Association of Intradialytic Hypotension and Ultrafiltration with AKI-D Outcomes in the Outpatient Dialysis Setting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO); Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, V.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Huang, T.-M.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lai, C.-F.; Shiao, C.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, S.-L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; et al. Long-Term Risk of Coronary Events after AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerdá, J.; Liu, K.D.; Cruz, D.N.; Jaber, B.L.; Koyner, J.L.; Heung, M.; Okusa, M.D.; Faubel, S. Promoting Kidney Function Recovery in Patients with AKI Requiring RRT. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.A.J.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchino, S. Acute Renal Failure in Critically Ill Patients. A Multinational, Multicenter Study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, R.K.; Mcculloch, C.E.; Dudley, R.A.; Lo, L.J.; Hsu, C.-Y. Temporal Changes in Incidence of Dialysis-Requiring AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoste, E.A.J.; Kellum, J.A.; Selby, N.M.; Zarbock, A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Cerdá, J.; Chawla, L.S. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Turgut, F.; Gautam, J.K.; Gautam, S.C. Determinants of Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury: Clinical Predictors and Beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.S.; Chopra, T.; Ma, J.Z.; Xin, W.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Long-Term Outcomes and Associated Risk Factors of Post-Hospitalization Dialysis-Dependent Acute Kidney Injury Patients. Nephron 2017, 137, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, M.; Steffick, D.E.; Zivin, K.; Gillespie, B.W.; Banerjee, T.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Powe, N.R.; Pavkov, M.E.; Williams, D.E.; Saran, R.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury Recovery Pattern and Subsequent Risk of CKD: An Analysis of Veterans Health Administration Data. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Chertow, G.M.; Mcculloch, C.E.; Fan, D.; Ordoñez, J.D.; Go, A.S. Nonrecovery of Kidney Function and Death after Acute on Chronic Renal Failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gautam, S.C.; Brooks, C.H.; Balogun, R.A.; Xin, W.; Ma, J.Z.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M. Predictors and Outcomes of Post-Hospitalization Dialysis Dependent Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2015, 131, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Okusa, M.D. Recovery from Acute Kidney Injury: Predicting Outcomes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 528–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, A.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Liu, K.D.; Goldstein, S.L.; Agarwal, A.; Okusa, M.D.; Cerda, J. Recovery after Critical Illness and Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.H.; Wald, R.; Blum, D.; Mcarthur, E.; James, M.T.; Burns, K.E.A.; Friedrich, J.O.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Nash, D.M.; Lebovic, G.; et al. Predicting mortality among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury treated with renal replacement therapy: Development and validation of new prediction models. J. Crit. Care 2020, 56, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.J.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Parikh, R.; Mcculloch, C.E.; Tan, T.C.; Liu, K.D.; Hsu, R.K.; Pravoverov, L.; Zheng, S.; Go, A.S. Predicting Renal Recovery After Dialysis-Requiring Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugan, R.; Kerti, S.J.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Gallagher, M.; Clermont, G.; Palevsky, P.M.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R. Association of Net Ultrafiltration Rate with Mortality Among Critically Ill Adults with Acute Kidney Injury Receiving Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Kerti, S.J.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Gallagher, M.; Neto, A.S.; Clermont, G.; Ronco, C.; Palevsky, P.M.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R. Association between Net Ultrafiltration Rate and Renal Recovery among Critically Ill Adults with Acute Kidney Injury Receiving Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Cohort Study. Blood Purif. 2021, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Sun, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, H.; Xing, C. Relationship among Mortality of Patients with Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Surgery, Fluid Balance and Ultrafiltration of Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Study. Blood Purif. 2017, 44, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Cheyron, D.; Terzi, N.; Seguin, A.; Valette, X.; Prevost, F.; Ramakers, M.; Daubin, C.; Charbonneau, P.; Parienti, J.-J. Use of online blood volume and blood temperature monitoring during haemodialysis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: A single-centre randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douvris, A.; Zeid, K.; Hiremath, S.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Wald, R.; Beaubien-Souligny, W.; Kong, J.; Ronco, C.; Clark, E.G. Mechanisms for hemodynamic instability related to renal replacement therapy: A narrative review. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45 (Suppl. S3), S1–S153. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Bommel, E.; Bouvy, N.D.; So, K.L.; Zietse, R.; Vincent, H.H.; Bruining, H.A.; Weimar, W. Acute dialytic support for the critically ill: Intermittent hemodialysis versus continuous arteriovenous hemodiafiltration. Am. J. Nephrol. 1995, 15, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Griesbach, D.; Baumgartel, M.; Weihprecht, H.; Schmieder, R.E.; Geiger, H. Effects of continuous haemofiltration vs intermittent haemodialysis on systemic haemodynamics and splanchnic regional perfusion in septic shock patients: A prospective, randomized clinical trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehlinger, D.E.; Jakob, S.M.; Ferrari, P.; Eichelberger, M.; Huynh-Do, U.; Marti, H.-P.; Mohaupt, M.G.; Vogt, B.; Rothen, H.U.; Regli, B.; et al. Comparison of continuous and intermittent renal replacement therapy for acute renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinsonneau, C.; Camus, C.; Combes, A.; de Beauregard, M.A.C.; Klouche, K.; Boulain, T.; Pallot, J.-L.; Chiche, J.-D.; Taupin, P.; Landais, P.; et al. Continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration versus intermittent haemodialysis for acute renal failure in patients with multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabindranath, K.; Adams, J.; Macleod, A.M.; Muirhead, N. Intermittent versus continuous renal replacement therapy for acute renal failure in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 3, CD003773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajewski, R.; Gipson, P.; Heung, M. Predictors of post-hospitalization recovery of renal function among patients with acute kidney injury requiring dialysis. Hemodial. Int. 2018, 22, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Astephen, P.; Andreou, P.; Beed, S.; Lundrigan, P.; Jindal, K. Blood volume monitoring in intermittent hemodialysis for acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitker, L.; Bayle, F.; Yonis, H.; Gobert, F.; Leray, V.; Taponnier, R.; Debord, S.; Stoian-Cividjian, A.; Guérin, C.; Richard, J.-C. Prevalence and risk factors of hypotension associated with preload-dependence during intermittent hemodialysis in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silversides, J.A.; Pinto, R.; Kuint, R.; Wald, R.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Lapinsky, S.E.; Adhikari, N.K. Fluid balance, intradialytic hypotension, and outcomes in critically ill patients undergoing renal replacement therapy: A cohort study. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schortgen, F.; Soubrier, N.; Delclaux, C.; Thuong, M.; Girou, E.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Lemaire, F.; Brochard, L. Hemodynamic Tolerance of Intermittent Hemodialysis in Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrees, F.Y.; Katari, S.; Baty, J.D.; Vijayan, A. A Pilot Study Evaluating the Effect of Cooler Dialysate Temperature on Hemodynamic Stability during Prolonged Intermittent Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvris, A.; Malhi, G.; Hiremath, S.; Mcintyre, L.; Silver, S.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Wald, R.; Ronco, C.; Sikora, L.; Weber, C.; et al. Interventions to prevent hemodynamic instability during renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Characteristic | Total N = 273 | Deceased N = 28 (%) | ESKD & N = 123 (%) | Recovered N = 122 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 115 | 13 (46.4) | 54 (43.9) | 48 (39.3) |
| Male | 158 | 15 (53.6) | 69 (56.1) | 74 (60.7) | |
| Race | American Indian | 1 | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 0 (0) |
| Black | 72 | 7 (25.0) | 34 (27.6) | 31 (25.4) | |
| Hispanic | 6 | 0 (0) | 6 (4.9) | 0 (0) | |
| Other | 8 | 2 (7.1) | 3 (2.4) | 3 (2.5) | |
| While | 182 | 19 (67.9) | 78 (63.4) | 85 (69.7) | |
| Missing | 4 | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 3 (2.5) | |
| CHF * | No | 211 | 22 (78.6) | 98 (79.7) | 91 (74.6) |
| Yes | 49 | 5 (17.9) | 23 (18.7) | 21 (17.2) | |
| Missing | 13 | 1 (3.6) | 2 (1.6) | 10 (8.2) | |
| CAD # | No | 185 | 20 (71.4) | 82 (66.7) | 83 (68.0) |
| Yes | 75 | 7 (25) | 39 (31.7) | 29 (23.8) | |
| Missing | 13 | 1 (3.6) | 2 (1.6) | 10 (8.2) | |
| Hypertension | No | 47 | 2 (7.1) | 18 (14.6) | 27 (22.1) |
| Yes | 213 | 25 (89.3) | 103 (83.7) | 85 (69.7) | |
| Missing | 13 | 1 (3.6) | 2 (1.6) | 10 (8.2) | |
| Prior AKI | No | 147 | 15 (53.6) | 59 (48.0) | 73 (59.8) |
| Yes | 99 | 10 (35.7) | 56 (45.5) | 33 (27.0) | |
| Missing | 27 | 3 (10.7) | 8 (6.5) | 16 (13.1) | |
| Diabetes | No | 158 | 16 (57.1) | 66 (53.7) | 76 (62.3) |
| Yes | 115 | 12 (42.9) | 57 (46.3) | 46 (37.7) |
| Odds Ratio Estimates | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covariate | 90 Day Outcome | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | Covariate | 90 Day Outcome | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Hypotensive Episodes, 2nd quartile vs. 1st | Deceased | 1.1 | 0.3–4.1 | Hypotensive Episodes, 2nd quartile vs. 1st | ESKD * | 2.3 | 1.0–5.7 |
| Hypotensive Episodes, 3rd quartile vs. 1st | Deceased | 1.2 | 0.3–4.6 | Hypotensive Episodes, 3rd quartile vs. 1st | ESKD | 3.8 | 1.4–9.8 |
| Hypotensive Episodes, 4th quartile vs. 1st | Deceased | 0.5 | 0.1–2.5 | Hypotensive Episodes, 4th quartile vs. 1st | ESKD | 2.7 | 1.0–7.9 |
| Prior AKI, Yes vs. No | Deceased | 1.8 | 0.6–4.8 | Prior AKI, Yes vs. No | ESKD | 2.1 | 1.1–4.1 |
| Age | Deceased | 1.1 | 1.0–1.1 | Age | ESKD | 1.0 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Baseline Kidney Function | Deceased | 1.0 | 1.0–1.0 | Baseline Kidney Function | ESKD | 1.0 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Hypertension, Yes, vs. No | Deceased | 2.5 | 0.5–12.2 | Hypertension, Yes, vs. No | ESKD | 1.4 | 0.9–3.2 |
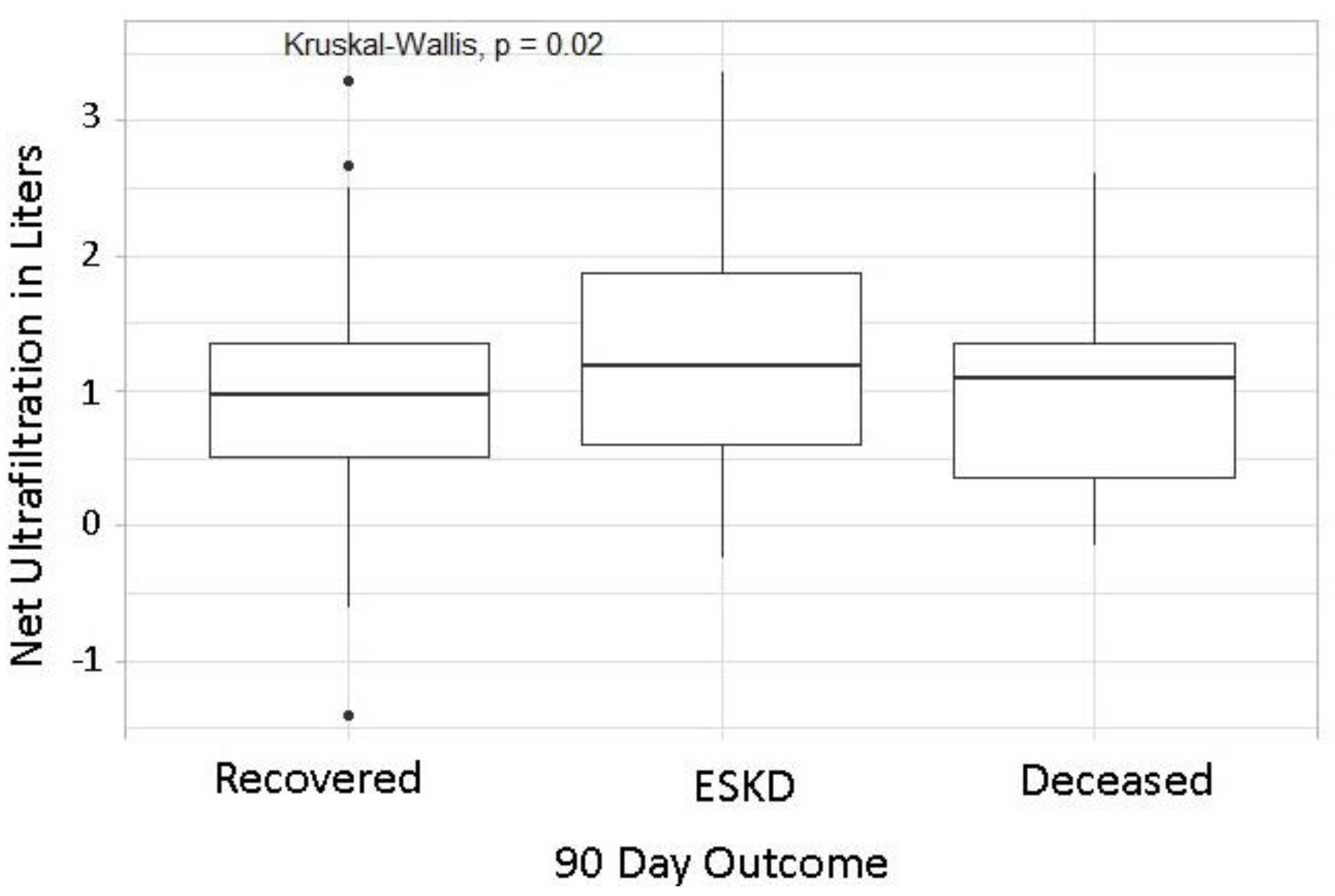
| Net Ultrafiltration, Liters | Deceased | 1.0 | 0.5–2.0 | Net Ultrafiltration, Liters | ESKD | 1.5 | 1.0–2.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Casimir, E.; Lyons, G.R.; Ma, J.Z.; Gautam, J.K. Association of Intradialytic Hypotension and Ultrafiltration with AKI-D Outcomes in the Outpatient Dialysis Setting. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113147
Abdel-Rahman EM, Casimir E, Lyons GR, Ma JZ, Gautam JK. Association of Intradialytic Hypotension and Ultrafiltration with AKI-D Outcomes in the Outpatient Dialysis Setting. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113147
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel-Rahman, Emaad M., Ernst Casimir, Genevieve R. Lyons, Jennie Z. Ma, and Jitendra K. Gautam. 2022. "Association of Intradialytic Hypotension and Ultrafiltration with AKI-D Outcomes in the Outpatient Dialysis Setting" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113147
APA StyleAbdel-Rahman, E. M., Casimir, E., Lyons, G. R., Ma, J. Z., & Gautam, J. K. (2022). Association of Intradialytic Hypotension and Ultrafiltration with AKI-D Outcomes in the Outpatient Dialysis Setting. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113147






