Prediction of Carotid In-Stent Restenosis by Computed Tomography Angiography Carotid Plaque-Based Radiomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
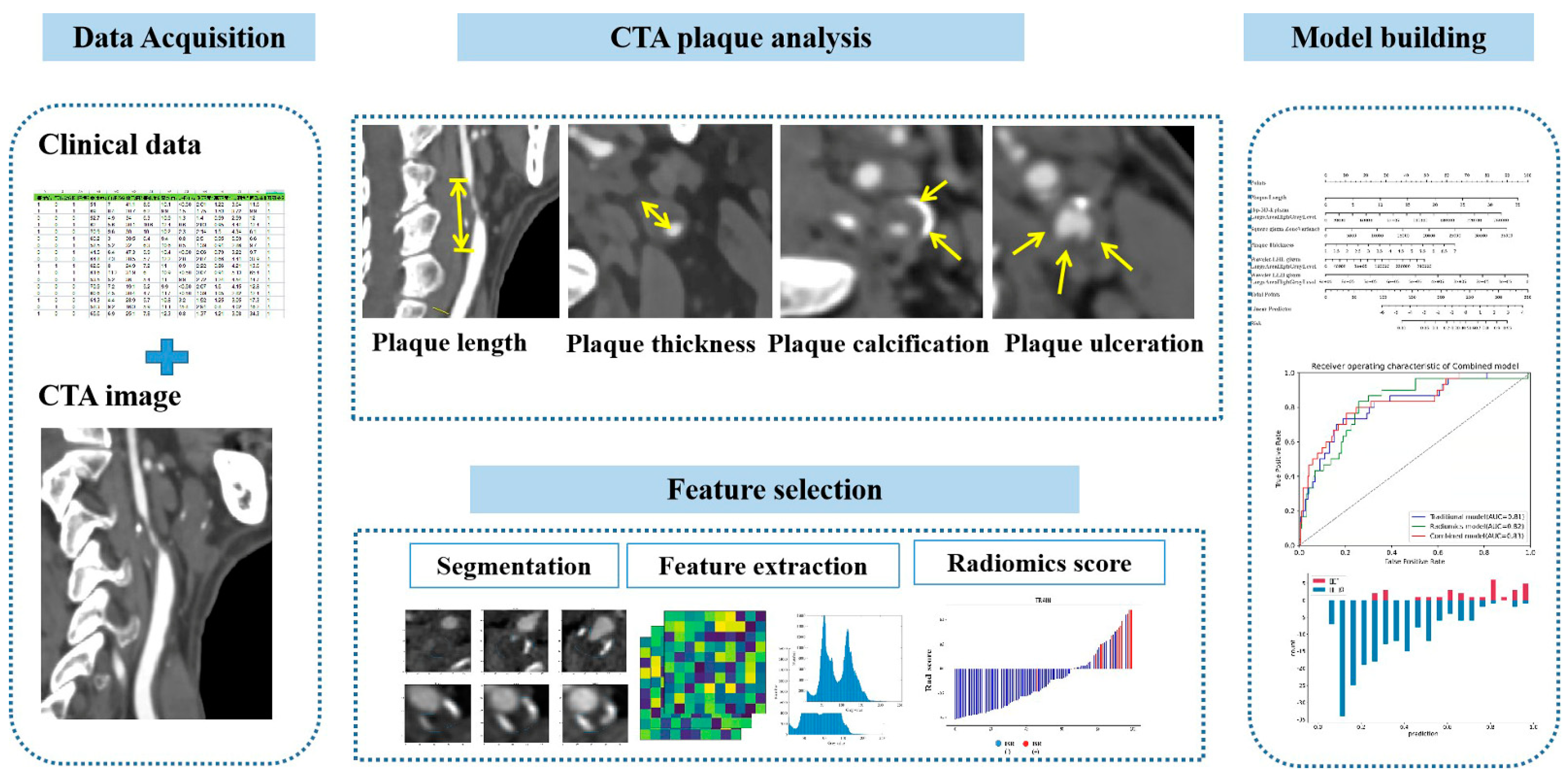
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. CTA Technique
2.3. CAS
2.4. Clinical and Imaging Data
2.5. Conventional CTA Plaque Analysis
2.6. Radiomic Calculations
2.7. Follow-Up Assessments
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
3.2. Traditional Predictive Models
3.3. Radiomics Prediction Model
3.4. Combined Prediction Model
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, E.I.; Mocco, J.; Samuelson, R.M.; Ecker, R.D.; Jahromi, B.S.; Hopkins, L.N. Optimal treatment of carotid artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janczak, D.; Malinowski, M.; Ziomek, A.; Kobecki, J.; Lesniak, M.; Dorobisz, T.; Dorobisz, K.; Janczak, D.; Chabowski, M. Carotid artery stenting versus endarterectomy for the treatment of both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with carotid artery stenosis: 2 years’ experience in a high-volume center. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, N.; Hagiwara, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Soga, K.; Tsuchihashi, Y.; Otsubo, H.; Tatsuno, K.; Takaishi, S.; Usuki, N.; Yoshie, T.; et al. Preprocedural Carotid Plaque Echolucency as a Predictor of In-Stent Intimal Restenosis after Carotid Artery Stenting. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonati, L.; Dobson, J.; Featherstone, R.L.; Ederle, J.; van der Worp, H.B.; de Borst, G.J.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Beard, J.D.; Cleveland, T.; Engelter, S.; et al. Long-term outcomes after stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of symptomatic carotid stenosis: The International Carotid Stenting Study (ICSS) randomised trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, K.; Gao, F.; Mo, D.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Gu, W.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X.; et al. Outcome of endovascular recanalization for intracranial in-stent restenosis. J. Neuroint. Surg. 2020, 12, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, B.K.; Beach, K.W.; Roubin, G.S.; Lutsep, H.L.; Moore, W.S.; Malas, M.B.; Chiu, D.; Gonzales, N.R.; Burke, J.L.; Rinaldi, M.; et al. Restenosis after carotid artery stenting and endarterectomy: A secondary analysis of CREST, a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Fiorella, D.; Lynn, M.J.; Turan, T.N.; Cotsonis, G.A.; Lane, B.F.; Montgomery, J.; Janis, L.S.; Chimowitz, M.I. Nonprocedural Symptomatic Infarction and In-Stent Restenosis after Intracranial Angioplasty and Stenting in the SAMMPRIS Trial (Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for the Prevention of Recurrent Stroke in Intracranial Stenosis). Stroke 2017, 48, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, M.; Exner, M.; Mlekusch, W.; Rumpold, H.; Ahmadi, R.; Sabeti, S.; Lang, W.; Wagner, O.; Minar, E. Acute-phase response after stent implantation in the carotid artery: Association with 6-month in-stent restenosis. Radiology 2003, 227, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, J.; Tian, C. Plaque Length Predicts the Incidence of Microembolic Signals in Acute Anterior Circulation Stroke. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 2005369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, H.; Al-Dasuqi, K.; Knight-Greenfield, A.; Giambrone, A.; Delgado, D.; Ebani, E.; Kamel, H.; Gupta, A. Association between carotid plaque features on CTA and cerebrovascular ischemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Baradaran, H.; Kamel, H.; Pandya, A.; Mangla, A.; Dunning, A.; Marshall, R.S.; Sanelli, P.C. Evaluation of computed tomography angiography plaque thickness measurements in high-grade carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 2014, 45, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homburg, P.J.; Rozie, S.; van Gils, M.J.; Bouwhuijsen, Q.J.V.D.; Niessen, W.J.; Dippel, D.W.; van der Lugt, A. Association between carotid artery plaque ulceration and plaque composition evaluated with multidetector CT angiography. Stroke 2011, 42, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, J.M.; Babiarz, L.S.; Forero, N.P.; Murphy, E.K.; Schaefer, P.W.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Lev, M.H. Arterial wall enhancement overlying carotid plaque on CT angiography correlates with symptoms in patients with high grade stenosis. Stroke 2009, 40, 1894–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anzidei, M.; Napoli, A.; Zaccagna, F.; Di Paolo, P.L.; Saba, L.; Marincola, B.C.; Zini, C.; Cartocci, G.; Di Mare, L.; Catalano, C.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of colour Doppler ultrasonography, CT angiography and blood-pool-enhanced MR angiography in assessing carotid stenosis: A comparative study with DSA in 170 patients. Radiol. Med. 2012, 117, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolossváry, M.; De Cecco, C.N.; Feuchtner, G.; Maurovich-Horvat, P. Advanced atherosclerosis imaging by CT: Radiomics, machine learning and deep learning. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2019, 13, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Siddique, M.; Antoniades, C. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: A radiomic guide to precision phenotyping of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 2040–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial. Methods, patient characteristics, and progress. Stroke 1991, 22, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baradaran, H.; Gupta, A. Carotid Vessel Wall Imaging on CTA. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saba, L.; Saam, T.; Jäger, H.R.; Yuan, C.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Saloner, D.; Wasserman, B.A.; Bonati, L.; Wintermark, M. Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, W.; Adib, K.; Natdanai, P.; Carmona-Rubio, A.; Karki, R.; Paily, J.; Ahmed, M.A.-A.; Vakkalanka, S.; Madam, N.; Gudleski, G.D.; et al. High-risk carotid plaques identified by CT-angiogram can predict acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 33, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Chen, Z.; Liang, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Mean Platelet Volume as a Predictor for Restenosis after Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting. Stroke 2018, 49, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidegger, M.; Kneihsl, M.; Niederkorn, K.; Deutschmann, H.; Augustin, M.; Wünsch, G.; Fandler-Höfler, S.; Horner, S.; Fazekas, F.; Enzinger, C.; et al. Mean Platelet Volume Does Not Predict Restenosis after Carotid Artery Stenting in Whites. Stroke 2020, 51, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhou, G.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.; Ye, Z.; Jiang, F. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio: Novel markers for the diagnosis and prognosis in patients with restenosis following CAS. Biomark. Med. 2020, 14, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Palop, R.; Carrillo, P.; Cordero, A.; Frutos, A.; Mateo, I.; Mashlab, S.; Roldán, J. Effect of lesion length on functional significance of intermediate long coronary lesions. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 81, E186–E194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Papadopoulou, S.-L.; Pugliese, F.; Russo, B.; Dharampal, A.S.; Dedic, A.; Kitslaar, P.H.; Broersen, A.; Meijboom, W.B.; van Geuns, R.-J.; et al. Quantitative computed tomographic coronary angiography: Does it predict functionally significant coronary stenoses? Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.S.; Kim, B.M.; Suh, S.H.; Jeon, P.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, B.-S.; Kim, K.H.; Heo, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, Y.D. Wingspan stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: Clinical outcomes and risk factors for in-stent restenosis. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.F.; Christopher, S.; Amankulor, N.; Din, R.; Poullis, M.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Ghogawala, Z. Extracranial carotid plaque length and parent vessel diameter significantly affect baseline ipsilateral intracranial blood flow. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonati, L.H.; Ederle, J.; Dobson, J.; Engelter, S.; Featherstone, R.L.; Gaines, P.A.; Beard, J.D.; Venables, G.S.; Markus, H.S.; Clifton, A.; et al. Length of carotid stenosis predicts peri-procedural stroke or death and restenosis in patients randomized to endovascular treatment or endarterectomy. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Cheng, X.-Q.; Liu, H.-Y.; Bi, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-N.; Lv, W.-Z.; Xiong, L.; Deng, Y.-B. Relation of Carotid Plaque Features Detected with Ultrasonography-Based Radiomics to Clinical Symptoms. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, A.; Lv, P.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Lin, J. Identification of high-risk carotid plaque with MRI-based radiomics and machine learning. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccagna, F.; Ganeshan, B.; Arca, M.; Rengo, M.; Napoli, A.; Rundo, L.; Groves, A.M.; Laghi, A.; Carbone, I.; Menezes, L.J. CT texture-based radiomics analysis of carotid arteries identifies vulnerable patients: A preliminary outcome study. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, E.P.V.; Rundo, L.; Tarkin, J.M.; Evans, N.R.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Coughlin, P.A.; Pavey, H.; Wall, C.; Zaccagna, F.; Gallagher, F.A.; et al. Assessing robustness of carotid artery CT angiography radiomics in the identification of culprit lesions in cerebrovascular events. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 221) | ISR Group (n = 30) | Non-ISR Group (n = 191) | Univariate Analysis p-Value | Multivariate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | |||||
| Demographics | ||||||
| Age, y, mean ± SD | 66.89 ± 8.07 | 68.73 ± 6.34 | 66.60 ± 8.29 | 0.37 | ||
| Male, n (%) | 186 (84.16) | 28 (93.33) | 158 (82.72) | 0.23 | ||
| Risk factors | ||||||
| Smoking, n (%) | 100 (45.25) | 13 (43.33) | 87 (45.55) | 0.82 | ||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 195 (88.24) | 29 (96.67) | 166 (86.91) | 0.22 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 78 (35.29) | 10 (33.33) | 68 (35.79) | 0.79 | ||
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 50 (22.62) | 9 (30.00) | 41 (21.47) | 0.30 | ||
| Past cerebral infarction, n (%) | 77 (34.84) | 16 (53.33) | 61 (31.94) | 0.02 | 0.59 (0.26–1.32) | 0.20 |
| Laboratory parameters | ||||||
| Neutrophil percentage, %, mean ± SD | 61.98 ± 8.93 | 62.62 ± 8.95 | 61.88 ± 8.94 | 0.59 | ||
| White blood cell count, 109/L, mean ± SD | 6.99 ± 2.38 | 7.97 ± 3.61 | 6.84 ± 2.10 | 0.17 | ||
| Lymphocyte percentage, %, mean ± SD | 27.80 ± 8.22 | 27.39 ± 7.64 | 27.87 ± 8.32 | 0.77 | ||
| Glycated hemoglobin, %, mean ± SD | 6.47 ± 1.20 | 6.30 ± 1.12 | 6.46 ± 1.20 | 0.43 | ||
| Mean platelet volume, fL, mean ± SD | 10.82 ± 1.25 | 11.29 ± 1.00 | 10.82 ± 1.25 | 0.02 | 1.32 (0.94–1.83) | 0.11 |
| C-reactive protein level, mg/L, mean ± SD | 4.10 ± 6.97 | 3.76 ± 4.86 | 4.10 ± 6.97 | 0.59 | ||
| Low-density lipoprotein, mmol/L, mean ± SD | 2.43 ± 0.90 | 2.36 ± 0.83 | 2.44 ± 0.91 | 0.86 | ||
| High-density lipoprotein, mmol/L, mean ± SD | 1.04 ± 0.34 | 0.99 ± 0.18 | 1.05 ± 0.35 | 0.57 | ||
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L, mean ± SD | 4.14 ± 1.09 | 4.14 ± 0.85 | 4.14 ± 1.12. | 0.74 | ||
| Homocysteine, mmol/L, mean ± SD | 16.06 ± 9.15 | 19.66 ± 12.00 | 15.49 ± 8.52 | 0.04 | 1.02 (0.98–1.07) | 0.28 |
| Carotid artery stenting | ||||||
| Open cell stent, n (%) | 158 (71.49) | 23 (76.67) | 135 (70.68) | 0.50 | ||
| Pre-dilation, n (%) | 192 (86.88) | 26 (86.67) | 166 (86.91) | 0.31 | ||
| Residual stenosis, %, mean ± SD | 10.38 ± 11.27 | 13.83 ± 14.37 | 9.84 ± 10.65 | 0.18 | ||
| Lesions | ||||||
| Stenosis, %, mean ± SD | 77.03 ± 13.38 | 83.10 ± 10.76 | 76.07 ± 13.52 | 0.01 | 2.17 (0.06–73.87) | 0.67 |
| Soft plaques n (%) | 164 (74.21) | 27 (90.00) | 137 (71.73) | 0.03 | 3.24 (0.98–10.67) | 0.05 |
| Lesion length, mm, mean ± SD | 15.49 ± 7.00 | 24.50 ± 5.60 | 14.08 ± 6.09 | <0.001 | 1.12 (1.06–1.18) | <0.005 |
| Plaque thickness, mm, mean ± SD | 3.30 ± 1.26 | 4.51 ± 1.09 | 3.10 ± 1.18 | <0.001 | 1.79 (1.26–2.55) | <0.005 |
| Plaque ulceration, n (%) | 83 (37.56) | 11 (36.67) | 72 (44.27) | 0.91 | ||
| Plaque enhancement, n (%) | 81 (36.65) | 13 (43.33) | 68 (35.60) | 0.41 | ||
| Positive remodeling, n (%) | 101 (45.70) | 21 (70.00) | 80 (41.88) | 0.004 | 0.65 (0.26–1.61) | 0.35 |
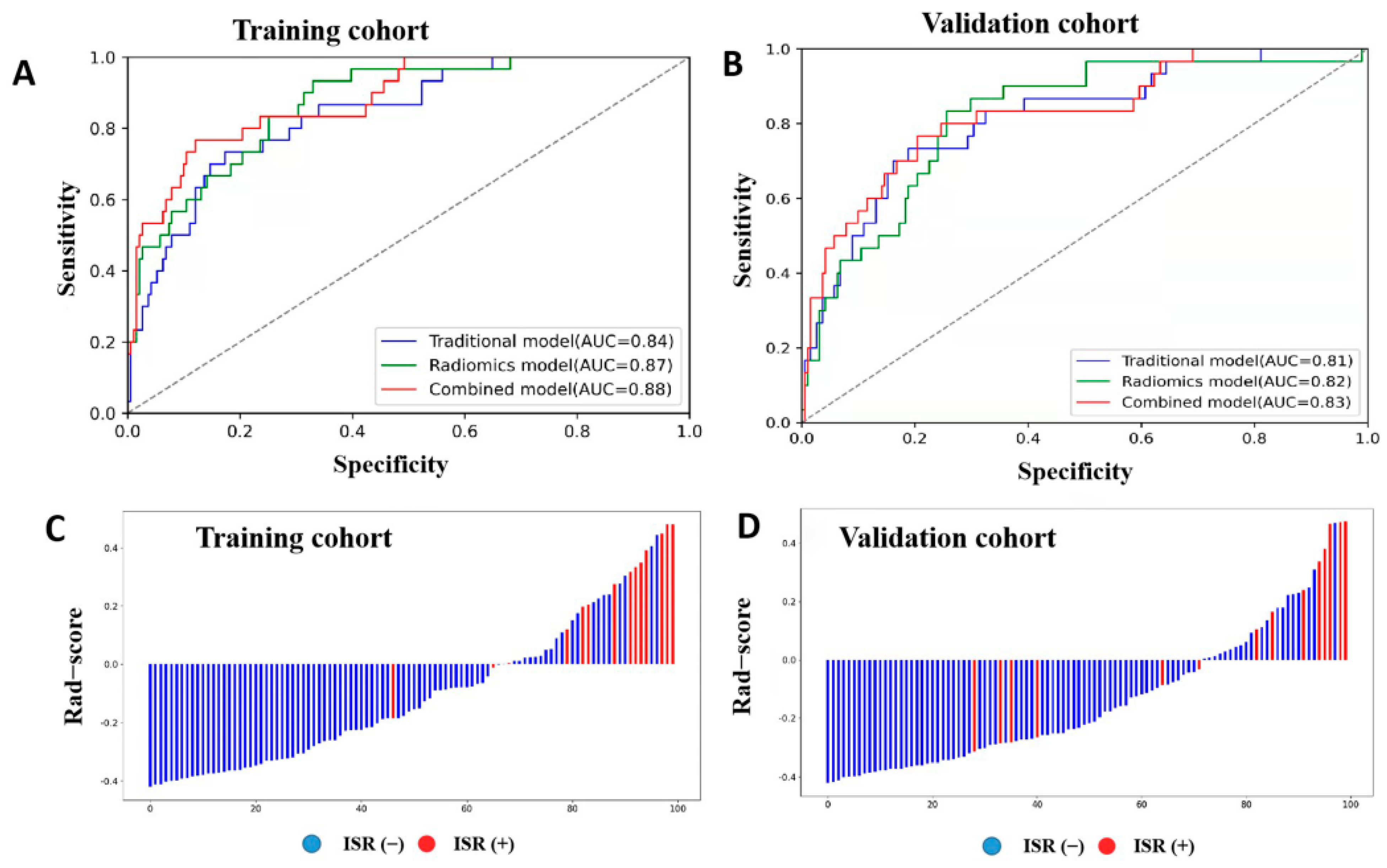
| Predictive Models | Cohort | AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional model | Training | 0.84 (0.77–0.91) | 0.77 | 0.72 |
| Validation | 0.81 (0.73–0.90) | 0.73 | 0.71 | |
| Radiomics model | Training | 0.87 (0.81–0.93) | 0.77 | 0.75 |
| Validation | 0.82 (0.74–0.90) | 0.77 | 0.74 | |
| Combined model | Training | 0.88 (0.82–0.95) | 0.80 | 0.79 |
| Validation | 0.83 (0.74–0.91) | 0.77 | 0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G. Prediction of Carotid In-Stent Restenosis by Computed Tomography Angiography Carotid Plaque-Based Radiomics. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113234
Cheng X, Dong Z, Liu J, Li H, Zhou C, Zhang F, Wang C, Zhang Z, Lu G. Prediction of Carotid In-Stent Restenosis by Computed Tomography Angiography Carotid Plaque-Based Radiomics. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113234
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xiaoqing, Zheng Dong, Jia Liu, Hongxia Li, Changsheng Zhou, Fandong Zhang, Churan Wang, Zhiqiang Zhang, and Guangming Lu. 2022. "Prediction of Carotid In-Stent Restenosis by Computed Tomography Angiography Carotid Plaque-Based Radiomics" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113234
APA StyleCheng, X., Dong, Z., Liu, J., Li, H., Zhou, C., Zhang, F., Wang, C., Zhang, Z., & Lu, G. (2022). Prediction of Carotid In-Stent Restenosis by Computed Tomography Angiography Carotid Plaque-Based Radiomics. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113234







