Elevated One-Hour Post-Load Glucose Is Independently Associated with Albuminuria: A Cross-Sectional Population Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. The Definition of the Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
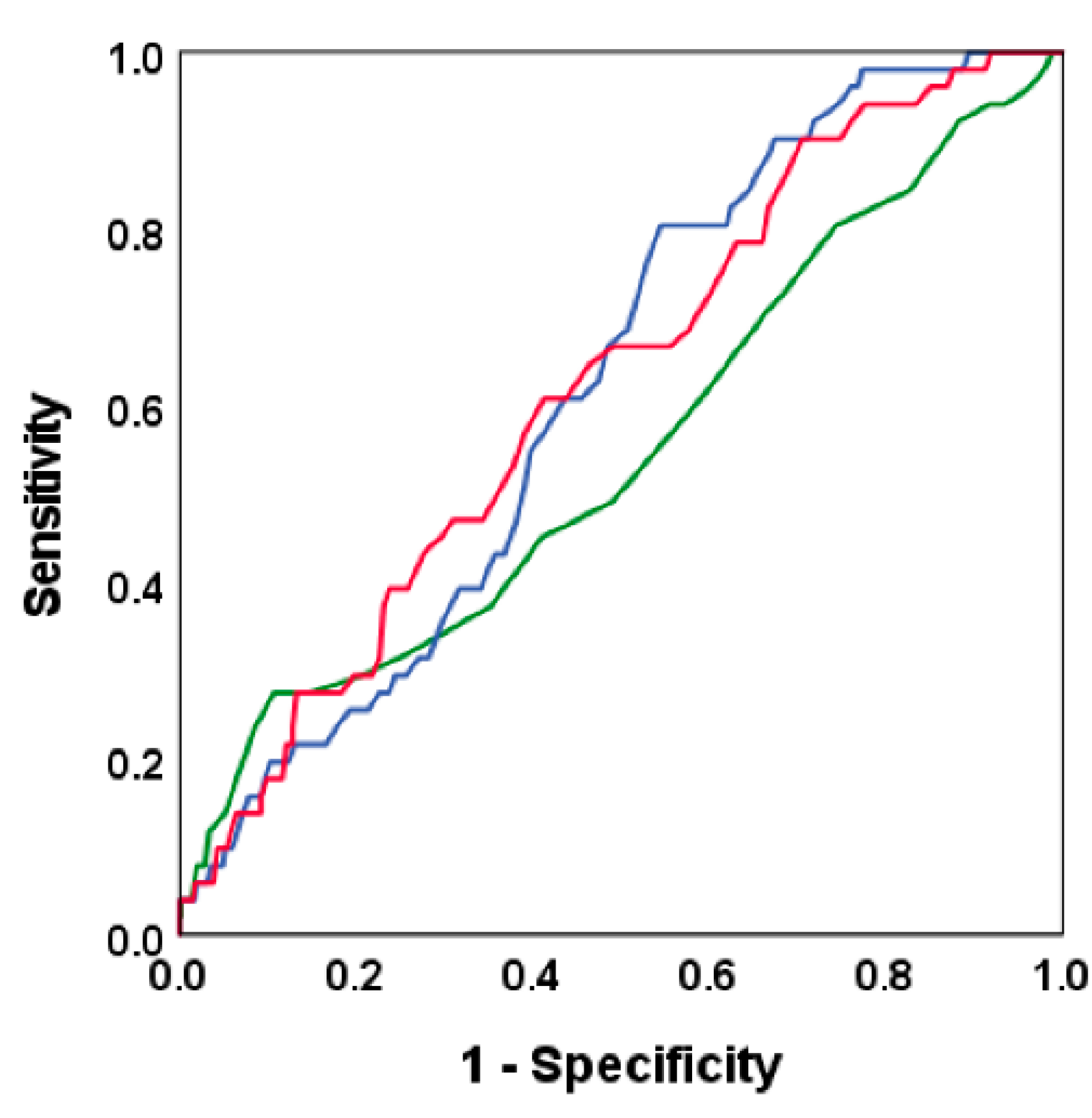
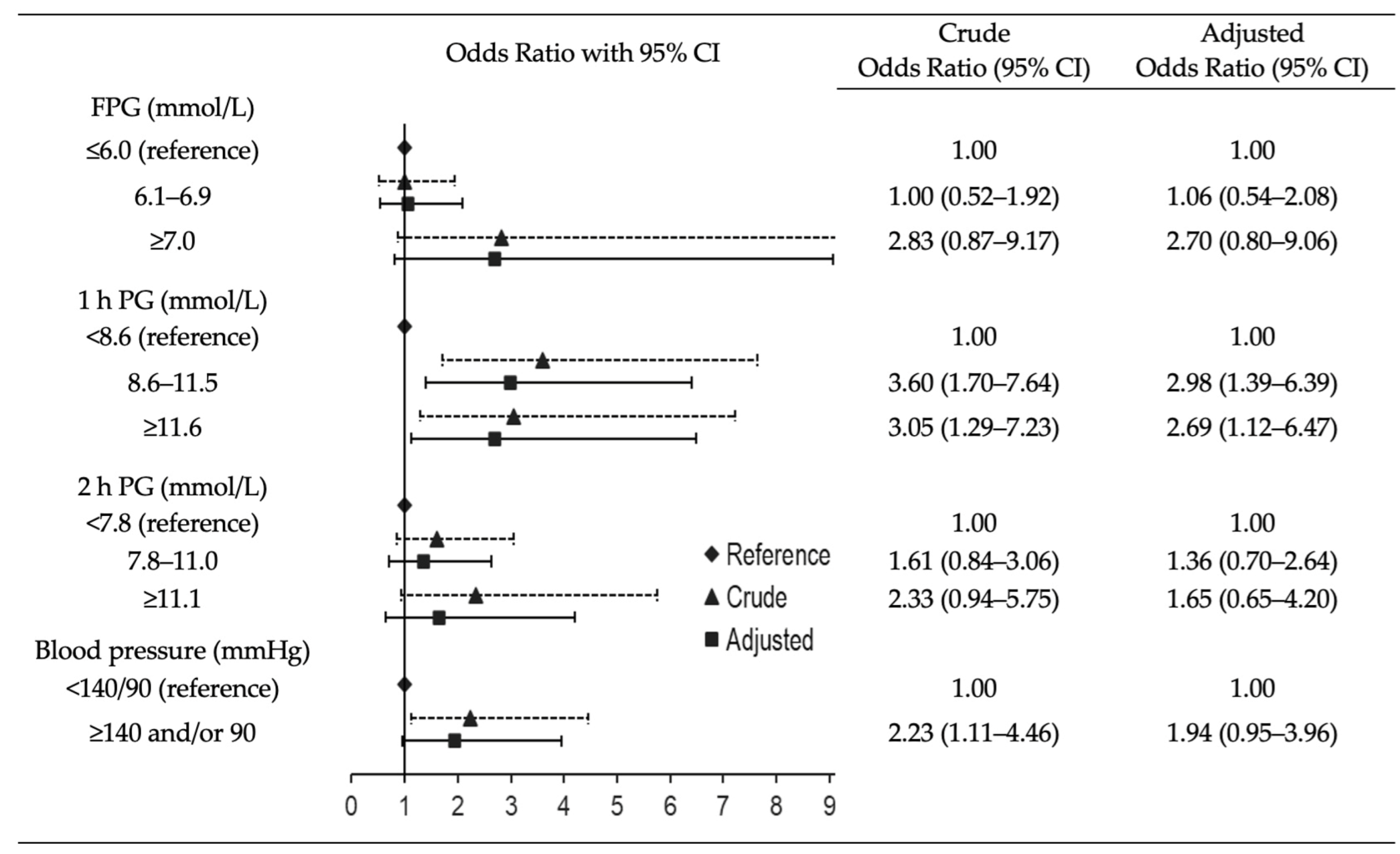
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration Diabetes Mellitus, Fasting Blood Glucose Concentration, and Risk of Vascular Disease: A Collaborative Meta-Analysis of 102 Prospective Studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DECODE Study Group. Is the Current Definition for Diabetes Relevant to Mortality Risk From All Causes and Cardiovascular and Noncardiovascular Diseases? Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DECODE Study Group. Glucose Tolerance and Mortality: Comparison of WHO and American Diabetic Association Diagnostic Criteria. The DECODE Study Group. European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Diabetes Epidemiology: Collaborative Analysis of Diagnostic Criteria in Europe. Lancet 1999, 354, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Lindström, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Valle, T.T.; Hämäläinen, H.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; Louheranta, A.; Rastas, M.; et al. Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Changes in Lifestyle among Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M.; Group, D.P.P.R. Reduction in the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes with Lifestyle Intervention or Metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Long-Term Effects of Lifestyle Intervention or Metformin on Diabetes Development and Microvascular Complications over 15-Year Follow-up: The Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.; Manco, M.; Sesti, G.; Dankner, R.; Pareek, M.; Jagannathan, R.; Chetrit, A.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Buysschaert, M.; Olsen, M.H.; et al. Petition to Replace Current OGTT Criteria for Diagnosing Prediabetes with the 1-Hour Post-Load Plasma Glucose ≥ 155 mg/Dl (8.6 mmol/L). Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 146, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Nielsen, M.L.; Jagannathan, R.; Eriksson, K.F.; Nilsson, P.M.; Bergman, M.; Olsen, M.H. Enhanced Predictive Capability of a 1-Hour Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.; Jagannathan, R.; Buysschaert, M.; Pareek, M.; Olsen, M.H.; Nilsson, P.M.; Medina, J.L.; Roth, J.; Chetrit, A.; Groop, L.; et al. Lessons Learned from the 1-Hour Post-Load Glucose Level during OGTT: Current Screening Recommendations for Dysglycaemia Should Be Revised. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Bakris, G.L.; Bilous, R.W.; Chiang, J.L.; de Boer, I.H.; Goldstein-Fuchs, J.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Narva, A.S.; Navaneethan, S.D.; et al. Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2864–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunajoki, A.; Auvinen, J.; Saarela, V.; Uusitalo, J.J.; Leiviskä, I.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Liinamaa, M.J.; Timonen, M. Association of Glucose Metabolism and Retinopathy Signs in Non-Diabetic Individuals in Midlife-The Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966 Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paddock, E.; Looker, H.C.; Piaggi, P.; Knowler, W.C.; Krakoff, J.; Chang, D.C. One-Hour Plasma Glucose Compared With 2-Hour Plasma Glucose in Relation to Diabetic Retinopathy in American Indians. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunajoki, A.; Auvinen, J.; Bloigu, A.; Ukkola, O.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Timonen, M. One-Hour Post-Load Glucose Improves the Prediction of Cardiovascular Events in the OPERA Study. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.L.; Pareek, M.; Leosdottir, M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Nilsson, P.M.; Olsen, M.H. One-Hour Glucose Value as a Long-Term Predictor of Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality: The Malmo Preventive Project. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverals, L.; van Dessel, K.; Verrijken, A.; Dirinck, E.; Peiffer, F.; Verhaegen, A.; de Block, C.; van Gaal, L. Cardiometabolic Importance of 1-h Plasma Glucose in Obese Subjects. Nutr. Diabetes 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramies, J.; Koiranen, M.; Auvinen, J.; Uusitalo, H.; Hussi, E.; Cederberg, H.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Tuomilehto, J. 22-Year Trends in Dysglycemia and Body Mass Index: A Population-Based Cohort Study in Savitaipale, Finland. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Provisional Report of a WHO Consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudek, C.D.; Herman, W.H.; Sacks, D.B.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Edelman, D.; Davidson, M.B. A New Look at Screening and Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Abdul-Ghani, T.; Ali, N.; Defronzo, R.A. One-Hour Plasma Glucose Concentration and the Metabolic Syndrome Identify Subjects at High Risk for Future Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, V.; Aronen, P.; Pramodkumar, T.A.; Looker, H.; Chetrit, A.; Bloigu, A.H.; Juutilainen, A.; Bianchi, C.; la Sala, L.; Anjana, R.M.; et al. Accuracy of 1-Hour Plasma Glucose During the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association 11. Microvascular Complications and Foot Care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S151–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Succurro, E.; Arturi, F.; Lugara, M.; Grembiale, A.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Caruso, V.; Andreozzi, F.; Sciacqua, A.; Hribal, M.L.; Perticone, F.; et al. One-Hour Postload Plasma Glucose Levels Are Associated with Kidney Dysfunction. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1922–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Narayan, K.M.; Weisman, D.; Golden, S.H.; Jaar, B.G. Association between Prediabetes and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Lu, J.M.; Pan, C.Y.; Tian, H.; Li, C.L. A Comparison of Urinary Albumin Excretion Rate and Microalbuminuria in Various Glucose Tolerance Subjects. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Li, J.; Huo, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Y. Impaired Fasting Blood Glucose Is Associated with Incident Albuminuria: Data from a Chinese Community-Based Cohort. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 36, 108125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, B.; Sun, W.; Lin, L.; Sun, J.; Xu, M.; Lu, J.; Bi, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Glycated Haemoglobin A1c Is Associated with Low-Grade Albuminuria in Chinese Adults. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parving, H.H.; Lewis, J.B.; Ravid, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Investigators, D. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Microalbuminuria in a Referred Cohort of Type II Diabetic Patients: A Global Perspective. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afghahi, H.; Cederholm, J.; Eliasson, B.; Zethelius, B.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Hadimeri, H.; Svensson, M.K. Risk Factors for the Development of Albuminuria and Renal Impairment in Type 2 Diabetes--the Swedish National Diabetes Register (NDR). Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, M.A.; Succurro, E.; Frontoni, S.; Mastroianni, S.; Arturi, F.; Sciacqua, A.; Lauro, R.; Hribal, M.L.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. Insulin Sensitivity, β-Cell Function, and Incretin Effect in Individuals with Elevated 1-Hour Postload Plasma Glucose Levels. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, S.; Rutters, F.; Nijpels, G.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; HØjlund, K.; Nolan, J.J.; Balkau, B.; Dekker, J.M. Insulin Sensitivity and Albuminuria: The Risc Study. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cosmo, S.; Menzaghi, C.; Prudente, S.; Trischitta, V. Role of Insulin Resistance in Kidney Dysfunction: Insights into the Mechanism and Epidemiological Evidence. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera-Chimal, J.; Jaisser, F. Pathophysiologic Mechanisms in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Focus on Current and Future Therapeutic Targets. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22 (Suppl. S1), 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesti, G.; Hribal, M.L.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Sciacqua, A.; Perticone, F. Elevated 1 h Postload Plasma Glucose Levels Identify Adults with Normal Glucose Tolerance but Increased Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2014, 2, e000016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers Heerspink, H.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; Parving, H.H.; Shahinfar, S.; de Zeeuw, D. Comparison of Different Measures of Urinary Protein Excretion for Prediction of Renal Events. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| U-Alb/Crea < 3.0 | U-Alb/Crea ≥ 3.0 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study population, n (%) | 445 (89.7) | 51 (10.3) | |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.209 | ||
| Men | 186 (87.7) | 26 (12.3) | |
| Women | 259 (91.2) | 25 (8.8) | |
| Age (years) | 71.8 ± 6.2 | 75.4 ± 6.4 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.9 ± 4.2 | 27.5 ± 5.4 | 0.444 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 92.7 ± 11.9 | 94.1 ± 13.6 | 0.424 |
| Men (cm) | 97.3 ± 10.7 | 97.7 ± 13.6 | 0.870 |
| Women (cm) | 89.4 ± 11.6 | 90.4 ± 12.7 | 0.693 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L) | |||
| Mean | 5.8 ± 0.6 | 6.0 ± 1.0 | 0.108 |
| ≤6.0, n (%) | 303 (68.1) | 33 (64.7) | 0.187 |
| 6.1–6.9, n (%) | 129 (29.0) | 14 (27.5) | |
| ≥7.0, n (%) | 13 (2.9) | 4 (7.8) | |
| 1 h post-load glucose (mmol/L) | |||
| Mean | 9.0 ± 2.7 | 10.3 ± 2.9 | 0.001 |
| <8.6, n (%) | 202 (45.4) | 10 (19.6) | 0.002 |
| 8.6–11.5, n (%) | 157 (35.3) | 28 (54.9) | |
| ≥11.6, n (%) | 86 (19.3) | 13 (25.5) | |
| 2 h post-load glucose (mmol/L) | |||
| Mean | 7.3 ± 2.3 | 8.5 ± 3.5 | 0.015 |
| <7.8, n (%) | 296 (66.5) | 27 (52.9) | 0.108 |
| 7.8–11.0, n (%) | 116 (26.1) | 17 (33.3) | |
| ≥11.1, n (%) | 33 (7.4) | 7 (13.7) | |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | |||
| Mean | 40.7 ± 5.0 | 42.0 ± 6.3 | 0.074 |
| <6.0% (42.0 mmol/mol), n (%) | 255 (57.3) | 21 (41.2) | 0.085 |
| 6.0–6.4 (42.0–47.0 mmol/mol), n (%) | 156 (35.1) | 24 (47.1) | |
| ≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol), n (%) | 34 (7.6) | 6 (11.8) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 146 ± 21 | 155 ± 25 | 0.005 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 83 ± 10 | 85 ± 12 | 0.260 |
| Hypertension | |||
| <140/90 mmHg, n (%) | 169 (38.0) | 11 (21.6) | 0.021 |
| ≥140 and/or 90 mmHg, n (%) | 276 (62.0) | 40 (78.4) | |
| Plasma total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.9 ± 1.0 | 4.8 ± 1.0 | 0.411 |
| Plasma HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 0.116 |
| Men (mmol/L) | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.372 |
| Women (mmol/L) | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 0.385 |
| Plasma LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 1.0 | 0.947 |
| Plasma triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 0.504 |
| Men (mmol/L) | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 0.186 |
| Women (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.320 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saunajoki, A.; Auvinen, J.; Bloigu, A.; Saramies, J.; Tuomilehto, J.; Uusitalo, H.; Hussi, E.; Cederberg-Tamminen, H.; Suija, K.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; et al. Elevated One-Hour Post-Load Glucose Is Independently Associated with Albuminuria: A Cross-Sectional Population Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144124
Saunajoki A, Auvinen J, Bloigu A, Saramies J, Tuomilehto J, Uusitalo H, Hussi E, Cederberg-Tamminen H, Suija K, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, et al. Elevated One-Hour Post-Load Glucose Is Independently Associated with Albuminuria: A Cross-Sectional Population Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144124
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaunajoki, Anni, Juha Auvinen, Aini Bloigu, Jouko Saramies, Jaakko Tuomilehto, Hannu Uusitalo, Esko Hussi, Henna Cederberg-Tamminen, Kadri Suija, Sirkka Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, and et al. 2022. "Elevated One-Hour Post-Load Glucose Is Independently Associated with Albuminuria: A Cross-Sectional Population Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144124
APA StyleSaunajoki, A., Auvinen, J., Bloigu, A., Saramies, J., Tuomilehto, J., Uusitalo, H., Hussi, E., Cederberg-Tamminen, H., Suija, K., Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S., & Timonen, M. (2022). Elevated One-Hour Post-Load Glucose Is Independently Associated with Albuminuria: A Cross-Sectional Population Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11144124







