Gray-Scale, Color Doppler, Spectral Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Renal Artery Ultrasound: Imaging Techniques and Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Aspects of RAS
3. Renal Artery US vs. Renal US
4. Renal Artery US: Imaging Techniques
5. Renal Artery US: Imaging Features
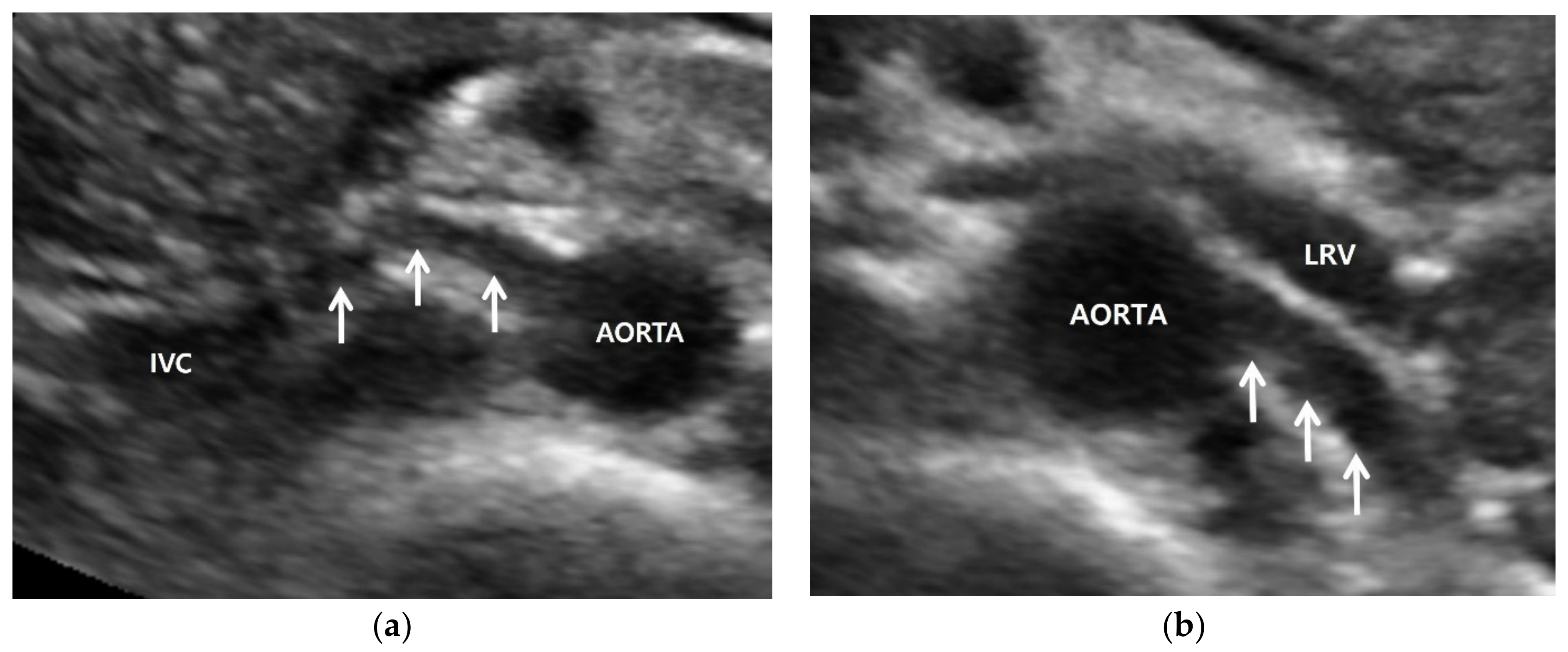
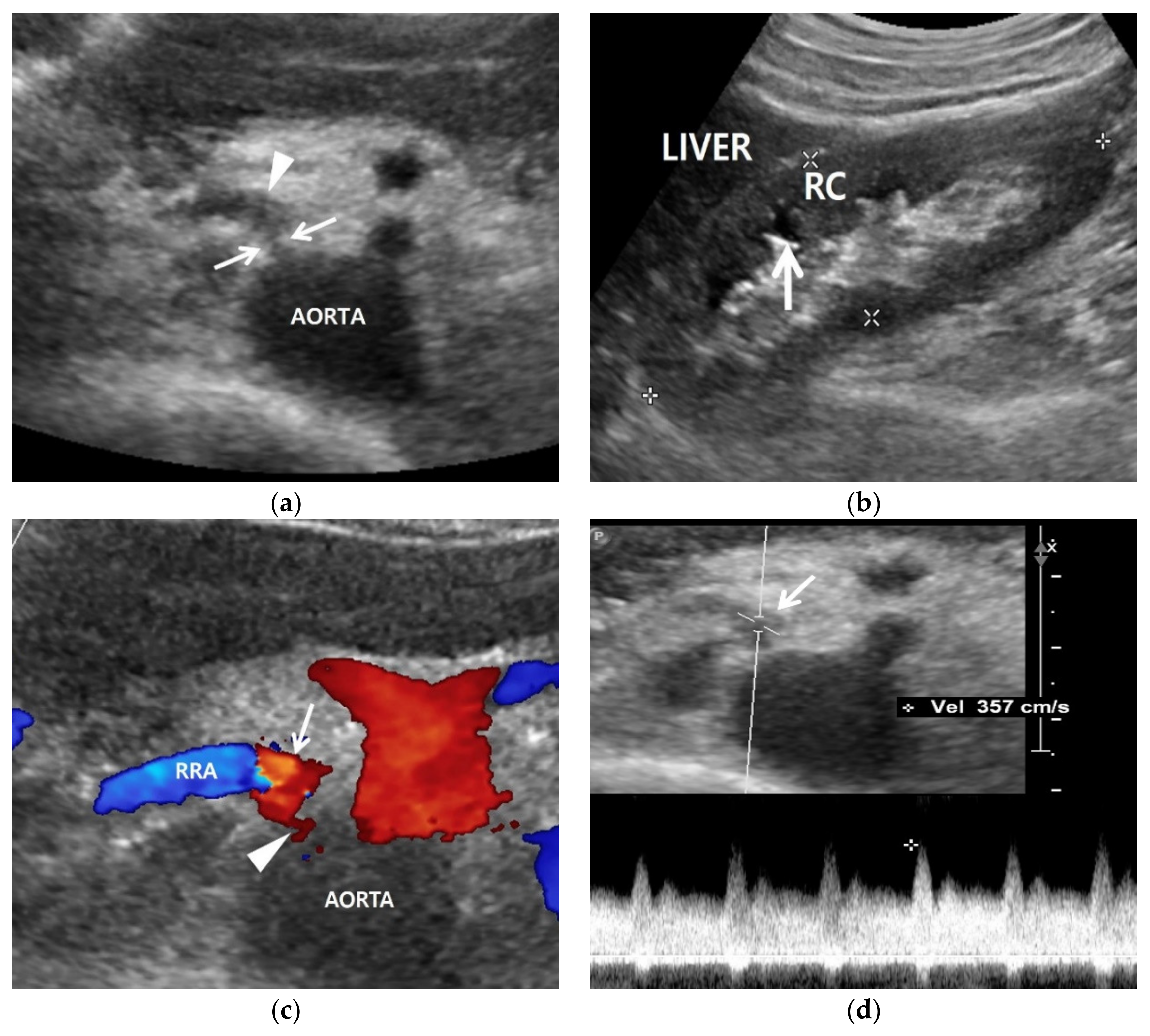
5.1. Gray-Scale US
5.2. Color Doppler US
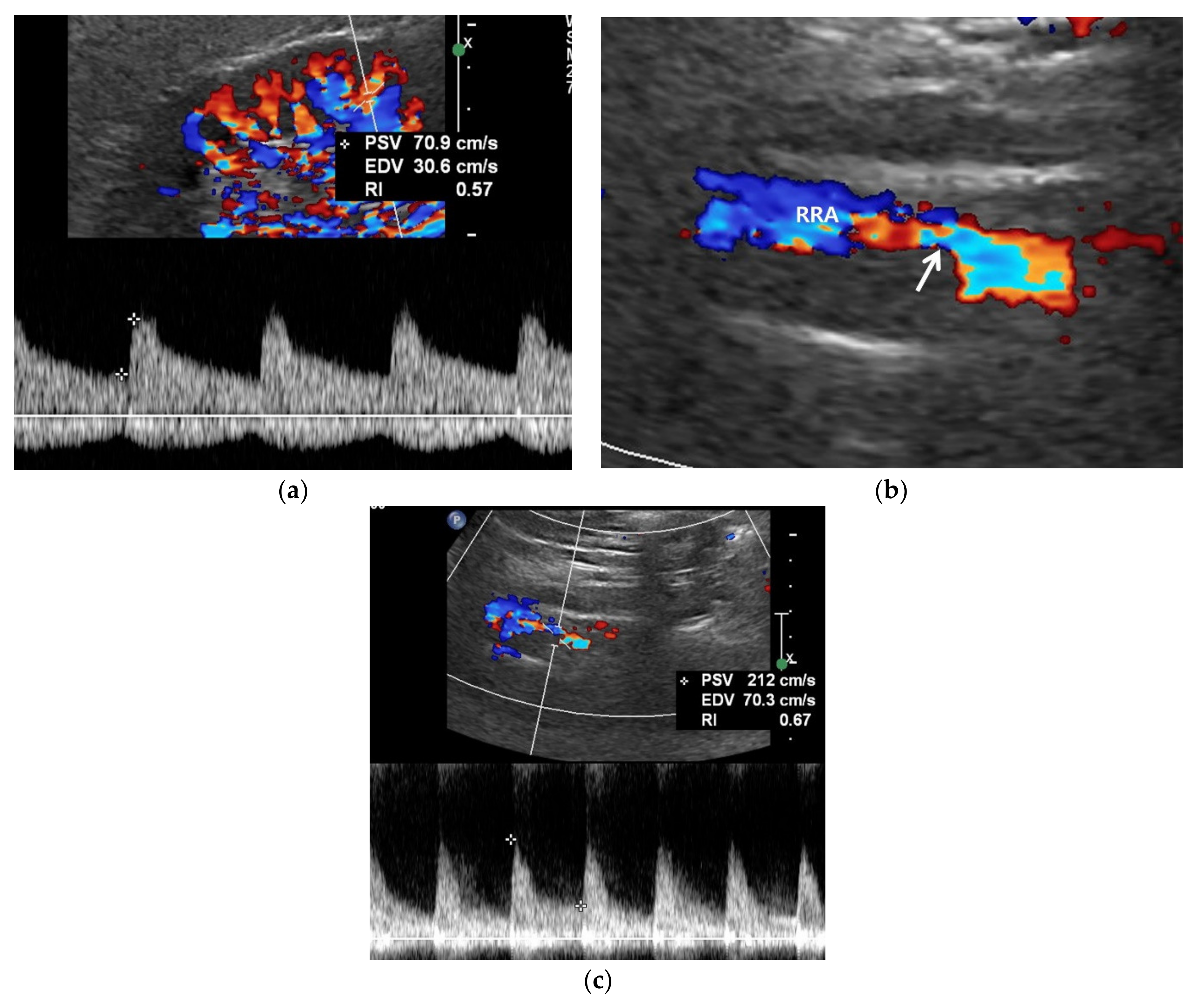
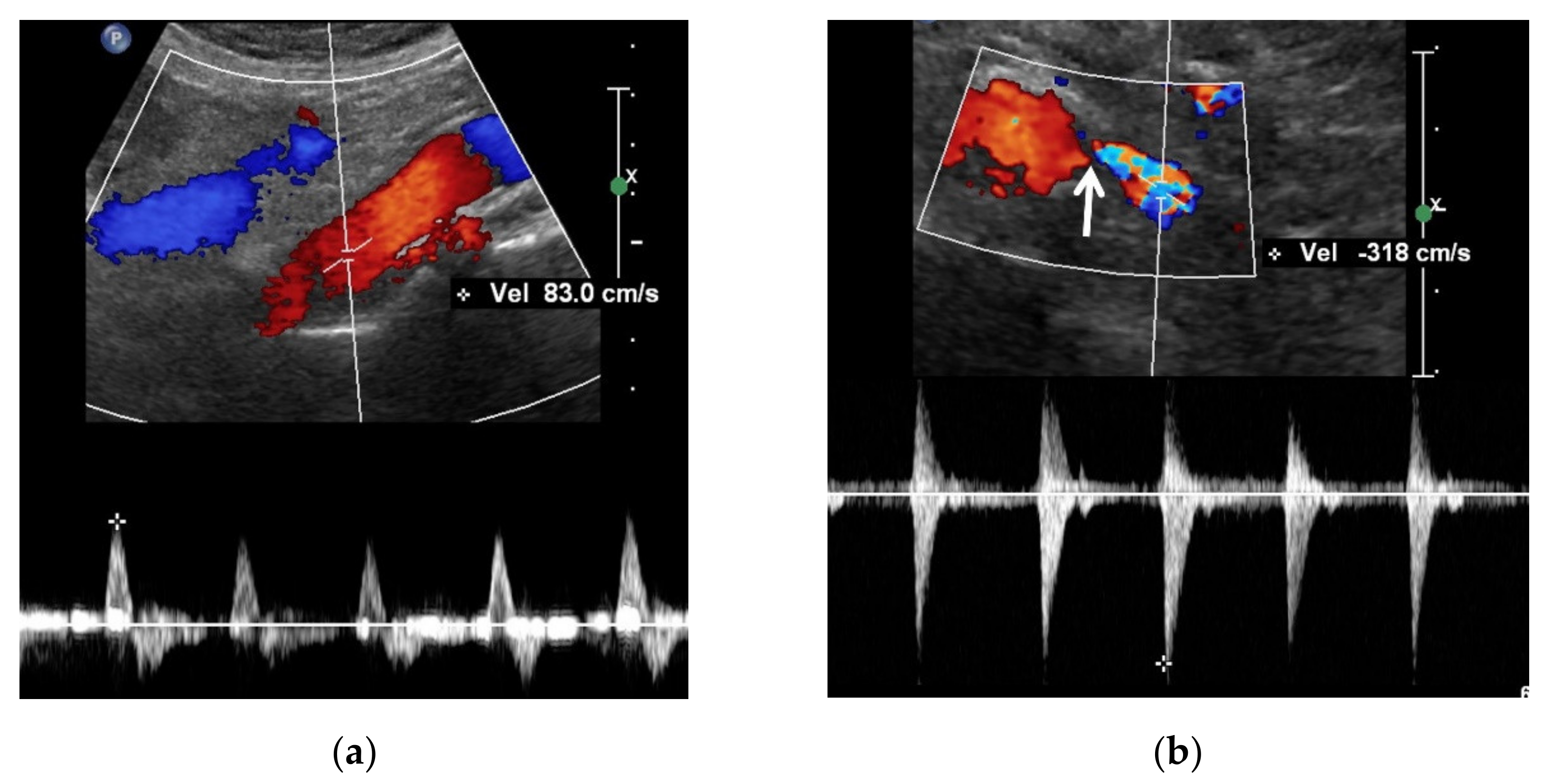
5.3. Spectral Doppler US
5.4. Contrast-Enhanced US
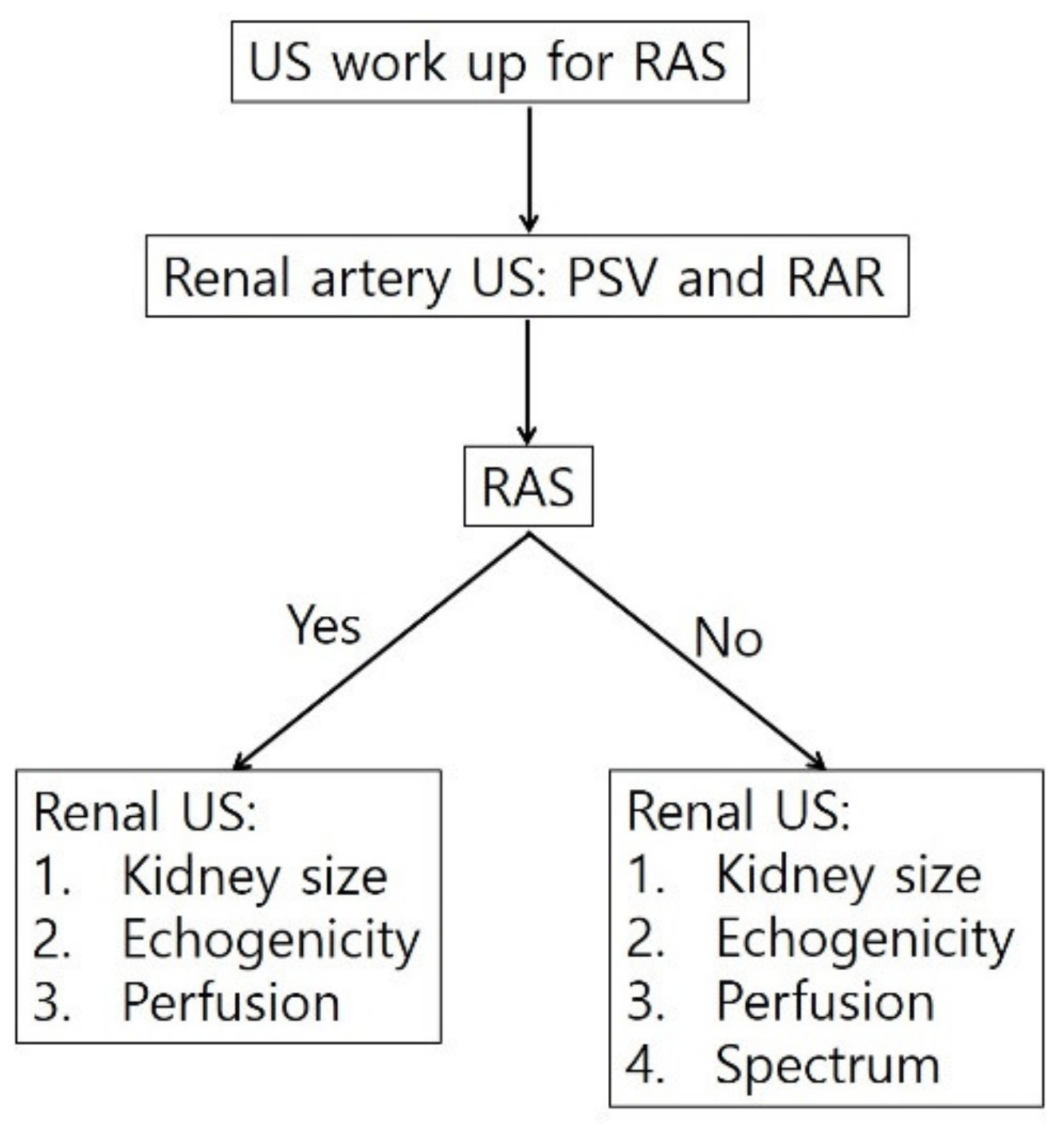
6. Diagnostic Steps for RAS
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colyer, W.R.; Eltahawy, E.; Cooper, C.J. Renal artery stenosis: Optimizing diagnosis and treatment. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 54, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, B.R.; Dieter, R.S. Renal artery stenosis: Epidemiology and treatment. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zierler, R.E. Is duplex scanning the best screening test for renal artery stenosis? Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 14, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, J.W.; Piedmonte, M.R.; Young, J.R.; DeAnna, S.; Grubb, M.; Childs, M.B. The utility of duplex ultrasound scanning of the renal arteries for diagnosing significant renal artery stenosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1995, 122, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehl, J.; Schmitt, H.; Bongartz, D.; Bergmann, D.; Sieberth, H.G. Renal artery stenosis: Evaluation with colour duplex ultrasonography. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1997, 12, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasbinder, G.B.; Nelemans, P.J.; Kessels, A.G.; Kroon, A.A.; de Leeuw, P.W.; van Engelshoven, J.M. Diagnostic tests for renal artery stenosis in patients suspected of having renovascular hypertension: A meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasbinder, G.B.; Nelemans, P.J.; Kessels, A.G.; Kroon, A.A.; Maki, J.H.; Leiner, T.; Beek, F.J.; Korst, M.B.; Flobbe, K.; de Haan, M.W.; et al. Accuracy of computed tomographic angiography and magnetic resonance angiography for diagnosing renal artery stenosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditi, G.; Maki, J.H.; Oliveira, G.; Michaely, H.J. Renovascular imaging in the NSF Era. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Porter, D.H.; Brown, R.; Crivello, M.S.; Silva, P.; Leeming, B.W. Renal artery imaging: A prospective comparison of intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography with conventional angiography. Angiology 1991, 42, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, I.F., Jr.; Wilcox, C.S.; Kerns, S.R.; Sabatelli, F.W. CO2 digital angiography: A safer contrast agent for renal vascular imaging? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1994, 24, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, P.; Eklof, H.; Hellberg, O.; Hagg, A.; Bostrom-Ardin, A.; Lofberg, A.M.; Olsson, U.; Orndahl, P.; Nilsson, H.; Hansell, P.; et al. Renal effects of CO2 and iodinated contrast media in patients undergoing renovascular intervention: A prospective, randomized study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratigis, S.; Stylianou, K.; Kyriazis, P.P.; Dermitzaki, E.K.; Lygerou, D.; Syngelaki, P.; Stratakis, S.; Koukouraki, S.; Parthenakis, F.; Tsetis, D.; et al. Renal artery stenting for atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis identified in patients with coronary artery disease: Does captopril renal scintigraphy predict outcomes? J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qanadli, S.D.; Soulez, G.; Therasse, E.; Nicolet, V.; Turpin, S.; Froment, D.; Courteau, M.; Guertin, M.C.; Oliva, V.L. Detection of renal artery stenosis: Prospective comparison of captopril-enhanced Doppler sonography, captopril-enhanced scintigraphy, and MR angiography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 177, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehran, R.; Nikolsky, E. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, S11–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morcos, S.K.; Thomsen, H.S.; Webb, J.A.; Contrast Media Safety Committee, European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR). Contrast-media-induced nephrotoxicity: A consensus report. Eur. Radiol. 1999, 9, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, T.G.; Bulugahapitiya, S. Contrast-Induced Nephropathy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 183, 1673–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobner, T.; Prischl, F.C. Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grobner, T. Gadolinium—A specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2006, 21, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozbek, S.S.; Aytaç, S.K.; Erden, M.I.; Sanlidilek, N.U. Intrarenal Doppler findings of upstream renal artery stenosis: A preliminary report. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1993, 19, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.M.; Aitchison, F.; Sheppard, D.; Moss, J.G.; McLeod, M.J.; Harden, P.N.; Love, J.G.; Robertson, M.; Taylor, G. Colour Doppler ultrasound in renal artery stenosis: Intrarenal waveform analysis. Br. J. Radiol. 1996, 69, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerk, W.B.; Restrepo, I.K.; Stellwaag, M.; Klose, K.J.; Schade-Brittinger, C. Renal artery stenosis: Grading with image-directed Doppler US evaluation of renal resistive index. Radiology 1994, 190, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.W.; Faxon, D.P. Current advances in the diagnosis and treatment of renal artery stenosis. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2004, 5, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Granata, A.; Fiorini, F.; Andrulli, S.; Logias, F.; Gallieni, M.; Romano, G.; Sicurezza, E.; Fiore, C.E. Doppler ultrasound and renal artery stenosis: An overview. J. Ultrasound 2009, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radermacher, J.; Chavan, A.; Schäffer, J.; Stoess, B.; Vitzthum, A.; Kliem, V.; Rademaker, J.; Bleck, J.; Gebel, M.J.; Galanski, M.; et al. Detection of significant renal artery stenosis with color Doppler sonography: Combining extrarenal and intrarenal approaches to minimize technical failure. Clin. Nephrol. 2000, 53, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.T.; Hood, D.B.; Jensen, C.C.; Hanks, S.E.; Weaver, F.A. The use of colorflow duplex scanning to detect significant renal artery stenosis. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 14, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, S.K.; Yigit, H.; Sancak, T.; Ozcan, H. Correlation between the diameter of the main renal artery and the presence of an accessory renal artery: Sonographic and angiographic evaluation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2003, 22, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bude, R.O.; Forauer, A.R.; Caoili, E.M.; Nghiem, H.V. Is it necessary to study accessory arteries when screening the renal arteries for renovascular hypertension? Radiology 2003, 226, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, U.; Edwards, J.M.; Carter, S.; Goldman, M.L.; Harley, J.D.; Zaccardi, M.J.; Strandness, D.E., Jr. Role of duplex scanning for the detection of atherosclerotic renal artery disease. Kidney Int. 1991, 39, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labropoulos, N.; Ayuste, B.; Leon, L.R., Jr. Renovascular disease among patients referred for renal duplex ultrasonography. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 46, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, G.M.; Murphy, T.P.; Singha, M.S.; Parada, A.; Jaff, M. Renal artery duplex ultrasonography as a screening and surveillance tool to detect renal artery stenosis: A comparison with current reference standard imaging. J. Ultrasound Med. 2006, 25, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.J.; Macaskill, P.; Chan, S.F.; Karplus, T.E.; Yung, W.; Hodson, E.M.; Craig, J.C. Comparative accuracy of renal duplex sonographic parameters in the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis: Paired and unpaired analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Lin, L.; Yang, M.; Niu, G.; Chen, L.; Shao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, B. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Evaluation of Renal Blood Perfusion Changes after Percutaneous Transluminal Renal Angioplasty and Stenting for Severe Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, S.; Nishida, N.; Uzu, T.; Takeji, M.; Nishimura, M.; Fujii, T.; Nakamura, S.; Inenaga, T.; Yutani, C.; Kimura, G. Prevalence of renal artery stenosis in autopsy patients with stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Finocchiaro, P. Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis: Epidemiology, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Clinical Prediction Rules. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burlacu, A.; Siriopol, D.; Voroneanu, L.; Nistor, I.; Hogas, S.; Nicolae, A.; Nedelciuc, I.; Tinica, G.; Covic, A. Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis Prevalence and Correlations in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: Data from Nonrandomized Single-Center Study (REN-ACS)—A Single Center, Prospective, Observational Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalra, P.A.; Guo, H.; Kausz, A.T.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.C.; Ishani, A.; Collins, A.J.; Foley, R.N. Atherosclerotic renovascular disease in United States patients aged 67 years or older: Risk factors, revascularization, and prognosis. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Dworkin, L.D.; Henrich, W.; Greco, B.A.; Steffes, M.; Tobe, S.; Shapiro, J.I.; Jamerson, K.; Lyass, A.; Pencina, K.; et al. Effects of Stenting for Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis on eGFR and Predictors of Clinical Events in the CORAL Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chrysant, S.G.; Chrysant, G.S. Treatment of hypertension in patients with renal artery stenosis due to fibromuscular dysplasia of the renal arteries. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 4, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Safian, R.D.; Textor, S.C. Renal-artery stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Katib, S.; Shetty, M.; Jafri, S.M.A.; Jafri, S.Z.H. Radiologic Assessment of Native Renal Vasculature: A Multimodality Review. RadioGraphics 2017, 37, 136–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzman, R.P.; Zierler, R.E.; Isaacson, J.A.; Bergelin, R.O.; Strandness, D.E., Jr. Renal atrophy and arterial stenosis. A prospective study with duplex ultrasound. Hypertension 1994, 23, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caps, M.T.; Zierler, R.E.; Polissar, N.L.; Bergelin, R.O.; Beach, K.W.; Cantwell-Gab, K.; Casadei, A.; Davidson, R.C.; Strandness, D.E., Jr. Risk of atrophy in kidneys with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawarada, O.; Yokoi, Y.; Morioka, N.; Takemoto, K. Renal artery stenosis in cardio-and cerebrovascular disease: Renal duplex ultrasonography as an initial screening examination. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schäberle, W.; Leyerer, L.; Schierling, W.; Pfister, K. Ultrasound diagnostics of renal artery stenosis: Stenosis criteria, CEUS and recurrent in-stent stenosis. Gefasschirurgie 2016, 21, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, M.H.; Jung, S.I. Imaging features of gray-scale and contrast-enhanced color Doppler US for the differentiation of transient renal arterial ischemia and arterial infarction. Korean J. Radiol. 2005, 6, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, C.L.; Ellis, J.H.; Korobkin, M.; Dunnick, N.R. CT-detected renal arterial calcification: Correlation with renal artery stenosis on angiography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 163, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freedman, B.I.; Hsu, F.-C.; Langefeld, C.D.; Bowden, D.W.; Moossavi, S.; Dryman, B.N.; Carr, J.J. Renal artery calcified plaque associations with subclinical renal and cardiovascular disease. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2262–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Revzin, M.V.; Imanzadeh, A.; Menias, C.; Pourjabbar, S.; Mustafa, A.; Nezami, N.; Spektor, M.; Pellerito, J.S. Optimizing Image Quality When Evaluating Blood Flow at Doppler US: A Tutorial. RadioGraphics 2019, 39, 1501–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierler, R.E.; Bergelin, R.O.; Davidson, R.C.; Cantwell-Gab, K.; Polissar, N.L.; Strandness, D.E., Jr. A prospective study of disease progression in patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Am. J. Hypertens. 1996, 9, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.X.; Dai, Q.; Cai, S.; Lv, K.; Qi, Z.H. Evaluation of renal artery stenosis with velocity parameters of Doppler sonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2006, 25, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Jiang, Y.X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, Y.S.; Qi, Z.H. Evaluation of renal artery stenosis with hemodynamic parameters of Doppler sonography. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 48, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grenier, N.; Hauger, O.; Cimpean, A.; Pérot, V. Update of renal imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 36, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysochou, C.; Cheung, C.M.; Durow, M.; Middleton, R.J.; Solomon, L.R.; Craig, A.; Venning, M.; Kalra, P.A. Proteinuria as a predictor of renal functional outcome after revascularization in atherosclerotic renovascular disease (ARVD). QJM 2009, 102, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, C.J. Optimizing outcomes for renal artery intervention. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, D. Renal artery revascularization: Is there a rationale to perform? JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 2, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morel, D.R.; Schwieger, I.; Hohn, L.; Terrettaz, J.; Llull, J.B.; Cornioley, Y.A.; Schneider, M. Human Pharmacokinetics and Safety Evaluation of SonoVue™, a New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2000, 35, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Characterization of renal cell carcinoma using agent detection imaging: Comparison with gray-scale US. Korean J. Radiol. 2005, 6, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, K.; Lee, H.M.; Choi, H.Y. Assessment of cystic renal masses based on Bosniak classification: Comparison of CT and contrast-enhanced US. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 61, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerst, S.; Hann, L.E.; Li, D.; Gonen, M.; Tickoo, S.; Sohn, M.J.; Russo, P. Evaluation of renal masses with contrast-enhanced ultrasound: Initial experience. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ignee, A.; Straub, B.; Schuessler, G.; Dietrich, C.F. Contrast enhanced ultrasound of renal masses. World J. Radiol. 2010, 2, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G. Use of lumason/sonovue in contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the kidney for characterization of renal masses-a meta-analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 47, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenant, S.C.; Gutteridge, C.M. The clinical use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the kidney. Ultrasound 2016, 24, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, W.P.; Cao, J.; Fan, P.; Lin, X. Early assessment of chronic kidney dysfunction using contrast-enhanced ultrasound: A pilot study. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, F.; Cang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Wu, T.; Song, Y.; Peng, A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound with SonoVue could accurately assess the renal microvascular perfusion in diabetic kidney damage. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Shao, X.; Tian, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, W.; et al. Improving Prognostic and Chronicity Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Index-Derived Peak Intensity. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2945–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, J.; Wu, J. The Value of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound versus Doppler Ultrasound in Grading Renal Artery Stenosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7145728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.-H.; Ma, N.; Wang, S.-Y.; Sun, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Guo, F.-J.; Li, Y.-J.; Li, T.-H.; Ai, H.; Zhang, W.-D.; et al. Rationale and study design for one-stop assessment of renal artery stenosis and renal microvascular perfusion with contrast-enhanced ultrasound for patients with suspected renovascular hypertension. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
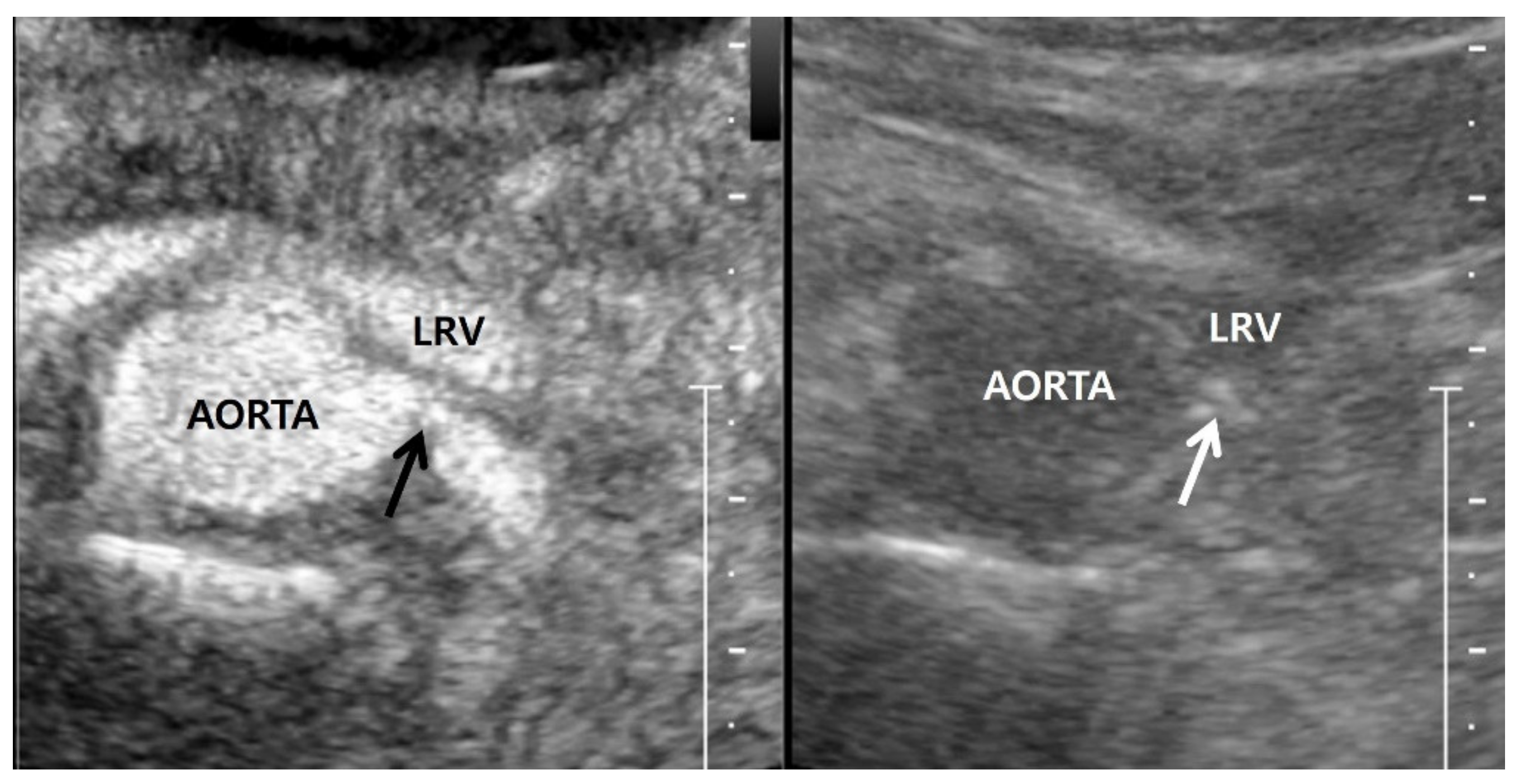
| Demographics | Atherosclerosis | Fibromuscular Dysplasia |
|---|---|---|
| Incidence | 90% | 10% |
| Sex ratio | No predominance | Women predominant |
| Common age | Older | Younger |
| Frequent location | Proximal one-third | Mid-to-distal two-thirds |
| Main imaging features | Single RAS | Multifocal RAS (beaded) |
| First treatment option | Angioplasty or stenting | Angioplasty |
| US Techniques and Accuracy | Renal Artery US | Renal US |
|---|---|---|
| Imaging techniques | More difficult | Less difficult |
| Scan time | Longer | Shorter |
| Breath hold | Unnecessary | Necessary |
| Bowel artifact | Frequent | Infrequent |
| Diagnostic performance | Higher | Lower |
| Imaging Features | Renal Artery US | Renal US |
|---|---|---|
| Direct signs | Focal stenosis or occlusion | NA |
| Hyperechoic thick wall | NA | |
| Indirect signs | Poststenotic dilatation | Unilateral small kidney |
| Calcification | Hyperechoic thin cortex | |
| Clear CM differentiation |
| Doppler US | Renal Artery US | Renal US |
|---|---|---|
| Color Doppler US | Bright blue or red | Normal/weak/no perfusion |
| Turbulent signal | ||
| Spectral Doppler US | PSV (>180–200 cm/s) | Pulsus tardus and parvus |
| Reno-aortic PSV ratio (>3.5) | Delayed acceleration | |
| Turbulent spectrum | Low resistive index |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, B.K. Gray-Scale, Color Doppler, Spectral Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Renal Artery Ultrasound: Imaging Techniques and Features. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143961
Park BK. Gray-Scale, Color Doppler, Spectral Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Renal Artery Ultrasound: Imaging Techniques and Features. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(14):3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143961
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Byung Kwan. 2022. "Gray-Scale, Color Doppler, Spectral Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Renal Artery Ultrasound: Imaging Techniques and Features" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 14: 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143961
APA StylePark, B. K. (2022). Gray-Scale, Color Doppler, Spectral Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced Renal Artery Ultrasound: Imaging Techniques and Features. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(14), 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143961






