Anemia Is an Indicator for Worse Organ Damage Trajectories in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population: PKUTH-SSc and PKUPH-SSc Cohort
2.2. Data Collection and Variables Definition
2.3. Outcome Definition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of PKUTH-SSc and PKUPH-SSc Cohort
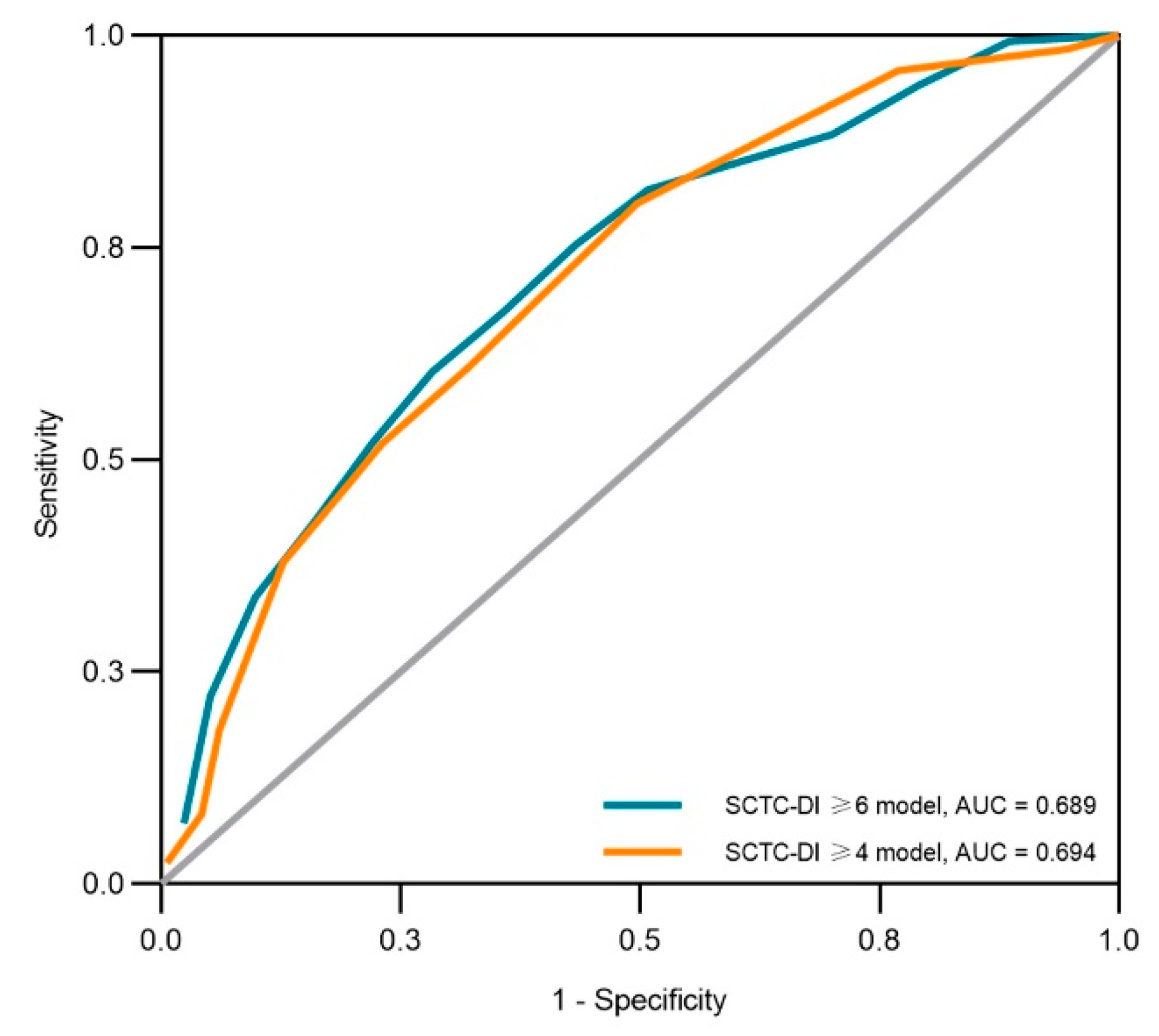
3.2. Anemia as an Indicator of High-Burden Organ Damage
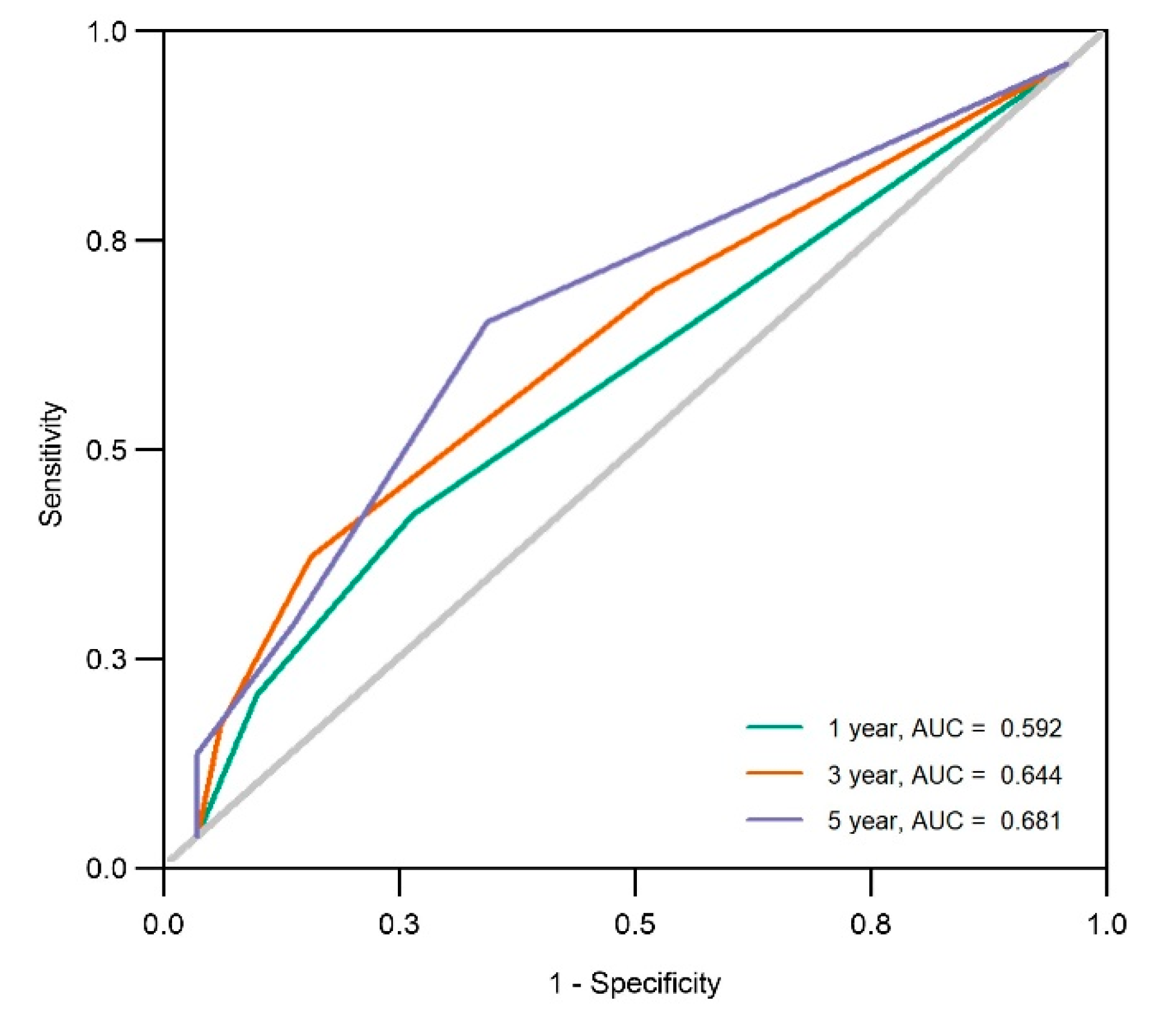
3.3. Anemia at the Initial Visit as a Risk Factor for Organ Damage Progression
3.4. Anemia Is Associated with the Inflammation of SSc
3.5. Anemia-Related Worse Organ Damage Trajectories within the SSc Subtypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaafar, S.; Lescoat, A.; Huang, S.Y.; Gordon, J.; Hinchcliff, M.; Shah, A.A.; Assassi, S.; Domsic, R.; Bernstein, E.J.; Steen, V.; et al. Clinical characteristics, visceral involvement, and mortality in at-risk or early diffuse systemic sclerosis: A longitudinal analysis of an observational prospective multicenter US cohort. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Hudson, M.; Baron, M.; Carreira, P.; Stevens, W.; Rabusa, C.; Tatibouet, S.; Carmona, L.; Joven, B.E.; Huq, M.; et al. Early Mortality in a Multinational Systemic Sclerosis Inception Cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and predicting mortality from systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokeerbux, M.R.; Giovannelli, J.; Dauchet, L.; Mouthon, L.; Agard, C.; Lega, J.C.; Allanore, Y.; Jego, P.; Bienvenu, B.; Berthier, S.; et al. Survival and prognosis factors in systemic sclerosis: Data of a French multicenter cohort, systematic review, and meta-analysis of the literature. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Xu, D.; Zeng, X. Prognostic profile of systemic sclerosis: Analysis of the clinical EUSTAR cohort in China. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czirják, L.; Kumánovics, G.; Varjú, C.; Nagy, Z.; Pákozdi, A.; Szekanecz, Z.; Szűcs, G. Survival and causes of death in 366 Hungarian patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Graf, N.; Sauter, R.; Allanore, Y.; Curram, J.; Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Pena, J.D.; Pope, J.E.; et al. Predictors of disease worsening defined by progression of organ damage in diffuse systemic sclerosis: A European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Allanore, Y.; Alves, M.; Brunborg, C.; Airó, P.; Ananieva, L.P.; Czirják, L.; Guiducci, S.; Hachulla, E.; Li, M.; et al. Progressive interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease in the EUSTAR database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, E.Y.; Singh, D.R.; Singh, R.R. Trends in Systemic Sclerosis Mortality Over Forty-Eight Years, 1968-2015: A US Population-Based Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanawatkul, P.; Solomon, J.J.; Kim, D.; George, M.P.; Matarrese McGibbon, L.R.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Maleki-Fischbach, M.; Amigues, I.; Kastsianok, L.; Fernandez Perez, E.R. Trends in systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension mortality in the USA. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobanski, V.; Giovannelli, J.; Allanore, Y.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Vettori, S.; Cozzi, F.; Distler, O.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Denton, C.; et al. Phenotypes Determined by Cluster Analysis and Their Survival in the Prospective European Scleroderma Trials and Research Cohort of Patients With Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1553–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Franks, J.M.; Yang, M.; Toledo, D.M.; Wood, T.A.; Hinchcliff, M.; Whitfield, M.L. Regulator combinations identify systemic sclerosis patients with more severe disease. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e137567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaug, B.; Khanna, D.; Swindell, W.R.; Hinchcliff, M.E.; Frech, T.M.; Steen, V.D.; Hant, F.N.; Gordon, J.K.; Shah, A.A.; Zhu, L.; et al. Global skin gene expression analysis of early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis shows a prominent innate and adaptive inflammatory profile. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, S.; Riccardi, A.; Messiniti, V.; Caramaschi, P.; Rosato, E.; Maurer, B.; Smith, V.; Siegert, E.; De Langhe, E.; Riccieri, V.; et al. Revised European Scleroderma Trials and Research Group Activity Index is the best predictor of short-term severity accrual. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevskaya, T.; Baron, M.; Pope, J.E.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Predictive value of European Scleroderma Group Activity Index in an early scleroderma cohort. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panopoulos, S.; Bournia, V.K.; Konstantonis, G.; Fragiadaki, K.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Tektonidou, M.G. Predictors of morbidity and mortality in early systemic sclerosis: Long-term follow-up data from a single-centre inception cohort. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdowsi, N.; Huq, M.; Stevens, W.; Hudson, M.; Wang, M.; Tay, T.; Burchell, J.L.; Mancuso, S.; Rabusa, C.; Sundararajan, V.; et al. Development and validation of the Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium Damage Index (SCTC-DI): A novel instrument to quantify organ damage in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbacki, A.; Baron, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Stevens, W.; Sahhar, J.; Proudman, S.; Nikpour, M.; Man, A. Damage Trajectories in Systemic Sclerosis Using Group-Based Trajectory Modeling. Arthritis Care Res. 2022. published online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, M.; Stevens, W.; Proudman, S.; Nikpour, M.; Baron, M.; Canadian Scleroderma Research, G.; Australian Scleroderma Interest, G. Associations between the Composite Response Index in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS), survival and other disease measures. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 53, 151973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, L.; Cai, R.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, G.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; et al. A multi-predictor model to predict risk of scleroderma renal crisis in systemic sclerosis: A multicentre, retrospective, cohort study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoy, E.C.; Black, C.; Fleischmajer, R.; Jablonska, S.; Krieg, T.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Rowell, N.; Wollheim, F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): Classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domsic, R.T.; Gao, S.; Laffoon, M.; Wisniewski, S.; Zhang, Y.; Steen, V.; Lafyatis, R.; Medsger, T.A. Defining the optimal disease duration of early diffuse systemic sclerosis for clinical trial design. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 4662–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, A.; Plebani, M.; Peng, M.; Lee, Y.K.; McCafferty, R.; Machin, S.J.; International Council for Standardization in, H. ICSH recommendations for modified and alternate methods measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, E.; Waalen, J. The definition of anemia: What is the lower limit of normal of the blood hemoglobin concentration? Blood 2006, 107, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, M.K.; Tedford, R.J.; Thenappan, T.; De Marco, T.; Park, M.; McLaughlin, V. Elevated Pulmonary Pressure Noted on Echocardiogram: A Simplified Approach to Next Steps. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e017684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: A retrospective. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2011, 73, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, A.H.; Johnson, S.R.; Lee, P. Ethnic influence on disease manifestations and autoantibodies in Chinese-descent patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheikh, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Johnson, S.R. Ethnic Variations in Systemic Sclerosis Disease Manifestations, Internal Organ Involvement, and Mortality. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisroe, K.; Stevens, W.; Sahhar, J.; Ngian, G.S.; Ferdowsi, N.; Hansen, D.; Patel, S.; Hill, C.L.; Roddy, J.; Walker, J.; et al. The clinical and economic burden of systemic sclerosis related interstitial lung disease. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, V.K.; Tikly, M.; Xu, D.; Siegert, E.; Hachulla, E.; Airo, P.; Valentini, G.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Distler, O.; Cozzi, F.; et al. Racial differences in systemic sclerosis disease presentation: A European Scleroderma Trials and Research group study. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, V.; Domsic, R.T.; Lucas, M.; Fertig, N.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. A clinical and serologic comparison of African American and Caucasian patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2986–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia Otero, C.; Assassi, S.; Hudson, M.; Mayes, M.D.; Estrada, Y.M.R.; Pedroza, C.; Mills, T.W.; Walker, J.; Baron, M.; Stevens, W.; et al. Antifibrillarin Antibodies Are Associated with Native North American Ethnicity and Poorer Survival in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, S.; Baron, M.; Hudson, M. Screening and management of subclinical interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: An international survey. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 3401–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.D.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Bloch, D.A.; Michel, B.A. Predictors of survival in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsic, R.T.; Nihtyanova, S.I.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Fine, M.J.; Lucas, M.; Kwoh, C.K.; Denton, C.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Derivation and validation of a prediction rule for two-year mortality in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehra, S.T.; Kelly, A.; Baker, J.F.; Derk, C.T. Predictors of inpatient mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis: A case control study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannarong, T.; Muangchan, C. High burden of skin sclerosis is associated with severe organ involvement in patients with systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis overlap syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayle, A.; Schoof, N.; Alves, M.; Clarke, D.; Raabe, C.; Das, P.; Del Galdo, F.; Maher, T.M. Healthcare Resource Utilization Among Patients in England with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Retrospective Database Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 2460–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinzadeh, P.; Aberer, E.; Ahmadi-Simab, K.; Blank, N.; Distler, J.H.; Fierlbeck, G.; Genth, E.; Guenther, C.; Hein, R.; Henes, J.; et al. Disease progression in systemic sclerosis-overlap syndrome is significantly different from limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P. Renal manifestations of systemic sclerosis--clinical features and outcome assessment. Rheumatology 2008, 47 (Suppl. 5), v54–v56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, K.M.; O’Brien, M.S.; Shenin, M.; Derk, C.T.; Steen, V.D. Gastric antral vascular ectasia in systemic sclerosis: Demographics and disease predictors. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souma, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Moriguchi, T.; Suzuki, N.; Hirano, I.; Pan, X.; Minegishi, N.; Abe, M.; Kiyomoto, H.; Ito, S.; et al. Plasticity of renal erythropoietin-producing cells governs fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2013, 24, 1599–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Sato, Y.; Uchino, E.; Toriu, N.; Shigeta, M.; Kiyonari, H.; Endo, S.; Fukuma, S.; Yanagita, M. Lineage tracing analysis defines erythropoietin-producing cells as a distinct subpopulation of resident fibroblasts with unique behaviors. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valletta, S.; Thomas, A.; Meng, Y.; Ren, X.; Drissen, R.; Sengul, H.; Di Genua, C.; Nerlov, C. Micro-environmental sensing by bone marrow stroma identifies IL-6 and TGFbeta1 as regulators of hematopoietic ageing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Ganz, T.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Marangoni, R.G.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Ye, B.; Shangguang, A.; Qin, W.; Wang, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Wei, J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor 9 Signaling Is Augmented in Systemic Sclerosis and Elicits Transforming Growth Factor beta-Dependent Fibroblast Activation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1989–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akilesh, H.M.; Buechler, M.B.; Duggan, J.M.; Hahn, W.O.; Matta, B.; Sun, X.; Gessay, G.; Whalen, E.; Mason, M.; Presnell, S.R.; et al. Chronic TLR7 and TLR9 signaling drives anemia via differentiation of specialized hemophagocytes. Science 2019, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitev, A.; Christ, L.; Feldmann, D.; Binder, M.; Moller, K.; Kanne, A.M.; Hugle, T.; Villiger, P.M.; Voll, R.E.; Finzel, S.; et al. Inflammatory stays inflammatory: A subgroup of systemic sclerosis characterized by high morbidity and inflammatory resistance to cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Kodera, M.; Matsushita, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Inaba, Y.; Usuda, T.; Kuwana, M.; Takehara, K.; Fujimoto, M. Clinical and immunologic predictors of scleroderma renal crisis in Japanese systemic sclerosis patients with anti-RNA polymerase III autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, S.; Toki, S.; Yamada, K.; Uchiyama, A.; Ishikawa, O. Demographic and clinical features of systemic sclerosis patients with anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Hou, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yan, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Analysis of anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies in Chinese Han systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Baseline (N = 433) | Follow-Up (N = 207) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at initial visit (years) | 52.0 ± 14.4 | 51.0 ± 15.1 | 0.389 |
| Sex, female | 373 (86.1%) | 180 (87.0%) | 0.779 |
| Disease duration (years) | 8.2 ± 9.5 | 8.6 ± 9.8 | 0.59 |
| Disease classification | |||
| lcSSc | 173 (40.0%) | 67 (32.4%) | 0.064 |
| dcSSc | 177 (40.9%) | 93 (44.9%) | 0.332 |
| Sine scleroderma | 13 (3.0%) | 3 (1.4%) | 0.239 |
| Overlap syndrome | 70 (16.2%) | 44 (21.3%) | 0.115 |
| RA | 27 (6.2%) | 18 (8.7%) | 0.255 |
| SLE | 29 (6.7%) | 18 (8.7%) | 0.365 |
| DM/PM | 14 (3.2%) | 8 (3.9%) | 0.682 |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| Anemia | 175 (40.4%) | 83 (40.1%) | 0.939 |
| High ESR | 156/409 (38.1%) | 78/192 (40.6%) | 0.56 |
| High CRP | 85/393 (21.6%) | 46/190 (24.2%) | 0.484 |
| Hypocomplementemia | 176/391 (45.0%) | 77/190 (40.5%) | 0.306 |
| Autoantibody profile | |||
| ANA | 312 (72.1%) | 152 (73.4%) | 0.716 |
| Anti-topoisomerase 1 | 129 (29.8%) | 60 (29.0%) | 0.834 |
| (Anti-Scl-70) | |||
| Anti-centromere proteins | 56 (12.9%) | 31 (15.0%) | 0.481 |
| Medication | |||
| Steroids | 191 (44.1%) | 77 (37.2%) | 0.097 |
| Immunosuppressants | 165 (38.1%) | 73 (35.5%) | 0.487 |
| Items | Baseline Assessment N = 433 |
|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal and skin | 208 (48.0%), Score: 1.69 ± 2.03 |
| Joint contracture (small joints) | 56 (12.9%) |
| Joint contracture (large joints) | 7 (1.6%) |
| Sicca symptoms | 160 (37.0%) |
| Proximal muscle weakness | 32 (7.4%) |
| Calcinosis complicated by infection or requiring surgery | 7 (1.6%) |
| Vascular | 87 (20.1%), Score: 0.45 ± 0.91 |
| Digital ulceration | 87 (20.1%) |
| Digital amputation required | 19 (4.4%) |
| Gastrointestinal | 224 (51.7%), Score: 1.16 ± 1.35 |
| Esophageal dysmotility | 69 (15.9%) |
| Esophageal stricture | 2 (0.5%) |
| Refractory gastro-esophageal reflux disease (heartburn) | 103 (23.8%) |
| GAVE | 0 (0.0%) |
| Pseudo-obstruction | 6 (1.4%) |
| BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 or weight loss > 10% in the last 12 months | 155 (35.8%) |
| Respiratory | 176 (40.6%), Score: 1.38 ± 2.21 |
| ILD > 20% extent on HRCT | 172 (39.7%) |
| FVC < 70% | 52 (12.0%) |
| Dependence on home oxygen | 9 (2.1%) |
| Cardiovascular | 55 (12.7%), Score: 0.49 ± 1.70 |
| PAH | 42 (9.7%) |
| Moderate to severe right ventricular dysfunction | 10 (2.3%) |
| Myocardial disease | 22 (5.1%) |
| Moderate to large pericardial effusion | 13 (3.0%) |
| Renal | 5 (1.2%), Score: 0.05 ± 0.41 |
| History of SRC | 5 (1.2%) |
| eGFR < 45mL/min/1.73m2 | 4 (0.9%) |
| CKD stage 5 and need for renal replacement therapy | 1 (0.2%) |
| SCTC-DI | 5.21 ± 4.60 |
| SCTC-DI = 0 (Baseline) | 68 (15.7%) |
| Characteristics at Baseline | High Burden: SCTC-DI ≥ 6 | Modified High Burden: SCTC-DI ≥4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | OR (95% CI) | p Value | β | SE | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age (years) | 0.03 | 0.01 | 1.04 (1.02, 1.05) | <0.001 | - | - | - | - |
| Disease Duration (years) | - | - | - | - | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.06 (1.03, 1.09) | <0.001 |
| Steroids usage | 0.66 | 0.22 | 1.93 (1.25, 2.99) | 0.003 | - | - | - | - |
| Anemia | 0.95 | 0.22 | 2.60 (1.70, 4.00) | <0.001 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 1.89 (1.24, 2.90) | 0.003 |
| Constant | −3.04 | 0.49 | 0.05 (0.02, 0.12) | <0.001 | −0.29 | 0.16 | 0.75 (0.55, 1.03) | 0.073 |
| Characteristics | Anemia | Non-Anemia | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 175 | N = 258 | ||
| Age at initial visit (years) | 53.03 ± 15.93 | 51.36 ± 13.28 | 0.253 |
| Sex, female | 156 (89.1%) | 217 (84.1%) | 0.137 |
| Disease duration (years) | 9.15 ± 9.80 | 7.55 ± 9.25 | 0.085 |
| Disease classification | |||
| lcSSc | 69 (39.4%) | 104 (40.3%) | 0.854 |
| dcSSc | 60 (34.3%) | 117 (45.3%) | 0.022 |
| Sine scleroderma | 5 (2.9%) | 8 (3.1%) | 0.884 |
| Overlap syndrome | 41 (23.4%) | 29 (11.2%) | 0.001 |
| RA | 18 (10.3%) | 9 (3.5%) | 0.004 |
| SLE | 15 (8.6%) | 14 (5.4%) | 0.199 |
| DM/PM | 8 (4.6%) | 6 (2.3%) | 0.195 |
| Inflammatory index | |||
| High ESR | 94/166 (56.6%) | 62/243 (25.5%) | <0.001 |
| High CRP | 45/160 (28.1%) | 40/233 (17.2%) | 0.01 |
| Hypocomplementemia | 85/162 (52.5%) | 91/229 (39.7%) | 0.013 |
| Autoantibody profile | |||
| ANA | 133 (76.0%) | 179 (69.4%) | 0.132 |
| Anti-topoisomerase 1 (Anti-Scl-70) | 52 (29.7%) | 77 (29.8%) | 0.977 |
| Anti-centromere proteins | 19 (10.9%) | 37 (14.3%) | 0.289 |
| Medication | |||
| Steroids | 76 (43.4%) | 115 (44.6%) | 0.814 |
| Immunosuppressants | 64 (36.6%) | 101 (39.1%) | 0.588 |
| SCTC-DI (Baseline) | 6.49 ± 5.12 | 4.34 ± 4.00 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Jiang, X.; Li, T.; Su, Y.; Mu, R. Anemia Is an Indicator for Worse Organ Damage Trajectories in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175013
Li Z, Xu D, Jiang X, Li T, Su Y, Mu R. Anemia Is an Indicator for Worse Organ Damage Trajectories in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175013
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhaohua, Dan Xu, Xintong Jiang, Ting Li, Yin Su, and Rong Mu. 2022. "Anemia Is an Indicator for Worse Organ Damage Trajectories in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175013
APA StyleLi, Z., Xu, D., Jiang, X., Li, T., Su, Y., & Mu, R. (2022). Anemia Is an Indicator for Worse Organ Damage Trajectories in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175013






