Abstract
The term mastocytosis refers to a heterogeneous group of disorders characterised by accumulation of clonal mast cells in different organs, most commonly in the skin. Little is known about the role of dermoscopy in the diagnostics of mastocytosis. To date, no systematic review on the dermoscopic features of cutaneous mastocytosis has been performed. The aim of this study was to summarise the current knowledge in the field as well as to identify the knowledge gaps to show possible directions for further studies, based on a systematic search of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases and related references published before 3 January 2022. Dermoscopic features, type of dermoscope, polarisation mode, magnification, and number of cases were analysed. In total, 16 articles were included in this review (3 case series and 13 case reports), analysing 148 patients with different variants of cutaneous mastocytosis; all of the studies analysed had a low level of evidence (V). The main dermoscopic features of urticaria pigmentosa included brown structureless areas, brown lines arranged in a network, and linear vessels distributed in a reticular pattern, with this last finding also being typical of telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans. The presence of either circumscribed yellow structureless areas or diffuse yellowish background was a constant pattern of mastocytoma, while nodular, pseudoangiomatous xanthelasmoid, and plaque-type mastocytosis were typified by light-brown structureless areas and/or pigment network, though the first two variants also showed yellow/yellow-orange structureless areas. Finally, pigmented streaks of radial distribution surrounding hair follicles were described to be a pathognomonic dermoscopic feature of pseudoxanthomatous mastocytosis. Although this review shows that the various clinical forms of cutaneous mastocytosis may feature diagnostic dermoscopic clues, it also underlines the need for further investigation as several relevant data are missing, including evaluation of dermoscopic pattern according to anatomical locations or “lesion age”, studies on rare mastocytosis variants, evaluation of the prognostic role of dermoscopy in the context of systemic involvement, and comparative analyses with common clinical mimickers.
1. Introduction
The term mastocytosis refers to a heterogeneous group of disorders characterised by accumulation of clonal mast cells in different organs, most commonly in the skin, bone marrow, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. Cutaneous involvement may be either the only manifestation of the disease (Cutaneous Mastocytosis, CM) or it may be associated with systemic disease (Systemic Mastocytosis, SM) [,,]. In contrast to adults, CM predominates in children [].
According to the current World Health Organization (WHO) classification, CM is divided into three forms: maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (MPCM) (including clinical subtypes previously known as urticaria pigmentosa [UP] and telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans [TMEP]), diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis (DCM), and mastocytoma of the skin []. Other clinical variants of CM have been described, e.g., nodular mastocytosis, plaque-type mastocytosis, pseudoangiomatous xanthelasmoid mastocytosis, and pseudoxanthomatous localised mastocytosis, though they are no longer recognised as separate entities but as clinical subtypes of either MPCM or mastocytoma based on the number of the lesions (>5 MPCM and ≤5 mastocytoma) [,,,,,,,,]. The diagnosis of cutaneous mastocytosis is generally based on clinical assessment (presentation of cutaneous lesions, positive Darier’s sign, and symptoms arising from mediator release) in association with additional investigations, such as histopathological, immunohistochemical, and sometimes genetic assessment.
Main differential diagnoses of CM include urticaria, juvenile xanthogranuloma, arthropod bites, bullous impetigo, autoimmune bullous skin disorders, epidermolysis bullosa, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, and café-au-lait macules (Supplementary Table S1) [,]. Dermoscopy is a supportive tool in the diagnosis of different cutaneous disorders []. In recent years, new papers describing the dermoscopic features of mastocytosis have been published. The aim of this study was to summarise current data on the diagnostic utility of (video) dermoscopy of skin involvement in patients with mastocytosis.
2. Materials and Methods
A comprehensive search of the literature using the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science electronic databases using the keywords ‘dermoscopy’ OR ‘dermatoscopy’ OR ‘trichoscopy’ OR ‘videodermoscopy’ OR ‘videodermatoscopy’ in combination with ‘mastocytosis’ OR ‘urticaria pigmentosa’ OR ‘mastocytoma’ OR ‘teleangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans’ was performed by two investigators (M. Sławińska., A. Kaszuba) over a time period from inception to 2 January 2022. After the initial search was performed, two reviewers independently screened titles and abstracts for inclusion and exclusion criteria. In doubtful cases, decision on inclusion was based on the opinion of the third investigator (M. So). Based on title and abstract analysis, researchers selected the articles concerning dermosopic features of mastocytosis. At this step, we excluded records not related to the topic, non-English language manuscripts, review articles, and duplicates. In the relevant articles assessed full-text, references were searched for additional records. Finally, articles not containing quantitative data on dermoscopic observations were excluded. In addition to dermoscopic features, type of dermoscope, polarisation mode, magnification, and number of cases were analysed and summarised. The Oxford 2011 Levels of Evidence was used to classify the level of evidence of each article []. As the analysed papers concerned diagnostic studies single case reports were labelled as level of evidence V. Additionally, corresponding terminology based on the International Dermoscopy Society consensus paper has been added [].
3. Results
Of the 245 records found initially in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases, a total of 17 articles were assessed full-text after title and abstract screening. Of these 17 articles, one was excluded as it did not meet the inclusion criteria, and none were included after reference screening. Thus, in total, 16 articles were included in this review (3 case series and 13 case reports), analysing 148 patients with different CM variants. The flow chart reporting the study selection process is presented in Figure 1.
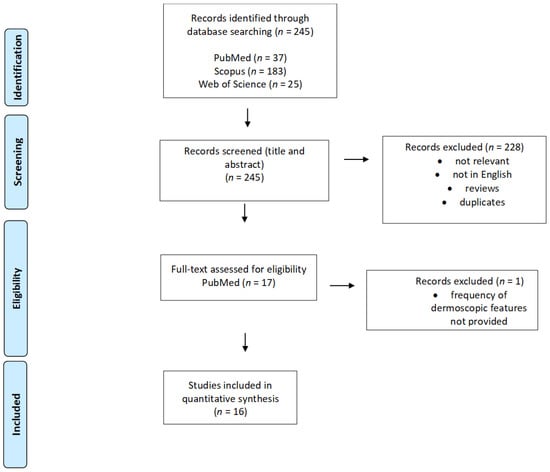
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram demonstrating the selection process for study inclusion in the systematic review.
The type of dermoscope used in the study was mentioned in seven records, magnification in eight (seven used ×10 magnification and one ×50 and ×200 magnification), polarisation was mentioned in five records (polarised light was applied in all of them), and information concerning the use or not of an immersion interface was not provided in any of the analysed studies.
Table 1 presents the details of the analysed studies.

Table 1.
The summary of the dermoscopic features for different forms of cutaneous mastocytosis.
3.1. Maculopapular Cutaneous Mastocytosis (UP Clinical Subtype)
The systematic review revealed 99 cases in seven studies. Most data on dermoscopy of this mastocytosis variant came from a study by Vano-Galvan et al. [], who analysed 90 patients with MPCM. The most prevalent dermoscopic findings were light-brown blots (structureless areas) (43/90; 47.8%), pigment networks (36/90; 40.0%), and vascular patterns including linear vessels in reticular distribution—described as reticular vessels—and dotted vessels (11/90; 12.2%). Interestingly, the study showed that the vascular dermoscopic pattern was an independent predictive factor for the need for daily anti-mediator therapy. The remaining data from smaller case reports/case series (six studies, nine patients) confirmed the presence of pigment network (brown reticular lines) in all cases (in two of them associated with a red or light-brown background) [,,,,,,] (Figure 2).
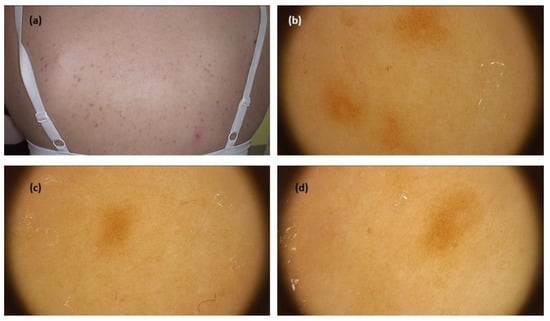
Figure 2.
(a) Maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa clinical subtype)—clinical presentation. (b–d) Dermoscopy shows brown reticular lines (pigment network)(FotoFinder, Medicam 800 HD, FotoFinder Systems GmbH, Bad Birnbach, Germany; ×20 magnification, immersion gel).
3.2. Maculopapular Cutaneous Mastocytosis (TMEP Clinical Subtype)
When it comes to TMEP, a systematic review revealed 13 cases from five studies, including one case limited only to acral areas. The three main dermoscopic patterns were reticular vascular pattern (thin reticular telangiectasias) observed in all cases, in three cases associated with an erythematous background, in two cases with pigment network (brown reticular lines), and in one with brownish background [,,,] (Figure 3).
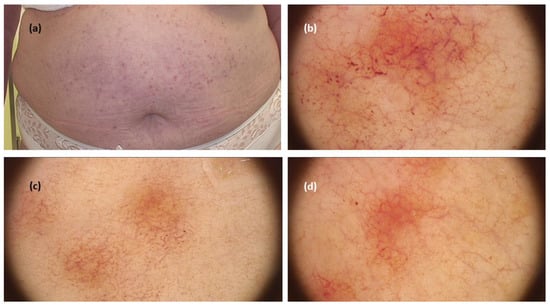
Figure 3.
(a) Maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans clinical subtype)—clinical presentation. (b–d). Dermoscopy shows reticular vascular pattern (thin reticular telangiectasias) over erythematous background (FotoFinder, Medicam 800 HD, FotoFinder Systems GmbH, Bad Birnbach, Germany; ×20 magnification, immersion gel).
3.3. Mastocytoma
The systematic review revealed 15 cases from five studies. In all cases, the authors described the presence of yellow structureless areas (blot)/yellowish background. In most of them (11/13; 84.6%), it was the only observed pattern [,,,,]. Additional structures were peripheral brown reticular lines (3/13), a central white structureless area (2/13), and vessels in a central distribution (vessel morphology was not described; 1/13) (Figure 4).
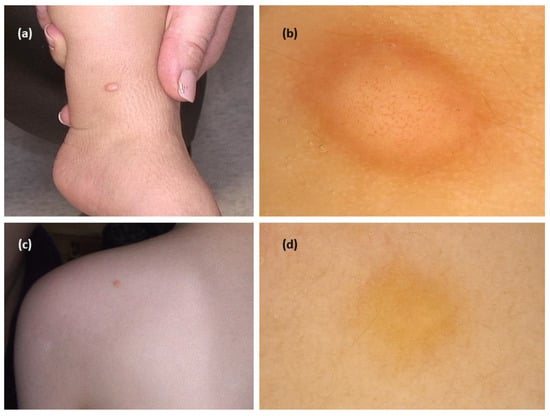
Figure 4.
(a) Mastocytoma—clinical presentation. (b) Dermoscopy shows central polymorphic vessels and peripheral yellow brownish structureless area (FotoFinder, Medicam 800 HD, FotoFinder Systems GmbH, Bad Birnbach, Germany; ×20 magnification, immersion gel). (c) Mastocytoma—clinical presentation. (d) Dermoscopy shows yellow structureless pattern (FotoFinder, Medicam 800 HD, FotoFinder Systems GmbH, Bad Birnbach, Germany; ×20 magnification, immersion gel).
3.4. Other Clinical Forms of CM
With regard to nodular mastocytosis and plaque-type mastocytosis, Vano-Galvan et al. [] in their study analysed eleven and eight instances of the former and latter variant, respectively. In detail, the main dermoscopic features of nodular mastocytosis were yellow-orange structureless areas (6/11; 54.6%), pigment networks (5/11; 45.5%), and light-brown structureless areas (3/11; 27.3%), while plaque-type mastocytosis was associated with light-brown structureless areas (5/8; 62.5%) and pigment networks (3/18; 37.5%) [] (Figure 5).
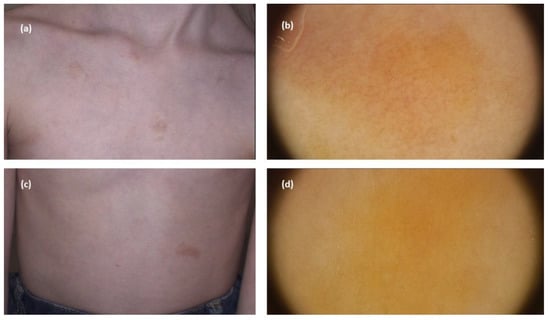
Figure 5.
(a,c) Maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis (plaque-type mastocytosis clinical subtype)—clinical presentation. (b) Dermoscopy shows reticular vascular pattern (thin reticular telangiectasias) over yellow background. (d) Dermoscopy shows yellow structureless areas (FotoFinder, Medicam 800 HD, FotoFinder Systems GmbH, Bad Birnbach, Germany; ×20 magnification, immersion gel).
Considering pseudoangiomatous xanthelasmoid mastocytosis, only one dermoscopic case of this rare entity was published revealing a pigment network (brown reticular lines) and yellow blots (structureless areas) [].
Finally, an instance of pseudoxanthomatous localised mastocytosis involving the vulva showed pigmented streaks with radial distribution surrounding hair follicles, and this pattern was considered pathognomonic by the authors [].
4. Discussion
The aim of this review was to summarise the current knowledge on the role of dermoscopy in diagnosis of mastocytosis. The analysis of published studies revealed that almost all data (127 out of 148 patients) came from one large case series, and the remaining were small case series/case reports. All of the analysed studies showed a low level of evidence (V).
Based on this review, the main dermoscopic features of UP included brown structureless areas, brown lines arranged in a network, and linear vessels distributed in a reticular pattern. The first two findings were due to basal cell layer hyperpigmentation, a typical histological feature of this form of mastocytosis, while the vascular pattern was the result of dermal vessel dilation. This last histological finding was also responsible for the main dermoscopic feature of TMEP—the so-called “vascular reticular pattern” (thin reticular telangiectasias). By contrast, the presence of either circumscribed yellow structureless areas or diffuse yellowish background was a repetitive dermoscopic pattern of mastocytoma histologically resulting from a compact mast cell infiltration of the dermis. Moving to nodular, pseudoangiomatous xanthelasmoid, and plaque-type mastocytosis, all of them may be typified by light-brown structureless areas and/or pigment network as a result of basal cell layer hyperpigmentation, yet only the first two variants may also show yellow/yellow-orange structureless areas, likely due to a denser cellular infiltration. Finally, pigmented streaks of radial distribution surrounding hair follicles were described as being a pathognomonic dermoscopic feature of pseudoxanthomatous mastocytosis, though this observation needs to be confirmed in further studies as it came from a single report [].
Importantly, most of the remaining mentioned findings were not specific to mastocytosis and thus, should be interpreted carefully along with clinical and histopathological findings. Brown lines arranged in a network should be differentiated from melanocytic lesions or dermatofibroma, while in cases of yellow-orange structureless areas, diagnosis of juvenile xanthogranuloma, xanthoma, solitary reticulohistiocytoma, sebaceous tumours, keratin accumulation or scaly disorders, elastic fibres disorders, and others should be considered [].
5. Conclusions
Despite several articles being published on the dermoscopy of CM, there is still a need for further investigations in this regard as the current evidence was from low-quality studies. Additionally, there were various aspects that have not been investigated so far, including evaluation according to anatomical locations or “lesion age”, studies on rare mastocytosis variants, evaluation of the prognostic role of dermoscopy in the context of systemic involvement, and comparative analyses with common clinical mimickers. Based on current knowledge, it seems that dermoscopy will remain a complementary technique in mastocytosis diagnosis, as potential overlap with structures observed in other entities exists.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm11164649/s1, Table S1: Dermoscopic features of the entities that may clinically resemble cutaneous mastocytosis. References [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska); Methodology: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska), A.K., M.L., M.S. (Michał Sobjanek), R.J.N. and E.E.; Formal analysis: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska) and A.K.; Investigation: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska), A.K. and E.E.; Writing—original draft preparation: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska) and M.L.; Writing—review and editing: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska), M.S. (Michał Sobjanek), R.J.N., E.E. and M.L.; Visualisation: M.S. (Martyna Sławińska); Supervision: E.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Medical University of Gdańsk.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Valent, P.; Akin, C.; Gleixner, K.V.; Sperr, W.R.; Reiter, A.; Arock, M.; Triggiani, M. Multidisciplinary challenges in mastocytosis and how to address with personalized medicine approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, K.; Escribano, L.; Grattan, C.; Brockow, K.; Carter, M.C.; Alvarez-Twose, I.; Matito, A.; Broesby-Olsen, S.; Siebenhaar, F.; Lange, M.; et al. Cutaneous manifestations in patients with mastocytosis: Consensus report of the European Competence Network on Mastocytosis; the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma &; Immunology; and the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 137, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brockow, K. Epidemiology, prognosis, and risk factors in mastocytosis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2014, 34, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.; Hartmann, K.; Carter, M.; Siebenhaar, F.; Alvarez-Twose, I.; Torrado, I.; Brockow, K.; Renke, J.; Irga-Jaworska, N.; Plata-Nazar, K.; et al. Molecular Background, Clinical Features and Management of Pediatric Mastocytosis: Status 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Akin, C.; Metcalfe, D.D. Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood 2017, 129, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, K.; Peng, X.; Wang, F. Dermoscopic findings of pseudoxanthomatous mastocytosis localised on vulva. An. Bras. de Dermatol. 2018, 93, 940–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, L.; Ljungberg, O.; Svensson, Å.; Rubin, A. Pseudoangiomatous Xanthelasmoid Mastocytosis—A New Histopathological Entity. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 31, e261–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut, J.; Mercieca, L.; Boffa, M.M.; Pisani, D.; Betts, A.; Boffa, M.J. Palmoplantar maculopapular cutaneous mastocytosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, E79–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vano-Galvan, S.; Alvarez-Twose, I.; De las Heras, E.; Morgado, J.M.; Matito, A.; Sánchez-Muñoz, L.; Plana, M.N.; Jaén, P.; Orfao, A.; Escribano, L. Dermoscopic features of skin lesions in patients with mastocytosis. Arch Dermatol. 2011, 147, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akay, B.N.; Kittler, H.; Sanlı, H.; Harmankaya, K.; Anadolu, R. Dermatoscopic findings of cutaneous mastocytosis. Dermatology 2008, 218, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Jakhar, D.; Misri, R. Dermoscopy of Telangiectasia Macularis Eruptiva Perstans. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unterstell, N.; Lavorato, F.G.; Nery, N.S.; Mann, D.; Alves, M.D.F.S.G.; Barcaui, C.B. Dermatoscopic findings in telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans. An. Bras. de Dermatol. 2013, 88, 643–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brockow, K.; Ring, J.; Alvarez-Twose, I.; Orfao, A.; Escribano, L. Extensive blistering is a predictor for severe complications in children with mastocytosis. Allergy 2012, 67, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Alanis, J.C.; Rosales-Mendoza, C.E.; Ocampo-Candiani, J. Bullous mastocytosis mimicking congenital epidermolysis bullosa. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2014, 6, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.; Niedoszytko, M.; Nedoszytko, B.; Łata, J.; Trzeciak, M.; Biernat, W. Diffuse cutaneus mastocytosis: Analysis of 10 cases and a brief review of the literature. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Errichetti, E. Dermoscopy in Monitoring and Predicting Therapeutic Response in General Dermatology (Non-Tumoral Dermatoses): An Up-To-Date Overview. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 1199–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. The Oxford 2011 Levels of Evidence. Available online: http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=5653 (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Errichetti, E.; Zalaudek, I.; Kittler, H.; Apalla, Z.; Argenziano, G.; Bakos, R.; Blum, A.; Braun, R.; Ioannides, D.; Lacarrubba, F.; et al. Standardization of dermoscopic terminology and basic dermoscopic parameters to evaluate in general dermatology (non-neoplastic dermatoses): An expert consensus on behalf of the International Dermoscopy Society. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 182, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-González, E.; Ginarte, M.; Toribio, J. Letter: Cutaneous mastocytosis with systemic involvement mimicking clinical and dermatoscopically multiple melanocytic nevi. Dermatol. Online J. 2011, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.D.B.; Nery, N.S.; Gripp, A.C.; Maceira, J.P.; Nascimento, G.M.D. Dermatoscopic findings of urticaria pigmentosa. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nirmal, B.; Krishnaram, A.S.; Muthu, Y.; Rajagopal, P. Dermatoscopy of Urticaria Pigmentosa with and without Darier’s Sign in Skin of Colour. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 10, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Bhardway, N.; Shirazi, N. Dermoscopy of Urticaria Pigmentosa. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, R.O.; Enokihara, M.M.S.S.; Ogawa, M.M.; Batista, M.D. Multiple lesions with pigmented network on dermoscopy on a 1-year-old boy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, e364–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adya, K.A.; Inamadar, A.C.; Palit, A. Dermoscopy of Cutaneous Mastocytoma. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2018, 9, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gündüz, Ö.; Yildirim, D.; Erdoğan, F.G.; Kaya, B.; Doğan, H. Solitary Bullous Mastocytoma with Dermoscopic Features in a Neonate. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2019, 9, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Kansal, N.K.; Anuragi, R.P. Cutaneous mastocytosis: Clinical, dermoscopic and pathological features. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e24016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Neema, S.; Sinha, P.; Sandhu, S.; Kashif, A.W.; Radhakrishnan, S. Dermoscopic Demonstration of Darier Sign. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2021, 11, e2021114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, C.E.H.; Radia, D.H. Mastocytosis. In Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology, 9th ed.; Griffiths, C.E.M., Barker, J., Bleiker, T., Chalmers, R., Creamer, D., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 46, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bañuls, J.; Arribas, P.; Berbegal, L.; DeLeón, F.J.; Francés, L.; Zaballos, P. Yellow and orange in cutaneous lesions: Clinical and dermoscopic data. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-López, F.; Fueyo, A.; Sánchez-Martín, J.; Pérez-Oliva, N. Dermoscopy for the Screening of Common Urticaria and Urticaria Vasculitis. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.; Kang, D.; Lee, K.; Han, S.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Jang, M. Evolution of urticarial vasculitis: A clinical, dermoscopic and histopathological study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 28, 674–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruilh-Bagolini, L.; Silva-Astorga, M.; Martín, M.J.H.S.; Manoli, M.-S.; Papageorgiou, C.; Apalla, Z.; Lallas, A. Dermoscopy of Juvenile Xanthogranuloma. Dermatology 2020, 237, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Brizzi, E.V.; Moscarella, E.; Scharf, C.; Argenziano, G.; Piccolo, V. Dermoscopy of juvenile xanthogranuloma: A retrospective descriptive study on 35 paediatric patients. J. Eur. Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.; Bowling, J. Dermoscopic appearance of juvenile xanthogranuloma. Dermatology 2007, 215, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalaudek, I.; Argenziano, G.; Di Stefani, A.; Ferrara, G.; Marghoob, A.A.; Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.; Soyer, H.P.; Braun, R.; Kerl, H. Dermoscopy in general dermatology. Dermatology 2006, 212, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichetti, E.; Stinco, G. Dermatoscopy in general dermatology: A practical overview. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 6, 471–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosseila, M.; Sonthalia, S.; Agrawal, M.; Bhatia, J.; Zeeshan, M.; Elsamanoudy, S.; Tiwary, P.; Bhat, Y.J.; Jha, A. Entodermoscopy update: A contemporary review on dermoscopy of cutaneous infections and infestations. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 12, 220–236. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, P.; Jindal, R.; Errichetti, E. Dermoscopy of skin parasitoses, bites and stings: A systematic review of the literature. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazel, M.; Desai, A.; Are, A.; Motaparthi, K. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome and Bullous Impetigo. Medicina 2021, 57, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, S.; Longhitano, S.; Ardigò, M.; Pampena, R.; Bs, S.C.; Bigi, L.; Mandel, V.D.; Msc, C.V.; Manfredini, M.; Pezzini, C.; et al. Dermoscopy, confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography features of main inflammatory and autoimmune skin diseases: A systematic review. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 63, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, N.D.; Nikham, B.; Jamale, V.; Hussain, A.; Kale, M. Evaluation of Dermoscopic Patterns of Vesiculobullous Disorders. Indian J. Dermatol. 2021, 66, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Errichetti, E.; Stinco, G. Dermatoscopy in life-threatening and severe acute rashes. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 38, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Ogawa, K.; Iioka, H.; Miyagawa, F.; Okazaki, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Asada, H. Adult case of staphylococcalscalded skin syndrome differentiated from toxic epidermal necrolysis withthe aid of dermatoscopy. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 842–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatya, B. Evaluation of Dermoscopic Features in Facial Melanosis with Wood Lamp Examination. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2022, 12, e2022030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).