The Impact of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities on the Outcomes after Renal Transplantation with a Living Donor vs. Deceased Donor Grafts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
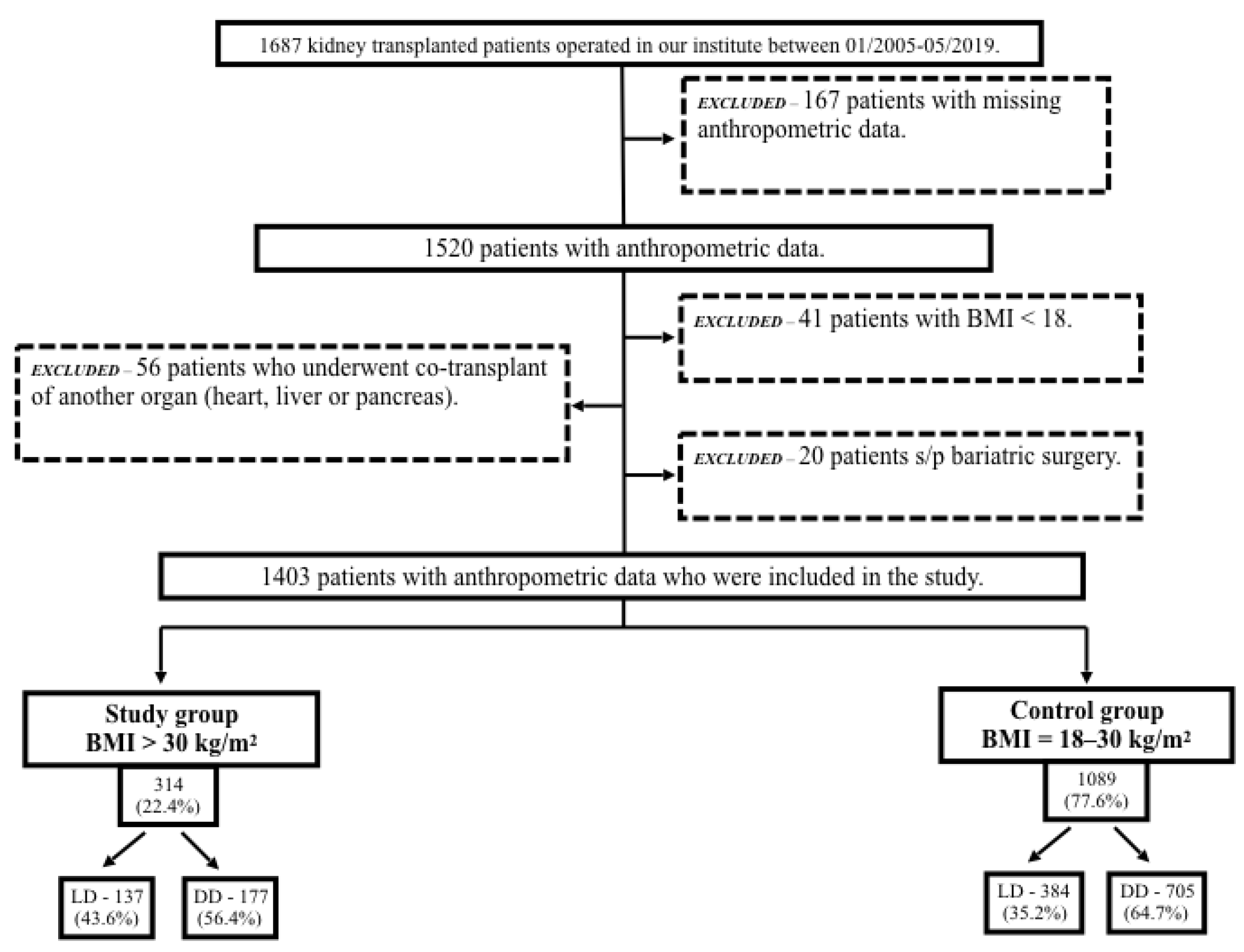
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Perioperative Management
2.3. Clinical Outcomes
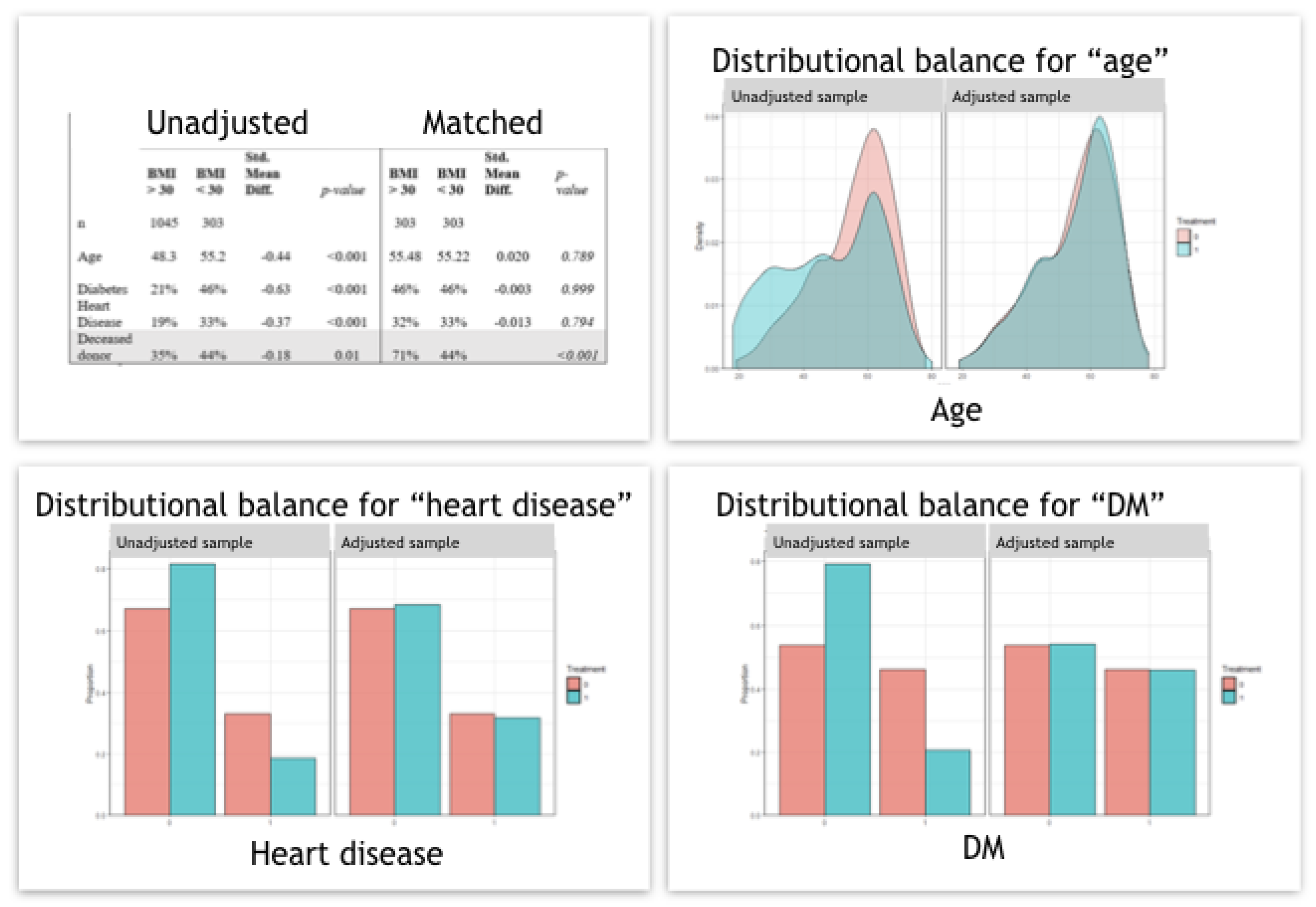
2.4. Statistical Analysis
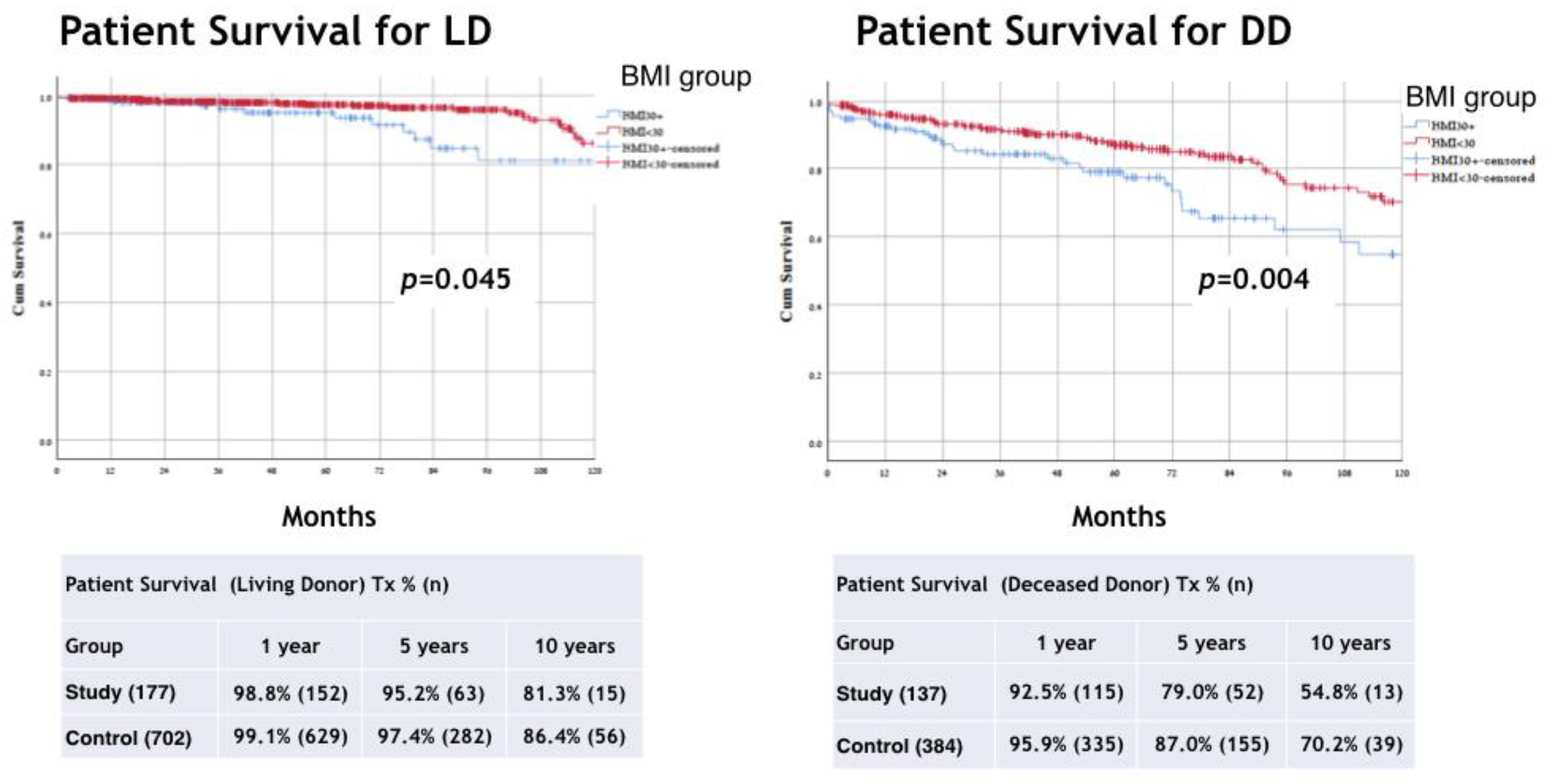
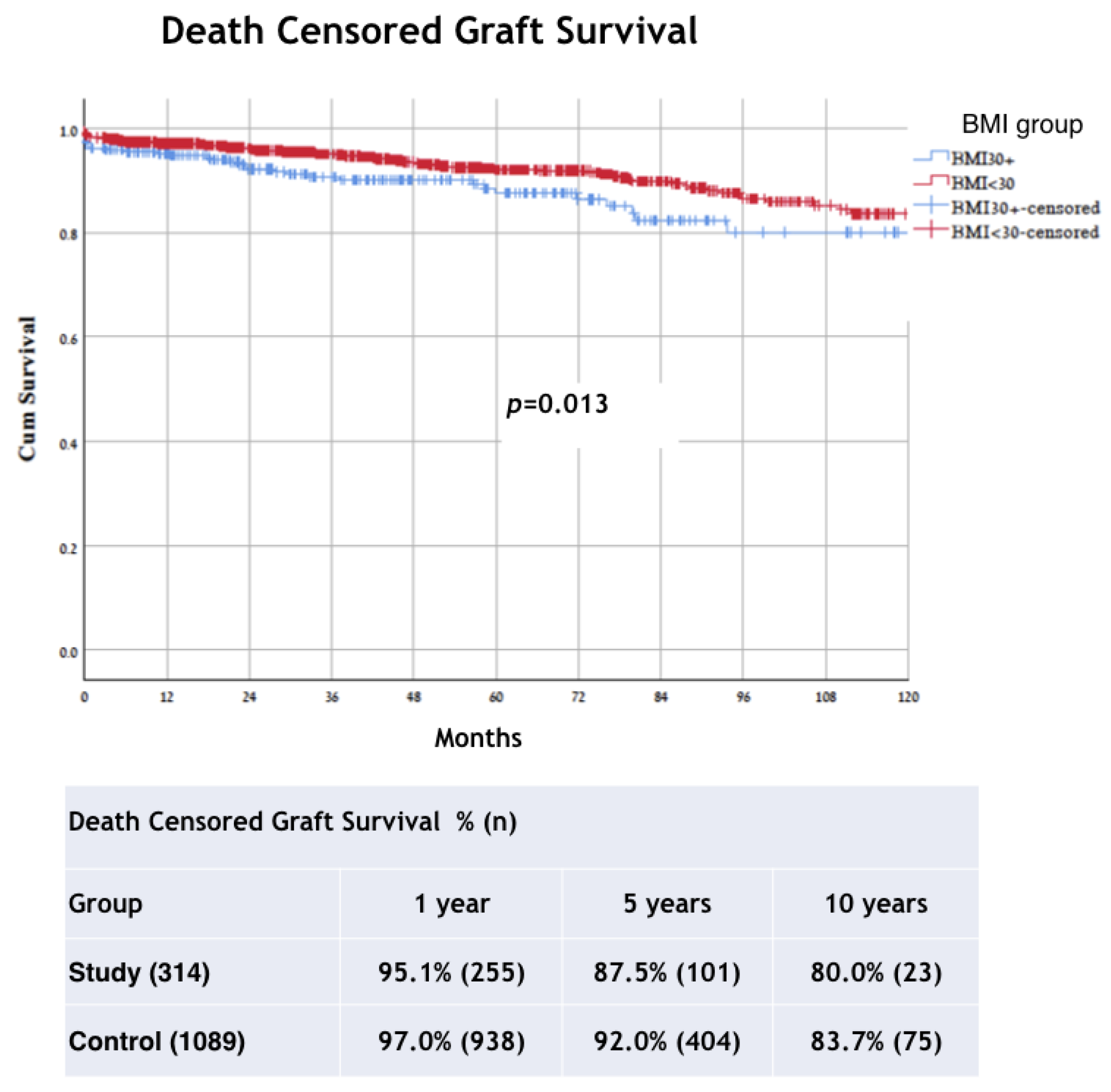
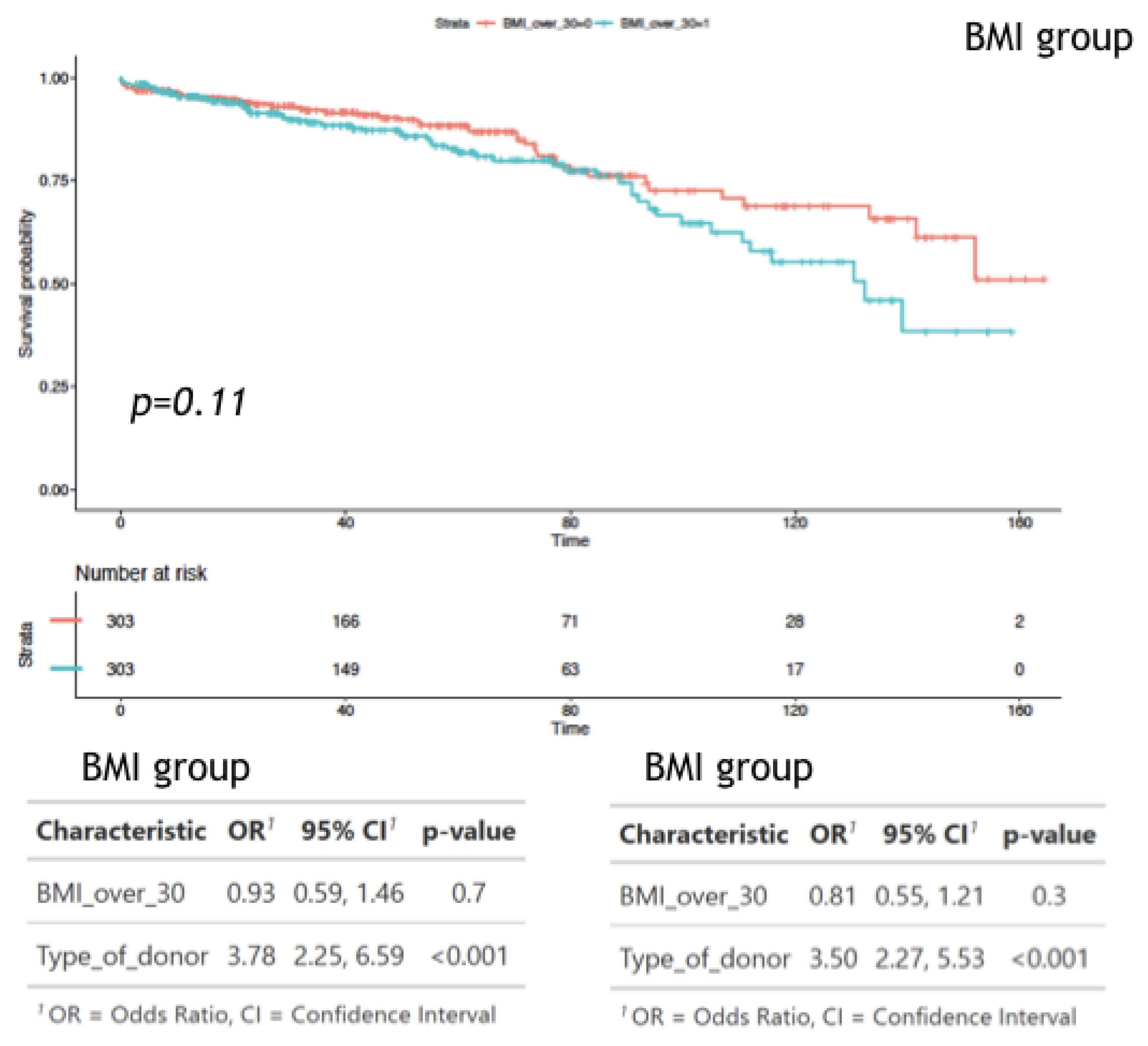
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gore, J.; Pham, P.T.; Danovitch, G.M.; Wilkinson, A.H.; Rosenthal, J.T.; Lipshutz, G.S.; Singer, J.S. Obesity and Outcome Following Renal Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaitzidis, R.G.; Siamopoulos, K.C. The role of obesity in kidney disease: Recent findings and potential mechanisms. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2011, 43, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickman, C.; Kramer, H. Obesity and Kidney Disease: Potential Mechanisms. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pączek, L.; Mucha, K.; Foroncewicz, B.; Ryter, M.; Florczak, M.; Krajewska, M.; Mulka-Gierek, M.; Jabiry-Zieniewicz, Z.; Chmura, A.; Lisik, W.; et al. Weight Gain in Renal Transplant Recipients in a Polish Single Centre. Ann. Transplant. 2015, 20, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Corona, D.; Mistretta, A.; Zerbo, D.; Sinagra, N.; Giaquinta, A.; Caglià, P.; Amodeo, C.; Leonardi, A.; Gula, R.; et al. The Role of Obesity in Kidney Transplantation Outcome. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanfack, M.K.; Bayoud, Y.; Marchand, C.; Cholley, I.; León, P.; Fournier, R.; Lassere, T.; Larre, S. Is obesity a barrier to kidney transplantation? Prog Urol. 2015, 25, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furriel, F.; Parada, B.; Campos, L.; Moreira, P.; Castelo, D.; Dias, V.; Mota, A. Pretransplantation Overweight and Obesity: Does It Really Affect Kidney Transplantation Outcomes? Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kriesche, H.-U.; Arndorfer, J.A.; Kaplan, B. The impact of body mass index on renal transplant outcomes: A significant independent risk factor for graft failure and patient death. Transplantation 2002, 73, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermann, U.; Babel, J.; Pietsch, U.-C.; Weimann, A.; Lyros, O.; Semmling, K.; Hau, H.-M.; Seehofer, D.; Rademacher, S.; Sucher, R. Recipient obesity as a risk factor in kidney transplantation. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen, E.K.; Aalten, J.; Rothman, K.; Roodnat, J.I.; Mallat, M.J.K.; Borm, G.; Weimar, W.; Hoitsma, A.J.; de Fijter, J.W. Effect of Obesity on the Outcome of Kidney Transplantation: A 20-Year Follow-Up. Transplantation 2011, 91, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciola, R.; Pujar, K.; Ilham, M.; Puliatti, C.; Asderakis, A.; Chavez, R. Effect of Degree of Obesity on Renal Transplant Outcome. Transplant. Proc. 2008, 40, 3408–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawn, M.T.; Bian, J.; Leeth, R.R.; Ritchie, G.; Allen, N.; Bland, K.I.; Vickers, S.M. Impact of Obesity on Resource Utilization for General Surgical Procedures. Ann. Surg. 2005, 241, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Montori, V.; Somers, V.K.; Korinek, J.; Thomas, R.; Allison, T.G.; Mookadam, F.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: A systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet 2006, 368, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalten, J.; Christiaans, M.H.; de Fijter, H.; Hené, R.; van der Heijde, J.H.; Roodnat, J.; Surachno, J.; Hoitsma, A. The influence of obesity on short- and long-term graft and patient survival after renal transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.J.; Courtney, A.E.; Cardwell, C.R.; Maxwell, A.P.; Lucarelli, G.; Veroux, M.; Furriel, F.; Cannon, R.M.; Hoogeveen, E.K.; Doshi, M.; et al. Recipient obesity and outcomes after kidney transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascual, M.; Theruvath, T.; Kawai, T.; Tolkoff-Rubin, N.; Cosimi, A.B. Strategies to Improve Long-Term Outcomes after Renal Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Chakkera, H.A.; Roel, J. Explained and Unexplained Ischemic Heart Disease Risk after Renal Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prommool, S.; Jhangri, G.S.; Cockfield, S.M.; Halloran, P. Time Dependency of Factors Affecting Renal Allograft Survival. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, W.D.; McCollum, D.A.; Tesi, R.J.; Owen, A.B.; Brennan, D.C.; Bailly, J.E.; Schnitzler, M.A. Nomogram for Predicting the Likelihood of Delayed Graft Function in Adult Cadaveric Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2967–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irish, W.D.; Ilsley, J.N.; Schnitzler, M.A.; Feng, S.; Brennan, D.C. A Risk Prediction Model for Delayed Graft Function in the Current Era of Deceased Donor Renal Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnac, A.; Herman, M.; Zingerman, B.; Erman, A.; Rozen-Zvi, B.; Hirsh, J.; Gafter, U. Obesity-induced glomerular hyperfiltration: Its involvement in the pathogenesis of tubular sodium reabsorption. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 3946–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ducloux, D.; Kazory, A.; Simula-Faivre, D.; Chalopin, J.-M. One-Year Post-Transplant Weight Gain is a Risk Factor for Graft Loss. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2922–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Hong, Y.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Sun, I.; Chung, B.; Choi, B.; Park, C.; Kim, Y.; Yang, C. Delayed Graft Function in Living-Donor Renal Transplantation: 10-Year Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grèze, C.; Pereira, B.; Boirie, Y.; Guy, L.; Millet, C.; Clerfond, G.; Garrouste, C.; Heng, A.-E. Impact of obesity in kidney transplantation: A prospective cohort study from French registries between 2008 and 2014. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Cangro, C.B.; Hariharan, S.; E Hricik, D.; Kerman, R.H.; Roth, D.; Rush, D.N.; A Vazquez, M.; Weir, M.R. The evaluation of renal transplantation candidates—Clinical practice guidelines. Am. J. Transplant. 2001, 1 (Suppl. S2), 3–95. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, J.S.; Hendren, E.; Dong, J.; Johnston, O.; Gill, J. Differential Association of Body Mass Index with Access to Kidney Transplantation in Men and Women. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segev, D.L.; Simpkins, C.E.; Thompson, R.E.; Locke, J.E.; Warren, D.S.; Montgomery, R.A. Obesity Impacts Access to Kidney Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.; Garneau, P.; Hajjar, R. The Impact and Treatment of Obesity in Kidney Transplant Candidates and Recipients. Can. J. Kidney Heal. Dis. 2015, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yemini, R.; Nesher, E.; Carmeli, I.; Winkler, J.; Rahamimov, R.; Mor, E.; Keidar, A. Bariatric Surgery Is Efficacious and Improves Access to Transplantation for Morbidly Obese Renal Transplant Candidates. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, H.; Avidor, Y.; Braunwald, E.; Jensen, M.D.; Pories, W.; Fahrbach, K.; Schoelles, K. Bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004, 292, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggard, M.A.; Shugarman, L.R.; Suttorp, M.; Maglione, M.; Sugerman, H.J.; Livingston, E.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Li, Z.; Mojica, W.A.; Hilton, L.; et al. Meta-Analysis: Surgical Treatment of Obesity. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abeling, T.; Scheffner, I.; Karch, A.; Broecker, V.; Koch, A.; Haller, H.; Schwarz, A.; Gwinner, W. Risk factors for death in kidney transplant patients: Analysis from a large protocol biopsy registry. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernichow, S.; Kengne, A.-P.; Stamatakis, E.; Hamer, M.; Batty, G.D. Body mass index, waist circumference and waist-hip ratio: Which is the better discriminator of cardiovascular disease mortality risk? Evidence from an individual-participant meta-analysis of 82 864 participants from nine cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziodzio, T.; Hillebrandt, K.H.; Knitter, S.; Nösser, M.; Globke, B.; Ritschl, P.V.; Biebl, M.; Denecke, C.; Raakow, J.; Lurje, G.; et al. Body Mass Index Thresholds and the Use of Bariatric Surgery in the Field of Kidney Transplantation in Germany. Obes. Surg. 2022, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecking, M.; Sharif, A.; Eller, K.; Jenssen, T. Management of post-transplant diabetes: Immunosuppression, early prevention, and novel antidiabetics. Transpl. Int. 2020, 34, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, A.; Hill, J.; Merzkani, M.; Bentall, A.; Lorenz, E.C.; Park, W.; D’Costa, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; Stegall, M.D.; Shah, P. The Use of GLP1R Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Cotiguala, L.; Tischer, S.; Park, J.M.; McMurry, K. Review of Newer Antidiabetic Agents for Diabetes Management in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 55, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemini, R.; Nesher, E.; Winkler, J.; Carmeli, I.; Azran, C.; Ben David, M.; Mor, E.; Keidar, A. Bariatric surgery in solid organ transplant patients: Long-term follow-up results of outcome, safety, and effect on immunosuppression. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.; Mirza, A.; Kim, Y.; Hanseman, D.; Woodle, E.S.; Quillin, R.C.; Johnson, B.L.; Govil, A.; Cardi, M.; Schauer, D.P.; et al. Long-term outcomes in patients with obesity and renal disease after sleeve gastrectomy. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 20, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Group Obese–Morbidly Obese | Control Group Normal Weight–Overweight | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients, number | 314 (22.4%) | 1089 (77.6%) | |
| Age, (year) [mean ± SD] | 55.40 ± 11.94 | 48.43 ± 15.53 | p < 0.001 |
| Gender, number | p = 0.158 | ||
| Male | 224 (71.3%) | 731 (67.1%) | |
| Female | 90 (28.7%) | 358 (32.9%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) ± SD | 33.25 ± 2.83 | 24.30 ± 3.18 | p < 0.001 |
| Weight (kg) ± SD | 94.92 ± 12.37 | 69.97 ± 13.25 | p < 0.001 |
| Comorbidity, number | |||
| T2DM | 147 (46.8%) | 235 (21.6%) | p < 0.001 |
| IHD | 100 (33%) | 194 (18.5%) | p < 0.001 |
| Kidney disease, number | p < 0.001 | ||
| T2DM | 101 (32.2%) | 158 (14.5%) | |
| HTN | 35 (11.1%) | 56 (5.1%) | |
| PKD | 30 (9.6%) | 153 (14.0%) | |
| FSGS | 29 (9.2%) | 86 (7.9%) | |
| GN | 21 (6.7%) | 99 (9.1%) | |
| Pyelonephritis | 5 (1.6%) | 63 (5.8%) | |
| Other | 29 (9.2%) | 143 (13.1%) | |
| Congenital | 4 (1.3%) | 76 (7.0%) | |
| Unknown | 45 (14.3%) | 178 (16.3%) | |
| Preemptive transplant | 49(17.7%) | 265 (23.5%) | p = 0.037 |
| Re-transplant, number | 27 (8.6%) | 188 (17.3%) | p < 0.001 |
| Donor age, mean ± SD | 47.67 ± 14.61 | 45.71 ± 13.95 | p = 0.005 |
| Donor type, number | p = 0.008 | ||
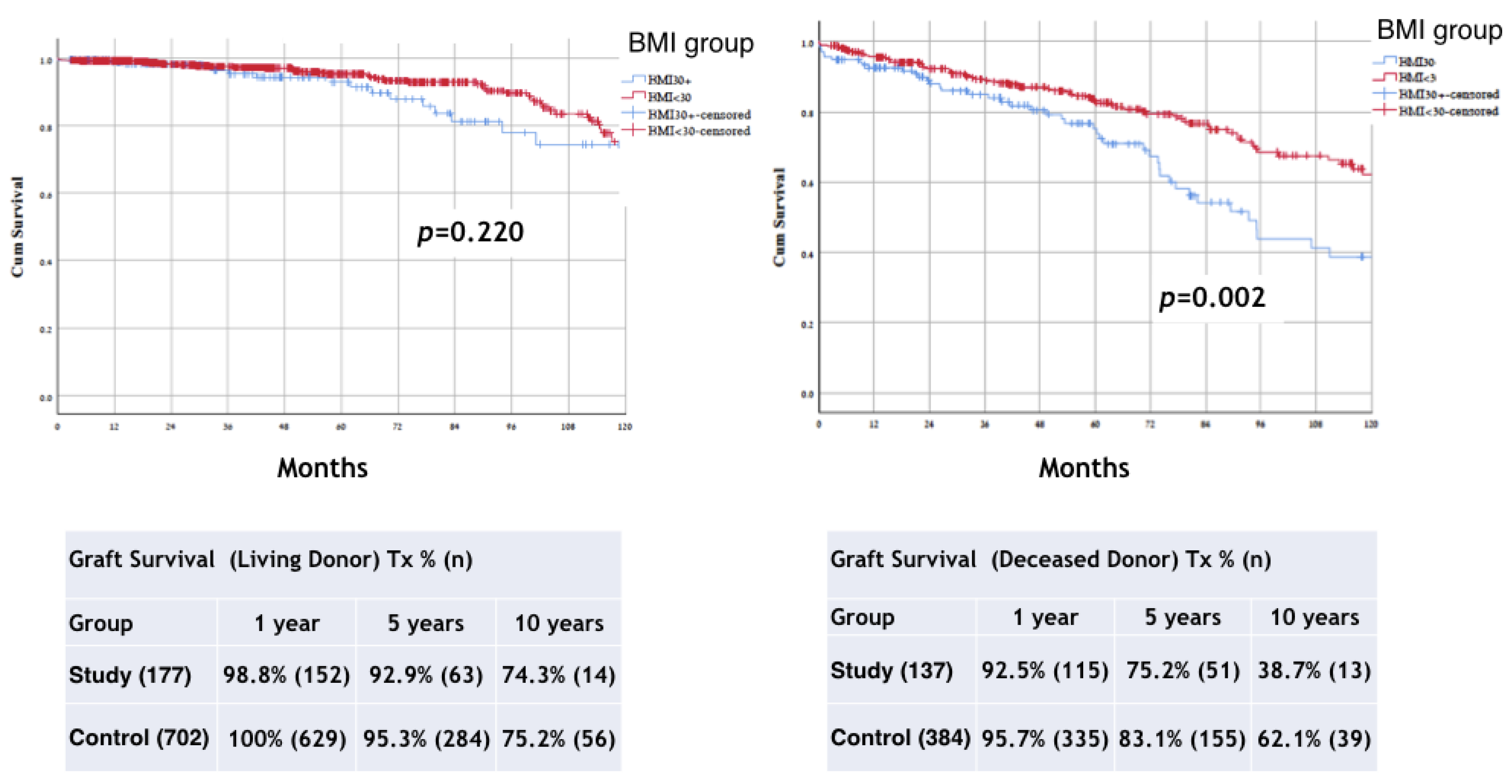
| Deceased | 137 (43.6%) | 384 (35.2%) | |
| Living | 177 (56.4%) | 705 (64.7%) | |
| Time on dialysis (months, mean ± SD) | 33.7 ± 39.6 | 37.0 ± 33.6 | p = 0.180 |
| Time on dialysis, LD | 16.5 ± 24.2 | 19.6 ±24.0 | p = 0.252 |
| Time on dialysis, DD | 60. 1 ± 29.9 | 65.2 ± 38.4 | p = 0.158 |
| PRA class I (+), number (%) | 15 (5.5%) | 75 (7.6%) | p = 0.103 |
| PRA class II (+), number (%) | 11(4%) | 67 (6.8%) | p = 0.103 |
| HLA-A 0 match, number (%) | 142 (50.2%) | 508 (49.4%) | p = 0.125 |
| HLA-B 0 match, number (%) | 164 (56.9%) | 582 (56.5%) | p = 0.016 |
| HLA-DR 0 match, number (%) | 121 (45.7%) | 409 (43.7%) | p = 0.575 |
| 6 HLA mismatch, number (%) | 54 (17.2%) | 212 (19.5%) | p = 0.901 |
| Study Group Obese-Morbidly Obese | Control Group Normal Weight- Overweight | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients, number | 314 (22.4%) | 1089 (77.6%) | |
| LOS (days), mean ± SD | 14.28 ± 25.27 | 10.89 ± 12.849 | p = 0.002 |
| DGF number | 95 (30.7%) | 182 (17.0%) | p < 0.001 |
| PNF, number | 7 (2.3%) | 8 (0.7%) | p < 0.001 |
| Rejection, number | p = 0.197 | ||
| Cellular | 25 (8.0%) | 64 (5.9%) | p = 0.228 |
| Humoral | 10 (3.2%) | 19 (1.7%) | p = 0.175 |
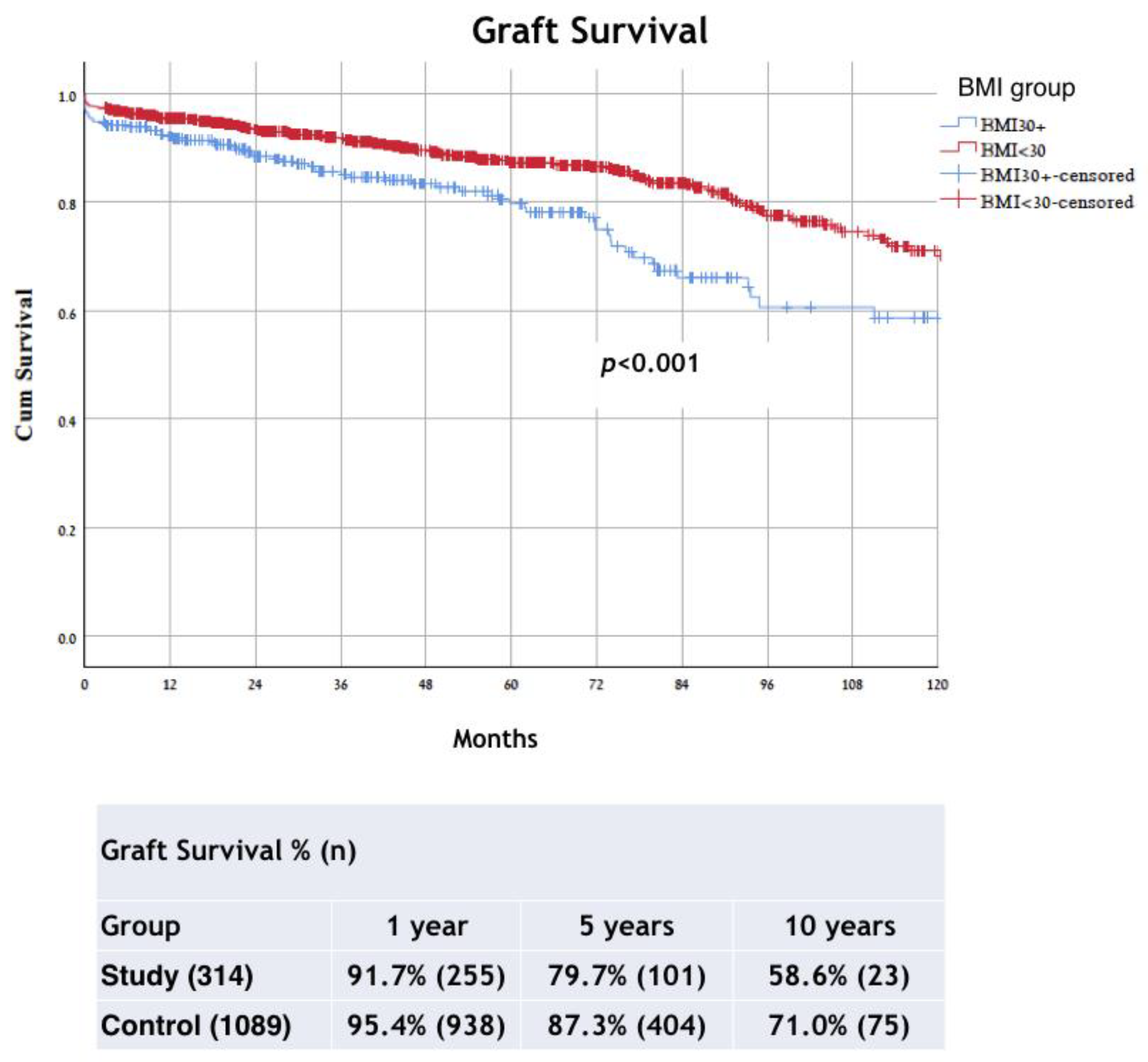
| Status of graft loss * | 69 (22.3%) | 148 (13.5%) | p < 0.001 |
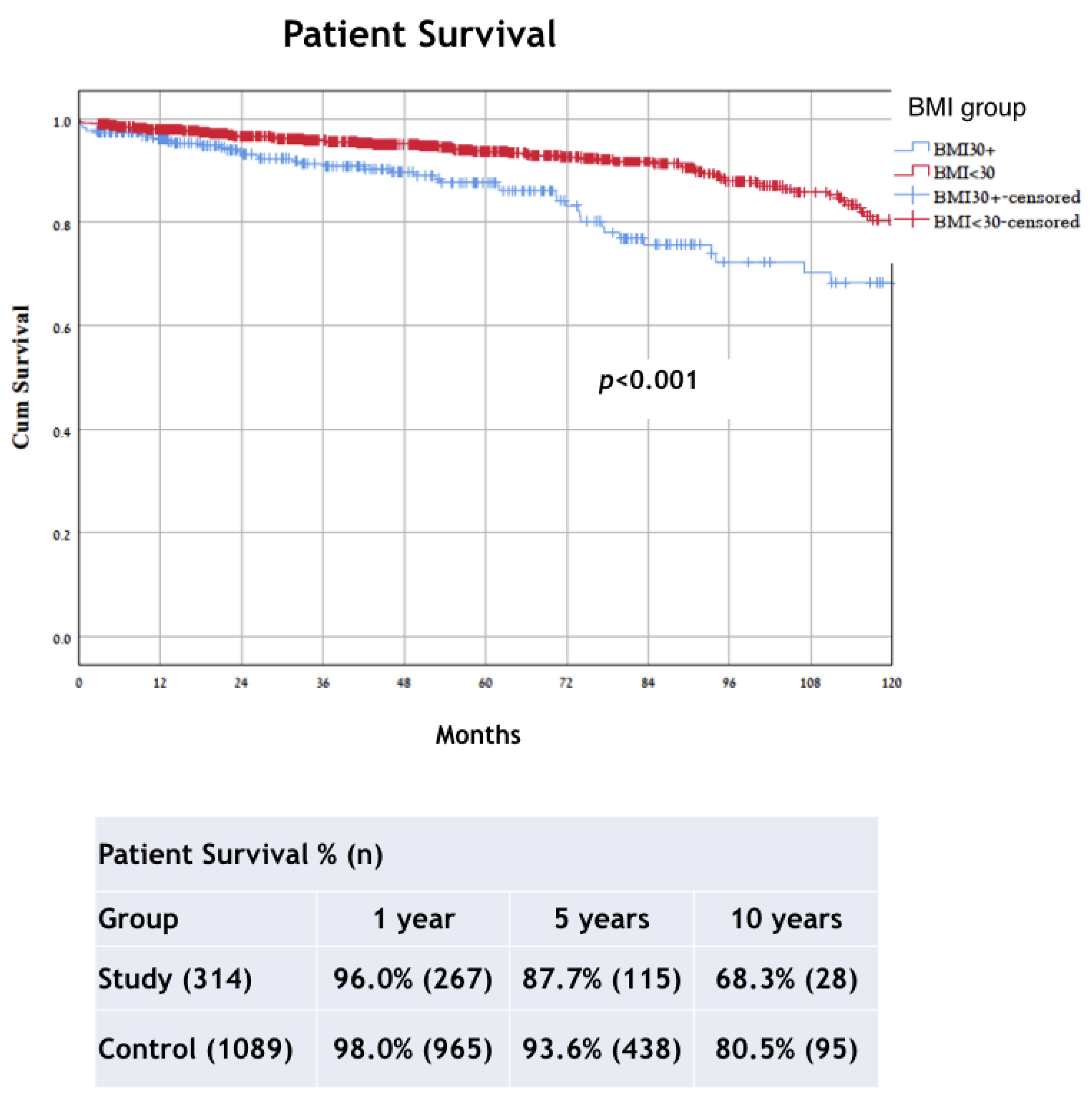
| Status death * | 36 (11.7%) | 84 (7.7%) | p = 0.027 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) (total number of patients), mean ± SD | |||
| 30 days (n = 1318) | 1.78 ± 1.16 | 1.52 ±0.99 | p < 0.001 |
| 180 days (n = 1197) | 1.52 ± 0.89 | 1.41 ± 0.68 | p = 0.031 |
| 1 year (n = 1099) | 1.48 ± 0.80 | 1.38 ± 0.78 | p = 0.097 |
| 3 years (n = 656) | 1.79 ± 1.92 | 1.52 ± 1.40 | p = 0.060 |
| HR [Exp(B)] | 95.0% CI for Exp(B) Lower | 95.0% CI for Exp(B) Upper | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cox regression for graft loss | ||||
| IHD (Y/N) | 1.892 | 1.496 | 2.687 | p < 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.038 | 1.010 | 1.066 | p = 0.007 |
| Donor Age (year) | 1.018 | 1.008 | 1.028 | p < 0.001 |
| 1st/reTx (Y/N) | 1.750 | 1.177 | 2.602 | p = 0.006 |
| LD/DD | 2.491 | 1.857 | 3.340 | p < 0.001 |
| Cox regression for mortality | ||||
| Age (year) | 1.054 | 1.033 | 1.074 | p < 0.001 |
| DM (Y/N) | 2.089 | 1.414 | 3.088 | p < 0.001 |
| IHD (Y/N) | 1.761 | 1.192 | 2.600 | p = 0.004 |
| LD/DD | 2.682 | 1.801 | 3.992 | p < 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yemini, R.; Rahamimov, R.; Nesher, E.; Anteby, R.; Ghinea, R.; Hod, T.; Mor, E. The Impact of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities on the Outcomes after Renal Transplantation with a Living Donor vs. Deceased Donor Grafts. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113069
Yemini R, Rahamimov R, Nesher E, Anteby R, Ghinea R, Hod T, Mor E. The Impact of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities on the Outcomes after Renal Transplantation with a Living Donor vs. Deceased Donor Grafts. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113069
Chicago/Turabian StyleYemini, Renana, Ruth Rahamimov, Eviatar Nesher, Roi Anteby, Ronen Ghinea, Tammy Hod, and Eytan Mor. 2022. "The Impact of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities on the Outcomes after Renal Transplantation with a Living Donor vs. Deceased Donor Grafts" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113069
APA StyleYemini, R., Rahamimov, R., Nesher, E., Anteby, R., Ghinea, R., Hod, T., & Mor, E. (2022). The Impact of Obesity and Associated Comorbidities on the Outcomes after Renal Transplantation with a Living Donor vs. Deceased Donor Grafts. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113069







