Scholar]
- Altekruse, S.F.; McGlynn, K.A.; Dickie, L.A.; Kleiner, D. Hepatocellular carcinoma confirmation, treatment, and survival in surveillance, epidemiology, and end results registries, 1992–2008. Hepatology 2011, 55, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar]
- Tzartzeva, K.; Obi, J.; Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Yopp, A.; Waljee, A.K.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1706–1718.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Mannalithara, A.; Piscitello, A.J.; Kisiel, J.B.; Gores, G.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Kim, W.R. Impact of surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma on survival in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geh, D.; Rana, F.A.; Reeves, H.L. Weighing the benefits of hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance against potential harms. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2019, 6, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyirioha, K.; Mittal, S.; Singal, A.G. Is hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in high-risk populations effective? Hepatic. Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Lampertico, P.; Nahon, P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: New trends. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokudo, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Akahane, M.; Igaki, H.; Izumi, N.; Ichida, T.; Uemoto, S.; Kaneko, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Ku, Y.; et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2013 update (3rd JSH-HCC Guidelines). Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.-L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.-H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia–Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, Q.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; He, M. Identification of circulating MicroRNAs as novel potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma detection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 17, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-F.; Liang, L.; Xing, H.; Shen, F.; Huang, D.-S.; Lau, W.Y.; Yang, T. Clinical utility of serum biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark. Med. 2021, 15, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Bent, S.; Kohlwes, J. Test characteristics of α-Fetoprotein for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.-Q.; Kyulo, N.L.; Lim, N.; Elhazin, B.; Hillebrand, D.J.; Bock, T. Clinical significance of elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in patients with chronic hepatitis C, but not hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Duan, Z.; Kramer, J.; Davila, J.A.; Tyson, G.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Determinants of serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in hepatitis C–Infected patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, Z.; Yan, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, W.; Long, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ming, K.; Xu, B. Evaluation of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Level in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Gama, H.; Chida, N.; Ueno, Y.; Shinzawa, H.; Takagi, T.; Toyota, T.; Takahashi, T.; Kasukawa, R.; the South Tohoku District Study Group. Simultaneous measurements of serum alpha-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazo, F.A.; Blatt, L.M.; Corey, W.G.; Lin, J.H.; Han, S.; Saab, S.; Busuttil, R.W.; Tong, M.J. Des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin, alpha-fetoprotein and AFP-L3 in patients with chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Nguyen, M.H.; Befeler, A.S.; Roberts, L.R.; Reedy, K.R.; Harnois, D.; Llovet, J.M.; Normolle, D.; et al. Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma carboxyprothrombin, and lectin-bound alpha-fetoprotein in early hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makuuchi, M.; Kokudo, N.; Arii, S.; Futagawa, S.; Kaneko, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Okita, K.; Omata, M.; et al. Development of evidence-based clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 38, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma—The Japan Society of Hepatology 2009 update. Hepatol Res. 2010, 40 (Suppl 1), 2–144.
- Kudo, M. Japan’s Successful Model of Nationwide Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Highlighting the Urgent Need for Global Surveillance. Liver Cancer 2012, 1, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.J.; Pirrie, S.J.; Cox, T.F.; Berhane, S.; Teng, M.; Palmer, D.; Morse, J.; Hull, D.; Patman, G.; Kagebayashi, C.; et al. The detection of hepatocellular carcinoma using a prospectively developed and validated model based on serological biomarkers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xing, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, N.; Liu, M.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; Wei, L.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; et al. A Novel Online Calculator Based on Serum Biomarkers to Detect Hepatocellular Carcinoma among Patients with Hepatitis B. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demler, O.V.; Pencina, M.J.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr. Misuse of DeLong test to compare AUCs for nested models. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Lesmana, L.A.; Tateishi, R.; Chen, P.-J.; Lin, S.-M.; Yoshida, H.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, B.I.; Poon, R.T.P.; et al. Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 2010, 4, 439–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Nakata, K.; Kato, Y.; Shima, M.; Ishii, N.; Koji, T.; Taketa, K.; Endo, Y.; Nagataki, S. Early recognition of hepatocellular carcinoma based on altered profiles of alpha-fetoprotein. N Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.-Z.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chan, S.C.; Hsu, C.; Shao, Y.-Y.; Cheng, A.-L.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M.; Sharr, W.W.; Chan, A.C.Y.; et al. Alpha-fetoprotein-L3: Useful or Useless for Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Liver Cancer 2013, 2, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Jeffers, L.; Gordon, F.; Venook, A.P.; Reddy, K.R.; Satomura, S.; Kanke, F.; Schwartz, M.E.; Sherman, M. Utility of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, alone or in combination, as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| n (%) | HCV-HCC (n = 105) | HCV Control (n = 172) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | |||
| Age, years * | 60.8 ± 9.3 | 55.8 ± 12.2 | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 82 (78.1) | 98 (57.0) | <0.001 |
| Child-Pugh classification | |||
| A | 92 (87.6) | 161 (93.6) | <0.001 |
| B/C | 13 (11.4) | 11 (7.4) | |
| Cirrhosis | 89 (84.8) | 127 (73.8) | 0.033 |
| Platelet, ×109/L * | 167.4 (89, 233) | 148.8 (71, 187) | 0.354 |
| Bilirubin, μmol/L * | 14.5 (11.5, 24.8) | 14.8 (11.9, 20.9) | 0.867 |
| Albumin, g/L * | 43.5 ± 5.7 | 45.3 ± 5.3 | 0.128 |
| AFP, ng/mL * | 87.0 (14.6, 1206.8) | 4.1 (2.4, 8.1) | 0.016 |
| Negative (<20 ng/mL) | 46 (43.7) | 155 (90.1) | <0.001 |
| Positive (≥20 ng/mL) | 59 (56.2) | 17 (9.9) | |
| PIVKA-II, mAU/mL * | 117.0 (47.1, 932.0) | 22.8 (19.0, 28.9) | 0.005 |
| Negative (<40 mAU/mL) | 23 (21.9) | 153 (89.0) | <0.001 |
| Positive (≥40 mAU/mL) | 82 (78.1) | 19 (11.0) | |
| AFP-L3, % * | 3.5 (0.5, 12.5) | 0.5 (0.5, 5.4) | <0.001 |
| Negative (<10%) | 67 (63.8) | 146 (84.9) | <0.001 |
| Positive (≥10%) | 38 (36.2) | 26 (15.1) | |
| Tumor characteristics | |||
| Tumor size, cm * | 4.1 (2.6, 7.0) | ||
| ≥3 cm | 72 (68.6) | ||
| Multiple tumors | 20 (19.0) | ||
| Macrovascular invasion | 15 (14.3) | ||
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 9 (8.6) | ||
| BCLC staging system | |||
| 0/A (Early stage) | 57 (54.3) | ||
| B/C (Intermediate/advanced stage) | 48 (45.7) | ||
| 8th TNM staging system | |||
| I (Early stage) | 57 (54.3) | ||
| II/III (Intermediate/advanced stage) | 48 (45.7) |
| AUC (95% CI) | Clinical Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | PPV (%) (95% CI) | NPV (%) (95% CI) | Positive LR | Negative LR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP | 0.802 (0.751–0.847) | 20 ng/mL | 56.2 (46.2–65.9) | 90.1 (84.1–94.1) | 77.6 (68.2–84.9) | 77.1 (73.0–80.8) | 5.7 | 0.5 |
| PIVKA-II | 0.903 (0.862–0.935) | 40 mAU/mL | 78.1 (69.0–85.6) | 89.0 (83.3–93.2) | 81.2 (73.6–87.0) | 86.9 (82.2–90.6) | 7.1 | 0.3 |
| AFP-L3 | 0.688 (0.630–0.742) | 10% | 36.2 (27.0–46.1) | 84.9 (78.6–89.9) | 59.4 (48.6–69.3) | 68.5 (65.1–71.8) | 2.4 | 0.8 |
| AFP + PIVKA-II | 0.934 (0.898–0.960) | 87.6 (79.3–93.2) | 90.7 (85.3–94.6) | 85.2 (78.2–90.2) | 92.3 (87.8–95.2) | 9.4 | 0.2 | |
| PIVKA-II+ AFP-L3 | 0.895 (0.853–0.929) | 76.2 (66.9–84.0) | 96.5 (92.6–98.7) | 93.0 (85.8–96.7) | 86.9 (82.5–90.3) | 21.8 | 0.3 | |
| AFP+ AFP-L3 | 0.779 (0.725–0.826) | 69.5 (59.8–78.1) | 80.2 (73.5–85.9) | 68.2 (60.8–74.9) | 81.2 (76.2–85.3) | 3.5 | 0.4 | |
| AFP + PIVKA-II + AFP-L3 | 0.926 (0.888–0.954) | 87.6 (79.8–93.2) | 92.4 (87.4–95.9) | 87.6 (80.7–92.3) | 92.4 (88.0–95.3) | 11.6 | 0.1 |
| AUC (95% CI) | Clinical Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | PPV (%) (95% CI) | NPV (%) (95% CI) | Positive LR | Negative LR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCLC Early-stage HCV-HCC | ||||||||
| AFP | 0.740 (0.678–0.795) | 20 ng/mL | 42.1 (29.1–55.9) | 90.1 (84.6–94.1) | 58.5 (45.0–70.9) | 82.4 (78.9–85.5) | 4.3 | 0.6 |
| PIVKA-II | 0.897 (0.851–0.933) | 40 mAU/mL | 77.2 (64.2–87.3) | 91.9 (86.7–95.5) | 69.8 (59.7–78.4) | 92.2 (87.9–95.0) | 9.5 | 0.3 |
| AFP-L3 | 0.634 (0.568–0.697) | 10% | 31.6 (19.9–45.2) | 84.9 (78.6–89.9) | 40.9 (29.1–53.8) | 78.9 (75.6–81.9) | 2.1 | 0.8 |
| AFP + PIVKA-II | 0.914 (0.870–0.947) | 89.5 (78.5–96.0) | 84.3 (78.0–89.4) | 65.4 (56.9–73.0) | 96.0 (91.9–98.1) | 5.7 | 0.1 | |
| PIVKA-II + AFP-L3 | 0.883 (0.834–0.921) | 73.7 (60.3- 84.5) | 97.7 (94.2–99.4) | 91.3 (79.7–96.6) | 91.8 (87.9–94.5) | 31.7 | 0.3 | |
| AFP + AFP-L3 | 0.708 (0.644–0.766) | 59.7 (45.8–72.4) | 80.2 (73.5–85.9) | 50.0 (40.9–59.1) | 85.7 (81.3–89.2) | 3.0 | 0.5 | |
| AFP + PIVKA-II + AFP-L3 | 0.907 (0.862–0.942) | 79.0 (66.1–88.6) | 97.1 (93.3–99.0) | 90.0 (79.0–95.6) | 93.3 (89.4–95.8) | 27.2 | 0.2 | |
| 8th TNM Early-stage HCV-HCC | ||||||||
| AFP | 0.754 (0.693–0.809) | 20 ng/mL | 43.9 (30.7–57.6) | 90.5 (85.6–95.1) | 59.5 (46.2–71.6) | 82.9 (79.3–86.0) | 4.4 | 0.6 |
| PIVKA-II | 0.881 (0.832–0.920) | 40 mAU/mL | 75.4 (62.2–85.9) | 91.9 (86.7–95.5) | 69.4 (59.1–78.0) | 91.6 (87.4–94.5) | 9.3 | 0.3 |
| AFP-L3 | 0.658 (0.592–0.719) | 10% | 36.8 (24.4–50.7) | 84.9 (78.6–89.9) | 44.7 (33.1–56.9) | 80.2 (76.7–83.3) | 2.6 | 0.7 |
| AFP + PIVKA-II | 0.898 (0.851–0.934) | 87.7 (76.3–94.9) | 84.3 (78.0–89.4) | 64.9 (56.4–72.6) | 95.4 (91.2–97.7) | 6.6 | 0.2 | |
| PIVKA-II+ AFP-L3 | 0.875 (0.825–0.915) | 73.7 (60.3–84.5) | 95.9 (91.8–98.3) | 85.7 (74.1–92.6) | 91.7 (87.7–94.4) | 18.1 | 0.3 | |
| AFP+ AFP-L3 | 0.718 (0.655–0.776) | 64.9 (51.1–77.1) | 75.0 (67.8–81.3) | 46.2 (38.4–54.3) | 86.6 (81.8–90.3) | 3.02 | 0.5 | |
| AFP + PIVKA-II + AFP-L3 | 0.889 (0.840–0.926) | 79.0 (66.1–88.6) | 94.8 (90.3–97.6) | 83.3 (72.3–90.5) | 93.1 (89.1–95.7) | 15.1 | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Yao, L.; Zhu, H.; Diao, Y.; Wang, M.; Xing, H.; Lau, W.Y.; Guan, M.; Pawlik, T.M.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of AFP, AFP-L3, or PIVKA-II for Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175075
Liu S, Sun L, Yao L, Zhu H, Diao Y, Wang M, Xing H, Lau WY, Guan M, Pawlik TM, et al. Diagnostic Performance of AFP, AFP-L3, or PIVKA-II for Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175075
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Siyu, Liyang Sun, Lanqing Yao, Hong Zhu, Yongkang Diao, Mingda Wang, Hao Xing, Wan Yee Lau, Mingcheng Guan, Timothy M. Pawlik, and et al. 2022. "Diagnostic Performance of AFP, AFP-L3, or PIVKA-II for Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175075
APA StyleLiu, S., Sun, L., Yao, L., Zhu, H., Diao, Y., Wang, M., Xing, H., Lau, W. Y., Guan, M., Pawlik, T. M., Shen, F., Xu, M., Tong, X., & Yang, T. (2022). Diagnostic Performance of AFP, AFP-L3, or PIVKA-II for Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5075. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175075








