The New Challenge in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Definition of Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection (cAMR)
- Compatible histology (both required): (a) unexplained mononuclear portal and/or perivenular inflammation with interface and/or perivenular necro inflammatory activity, and (b) moderate portal/periportal, sinusoidal and/or perivenular fibrosis.
- Positivity for DSAs within 3 months of biopsy.
- Focal C4d positivity (>10% portal tract microvascular endothelia).
- Reasonable exclusion of other liver insults that may cause a similar pattern of injury.
3.2. Prevalence
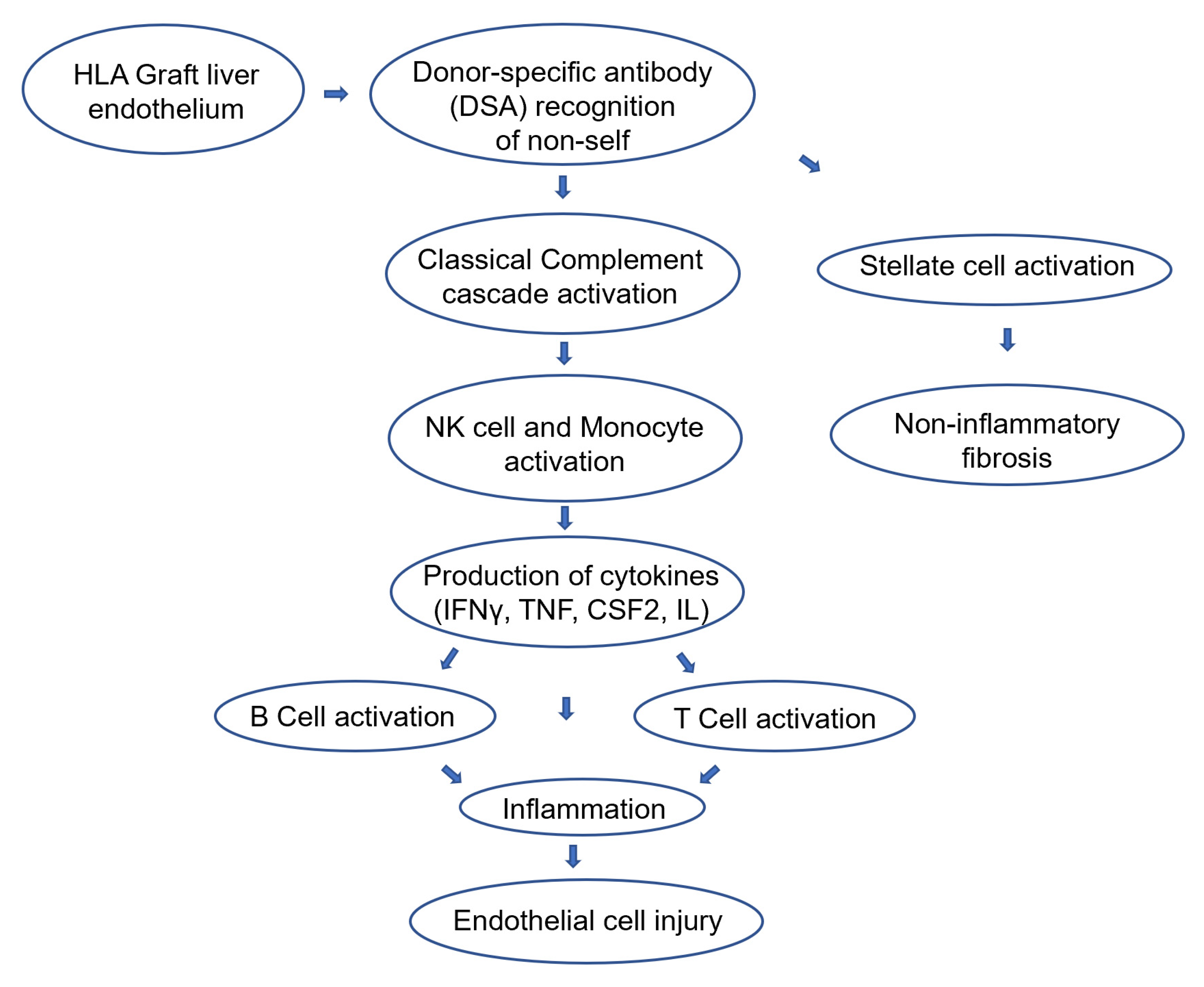
3.3. Physio-Pathology
3.4. Clinical and Histopathological Aspects
3.5. Treatment of cAMR
3.5.1. Calcineurin-Inhibitor (CNI) Conversion
3.5.2. Immunosuppression Adherence
3.5.3. mTOR Inhibitors
3.5.4. Rituximab, Bortezomib and Eculizumab
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasahara, M.; Umeshita, K.; Eguchi, S.; Eguchi, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Fukuda, A.; Egawa, H.; Haga, H.; Kokudo, N.; Sakisaka, S.; et al. Outcomes of Pediatric Liver Transplantation in Japan: A Report from the Registry of the Japanese Liver Transplantation Society. Transplantation 2021, 105, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetris, A.J.; Bellamy, C.; Hübscher, S.G.; O’Leary, J.; Randhawa, P.S.; Feng, S.; Neil, D.; Colvin, R.B.; McCaughan, G.; Fung, J.J.; et al. 2016 Comprehensive Update of the Banff Working Group on Liver Allograft Pathology: Introduction of Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2816–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.T.; Fiel, M.I.; Schiano, T.D. Antibody-mediated rejection of the liver allograft: An update and a clinico-pathological perspective. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, J.G.; Kaneku, H.; Susskind, B.M.; Jennings, L.W.; Neri, M.A.; Davis, G.L.; Klintmalm, G.B.; Terasaki, P.I. High mean fluorescence intensity donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies associated with chronic rejection post liver transplant. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa-Hayashino, A.; Yoshizawa, A.; Uchida, Y.; Egawa, H.; Yurugi, K.; Masuda, S.; Minamiguchi, S.; Maekawa, T.; Uemoto, S.; Haga, H. Progressive graft fibrosis and donor-specific human leukocyte antigen antibodies in pediatric late liver allografts. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, L.J.; Hickey, M.J.; Venick, R.S.; Vargas, J.H.; Farmer, D.G.; Busuttil, R.W.; McDiarmid, S.V.; Reed, E.F. Donor-specific HLA Antibodies Are Associated with Late Allograft Dysfunction After Pediatric Liver Transplantation. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, J.G.; Cai, J.; Freeman, R.; Banuelos, N.; Hart, B.; Johnson, M.; Jennings, L.W.; Kaneku, H.; Terasaki, P.I.; Klintmalm, G.B.; et al. Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Liver Allografts. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Bucuvalas, J.C.; Demetris, A.J.; Burrell, B.E.; Spain, K.M.; Kanaparthi, S.; Magee, J.C.; Ikle, D.; Lesniak, A.; Lozano, J.J.; et al. Evidence of Chronic Allograft Injury in Liver Biopsies from Long-term Pediatric Recipients of Liver Transplants. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1838–1851.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, M.; Habès, D.; Taupin, J.L.; Mussini, C.; Redon, M.J.; Suberbielle, C.; Jacquemin, E.; Gonzales, E.; Guettier, C. Morphological characterization of chronic antibody-mediated rejection in ABO-identical or ABO-compatible pediatric liver graft recipients. Liver Transplant. 2018, 24, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, A.; Congy-Jolivet, N.; Muscari, F.; Lavayssière, L.; Esposito, L.; Cardeau-Desangles, I.; Guitard, J.; Dörr, G.; Suc, B.; Duffas, J.P.; et al. Prevalence, incidence and risk factors for donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies in maintenance liver transplant patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musat, A.I.; Agni, R.M.; Wai, P.Y.; Pirsch, J.D.; Lorentzen, D.F.; Powell, A.; Leverson, G.E.; Bellingham, J.M.; Fernandez, L.A.; Foley, D.P.; et al. The significance of donor-specific HLA antibodies in rejection and ductopenia development in ABO compatible liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, J.; Habes, D.; Majed, L.; Guettier, C.; Gonzalès, E.; Linglart, A.; Larue, C.; Furlan, V.; Pariente, D.; Baujard, C.; et al. Long-term outcome of liver transplantation in childhood: A study of 20-year survivors. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakashita, H.; Haga, H.; Ashihara, E.; Wen, M.C.; Tsuji, H.; Miyagawa-Hayashino, A.; Egawa, H.; Takada, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Uemoto, S.; et al. Significance of C4d staining in ABO-identical/compatible liver transplantation. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, H.M.; Kelly, D.A.; McKiernan, P.J.; Hübscher, S. Progressive histological damage in liver allografts following pediatric liver transplantation. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.M.; Kanaparthi, S.; Burrell, B.E.; Lucas, D.P.; Vega, R.M.; Demetris, A.J.; Feng, S. IgG4 donor-specific HLA antibody profile is associated with subclinical rejection in stable pediatric liver recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.R.; Naini, B.V.; Scapa, J.V.; Reed, E.F.; Busuttil, R.W.; Cheng, E.Y.; Farmer, D.G.; Vargas, J.H.; Venick, R.S.; McDiarmid, S.V.; et al. Obliterative portal venopathy: A histopathologic finding associated with chronic antibody-mediated rejection in pediatric liver allografts. Pediatr. Transplant. 2018, 22, e13124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, C.; Sempoux, C.; Quinones, J.A.; Bourdeaux, C.; Hoyos, S.P.; Sokal, E.; Reding, R. Dynamics of allograft fibrosis in pediatric liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Spada, M.; Liccardo, D.; Pedini, D.; Grimaldi, C.; Pietrobattista, A.; Basso, M.S.; Della Corte, C.; Mosca, A.; Saffioti, M.C.; et al. Allograft Fibrosis After Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Evolution. Liver Transplant. 2022, 28, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Sensi, B.; Manzia, T.M.; Tisone, G.; Grassi, G.; Signorello, A.; Milana, M.; Lenci, I.; Baiocchi, L. Chronic rejection after liver transplantation: Opening the Pandora’s box. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7771–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Fujimoto, M.; Yoshizawa, A.; Yurugi, K.; Miyagawa-Hayashino, A.; Sumiyoshi, S.; Minamiguchi, S.; Uemoto, S.; Maekawa, T.; Haga, H. Application of complement component 4d immunohistochemistry to ABO-compatible and ABO-incompatible liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2014, 20, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, I.; Aguado-Dominguez, E.; Sousa, J.M.; Nuñez-Roldan, A. Rethinking de novo immune hepatitis, an old concept for liver allograft rejection: Relevance of glutathione S-transferase T1 mismatch. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3239–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Ekong, U.D.; Lobritto, S.J.; Demetris, A.J.; Roberts, J.P.; Rosenthal, P.; Alonso, E.M.; Philogene, M.C.; Ikle, D.; Poole, K.M.; et al. Complete immunosuppression withdrawal and subsequent allograft function among pediatric recipients of parental living donor liver transplants. JAMA 2012, 307, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetris, A.J.; Bellamy, C.O.; Gandhi, C.R.; Prost, S.; Nakanuma, Y.; Stolz, D.B. Functional Immune Anatomy of the Liver-As an Allograft. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1653–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burra, P. The adolescent and liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupy, A.; Lefaucheur, C. Antibody-Mediated Rejection of Solid-Organ Allografts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, M.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, R.; Gu, G.; Xia, Q. Role of Innate Immunity in Pediatric Post-transplant Idiopathic Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves Souza, L.; de Martino, R.B.; Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Rela, M.; Dhawan, A.; O’Grady, J.; Heaton, N.; Quaglia, A. Histopathology of 460 liver allografts removed at retransplantation: A shift in disease patterns over 27 years. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Akamatsu, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Ohdan, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Egawa, H. The efficacy of rituximab treatment for antibody-mediated rejection in liver transplantation: A retrospective Japanese nationwide study. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Multicenter Liver Study Group. Efficacy of tacrolimus as rescue therapy for chronic rejection in orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation 1997, 64, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, P.; Klupp, J.; Langrehr, J.M. mTOR inhibitors: An overview. Liver Transplant. 2001, 6, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.; Briem-Richter, A.; Sornsakrin, M.; Fischer, L.; Nashan, B.; Ganschow, R. The use of everolimus in pediatric liver transplant recipients: First experience in a single center. Pediatr. Transplant. 2011, 15, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Hiwatashi, S.; Saka, R.; Yamanaka, H.; Takama, Y.; Tazuke, Y.; Bessho, K.; Okuyama, H. Everolimus Rescue Treatment for Chronic Rejection After Pediatric Living Donor Liver Transplantation: 2 Case Reports. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 2872–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection (cAMR) | |
|---|---|
| Histological findings | Probable cAMR (all four criteria are required):
|
Possible cAMR:
| |
| Incidence | Unknown; estimated to be present in 8 to 15% of de novo or persistent DSA |
| Risk factors |
|
| Clinical implications | Increased fibrosis and graft failure in an unknown percentage of patients |
| Authors | Year | Number of Patients | Time after LT | DSA+ | C4d | Histological Findings | Type of Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miyagawa-Hayashino A, et al. [5] | 2012 | 79 | median 11 (5–20) years | 48% (32/67) | 15.6% of DSA+ | DSA+: present more bridging fibrosis, endothelial C4d, acute rejection | Single center, retrospective |
| Wozniak L, et al. [6] | 2015 | 50 | 3.7 ± 4.4 years at LT; 16 ± 4.9 years at study | 54% | N.A. | Non-tolerant patients have more DQ DSA positivity (61%) compared to stable (20%) or tolerant (29%) patients. | Single center, retrospective |
| Feng S, et al. [8] | 2018 | 157 | 8.9 ± 3.46 years | Class II 55.6% (80/144) | Score 0–3: 29%; 4–6: 42%; 7–9: 18%; >9: 10% | DSA class II+: more fibrosis, portal inflammation and higher C4d score | Multicenter, prospective |
| Dao M, et al. [9] | 2018 | 53 | 131.3 ± 15.3 months | 48% (20/44) | 48% (31/53) | LAFSc, perivenular fibrosis and portal inflammation higher in double DSA and C4d positive | Single center, retrospective |
| Neves Souza L, et al. [27] | 2018 | 118 pediatric retransplants | >10 years post LT | N.A. | N.A. | Increased incidence of IPTH among children (40%) in the recent era | Single center, retrospective |
| Evans HM, et al. [14] | 2006 | 158 | >5 years post LT (protocol biopsies 1, 5, and 10 years after LT) | N.A. | N.A. | Increasing rates of chronic hepatitis (22%, 43%, 64% at 1, 5, 10 years post LT) and allograft fibrosis (52%, 81%, 91%) along the years | Single center, retrospective |
| Guerra MAR, et al. [16] | 2018 | 45 | 2–14 years post LT | Positive in all 4 patients with OPV | Positive in 2 of 4 patients with OPV | OPV was present in four patients with cAMR features | Single center, retrospective |
| Jackson AM, et al. [15] | 2020 | 129 | 1.9 (1.74) at LT, 10.9 (3.54) at study | 65 (50%) | N.A. | 67 (43%) subclinical chronic graft injury | Multicenter, prospective |
| Angelico R, et al. [18] | 2022 | 80 | >5 years | N.A. | N.A. | AF 6 mo after LT: 73.8% AF 5 y after LT: 90% AF 10 y after LT: 90% Risk factors for AF: CIT > 8 h, donor ager > 40 y, low FK trough 1 y post LT. | Single center, retrospective |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uebayashi, E.Y.; Okajima, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ogawa, E.; Okamoto, T.; Haga, H.; Hatano, E. The New Challenge in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164834
Uebayashi EY, Okajima H, Yamamoto M, Ogawa E, Okamoto T, Haga H, Hatano E. The New Challenge in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(16):4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164834
Chicago/Turabian StyleUebayashi, Elena Yukie, Hideaki Okajima, Miki Yamamoto, Eri Ogawa, Tatsuya Okamoto, Hironori Haga, and Etsurou Hatano. 2022. "The New Challenge in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 16: 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164834
APA StyleUebayashi, E. Y., Okajima, H., Yamamoto, M., Ogawa, E., Okamoto, T., Haga, H., & Hatano, E. (2022). The New Challenge in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(16), 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164834






