Pretransplant BMI Significantly Affects Perioperative Course and Graft Survival after Kidney Transplantation: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Mortality and Graft Loss after Kidney Transplantation in BMI Stratified Groups of Patients
3.2. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Patient Death and Graft Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, M.-H.; Foster, C.E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ichii, H. Kidney transplantation in obese patients. World J. Transpl. 2016, 6, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H.; Gutiérrez, O.M.; Judd, S.E.; Muntner, P.; Warnock, D.G.; Tanner, R.M.; Panwar, B.; Shoham, D.A.; McClellan, W. Waist Circumference, Body Mass Index, and ESRD in the REGARDS (Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R. Defining end-stage renal disease in clinical trials: A framework for adjudication. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2016, 31, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, J.H.; Kang, S.S.; Park, W.Y.; Jin, K.; Park, S.B.; Han, S.; Kim, C.-D.; Ro, H.; Lee, S.; Woong Jung, C.; et al. Incidence of Post-transplantation Diabetes Mellitus Within 1 Year After Kidney Transplantation and Related Factors in Korean Cohort Study. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 2714–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, M.Z.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mucsi, I.; Bunnapradist, S.; Streja, E.; Krishnan, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Higher recipient body mass index is associated with post-transplant delayed kidney graft function. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletto, B.B.; Fonseca, N.K.O.; Manfro, R.C.; Gonçalves, L.F.S.; Leitão, C.B.; Souza, G.C. Effects of Obesity on Kidney Transplantation Outcomes. Transplantation 2014, 98, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafranca, J.A.; IJermans, J.N.M.; Betjes, M.G.H.; Dor, F.J.M.F. Body mass index and outcome in renal transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, D.; Cochat, P.; Claas, F.H.J.; Heemann, U.; Pascual, J.; Dudley, C.; Harden, P.; Hourmant, M.; Maggiore, U.; Salvadori, M.; et al. European Renal Best Practice Guideline on kidney donor and recipient evaluation and perioperative care. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2015, 30, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.S.; Lan, J.; Dong, J.; Rose, C.; Hendren, E.; Johnston, O.; Gill, J. The Survival Benefit of Kidney Transplantation in Obese Patients. Am. J. Transpl. 2013, 13, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentine, K.L.; Delos Santos, R.; Axelrod, D.; Schnitzler, M.A.; Brennan, D.C.; Tuttle-Newhall, J.E. Obesity and kidney transplant candidates: How big is too big for transplantation? Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Corona, D.; Mistretta, A.; Zerbo, D.; Sinagra, N.; Giaquinta, A.; Caglià, P.; Amodeo, C.; Leonardi, A.; Gula, R.; et al. The role of obesity in kidney transplantation outcome. Transpl. Proc. 2012, 44, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, G.; Cockfield, S.; Blydt-Hansen, T.; Baran, D.; Kiberd, B.; Landsberg, D.; Rush, D.; Cole, E. Canadian Society of Transplantation: Consensus guidelines on eligibility for kidney transplantation. CMAJ 2005, 173, S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.P.; White, J.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Docherty, N.G.; le Roux, C.W. Metabolic Surgery to Treat Obesity in Diabetic Kidney Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, and End-Stage Kidney Disease; What Are the Unanswered Questions? Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijs-Moeke, G.J.; Pischke, S.E.; Berger, S.P.; Sanders, J.S.F.; Pol, R.A.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Ploeg, R.J.; Leuvenink, H.G.D. Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation: Relevant Mechanisms in Injury and Repair. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Chapman, W.C.; Hanto, D.W. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2015, 7, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Huang, L.; Raftery, A.T.; Ahmed, A.K.; Fahmy, H.; El Nahas, A.M.; Haylor, J.L. Cyclosporine A sensitizes the kidney to tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by renal warm ischemia. Transplantation 2004, 77, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalten, J.; Christiaans, M.H.; De Fijter, H.; Hené, R.; Homan Van Der Heijde, J.; Roodnat, J.; Surachno, J.; Hoitsma, A. The influence of obesity on short- and long-term graft and patient survival after renal transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, F.; Friesen, E.L.; Clark, K.E.; Motaghi, S.; Zyla, R.; Lee, Y.; Kamran, R.; Ali, E.; De Snoo, M.; Orchanian-Cheff, A.; et al. Risk Factors for 1-Year Graft Loss After Kidney Transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chang, A.L.; Wima, K.; Ertel, A.E.; Diwan, T.S.; Abbott, D.E.; Shah, S.A. The impact of morbid obesity on resource utilization after renal transplantation. Surgery 2016, 160, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, M.; Garg, A.; Bota, S. Risk of major hemorrhage after kidney transplantation. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, A.; Queruel, V.; Kabore, R.; Leffondre, K.; Couzi, L.; Moreau, K.; Bensadoun, H.; Robert, G.; Ferriere, J.-M.; Alezra, E.; et al. Risk Factors of Early Kidney Graft Transplantectomy. Transpl. Proc. 2019, 51, 3309–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruintjes, M.H.D.; d’Ancona, F.C.H.; Zhu, X.; Hoitsma, A.J.; Warlé, M.C. An Update on Early Urological Complications in Kidney Transplantation: A National Cohort Study. Ann. Transpl. 2019, 24, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberal, M.; Boyvat, F.; Akdur, A.; Kırnap, M.; Özçelik, Ü.; Yarbuğ Karakayalı, F. Surgical Complications After Kidney Transplantation. Exp. Clin. Transpl. 2016, 14, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Salamin, P.; Deslarzes-Dubuis, C.; Longchamp, A.; Petitprez, S.; Venetz, J.P.; Corpataux, J.M.; Déglise, S. Predictive Factors of Surgical Complications in the First Year Following Kidney Transplantation. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 83, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna-Sepúlveda, F.; Ponce-Escobedo, A.; Guevara-Charles, A.; Escobedo-Villarreal, M.; Pérez-Rodríguez, E.; Muñoz-Maldonado, G.; Hernández-Guedea, M. Outcomes and Surgical Complications in Kidney Transplantation. Int. J. Organ. Transpl. Med. 2017, 8, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta, P.G.; Bissolati, M.; Saibene, A.; Ghidini, C.G.A.; Guarneri, G.; Giannone, F.; Adamenko, O.; Secchi, A.; Rosati, R.; Socci, C. Bariatric Surgery to Target Obesity in the Renal Transplant Population: Preliminary Experience in a Single Center. Transpl. Proc. 2017, 49, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proczko, M.; Kaska, Ł.; Kobiela, J.; Stefaniak, T.; Zadrożny, D.; Śledziński, Z. Bariatric surgery in morbidly obese patients with chronic renal failure, prepared for kidney transplantation—case reports. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2013, 85, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dobrzycka, M.; Proczko-Stepaniak, M.; Kaska, Ł.; Wilczyński, M.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Kobiela, J. Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery in Morbidly Obese End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients as Preparation for Kidney Transplantation. Matched Pair Analysis in a High-Volume Bariatric and Transplant Center. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 2708–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | All Patients (n = 433) | Normal BMI 18.5–24.9 (n = 208) | Overweight BMI 25–29.9 (n = 153) | Obese BMI ≥ 30 (n = 72) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor | |||||
| Age | 48.6 (51) | 47.1 (49) | 49.8 (51) | 50.9 (52) | p = 0.05 |
| Body weight (kg) | 77.9 (76) | 76.7 (75) | 78.1 (75) | 80.7 (80) | p = 0.06 |
| Body height (cm) | 173.1 (174) | 173.1 (174) | 172.9 (173.5) | 173.5 (174) | p = 0.95 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 25.9 (24.9) | 25.5 (24.7) | 26.1 (24.9) | 26.7 (26) | p = 0.08 |
| Donor/recipient BMI ratio | 1 (1) | 1.2 (1.2) | 0.9 (0.9) | 0.8 (0.8) | p < 0.05 |
| Donor/recipient body weight ratio | 1.1 (1.1) | 1.3 (1.2) | 0.9 (1) | 0.9 (0.8) | p < 0.05 |
| Recipient | |||||
| Male (%) | 272 (62.8) | 115 (55.3) | 114 (74.5) | 42 (58.3) | normal vs. overweight p = 0.0002 normal vs. obese p = 0.65 overweight vs. obese p = 0.014 |
| Female (%) | 161 (37.2) | 93 (44.7) | 39 (25.5) | 30 (41.7) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.3 | 21.97 | 27.22 | 31.71 | p < 0.05 |
| Mean age (median; years) | 49.3 ± 13.8 (51 ± 11.5) | 45.3 ± 14.4 (46 ± 12) | 52.7 ± 11.6 (55 ± 9) | 53.3 ± 13.1 (57 ± 8.5) | normal vs. overweight p = 0.00 normal vs. obese p = 0.00 overweight vs. obese p = 1 |
| Mean Charlson Comorbidity Index (median) | 3.4 ± 1.4 (3 ± 1) | 3.14 ± 1.2 (3 ± 1) | 3.6 ± 1.4 (4 ± 1.5) | 3.86 ± 1.7 (3 ± 1.5) | p = 0.029 normal vs. overweight p = 0.01 normal vs. obese p = 0.01 overweight vs. obese p = 1 |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Hypertension | 322 (74.3) | 147 (70.3) | 121 (76.1) | 54 (83.1) | p = 0.09 |
| Diabetes Mellitus type 1 and | 64 (14.8) | 16 (7.7) | 31 (19.5) | 17 (26.2) | p = 0.0001 |
| Coronary artery disease | 65 (15) | 30 (13.4) | 21 (13.2) | 14 (21.5) | p = 0.26 |
| Other heart diseases 1 | 44 (10.2) | 26 (12.4) | 13 (8.2) | 5 (7.7) | p = 0.31 |
| Benign prostate hyperplasia | 22 (5.1) | 7 (3.3) | 11 (6.9) | 4 (6.2) | p = 0.27 |
| Thyroid disease | 32 (7.4) | 15 (7.2) | 12 (7.5) | 5 (7.7) | p = 0.98 |
| Parathyroid disease | 47 (10.9) | 18 (8.6) | 24 (15.1) | 5 (7.7) | p = 0.09 |
| Pulmonary disease 2 | 30 (6.9) | 14 (6.7) | 10 (6.3) | 6 (9.2) | p = 0.72 |
| Cerebral stroke | 17 (3.9) | 8 (3.8) | 7 (4.4) | 2 (3.1) | p = 0.89 |
| Digestive track diseases 3 | 72 (16.6) | 28 (13.4) | 28 (17.6) | 16 (24.6) | p = 0.1 |
| Neoplasms history | 29 (6.7) | 13 (6.2) | 11 (6.9) | 5 (7.7) | p = 0.91 |
| Hepatitis infection Active tobacco abuse | 34 (7.9) 10 (2.3) | 21 (10) 4 (1.9) | 12 (7.5) 2 (1.3) | 1 (1.5) 4 (6.2) | p = 0.08 p = 0.08 |
| ESKD etiology | n/a | ||||
| Glomerulonephritis | 151 (35.6) | 83 (39.9) | 49 (32) | 19 (26.4) | |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 52 (12.3) | 18 (8.7) | 22 (14.4) | 12 (16.7) | |
| Hypertensive nephropathy | 38 (8.9) | 11 (5.3) | 20 (13.1) | 7 (9.7) | |
| Interstitial nephropathy | 49 (11.6) | 28 (13.5) | 16 (10.5) | 5 (6.9) | |
| ADPKD | 56 (13.2) | 19 (9.1) | 28 (18.3) | 9 (12.5) | |
| Other 4 | 22 (5.2) | 10 (4.8) | 6 (3.9) | 6 (8.3) | |
| Unknown | 56 (13.2) | 25 (12) | 23 (15) | 8 (11.1) | |
| Dialysis modality before KT (%) | HD 329 (76) PD 70 (16.2) PREE 34 (7.8) | HD 151 (72.6) PD 34 (16.3) PREE 14 (6.7) | HD 120 (78.4) PD 27 (17.6) PREE 16 (10.4) | HD 58 (82.8) PD 9 (11.4) PREE 4 (5.7) | p = 0.09 p = 0.16 p = 0.33 |
| Transplantation | |||||
| 2nd and 3rd KT (%) | 59 (13.6) | 38 (18.2) | 16 (10.5) | 5 (6.9) | p = 0.056 normal vs. overweight p = 0.04 normal vs. obese p = 0.02 overweight vs. obese p = 0.52 |
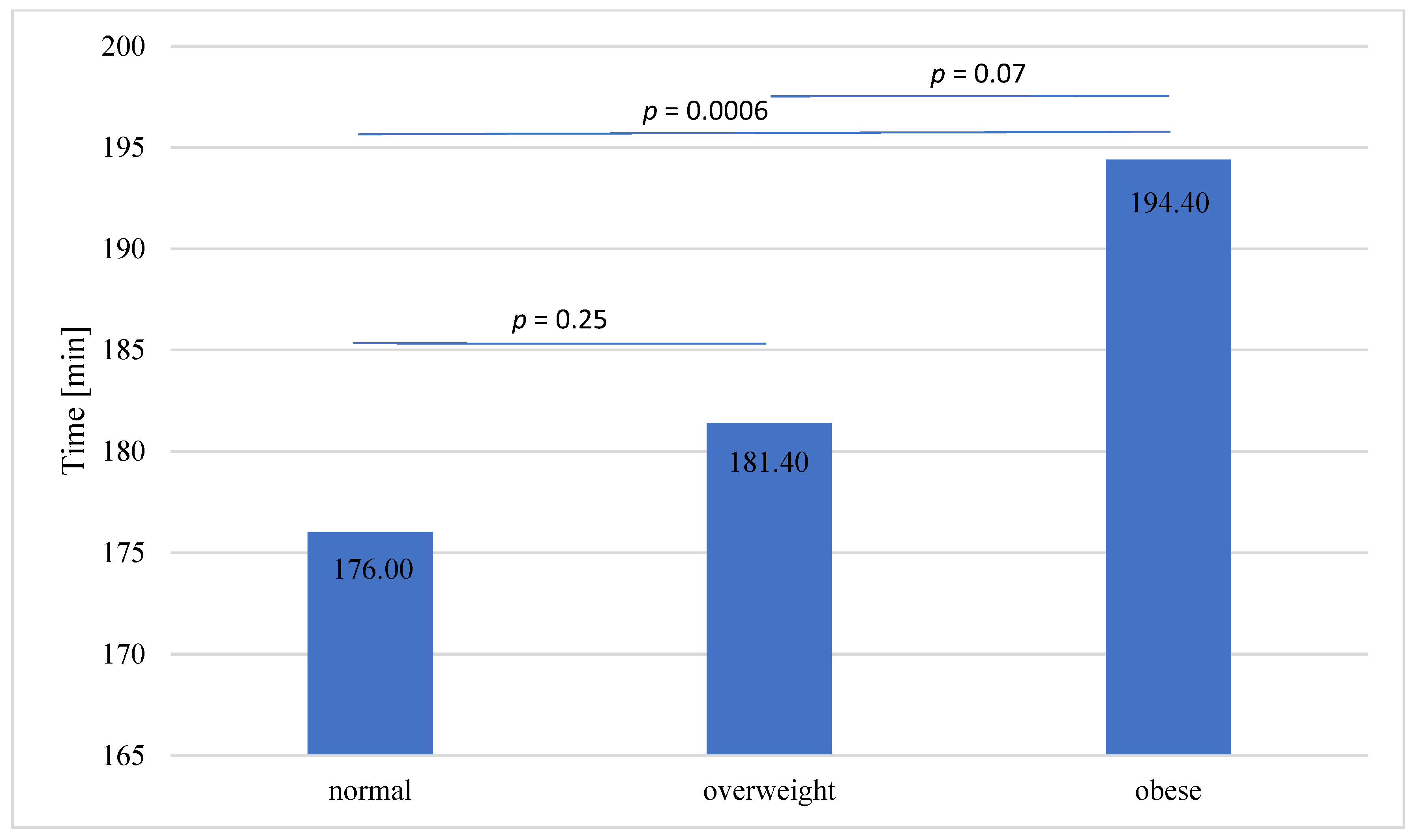
| Total procedure time, mean (median; min) | 181.98 (180) | 176 ± 36.2 (180 ± 22.5) | 181.4 ± 36.1 (180 ± 17.5) | 194.4 ± 38.9 (195 ± 30.0) | p = 0.0025 |
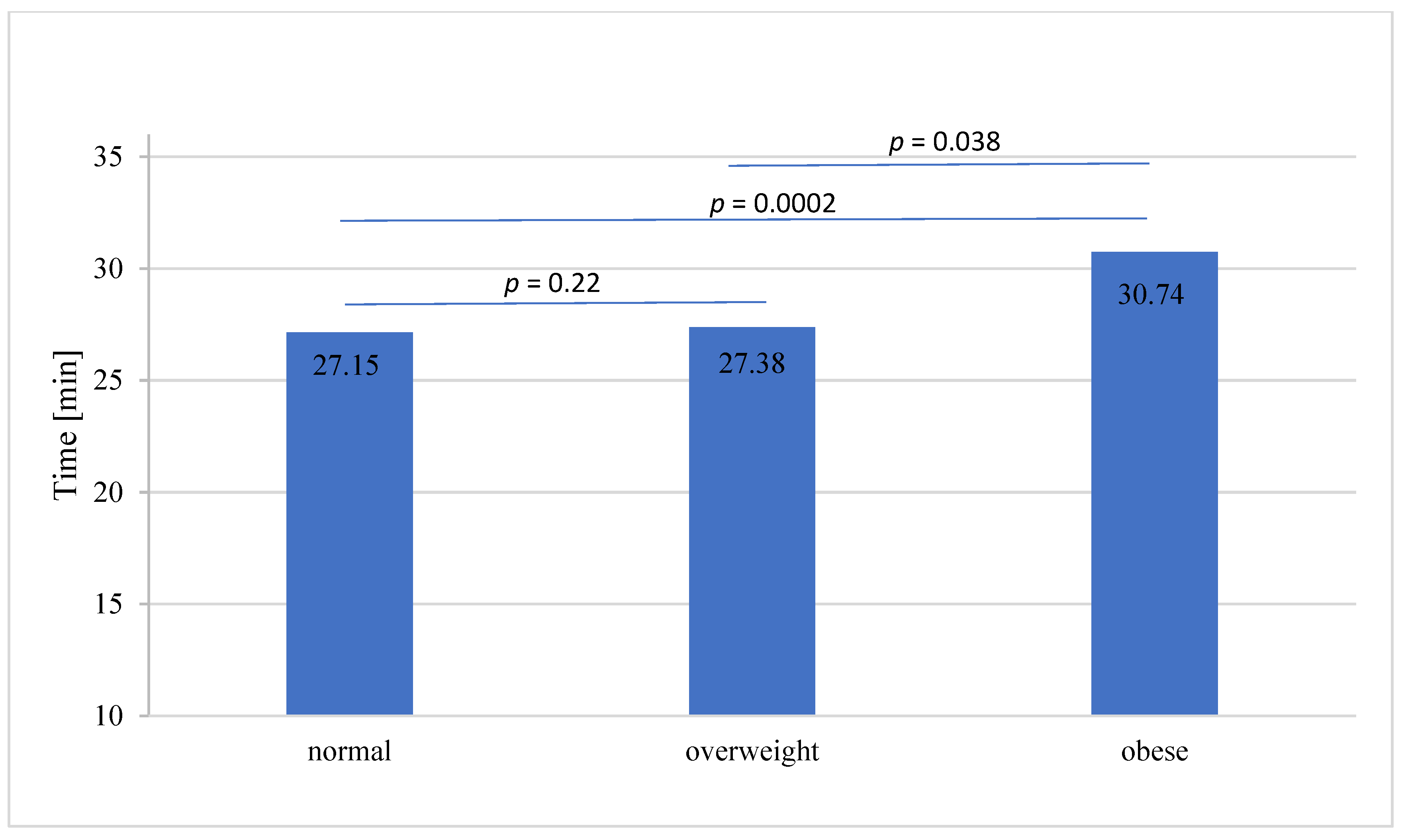
| WIT mean (median; min) | 27.83 ± 9.3 (26 ± 4.5) | 27.15 ± 10.6 (25 ± 4.5) | 27.38 ± 7.0 (27 ± 4.5) | 30.74 ± 9.2 (30.0 ± 5.5) | p = 0.0003 |
| CIT mean (median; min) | 922.6 ± 636 (894 ± 223) | 927.0 ± 370 (903 ± 206) | 899.5 ± 343 (863 ± 215) | 958.7 ± 389 (935 ± 236) | p = 0.1509 |
| Post-transplant hospitalization | |||||
| Serum creatinine mean (median) one month after KT (mg/dL) | 1.575 ± 0.571 (1.52 ± 0.34) | 1.474 ± 0.527 (1.360 ± 0.345) | 1.596 ± 0.502 (1.545 ± 0.335) | 1.838 ± 0.742 (1.750 ± 0.225) | p = 0.000 normal vs. overweight p = 0.014 normal vs. obese p = 0.027 overweight vs. obese p = 0.000 |
| AR (%) | 42 (9.7) | 21 (10.04) | 13 (8.5) | 8 (11.3) | p = 0.36 |
| DGF (%) | 144 (33.2) | 61 (29.2) | 46 (30.1) | 37(52.8) | p = 0.0002 |
| Total hospitalization time (days) | 21.57 ± 12.3 (18 ± 5.5) | 20.19 ± 11.3 (18 ± 4.5) | 21.87 ± 12.6 (19 ± 6.0) | 25.04 ± 13.6 (20 ± 8.5) | p = 0.1509 |
| Adverse Event | All Patients (n = 433) | Normal (n = 209) | Overweight (n = 153) | Obese (n = 71) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative kidney function | |||||
| Acute rejection (%) | 42 (9.7) | 21 (10.04) | 13 (8.5) | 8 (11.3) | p > 0.05 |
| Delayed graft function (%) | 144 (33.2) | 61 (29.2) | 46 (30.1) | 37 (52.1) | obese vs. normal p = 0.0005 obese vs. overweight p = 0.0015 normal vs. overweight p = 0.86 |
| General adverse events | |||||
| Cardiological complications 1 (%) | 20 (4.6) | 9 (4.3) | 8 (5.2) | 3 (4.2) | p > 0.05 |
| Infectious complications 2 (%) | 106 (24.5) | 44 (21.0) | 41 (26.8) | 21 (29.6) | p > 0.05 |
| Posttransplant diabetes (%) | 46 (10.6) | 19 (9.1) | 22 (14.4) | 5 (7.0) | p > 0.05 |
| Surgical adverse events | |||||
| Surgical complications < 30 days (%) | 111 (25.65) | 53 (25.3) | 27 (16.3) | 31 (43.7) | obese vs. normal p = 0.0036 obese vs. overweight p = 0.00001 normal vs. overweight p = 0.08 |
| Surgical complications > 30 days (%) | 24 (5.5) | 10 (4.8) | 7 (4.6) | 7 (9.8) | p > 0.05 |
| Reoperation (%) | 86 (19.9) | 37 (17.7) | 23 (15.0) | 26 (36.6) | obese vs. normal p = 0.001 obese vs. overweight p = 0.0003 normal vs. overweight p = 0.4997 |
| Lymphocele (%) | 51 (11.8) | 17 (8.1) | 15 (9.8) | 19 (26.8) | obese vs. normal p = 0.0001 obese vs. overweight p = 0.01 normal vs. overweight p = 0.58 |
| Urological complications (%) | 32 (7.4) | 18 (8.6) | 7 (4.6) | 7 (9.8) | p > 0.05 |
| Wound dehiscence (%) | 21 (4.8) | 2 (0.96) | 7 (4.6) | 12 (16.9) | obese vs. normal p = 0.0000 obese vs. overweight p = 0.0021 normal vs. overweight p = 0.0329 |
| Vascular complications (%) | 76 (17.5) | 42 (20.1) | 15 (9.8) | 19 (26.8) | obese vs. normal p = 0.2398 obese vs. overweight p = 0.001 normal vs. overweight p = 0.0079 |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis, OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate Analysis, OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 0.997 (0975–1.02) | 0.8 | - | - |
| Gender (F/M) | 2.2 (1.073–4.55) | 0.69 | - | - |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 0.84 (0.664–1.076) | 0.16 | - | - |
| HD before KT | 1.221 (0.565–2.637) | 0.6 | - | - |
| BMI | 1.05 (0.973–1.131) | 0.21 | - | - |
| BMI > 30 | 2.209 (1.073–4.55) | 0.04 | 1.9 (0.898–4.035) | 0.09 |
| ARE | 2.293 (1.215–4.327) | 0.005 | 2.9 (1.295–6.649) | 0.01 |
| DGF | 2.293 (1.215–4.327) | 0.001 | 1.84 (0.947–3.576) | 0.07 |
| WIT | 1.019 (0.978–1.061) | 0.4 | - | - |
| CIT | 1.0 (0.999–1.001) | 0.76 | - | - |
| KT number 1 | 1.051 (0.423–2.613) | 0.42 | - | - |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis, OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate Analysis, OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 1.079 (1.04–1.119) | 0.00 | 1.04 (0.994–1.087) | 0.088 |
| Gender (F/M) | 1.167 (0.055–2.474) | 0.686 | - | - |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 1.833 (1.442–2.33) | 0.00 | 1.521 (1.107–2.09) | 0.01 |
| HD before KT | 1.465 (0.588–3.653) | 0.412 | - | - |
| BMI | 0.983 (0.902-1.07) | 0.691 | - | - |
| BMI > 30 | 0.505 (0.15-1.702) | 0.27 | - | - |
| PD before KT | 0.918 (0.342–2.464) | 0.863 | - | - |
| KT number 2 or 3 | 0.863 (0.292–2.549) | 0.786 | - | - |
| Serum creatinine concentration mg/dL one month after KT | 1.389 (0.741–2.601) | 0.305 | - | - |
| Kidney graft loss | 0.921 (0.269–3.156) | 0.894 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrzycka, M.; Bzoma, B.; Bieniaszewski, K.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Kobiela, J. Pretransplant BMI Significantly Affects Perioperative Course and Graft Survival after Kidney Transplantation: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154393
Dobrzycka M, Bzoma B, Bieniaszewski K, Dębska-Ślizień A, Kobiela J. Pretransplant BMI Significantly Affects Perioperative Course and Graft Survival after Kidney Transplantation: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(15):4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154393
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrzycka, Małgorzata, Beata Bzoma, Ksawery Bieniaszewski, Alicja Dębska-Ślizień, and Jarek Kobiela. 2022. "Pretransplant BMI Significantly Affects Perioperative Course and Graft Survival after Kidney Transplantation: A Retrospective Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 15: 4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154393
APA StyleDobrzycka, M., Bzoma, B., Bieniaszewski, K., Dębska-Ślizień, A., & Kobiela, J. (2022). Pretransplant BMI Significantly Affects Perioperative Course and Graft Survival after Kidney Transplantation: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(15), 4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154393







