Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Microvascular Doppler for Perfusion Monitoring of Free Flaps in an In Vivo Rodent Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
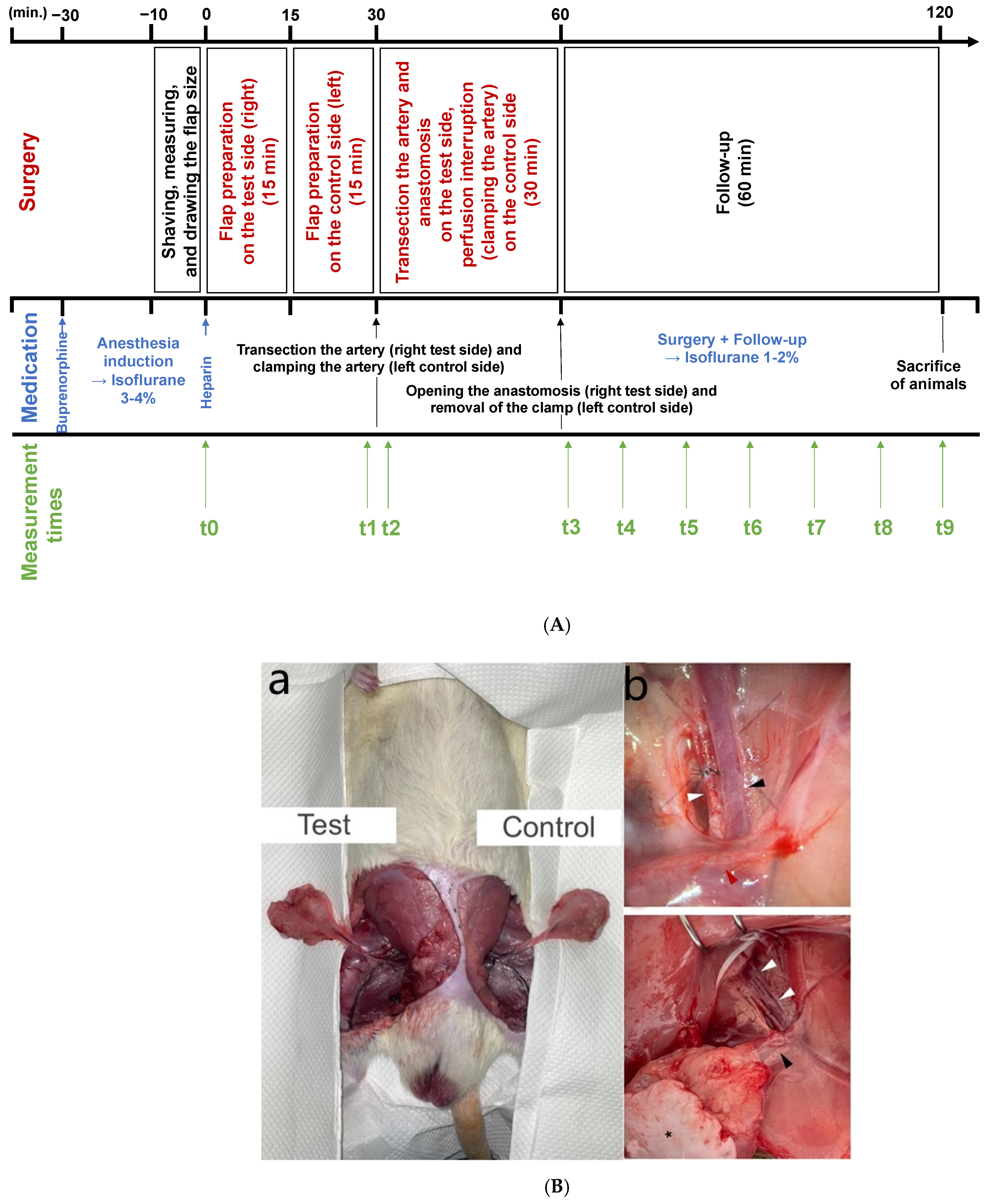
2.1. Surgery
2.2. Hyperspectral Imaging
2.3. Micro-Doppler Sonographic Measurement
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
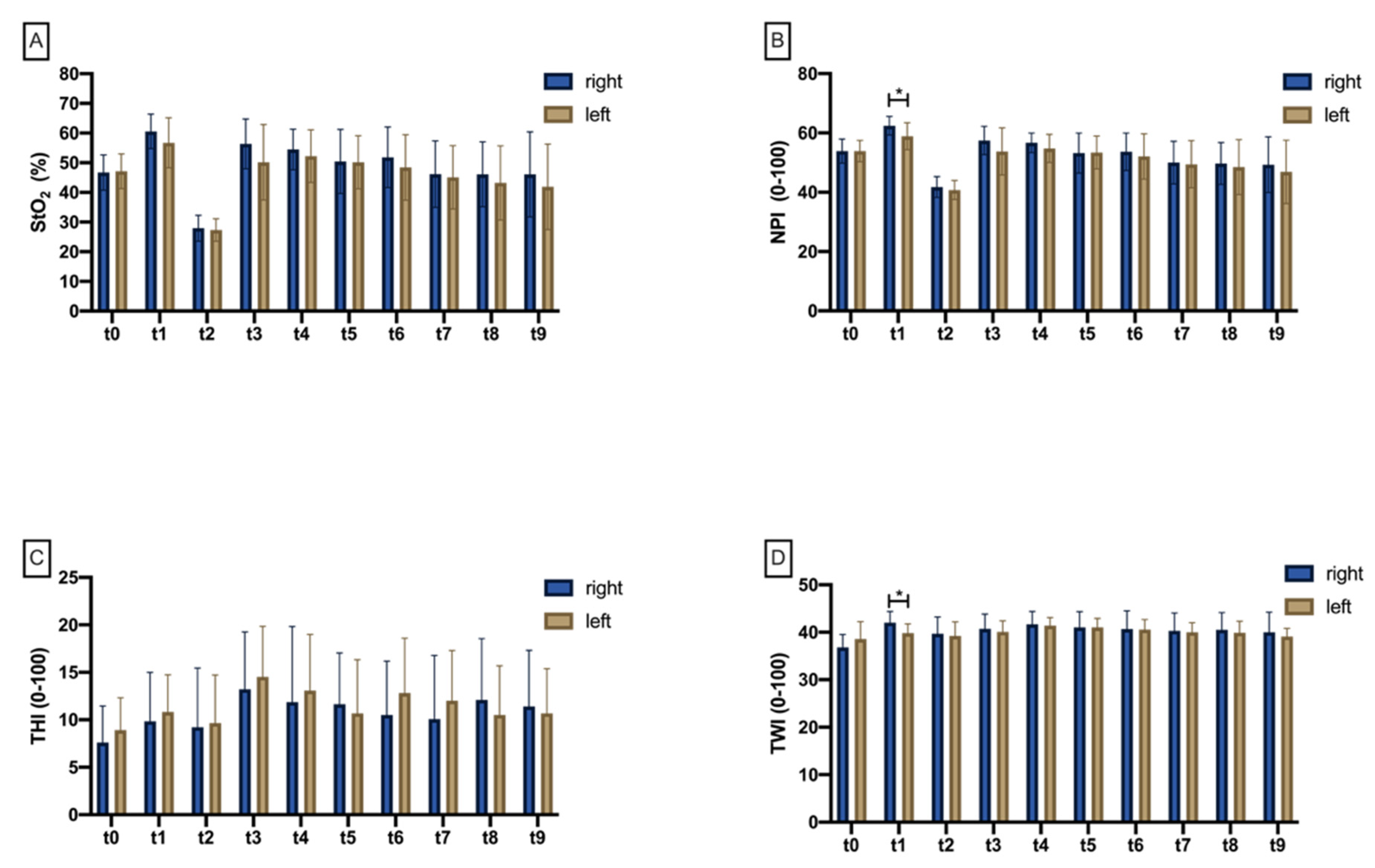
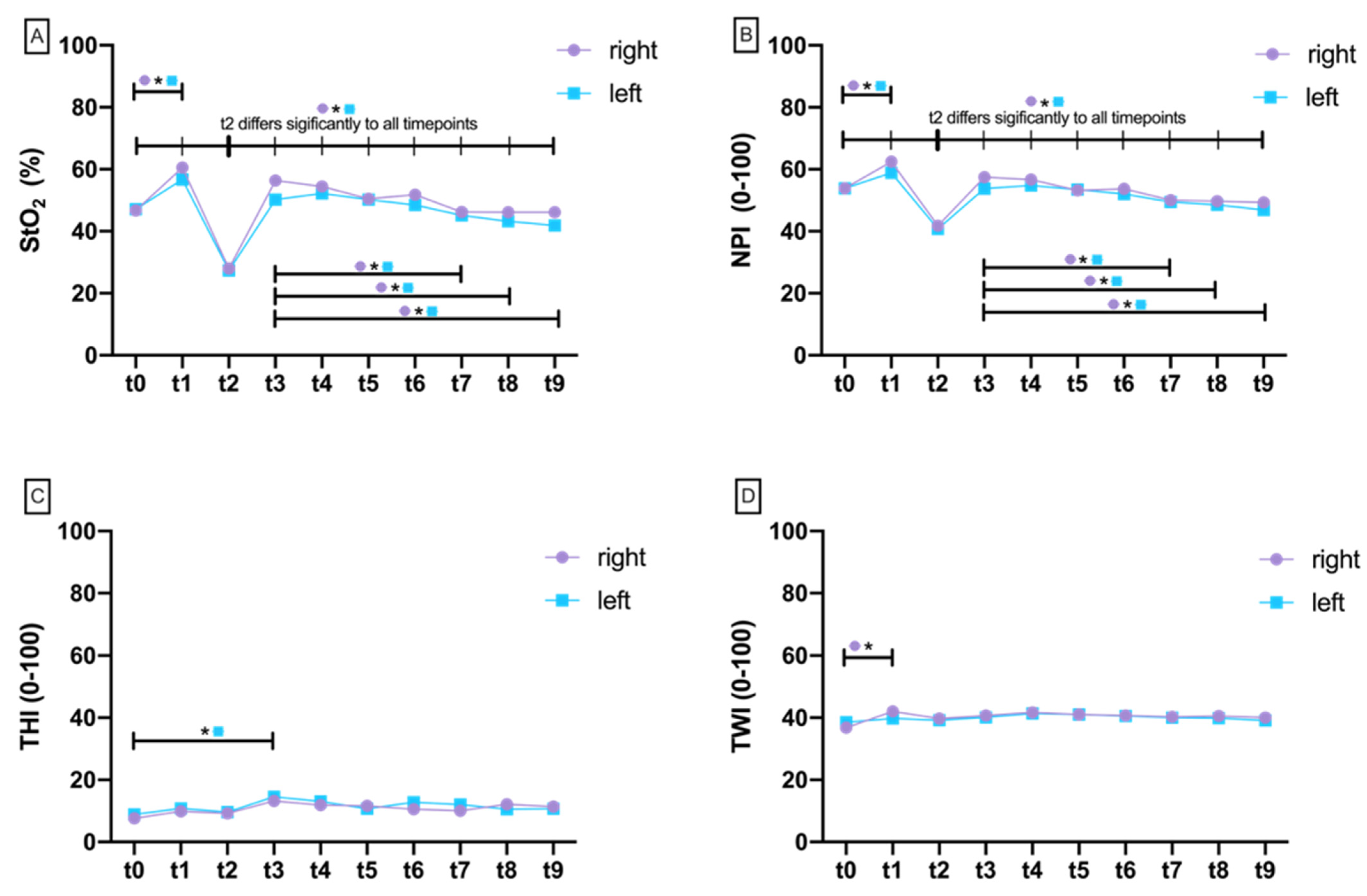
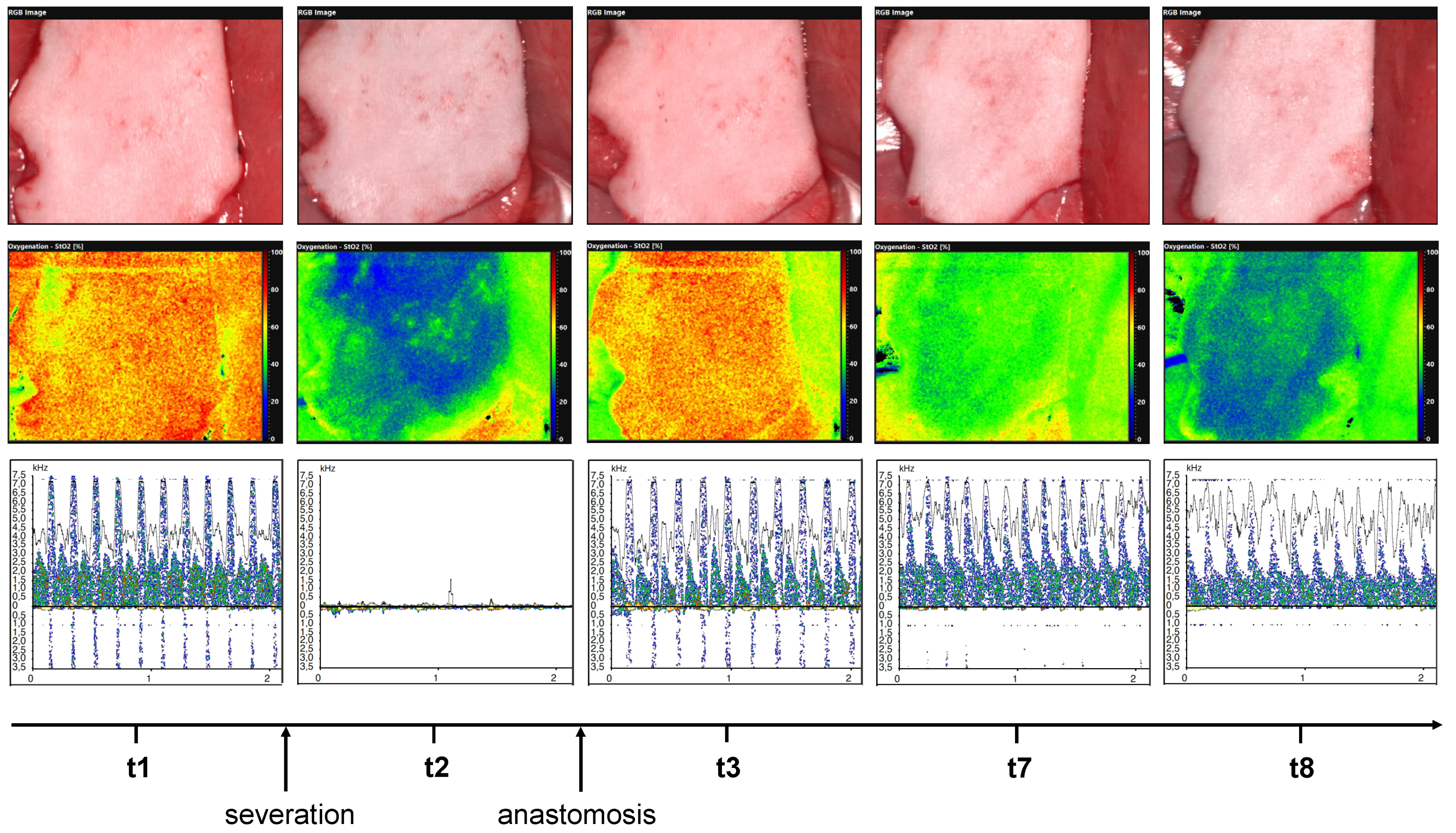
3.1. Hyperspectral Perfusion Analysis
3.1.1. Tissue Oxygenation Saturation (StO2)
3.1.2. Near Perfusion Index (NPI)
3.1.3. Tissue Hemoglobin Index (THI)
3.1.4. Tissue Water Index (TWI)
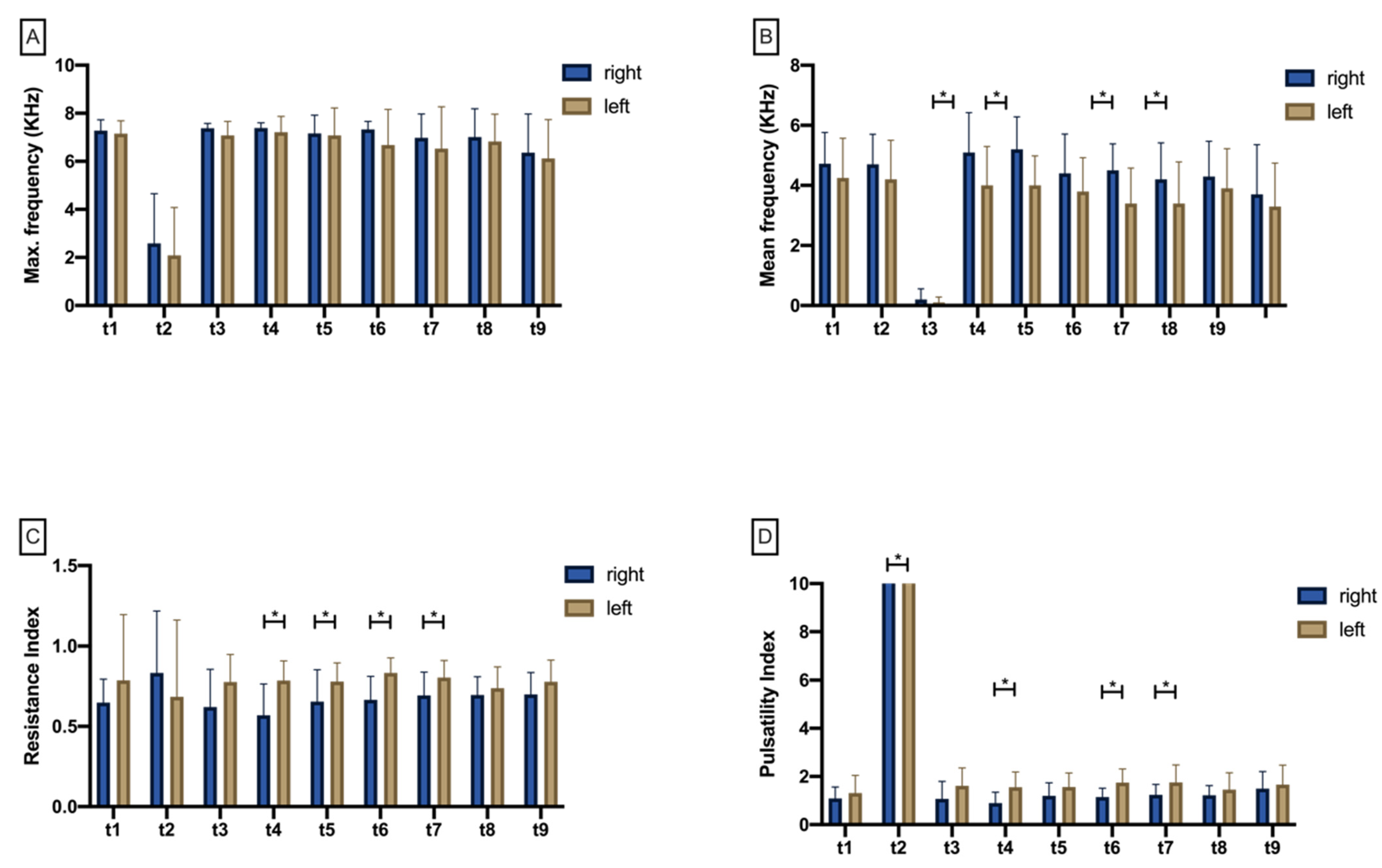
3.2. Micro-Doppler Sonographic Measurement
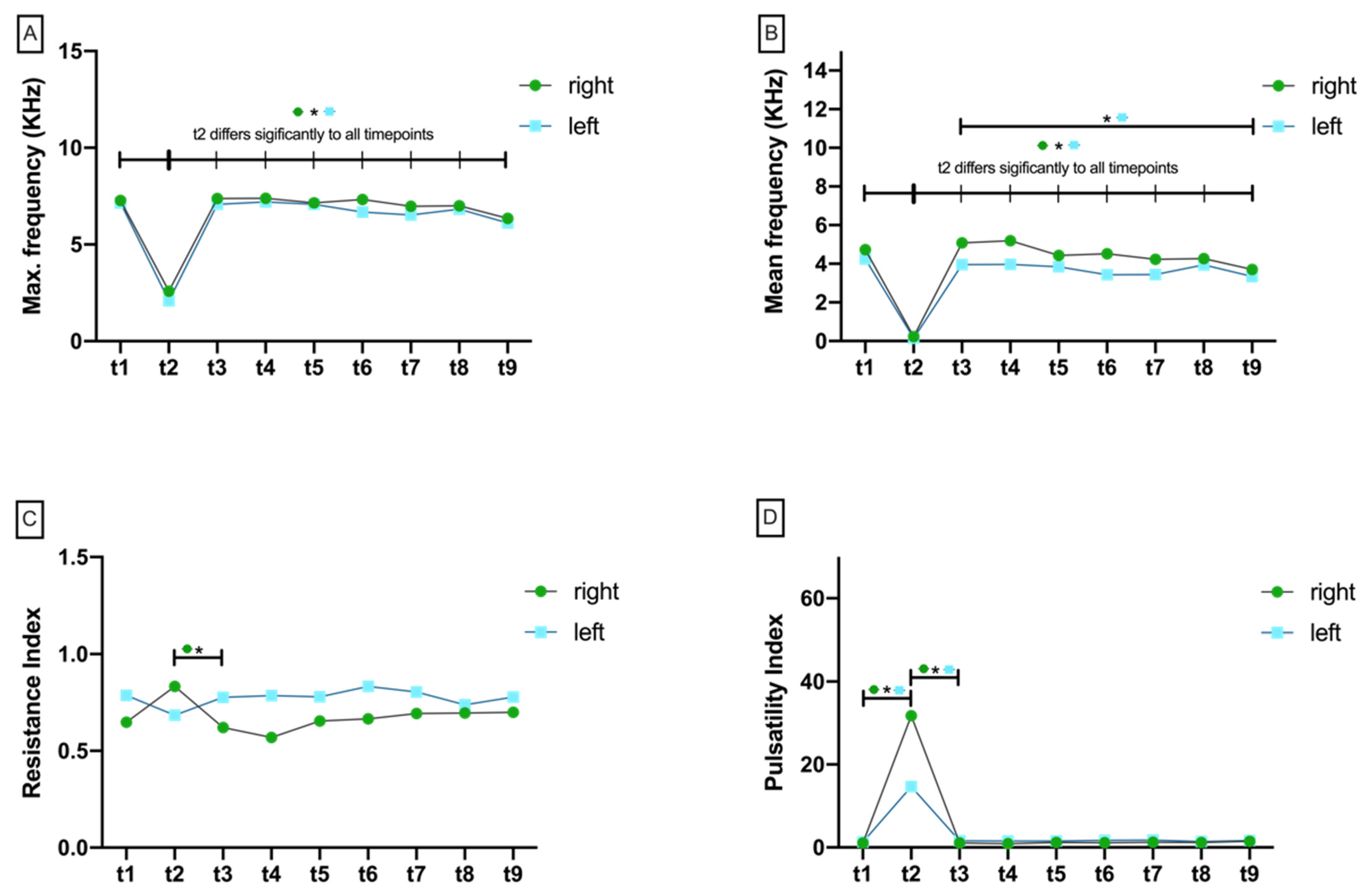
3.2.1. Maximum Doppler Frequency (Max.KHz)
3.2.2. Mean Doppler Frequency (Mean.KHz)
3.2.3. Resistance Index (RI)
3.2.4. Pulsatility Index (PI)
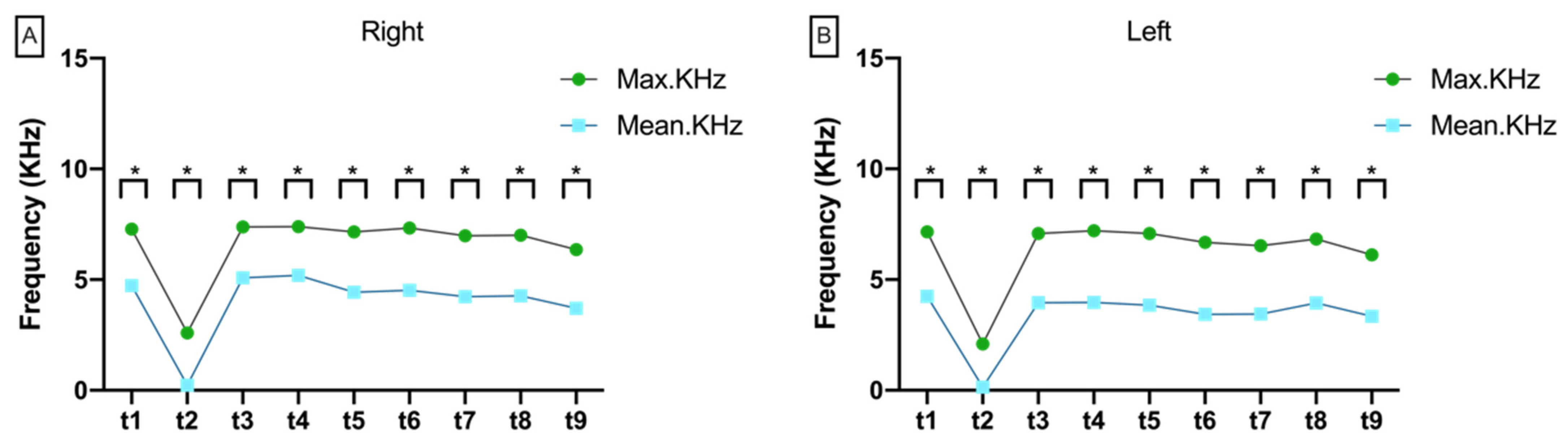
3.2.5. Variance between Max.KHz and Mean.KHz
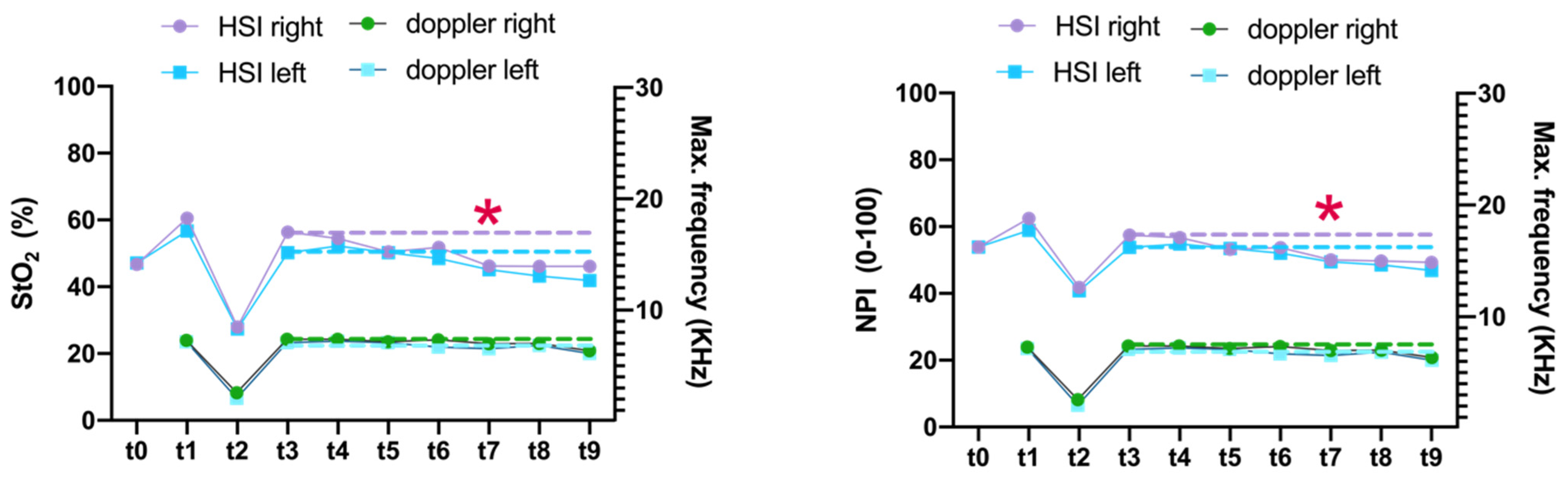
3.3. Comparison of HSI and MDS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiem, D.G.E.; Frick, R.W.; Goetze, E.; Gielisch, M.; Al-Nawas, B.; Kämmerer, P.W. Hyperspectral analysis for perioperative perfusion monitoring-a clinical feasibility study on free and pedicled flaps. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendenbach, C.; Hölterhoff, N.; Hischke, S.; Kreutzer, K.; Smeets, R.; Assaf, A.T.; Heiland, M.; Wikner, J. Free flap surgery in Europe: An interdisciplinary survey. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoyler, D.; Losco, L.; Bolletta, A.; Ercan, A.; Chen, S.H.; Velazquez-Mujica, J.; Tang, Y.B.; Chen, H.C. Three salvage strategies in microvascular fibula osteocutaneous flap for mandible reconstruction with vascular compromise and establishment of an algorithm. Microsurgery 2021, 41, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansy, K.; Mueller, A.A.; Mücke, T.; Koersgen, F.; Wolff, K.D.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Hölzle, F.; Pradel, W.; Schneider, M.; Kolk, A.; et al. Microsurgical reconstruction of the head and neck region: Current concepts of maxillofacial surgery units worldwide. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Harii, K.; Asato, H.; Takushima, A.; Ebihara, S.; Kimata, Y.; Yamada, A.; Ueda, K.; Ichioka, S. Analytic review of 2372 free flap transfers for head and neck reconstruction following cancer resection. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2003, 19, 363–368, discussion 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiem, D.G.E.; Römer, P.; Blatt, S.; Al-Nawas, B.; Kämmerer, P.W. New Approach to the Old Challenge of Free Flap Monitoring-Hyperspectral Imaging Outperforms Clinical Assessment by Earlier Detection of Perfusion Failure. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeny, L.; Curry, J.; Crawley, M.; Cave, T.; Stewart, M.; Luginbuhl, A.; Heffelfinger, R.; Krein, H.; Petrisor, D.; Bender-Heine, A.; et al. Factors impacting successful salvage of the failing free flap. Head Neck 2020, 42, 3568–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gijn, D.R.; D’Souza, J.; King, W.; Bater, M. Free Flap Head and Neck Reconstruction with an Emphasis on Postoperative Care. Facial Plast. Surg. 2018, 34, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.S.; Chu, M.W.; Nelson, J.A.; Basta, M.; Gerety, P.; Kanchwala, S.K.; Wu, L.C. Complications and Cost Analysis of Intraoperative Arterial Complications in Head and Neck Free Flap Reconstruction. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2017, 33, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeny, L.; Rosenthal, E.L.; Light, T.; Grayson, J.; Petrisor, D.; Troob, S.H.; Greene, B.J.; Carroll, W.R.; Wax, M.K. Outcomes and cost implications of microvascular reconstructions of the head and neck. Head Neck 2019, 41, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlenz, P.; Klatt, J.; Schön, G.; Blessmann, M.; Li, L.; Schmelzle, R. Microvascular free flaps in head and neck surgery: Complications and outcome of 1000 flaps. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Lin, P.Y.; Chew, K.Y.; Kuo, Y.R. Free tissue transfers in head and neck reconstruction: Complications, outcomes and strategies for management of flap failure: Analysis of 2019 flaps in single institute. Microsurgery 2014, 34, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A.H.; Meyerson, J.; Povoski, S.P.; Kocak, E. A review of devices used in the monitoring of microvascular free tissue transfers. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2013, 10, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.P.; Rozen, W.M.; Whitaker, I.S.; Chubb, D.; Grinsell, D.; Ashton, M.W.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Lineaweaver, W.C. Current evidence for postoperative monitoring of microvascular free flaps: A systematic review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 74, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kansy, K.; Mueller, A.A.; Mücke, T.; Kopp, J.B.; Koersgen, F.; Wolff, K.D.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Hölzle, F.; Pradel, W.; Schneider, M.; et al. Microsurgical reconstruction of the head and neck—Current concepts of maxillofacial surgery in Europe. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.M.; Cullom, M.E.; Egan, K.G.; Nazir, N.; Elver, A.A.; Limpiado, M.J.; Lai, E.C.; Butterworth, J.A. Comparing tissue oximetry to doppler monitoring in 1367 consecutive breast free flaps. Microsurgery 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, M.A.; Parasca, S.V.; Savastru, R.; Manea, D. Characterization of burns using hyperspectral imaging technique—A preliminary study. Burns 2015, 41, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Fei, B. Medical hyperspectral imaging: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.K.; Prantl, L.; Müller, S.; Moralis, A.; Liebsch, G.; Gosau, M. Simple, fast and reliable perfusion monitoring of microvascular flaps. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 50, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiko, G.; Lombardi, P.; Au, Y.; Queen, D.; Armstrong, D.; Harding, K. Hyperspectral imaging in wound care: A systematic review. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 1840–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudovsky, D.; Nouvong, A.; Pilon, L. Hyperspectral imaging in diabetic foot wound care. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmer, A.; Marotz, J.; Wahl, P.; Dau, M.; Kämmerer, P.W. Hyperspectral imaging in perfusion and wound diagnostics—Methods and algorithms for the determination of tissue parameters. Biomed. Tech. 2018, 63, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grambow, E.; Dau, M.; Holmer, A.; Lipp, V.; Frerich, B.; Klar, E.; Vollmar, B.; Kämmerer, P.W. Hyperspectral imaging for monitoring of perfusion failure upon microvascular anastomosis in the rat hind limb. Microvasc. Res. 2018, 116, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, W.M.; Jones, N.F.; Cherup, L.; Klein, A. Direct monitoring of microvascular anastomoses with the 20-MHz ultrasonic Doppler probe: An experimental and clinical study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1988, 81, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wong, S.T.; Hsueh, Y.Y.; Kuo, Y.L.; Shieh, S.J.; Lee, J.W. Implantable Doppler Probes for Postoperatively Monitoring Free Flaps: Efficacy. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2016, 4, e1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.F.; Guo, L.L.; Liu, L.B.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wei, A.Z.; Guo, P.F. A comparison of the Cook-Swartz Doppler with conventional clinical methods for free flap monitoring: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 32, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.A.; Ducic, Y.; Pipkorn, P.; Wax, M.K. Implantable Doppler Removal After Free Flap Monitoring Among Head and Neck Microvascular Surgeons. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücke, T.; Wolff, K.D.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Hölzle, F.; Scholz, M. Reliability of near-infrared angiography and micro-Doppler sonography for evaluating microvascular anastomoses. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailes, J.E.; Tantuwaya, L.S.; Fukushima, T.; Schurman, G.W.; Davis, D. Intraoperative microvascular Doppler sonography in aneurysm surgery. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 965–970, discussion 970–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, L.H.; Köhler, H.; Kohler, S.; Langer, S.; Nuwayhid, R.; Gockel, I.; Spindler, N.; Osterhoff, G. Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) as a new diagnostic tool in free flap monitoring for soft tissue reconstruction: A proof of concept study. BMC Surg. 2021, 21, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmichrath, J.; Baumeister, R.G.; Gottschalk, O.; Giunta, R.E.; Frick, A. The free groin flap in the rat: A model for improving microsurgical skills and for microvascular perfusion studies. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2014, 48, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauch, B.; Murray, D.E. Transfer of composite graft with immediate suture anastomosis of its vascular pedicle measuring less than 1 mm. in external diameter using microsurgical techniques. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1967, 40, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mücke, T.; Borgmann, A.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Günzinger, R.; Nöbauer, C.; Lange, R.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Hölzle, F.; Wolff, K.D. Autonomization of epigastric flaps in rats. Microsurgery 2011, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücke, T.; Scholz, M.; Kesting, M.R.; Wolff, K.D.; Schmieder, K.; Harders, A.G. Microsurgically induced aneurysm models in rats, Part II: Clipping, shrinking and micro-Doppler sonography. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2008, 51, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulcke, A.; Holmer, A.; Wahl, P.; Siemers, F.; Wild, T.; Daeschlein, G. A compact hyperspectral camera for measurement of perfusion parameters in medicine. Biomed. Tech. 2018, 63, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmer, A.; Tetschke, F.; Marotz, J.; Malberg, H.; Markgraf, W.; Thiele, C.; Kulcke, A. Oxygenation and perfusion monitoring with a hyperspectral camera system for chemical based tissue analysis of skin and organs. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 2064–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimes, D.; Becker, P.; Thiem, D.G.E.; Kuchen, R.; Kyyak, S.; Kämmerer, P.W. Is Hyperspectral Imaging Suitable for Assessing Collateral Circulation Prior Radial Forearm Free Flap Harvesting? Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Conventional Allen’s Test. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickler, P.E.; Feiner, J.R.; Rollins, M.D. Factors affecting the performance of 5 cerebral oximeters during hypoxia in healthy volunteers. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, C.P. The Doppler shift and speed of sound in blood. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1989, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, P.N. The physical principles of Doppler and spectral analysis. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1987, 15, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.R.; Pretorius, D.H. The Doppler signal: Where does it come from and what does it mean? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1988, 151, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L. Microvascular anastomosis of submillimeter vessels-a training model in rats. J. Hand Microsurg. 2013, 5, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenderka, K.V.; Delorme, S. Principles of Doppler sonography. Radiologe 2015, 55, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.O.; Jones, B.M.; Greenhalgh, R.M. An implanted ultrasound Doppler probe for microvascular monitoring: An experimental study. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1986, 39, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, G.; Luo, F.; Blegen, H.; Kalin, B.; Wahlberg, E. A rat model for severe limb ischemia at rest. Eur. Surg. Res. 2003, 35, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.L.; Chang, D.S.; Sarkar, R.; Wang, R.; Messina, L.M. The effect of gradual or acute arterial occlusion on skeletal muscle blood flow, arteriogenesis, and inflammation in rat hindlimb ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2005, 41, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mücke, T.; Hölzle, F.; Loeffelbein, D.J.; Haarmann, S.; Becker, K.; Wolff, K.D.; Kesting, M.R. Intraoral coverage of defects with the superficial epigastric fat flap in rats. Microsurgery 2008, 28, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasnicki, R.M.; Noakes, A.J.; Banhidy, N.; Hettiaratchy, S. Quantifying the Limitations of Clinical and Technology-based Flap Monitoring Strategies using a Systematic Thematic Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindelauf, A.; Saelmans, A.G.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; van der Hulst, R.; Schols, R.M. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) versus Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) to Detect Flap Failure in Reconstructive Surgery: A Systematic Review. Life 2022, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprottka, F.J.; Klimas, D.; Krezdorn, N.; Schlarb, D.; Trevatt, A.E.J.; Hebebrand, D. Cook-Swartz Doppler Probe Surveillance for Free Flaps-Defining Pros and Cons. Surg. J. 2020, 6, e42–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darmon, M.; Schnell, D.; Zeni, F. Doppler-Based Renal Resistive Index: A Comprehensive Review. In Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Iacobellis, F.; Segreto, T.; Berritto, D.; Nettuno, F.; Cozzolino, S.; Di Napoli, D.; Montella, M.; Natella, R.; Cappabianca, S.; Brunese, L.; et al. A rat model of acute kidney injury through systemic hypoperfusion evaluated by micro-US, color and PW-Doppler. Radiol. Med. 2018, 124, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, R.G.; King, D.H. Arterial assessment by Doppler-shift ultrasound. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1974, 67, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayler, R.; Low, T.H.; Fung, K.; Nichols, A.C.; MacNeil, S.D.; Yoo, J. Implantable Doppler Ultrasound Monitoring in Head and Neck Free Flaps: Balancing the Pros and Cons. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1854–E1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibig, N.; Ha-Phuoc, A.; Stark, G.B.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Metzger, M.C.; Eisenhardt, S.U.; Voss, P.J. Retrospective evaluation of diagnostic accuracy of free flap monitoring with the Cook-Swartz-Doppler probe in head and neck reconstruction. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.S.; Chappell, A.G.; Giatsidis, G.; Perry, D.J.; Lujan-Hernandez, J.; Haddad, A.; Matsumine, H.; Orgill, D.P.; Lalikos, J.F. Hyperspectral Imaging Provides Early Prediction of Random Axial Flap Necrosis in a Preclinical Model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1285e–1290e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Seubert, W.; Ostermaier, P.; Horch, R.E.; Distel, L.; Frey, B.; Cai, A.; Arkudas, A. Intra- and Early Postoperative Evaluation of Malperfused Areas in an Irradiated Random Pattern Skin Flap Model Using Indocyanine Green Angiography and Near-Infrared Reflectance-Based Imaging and Infrared Thermography. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiem, D.G.E.; Römer, P.; Gielisch, M.; Al-Nawas, B.; Schlüter, M.; Plaß, B.; Kämmerer, P.W. Hyperspectral imaging and artificial intelligence to detect oral malignancy—Part 1—Automated tissue classification of oral muscle, fat and mucosa using a light-weight 6-layer deep neural network. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becker, P.; Blatt, S.; Pabst, A.; Heimes, D.; Al-Nawas, B.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Thiem, D.G.E. Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Microvascular Doppler for Perfusion Monitoring of Free Flaps in an In Vivo Rodent Model. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144134
Becker P, Blatt S, Pabst A, Heimes D, Al-Nawas B, Kämmerer PW, Thiem DGE. Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Microvascular Doppler for Perfusion Monitoring of Free Flaps in an In Vivo Rodent Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144134
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecker, Philipp, Sebastian Blatt, Andreas Pabst, Diana Heimes, Bilal Al-Nawas, Peer W. Kämmerer, and Daniel G. E. Thiem. 2022. "Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Microvascular Doppler for Perfusion Monitoring of Free Flaps in an In Vivo Rodent Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144134
APA StyleBecker, P., Blatt, S., Pabst, A., Heimes, D., Al-Nawas, B., Kämmerer, P. W., & Thiem, D. G. E. (2022). Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Microvascular Doppler for Perfusion Monitoring of Free Flaps in an In Vivo Rodent Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144134







