Andexanet Alfa for Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Intracranial Hemorrhage: Observational Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
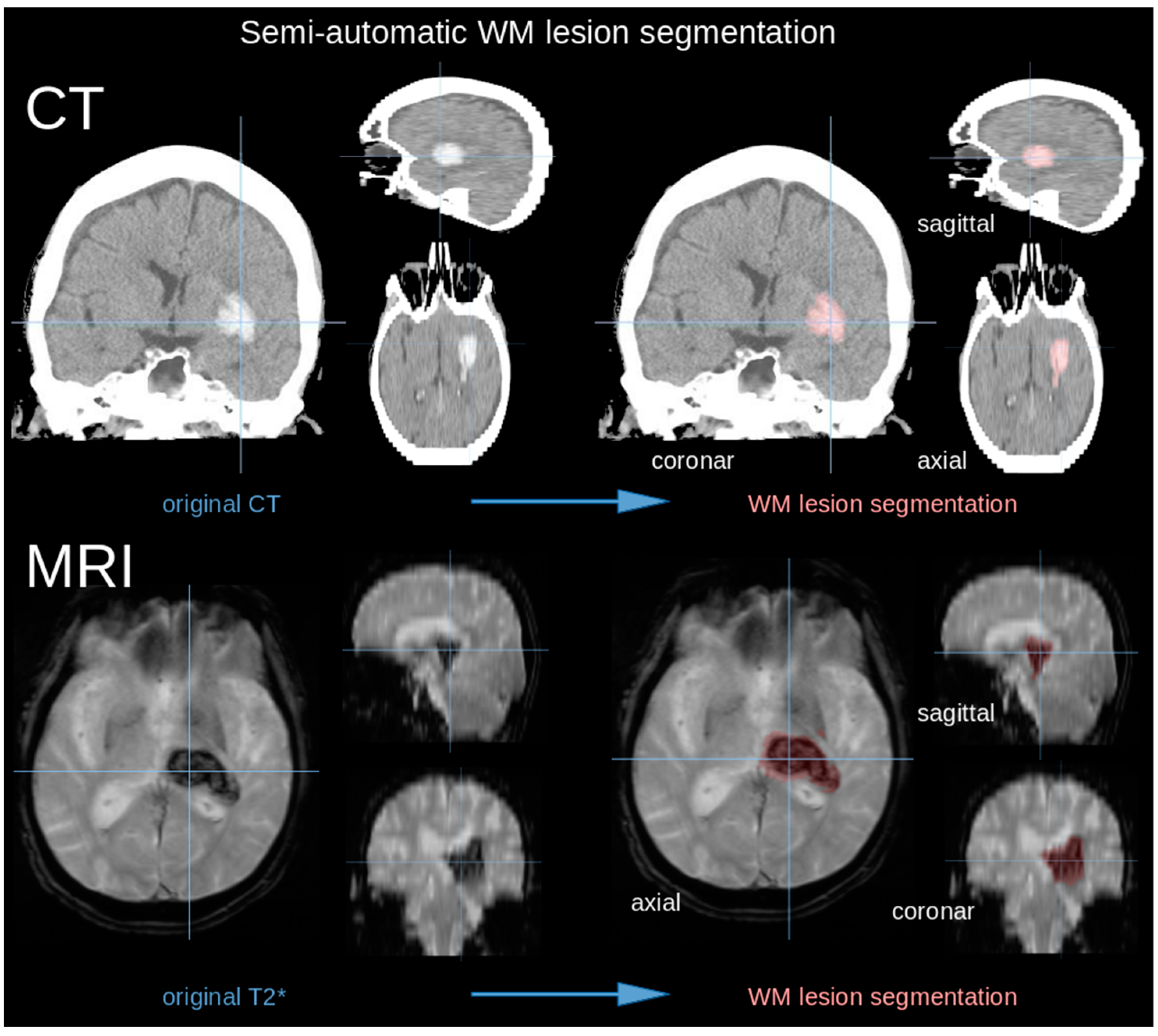
2.2. Imaging
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics
3.2. Efficacy and Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersen, K.K.; Olsen, T.S.; Dehlendorff, C.; Kammersgaard, L.P. Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes compared: Stroke severity, mortality, and risk factors. Stroke 2009, 40, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hemphill, J.C., 3rd; Greenberg, S.M.; Anderson, C.S.; Becker, K.; Bendok, B.R.; Cushman, M.; Fung, G.L.; Goldstein, J.N.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mitchell, P.H.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2015, 46, 2032–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steiner, T.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Beer, R.; Christensen, H.; Cordonnier, C.; Csiba, L.; Forsting, M.; Harnof, S.; Klijn, C.J.; Krieger, D.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.; Poli, S.; Griebe, M.; Hüsing, J.; Hajda, J.; Freiberger, A.; Bendszus, M.; Bösel, J.; Christensen, H.; Dohmen, C.; et al. Fresh frozen plasma versus prothrombin complex concentrate in patients with intracranial haemorrhage related to vitamin K antagonists (INCH): A randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramatsu, J.B.; Sembill, J.A.; Huttner, H.B. Reversal of oral anticoagulation in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollack, C.V., Jr.; Reilly, P.A.; Eikelboom, J.; Glund, S.; Verhamme, P.; Bernstein, R.A.; Dubiel, R.; Huisman, M.V.; Hylek, E.M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; et al. Idarucizumab for Dabigatran Reversal. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kermer, P.; Eschenfelder, C.C.; Diener, H.C.; Grond, M.; Abdalla, Y.; Abraham, A.; Althaus, K.; Becks, G.; Berrouschot, J.; Berthel, J.; et al. Antagonizing dabigatran by idarucizumab in cases of ischemic stroke or intracranial hemorrhage in Germany-Updated series of 120 cases. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.; Köhrmann, M.; Schellinger, P.D.; Tsivgoulis, G. Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants Associated Bleeding and Its Antidotes. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connolly, S.J.; Crowther, M.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Gibson, C.M.; Curnutte, J.T.; Lawrence, J.H.; Yue, P.; Bronson, M.D.; Lu, G.; Conley, P.B.; et al. Full Study Report of Andexanet Alfa for Bleeding Associated with Factor Xa Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegal, D.M.; Curnutte, J.T.; Connolly, S.J.; Lu, G.; Conley, P.B.; Wiens, B.L.; Mathur, V.S.; Castillo, J.; Bronson, M.D.; Leeds, J.M.; et al. Andexanet Alfa for the Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitor Activity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency; Ondexxya, B.L. Ondexxya. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ondexxya (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Xia, X.; Ren, Q.; Cui, J.; Dong, H.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Guan, S.; Huang, C.; Yin, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Radiomics for predicting revised hematoma expansion with the inclusion of intraventricular hemorrhage growth in patients with supratentorial spontaneous intraparenchymal hematomas. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchell, S.R.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Hematoma Expansion Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Mechanisms Targeting the Coagulation Cascade and Platelet Activation. Curr. Drug. Targets 2017, 18, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.S.; Huang, Y.; Arima, H.; Heeley, E.; Skulina, C.; Parsons, M.W.; Peng, B.; Li, Q.; Su, S.; Tao, Q.L.; et al. Effects of Early Intensive Blood Pressure-Lowering Treatment on the Growth of Hematoma and Perihematomal Edema in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage: The Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction in Acute Cerebral Haemorrhage Trial (INTERACT). Stroke 2010, 41, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Foster, L.D.; Lobanova, I.; Huang, W.; Suarez, J.I. Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering in Patients with Moderate to Severe Grade Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage: Post Hoc Analysis of Antihypertensive Treatment of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage (ATACH)-2 Trial. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 49, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, M.L.; Tao, H.; Haverbusch, M.; Sekar, P.; Kleindorfer, D.; Kissela, B.; Khatri, P.; Stettler, B.; Adeoye, O.; Moomaw, C.J.; et al. Warfarin use leads to larger intracerebral hematomas. Neurology 2008, 71, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramatsu, J.B.; Gerner, S.T.; Schellinger, P.D.; Glahn, J.; Endres, M.; Sobesky, J.; Flechsenhar, J.; Neugebauer, H.; Jüttler, E.; Grau, A.; et al. Anticoagulant reversal, blood pressure levels, and anticoagulant resumption in patients with anticoagulation-related intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA 2015, 313, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwah, L.K.; Diong, J. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS). J. Physiother. 2014, 60, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, T.J.; Dawson, J.; Walters, M.R.; Lees, K.R. Reliability of the modified Rankin Scale: A systematic review. Stroke 2009, 40, 3393–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Andexxa (Coagulation Factor Xa (Recombinant), Inactivated-Zhzo) [Package Insert]. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/113279/download (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Althaus, K.D.J.; Hyrenbach, S.; Kassubek, J.; Pinkhardt, E.; Ludolph, A. MRI as a first-line imaging modality in acute ischemic stroke—A sustainable concept. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, H.P.; Unrath, A.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J. Preservation of diffusion tensor properties during spatial normalization by use of tensor imaging and fibre tracking on a normal brain database. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, N99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, C.; Knauer, K.; Muller, S.; Ludolph, A.C.; Bengel, D.; Muller, H.P.; Huber, R. A biochemical marker panel in MRI-proven hyperacute ischemic stroke-a prospective study. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehrieder, D.; Layer, K.; Müller, H.P.; Rücker, V.; Kassubek, J.; Juettler, E.; Neugebauer, H. Association of Infarct Volume Before Hemicraniectomy and Outcome After Malignant Infarction. Neurology 2021, 96, e2704–e2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchuk, A.M.; Yue, P.; Zotova, E.; Nakamya, J.; Xu, L.; Milling, T.J., Jr.; Ohara, T.; Goldstein, J.N.; Middeldorp, S.; Verhamme, P.; et al. Hemostatic Efficacy and Anti-FXa (Factor Xa) Reversal with Andexanet Alfa in Intracranial Hemorrhage: ANNEXA-4 Substudy. Stroke 2021, 52, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, A.A.; Ammar, M.A.; Owusu, K.A.; Brown, S.C.; Kaddouh, F.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Acosta, J.N.; Falcone, G.J. Andexanet Alfa Versus 4-Factor Prothrombin Complex Concentrate for Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Intracranial Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2021, 35, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, M.E.; Das, A.S.; Hayes, B.D.; Rosenthal, E.S.; Rosovsky, R.P.; Fuh, L.; Patel, A.B.; Goldstein, J.N.; Roberts, R.J. Evaluation of andexanet alfa and four-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (4F-PCC) for reversal of rivaroxaban- and apixaban-associated intracranial hemorrhages. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Overall FXa-I-ICH * (n = 46) | FXa-I-ICH with AA Treatment (n = 23) | FXa-I-ICH with UC (n = 23) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y, mean ± SD | 79.8 ± 7.2 | 78.1 ± 7.3 | 81.5 ± 6.9 | 0.11 |
| Male, n (%) | 25 (54.4%) | 14 (60.9%) | 11 (47.8%) | 0.37 |
| risk factors n (%) | ||||
| aHT | 42 (91.3%) | 21 (91.3%) | 21 (91.3%) | 1.00 |
| atrial fibrillation | 40 (87.0%) | 19 (82.6%) | 21 (91.3%) | 0.67 |
| renal Insufficiency | 6 (13.0%) | 4 (17.4%) | 2 (8.7%) | 0.67 |
| coronary heart disease | 16 (34.8%) | 8 (34.8%) | 8 (34.8%) | 1.00 |
| Indication of FXa inhibition, n (%) | ||||
| Atrial fibrillation | 40 (87.0%) | 19 (82.6%) | 21 (91.3%) | 0.67 |
| Venous thromboembolic disease | 8 (17.4%) | 6 (26.1%) | 2 (8.7%) | 0.24 |
| Unclear indication | 1 (2.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1.00 |
| FXa inhibitor therapy, n (%) | ||||
| Rivaroxaban | 27 (58.7%) | 17 (73.9%) | 10 (43.5%) | 0.12 |
| Apixaban | 14 (30.4%) | 5 (21.7%) | 9 (39.1%) | |
| Edoxaban | 5 (10.9%) | 1 (4.3%) | 4 (17.4%) | |
| Scores, median (IQR) | ||||
| NIHSS score admission | 10.0 (4.0–20.0) | 11.0 (9.0–21.0) | 7.0 (2.0–19.0) | 0.03 |
| Modified Rankin Scale score ‡ | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 3.0 (1.0–4.0) | 1.0 (1.0–3.0) | 0.06 |
| Imaging at admission | ||||
| CT/MRI at admission n (%) | 8 (17.4%)/38 (82.6%) | 3 (13.0%)/20 (87.0%) | 5 (21.7%)/18 (78.3%) | 0.70 |
| ICH volume, mL, Median (IQR) (min–max) | 20.5 (9.4–37.1) (2.3–132.5) | 19.8 (11.4–50.0) (4.4–123.6) | 24.7 (6.5–36.1) (2.3–132.5) | 0.46 |
| laboratory, median (IQR) | ||||
| INR | 1.17 (1.08–1.27) | 1.11 (1.11–1.27) | 1.17 (1.04–1.30) | 0.48 |
| PTT, s | 33.7 (30.8–36.7) | 33.4 (30.3–36.7) | 33.8 (31.7–40.2) | 0.69 |
| Anti-FXa-activity | ||||
| Rivaroxaban (ng/mL) | 147.0 (58.7–241.0) | 166.7 (93.1–241.0) | 102.9 (33.3–233.8) | 0.38 |
| Apixaban (ng/mL) | 96.4 (66.3–138.3) | 100.8 (85.8–121.8) | 92.0 (66.3–196.6) | 1.00 |
| Edoxaban § (ng/mL) | 16.0, 26.2, 372.0 | - | 16.0, 26.2, 372.0 | - |
| Overall FXa-I-ICH * (n = 46) | FXa-I-ICH with AA Treatment (n = 23) | FXa-I-ICH with UC Treatment (n = 23) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imaging | ||||
| CT/MRI follow-up n (%) ‡ | 16/24 | 6 (28.6%)/15 (71.4%) | 10 (52.6%)/9 (47.4%) | 0.12 |
| Hematoma volume follow-up, ml; median (IQR) (min-max) ‡ | 20.0 (8.2–33.4) (1.7–139.8) | 20.8 (11.2–35.2) (3.0–75.2) | 14.5 (5.8–31.7) (1.7–139.8) | 0.53 |
| Number of patients with hematoma expansion >33%, n (%) ‡ | 6 (26.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (26.1%) | 0.02 |
| Clinical outcome | ||||
| Good outcome (mRS ≤ 3) on discharge n (%) | 11 (23.9%) | 2 (8.7%) | 9 (39.1%) | 0.02 |
| NIHSS score on discharge median (IQR) | 9.0 (2.0–42.0) | 13.0 (6.0–42.0) | 4.0 (2.0–42.0) | 0.05 |
| Death/palliative course on discharge n (%) | 16 (34.8) | 10 (43.5%) | 6 (26.1%) | 0.22 |
| Adverse events | ||||
| Total thromboembolic events n (%) | 8 (17.4%) | 7 (30.4%) | 1 (4.3%) | 0.05 |
| Ischemic stroke n (%) | 8 (17.4%) | 7 (30.4%) | 1 (4.3%) | 0.05 |
| Myocardial infarction n (%) | 3 (6.5%) | 3 (13.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.23 |
| Both # n (%) | 3 (6.5%) | 3 (13.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.23 |
| Deep vein thrombosis n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Pulmonary embolism n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Pneumonia | 12 (26.1%) | 8 (34.8%) | 4 (17.4%) | 0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rauch, S.; Müller, H.-P.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J.; Althaus, K. Andexanet Alfa for Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Intracranial Hemorrhage: Observational Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123399
Rauch S, Müller H-P, Dreyhaupt J, Ludolph AC, Kassubek J, Althaus K. Andexanet Alfa for Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Intracranial Hemorrhage: Observational Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123399
Chicago/Turabian StyleRauch, Sebastian, Hans-Peter Müller, Jens Dreyhaupt, Albert C. Ludolph, Jan Kassubek, and Katharina Althaus. 2022. "Andexanet Alfa for Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Intracranial Hemorrhage: Observational Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123399
APA StyleRauch, S., Müller, H.-P., Dreyhaupt, J., Ludolph, A. C., Kassubek, J., & Althaus, K. (2022). Andexanet Alfa for Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitors in Intracranial Hemorrhage: Observational Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123399






