Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Potential and Pitfalls
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Selection of the Literature
3. Pathophysiology of Neuropathic Pain
3.1. Peripheral Sensitization
3.2. Central Sensitization
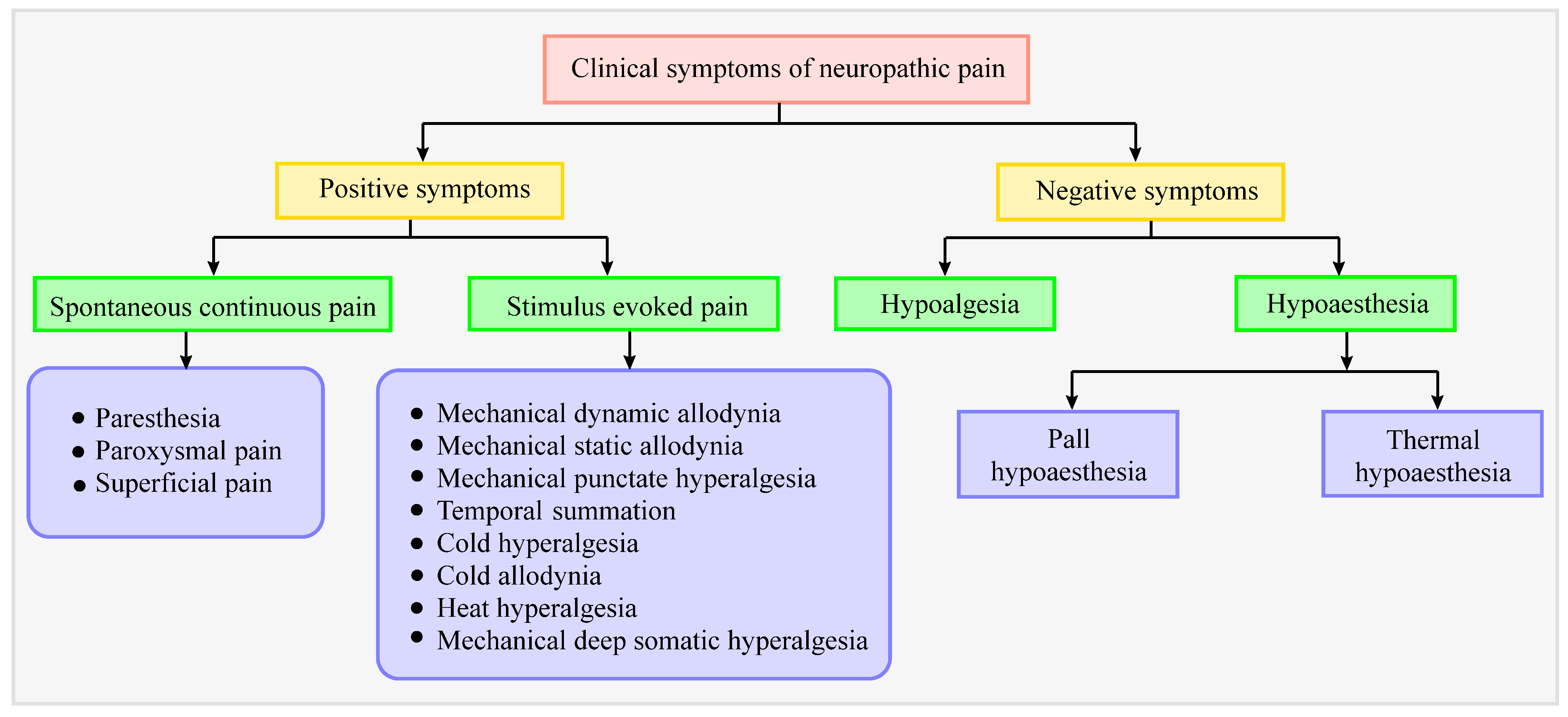
4. Clinical Symptoms in Patients with Neuropathic Pain
5. Diagnosis of Neuropathic Pain
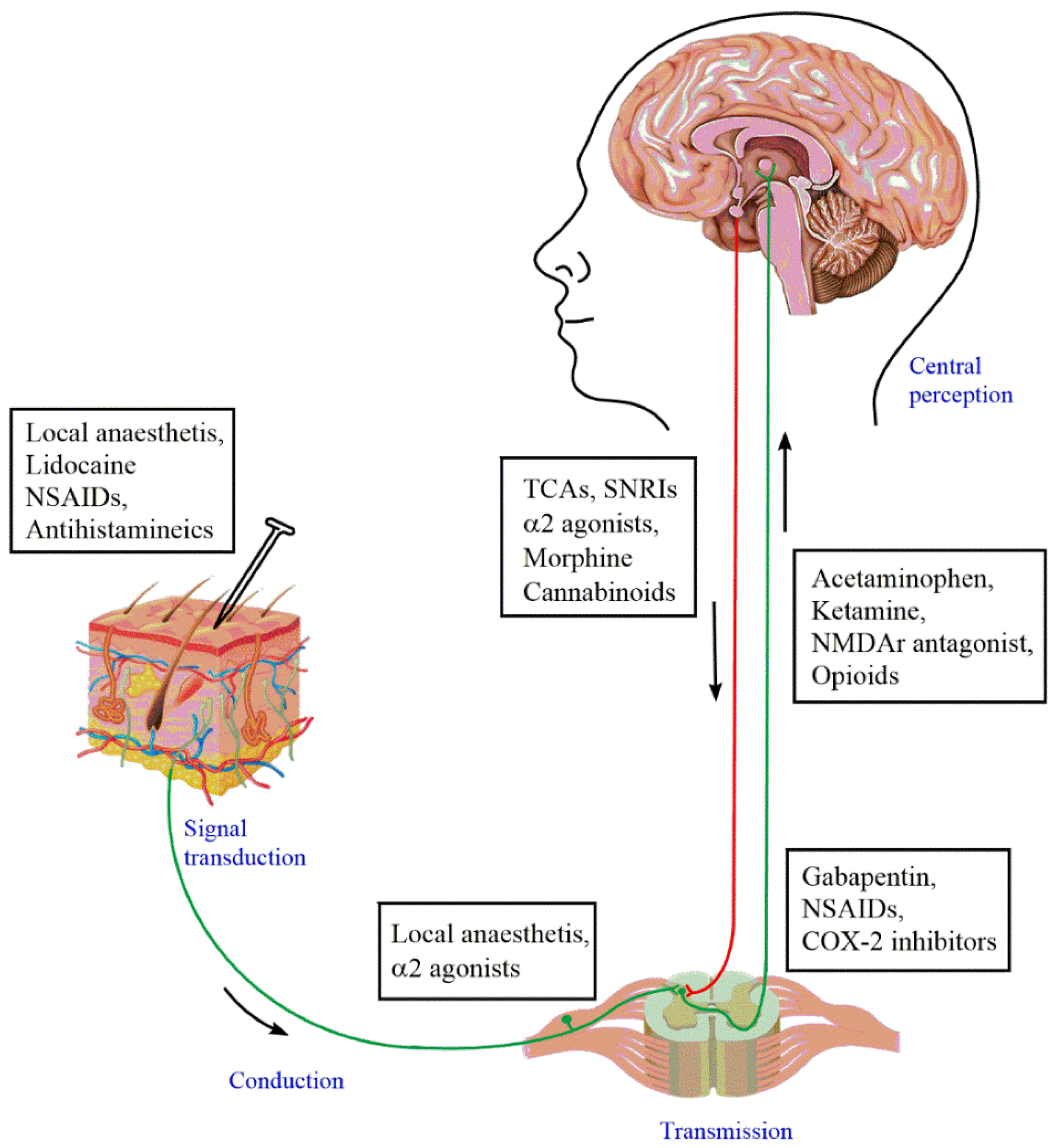
6. Current Status of Pharmacotherapies for Neuropathic Pain: Advantages and Disadvantages
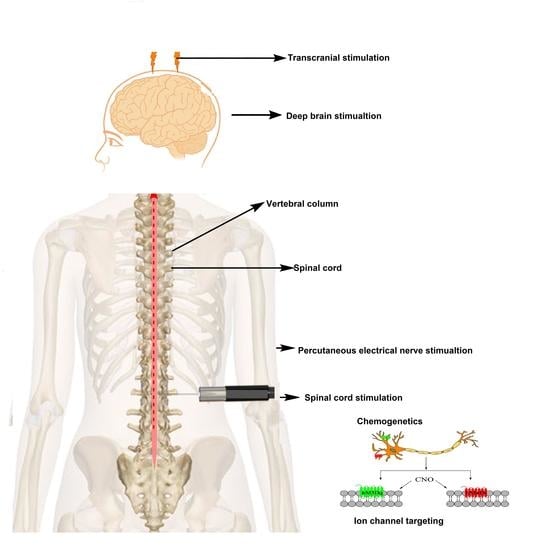
7. Interventional Methods as an Effective Treatment Approach against Neuropathic Pain
7.1. Clinical Interventional Techniques
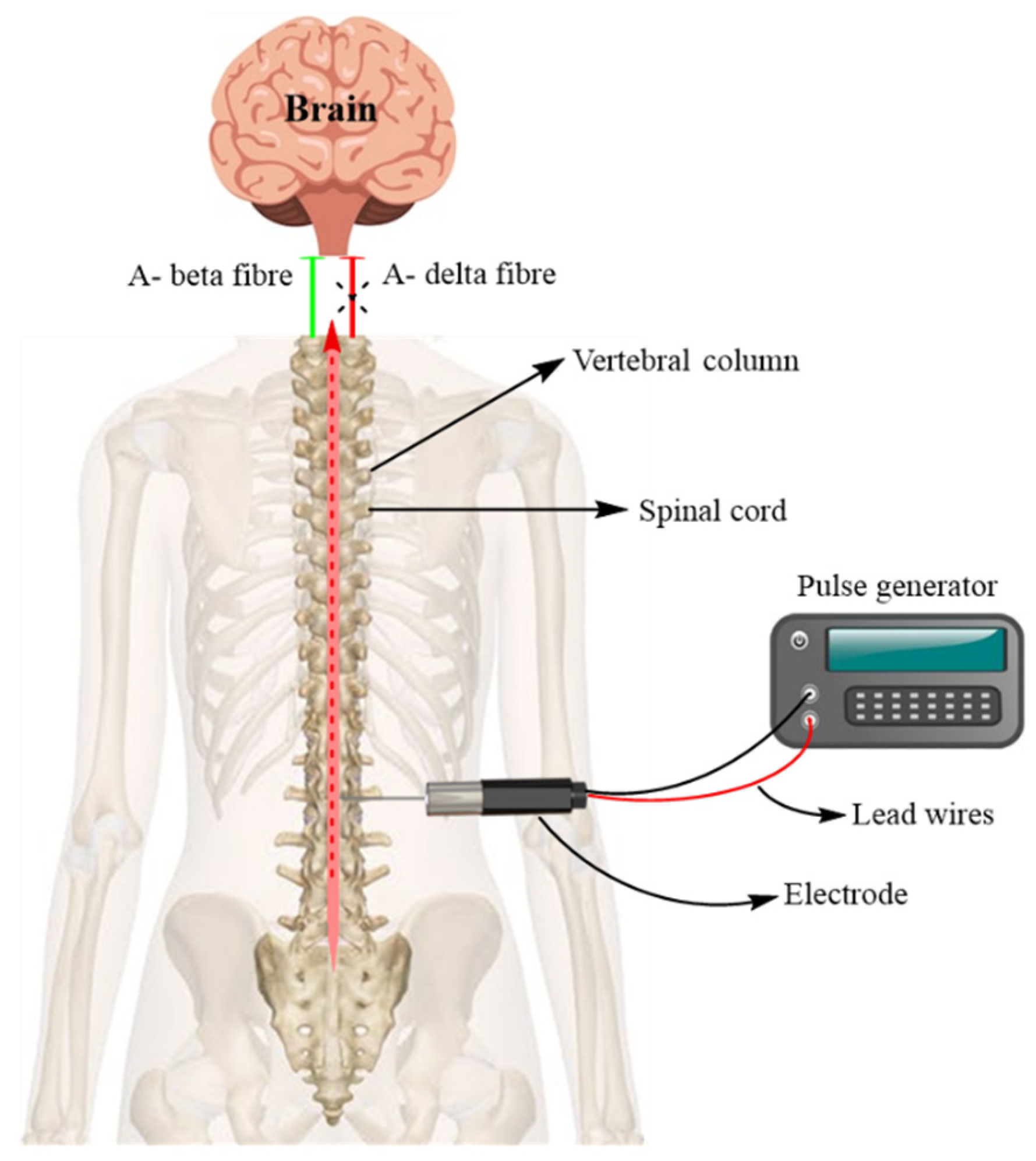
7.1.1. Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS)
7.1.2. Steroid Injection and Neural Blockade
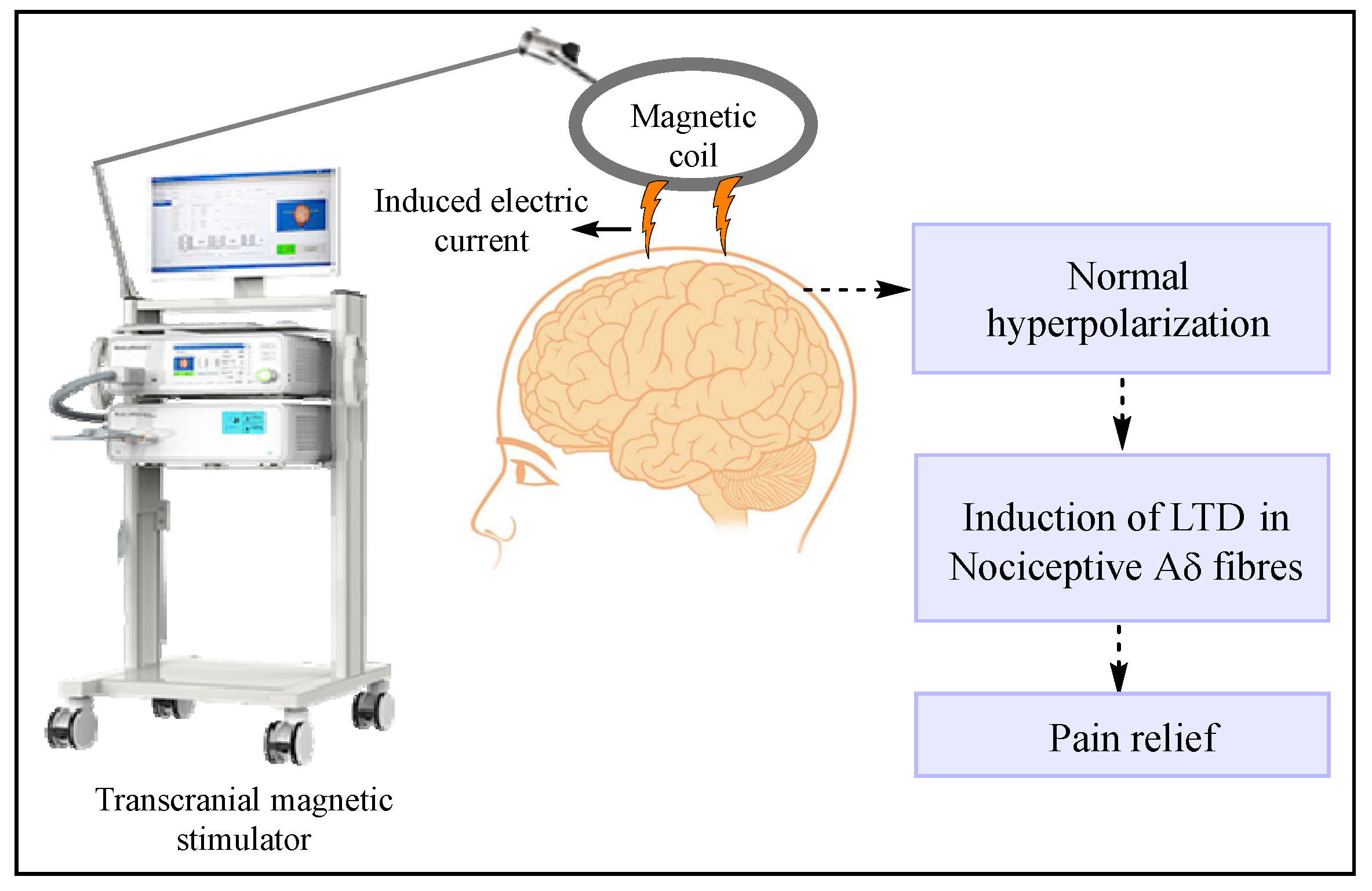
7.1.3. Transcranial and Epidural Stimulation
7.1.4. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
7.1.5. PENS
7.1.6. Neuroablative Procedures and Stimulation of DRG and the Peripheral Nerve or Nerve Field
7.2. Preclinical (or New Experimental) Pain-Controlling Agents
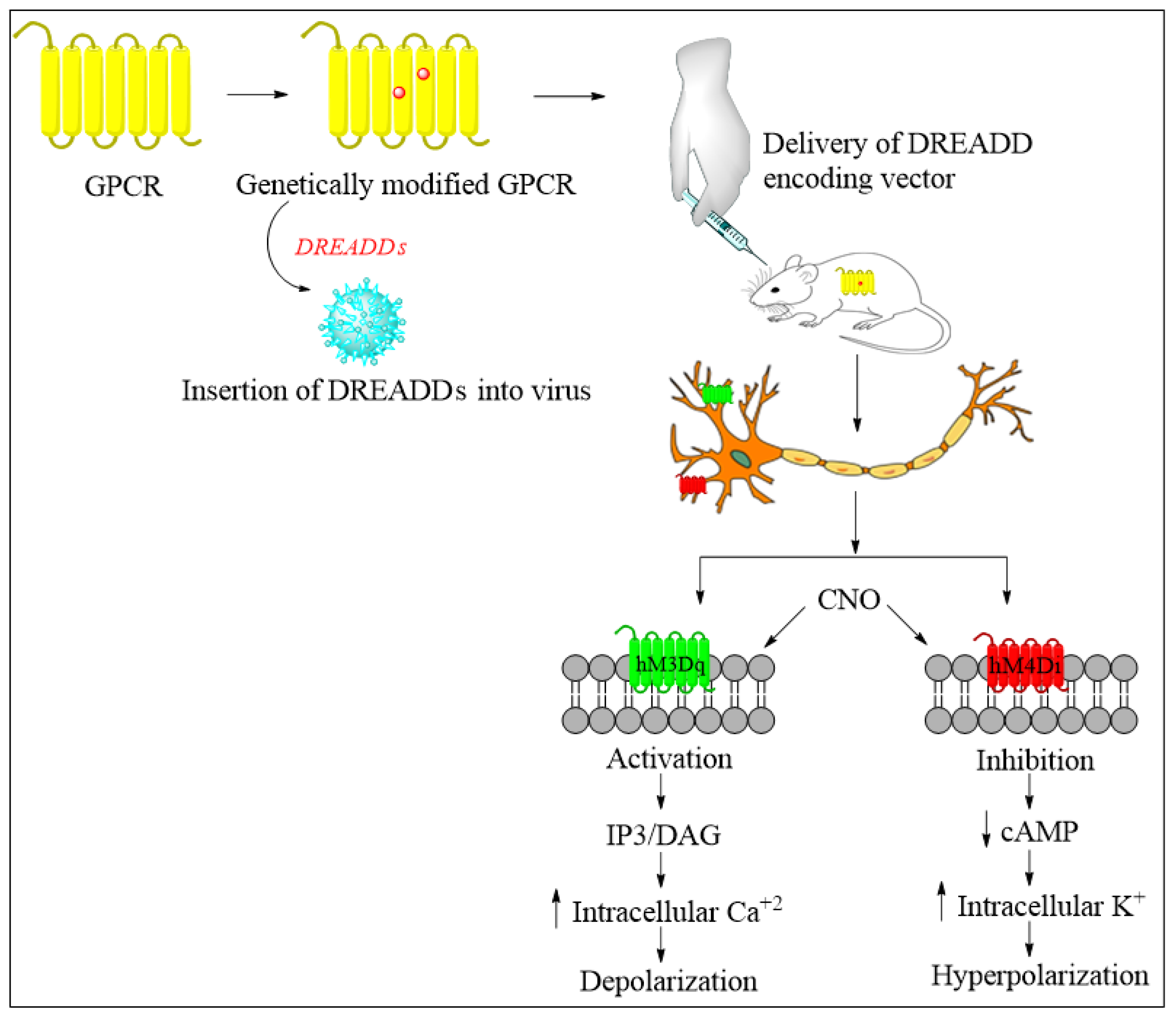
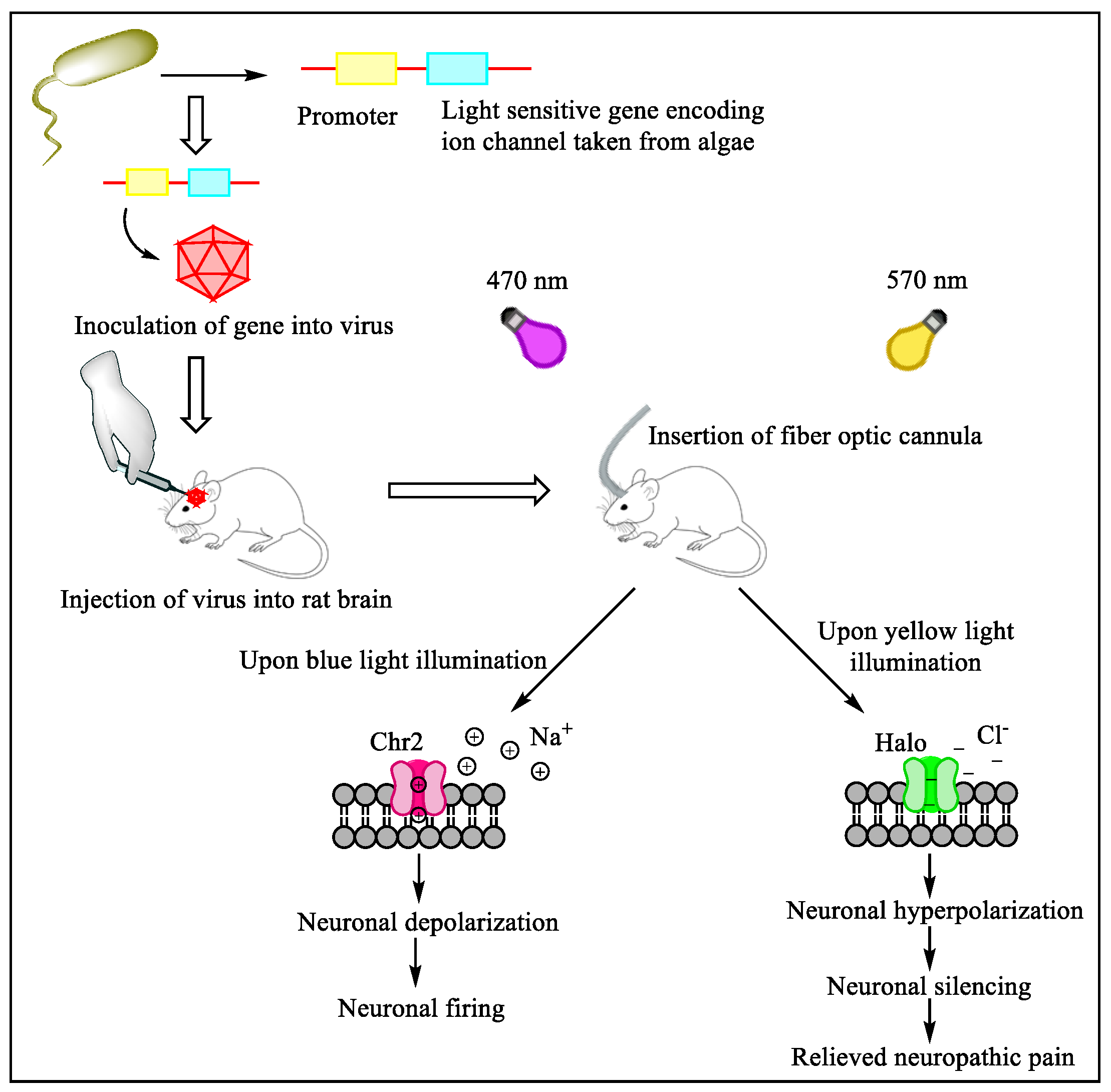
Future Directions of Chemogenetics and Optogenetics as Potential Interventional Strategies
7.3. Gene Therapy against Neuropathic Pain
7.4. Spinal Opioid Gene Therapy
Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Gene Therapy
7.5. Ion Channel Targeting
7.5.1. Sodium Channel Modulation
7.5.2. Calcium Channel Modulation
7.5.3. Potassium and Chloride Channel Modulation
8. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlereth, T. Guideline “diagnosis and non interventional therapy of neuropathic pain” of the German Society of Neurology (deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie). Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, C.A.; Malik, R.A.; van Ross, E.R.; Kulkarni, J.; Boulton, A.J. Prevalence and characteristics of painful diabetic neuropathy in a large community-based diabetic population in the U.K. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, Y.; Izumi, M.; Aso, K.; Igarashi, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ikeuchi, M. Comparison of Predisposing Factors Between Pain on Walking and Pain at Rest in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayaz, A.; Croft, P.; Langford, R.M.; Donaldson, L.J.; Jones, G.T. Prevalence of chronic pain in the UK: A systematic review and meta-analysis of population studies. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiBonaventura, M.D.; Sadosky, A.; Concialdi, K.; Hopps, M.; Kudel, I.; Parsons, B.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Hlavacek, P.; Alexander, A.H.; Stacey, B.R.; et al. The prevalence of probable neuropathic pain in the US: Results from a multimodal general-population health survey. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2525–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Aziz, Q.; Baron, R.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Cruccu, G.; Davis, K.D.; et al. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: Chronic neuropathic pain. Pain 2019, 160, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylius, V.; Lloret, S.P.; Cury, R.G.; Teixeira, M.J.; Barbosa, V.R.; Barbosa, E.R.; Moreira, L.I.; Listik, C.; Fernandes, A.M.; de Lacerda Veiga, D. The Parkinson disease pain classification system: Results from an international mechanism-based classification approach. Pain 2021, 162, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; Bouhassira, D. Pharmacotherapy of neuropathic pain: Which drugs, which treatment algorithms? Pain 2015, 156, S104–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosenovic, S.; Jelicic Kadic, A.; Miljanovic, M.; Biocic, M.; Boric, K.; Cavar, M.; Markovina, N.; Vucic, K.; Puljak, L. Interventions for Neuropathic Pain: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; O’Connor, A.B.; Kent, J.; Mackey, S.C.; Raja, S.N.; Stacey, B.R.; Levy, R.M.; Backonja, M.; Baron, R.; Harke, H.; et al. Interventional management of neuropathic pain: NeuPSIG recommendations. Pain 2013, 154, 2249–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.; Sia, A.T.; Sultana, R.; Sng, B.L.; Tan, E.C. Analysis of SCN9A Gene Variants for Acute and Chronic Postoperative Pain and Morphine Consumption After Total Hysterectomy. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Ping, X.; Ripsch, M.S.; Chavez, G.S.C.; Hannon, H.E.; Jiang, K.; Bao, C.; Jadhav, V.; Chen, L.; Chai, Z.; et al. Enhancing excitatory activity of somatosensory cortex alleviates neuropathic pain through regulating homeostatic plasticity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.-F.; Yeh, S.-R.; Lu, K.-T.; Hsu, J.-L.; Chao, P.-K.; Hsu, H.-C.; Peng, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-L.; Hung, Y.-H.; Ro, L.-S. Interactions between Autophagy, Proinflammatory Cytokines, and Apoptosis in Neuropathic Pain: Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor as a Multipotent Therapy in Rats with Chronic Constriction Injury. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Binder, A.; Wasner, G. Neuropathic pain: Diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R. Mechanisms of disease: Neuropathic pain--a clinical perspective. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svajdova, S.; Buday, T.; Brozmanova, M. Lidocaine, a Non-selective Inhibitor of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels, Blocks Chemically-Induced Cough in Awake Naïve Guinea Pigs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1160, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, L.A.; Weir, G.A.; Themistocleous, A.C.; Segerdahl, A.R.; Blesneac, I.; Baskozos, G.; Clark, A.J.; Millar, V.; Peck, L.J.; Ebner, D.; et al. Defining the Functional Role of Na(V)1.7 in Human Nociception. Neuron 2019, 101, 905–919.e908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.I.; Sikandar, S.; Weiss, J.; Pyrski, M.; Luiz, A.P.; Millet, Q.; Emery, E.C.; Mancini, F.; Iannetti, G.D.; Alles, S.R.A.; et al. A central mechanism of analgesia in mice and humans lacking the sodium channel Na(V)1.7. Neuron 2021, 109, 1497–1512.e1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.A.; Frézel, N.; Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Waxman, S.G. Expression of Nav1.7 in DRG neurons extends from peripheral terminals in the skin to central preterminal branches and terminals in the dorsal horn. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Yang, J.J.; Fang, D.; Cai, J.; Wan, Y.; Xing, G.G. Functional upregulation of nav1.8 sodium channels on the membrane of dorsal root Ganglia neurons contributes to the development of cancer-induced bone pain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockley, J.R.; Boundouki, G.; Cibert-Goton, V.; McGuire, C.; Yip, P.K.; Chan, C.; Tranter, M.; Wood, J.N.; Nassar, M.A.; Blackshaw, L.A.; et al. Multiple roles for NaV1.9 in the activation of visceral afferents by noxious inflammatory, mechanical, and human disease-derived stimuli. Pain 2014, 155, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griensven, H.; Schmid, A.; Trendafilova, T.; Low, M. Central Sensitization in Musculoskeletal Pain: Lost in Translation? J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2020, 50, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Kohno, T.; Moore, K.A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization and LTP: Do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L. Pathophysiology of pain. In Essentials of Pediatric Anesthesiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; p. 213. [Google Scholar]
- Alles, S.R.A.; Smith, P.A. Etiology and Pharmacology of Neuropathic Pain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 315–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zou, W.; Lee, K.; Wang, E.; Zhu, X.; Guo, Q. Different symptoms of neuropathic pain can be induced by different degrees of compressive force on the C7 dorsal root of rats. Spine J. 2012, 12, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussa, M.; Mascaro, A.; Sbacchi, E.; Dourandish, M.; Rinaldi, S. Understanding peripheral neuropathic pain in primary care: Diagnosis and management. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 25, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bidve, P.; Prajapati, N.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.; Tiwari, V. Emerging role of nanomedicine in the treatment of neuropathic pain. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernetti, A.; Agostini, F.; de Sire, A.; Mangone, M.; Tognolo, L.; Di Cesare, A.; Ruiu, P.; Paolucci, T.; Invernizzi, M.; Paoloni, M. Neuropathic pain and rehabilitation: A systematic review of international guidelines. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanpää, M.L.; Backonja, M.-M.; Bennett, M.I.; Bouhassira, D.; Cruccu, G.; Hansson, P.T.; Jensen, T.S.; Kauppila, T.; Rice, A.S.; Smith, B.H. Assessment of neuropathic pain in primary care. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, A.; Gigliucci, G.; Moretti, A.; Pietrella, A.; Peresson, M.; Atzeni, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Bazzichi, L.; Liguori, S.; Iolascon, G. Cross Cultural Adaptation and Validation of Italian Version of the Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs Scale and Pain DETECT Questionnaire for the Distinction between Nociceptive and Neuropathic Pain. Pain Res. Manag. 2021, 2021, 6623651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, T.L.; Dworkin, R.H.; Polomano, R.C.; Carr, D.B.; Edwards, R.R.; Finnerup, N.B.; Freeman, R.L.; Paice, J.A.; Weisman, S.J.; Raja, S.N. AAAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Acute Neuropathic Pain. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 616–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, S.K.; Shim, J.H. Usefulness of ultrasound for detecting suspected peripheral nerve lesions in diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy: Case report and brief review of the literature. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2013, 53, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P.; Backonja, M.; Bouhassira, D. Usefulness and limitations of quantitative sensory testing: Clinical and research application in neuropathic pain states. Pain 2007, 129, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, F.; Broski, S.M.; Yoon, D.; Gold, G.E. Applications of PET-MRI in musculoskeletal disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2018, 48, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, L.; Galosi, E.; Vanoli, F.; Fasolino, A.; Di Pietro, G.; Luigetti, M.; Sabatelli, M.; Fionda, L.; Garibaldi, M.; Alfieri, G. Skin biopsy and quantitative sensory assessment in an Italian cohort of ATTRv patients with polyneuropathy and asymptomatic carriers: Possible evidence of early non-length dependent denervation. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 43, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruccu, G.; Anand, P.; Attal, N.; Garcia-Larrea, L.; Haanpää, M.; Jørum, E.; Serra, J.; Jensen, T. EFNS guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, G.W.; Barkin, R.L. Neuropathic pain: Etiology, pathophysiology, mechanisms, and evaluations. Dis.-A-Mon. 2014, 60, 6–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N. Pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: The latest recommendations. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennemann-Krause, L.; Sredni, S. Systemic drug therapy for neuropathic pain. Rev. Dor 2016, 17, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowbotham, M.C. Tricyclic antidepressants and opioids—better together? Pain 2015, 156, 1373–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Du, X.; Wu, L.; Wei, J.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, R.; Lei, M.; Zhao, L. Discontinuation Syndrome of Extended-Release Venlafaxine during the COVID-19 Epidemic. Psychiatr. Danub. 2021, 33, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fava, M.; Mulroy, R.; Alpert, J.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Rosenbaum, J.F. Emergence of adverse events following discontinuation of treatment with extended-release venlafaxine. Am. J. Psychiatry 1997, 154, 1760–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiyaam, N.; Nopitasari, B.L.; Muhajiji, H. IAI CONFERENCE: Comparing the quality of life of neuropathic patients treated with gabapentin and pregabalin at the neuropathic poly of the NTB provincial hospital in 2019. Pharm. Educ. 2021, 21, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayur, M.N. Potential Adverse Consequences of Combination Therapy with Gabapentin and Pregabalin. Case Rep. Med. 2021, 2021, 5559981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, G.G.M.; Owish, K.A.; Zaroug, M.S. The analgesic effect of tramadol versus morphine in the treatment of cancer pain in National Cancer Institute, University of Gezira, Sudan (2018). Open J. Pain Med. 2021, 5, 012–019. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiullah, M.; Siddiqui, K. Pharmacological Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: An Update. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Sindrup, S.H.; Jensen, T.S. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.; Cox, F. Acute pain management in patients with drug dependence syndrome. Pain Rep. 2017, 2, e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N.; de Andrade, D.C.; Adam, F.; Ranoux, D.; Teixeira, M.J.; Galhardoni, R.; Raicher, I.; Üçeyler, N.; Sommer, C.; Bouhassira, D. Safety and efficacy of repeated injections of botulinum toxin A in peripheral neuropathic pain (BOTNEP): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Carvalho, T.T.; Manchope, M.F.; Artero, N.A.; Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Fattori, V.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Therapeutic Potential of Flavonoids in Pain and Inflammation: Mechanisms of Action, Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data, and Pharmaceutical Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, A.; Karamanlıoğlu, B.; Memiş, D.; Hamamcıoglu, M.K.; Tükenmez, B.; Pamukçu, Z.; Kurt, I. Analgesic effects of gabapentin after spinal surgery. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2004, 100, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruccu, G.; Aziz, T.Z.; Garcia-Larrea, L.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; Simpson, B.A.; Taylor, R.S. EFNS guidelines on neurostimulation therapy for neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 952–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caylor, J.; Reddy, R.; Yin, S.; Cui, C.; Huang, M.; Huang, C.; Ramesh, R.; Baker, D.G.; Simmons, A.; Souza, D.; et al. Spinal cord stimulation in chronic pain: Evidence and theory for mechanisms of action. Bioelectron. Med. 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzack, R.; Wall, P.D. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Surv. Anesthesiol. 1967, 11, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazorthes, Y.; Verdié, J.-C.; Sol, J.-C. Spinal cord stimulation for neuropathic pain. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2006, 81, 887–899. [Google Scholar]
- Eckermann, J.M.; Pilitsis, J.G.; Vannaboutathong, C.; Wagner, B.J.; Province-Azalde, R.; Bendel, M.A. Systematic Literature Review of Spinal Cord Stimulation in Patients with Chronic Back Pain without Prior Spine Surgery. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.O.; Reis, C.L.; Hatheway, J.A.; Schmidt, T.E.; Pico, T.C.; Sanapati, M.R.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Patel, A.S.; Calodney, A.; Johanek, L. Using Lower Amplitudes to Maintain Effective High Dose Spinal Cord Stimulation Therapy (SCS Dosing Pilot Study). Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2021, 24, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, V.; Scowcroft, J.; Chang, P.; Li, S.; Staats, P.; Subbaroyan, J.; Caraway, D. 10 kHz Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) for the Treatment of Chronic Peripheral Polyneuropathy (PPN): 12-month Results from Prospective Open-Label Pilot Study. Pain Pract. 2021, 21, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, H.; Jacob, S.; Shehata, T.M.; Morsy, M.A. Enhancement in antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of tramadol by transdermal proniosome gel. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y. Spinal cord stimulation: Neurophysiological and neurochemical mechanisms of action. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shechter, R.; Yang, F.; Xu, Q.; Cheong, Y.K.; He, S.Q.; Sdrulla, A.; Carteret, A.F.; Wacnik, P.W.; Dong, X.; Meyer, R.A.; et al. Conventional and kilohertz-frequency spinal cord stimulation produces intensity- and frequency-dependent inhibition of mechanical hypersensitivity in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botros, D. Pain Reduction in Chronic Lumbar Patients Using Spinal Cord Stimulation; Theses and Graduate Projects; Augsburg University: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Manca, A.; Kumar, K.; Taylor, R.S.; Jacques, L.; Eldabe, S.; Meglio, M.; Molet, J.; Thomson, S.; O’Callaghan, J.; Eisenberg, E.; et al. Quality of life, resource consumption and costs of spinal cord stimulation versus conventional medical management in neuropathic pain patients with failed back surgery syndrome (PROCESS trial). Eur. J. Pain 2008, 12, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Rizvi, S. Cost-effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation therapy in management of chronic pain. Pain Med. 2013, 14, 1631–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, T.R.; Krames, E.; Mekhail, N.; Pope, J.; Leong, M.; Stanton-Hicks, M.; Golovac, S.; Kapural, L.; Alo, K.; Anderson, J.; et al. The appropriate use of neurostimulation: New and evolving neurostimulation therapies and applicable treatment for chronic pain and selected disease states. Neuromodulation Appropriateness Consensus Committee. Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodulation Soc. 2014, 17, 599–615, discussion 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudman, L.; Duarte, R.V.; De Smedt, A.; Copley, S.; Eldabe, S.; Moens, M. Cross-Country Differences in Pain Medication Before and After Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Patient Data From Two Prospective Studies in the United Kingdom and Belgium. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana Al-Jumah, M. Spinal Cord Stimulator Trial in a Patient on Chronic Warfarin Therapy; American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians: Paducah, KY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- North, R.B.; Kumar, K.; Wallace, M.S.; Henderson, J.M.; Shipley, J.; Hernandez, J.; Mekel-Bobrov, N.; Jaax, K.N. Spinal cord stimulation versus re-operation in patients with failed back surgery syndrome: An international multicenter randomized controlled trial (EVIDENCE study). Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodulation Soc. 2011, 14, 330–335, discussion 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemler, M.A.; De Vet, H.C.; Barendse, G.A.; Van Den Wildenberg, F.A.; Van Kleef, M. The effect of spinal cord stimulation in patients with chronic reflex sympathetic dystrophy: Two years’ follow-up of the randomized controlled trial. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Taylor, R.S.; Jacques, L.; Eldabe, S.; Meglio, M.; Molet, J.; Thomson, S.; O’Callaghan, J.; Eisenberg, E.; Milbouw, G.; et al. Spinal cord stimulation versus conventional medical management for neuropathic pain: A multicentre randomised controlled trial in patients with failed back surgery syndrome. Pain 2007, 132, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Duenas, A.; Holmes, M.W.; Papaioannou, D.; Chilcott, J. Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain of neuropathic or ischaemic origin: Systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13, iii, ix-x, 1–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Taylor, R.S.; Jacques, L.; Eldabe, S.; Meglio, M.; Molet, J.; Thomson, S.; O’Callaghan, J.; Eisenberg, E.; Milbouw, G.; et al. The effects of spinal cord stimulation in neuropathic pain are sustained: A 24-month follow-up of the prospective randomized controlled multicenter trial of the effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 762–770, discussion 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, C.C.; Meier, K.; Zaalberg, P.B.; Nijhuis, H.J.; Duyvendak, W.; Vesper, J.; Enggaard, T.P.; Lenders, M.W. Spinal cord stimulation in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy: A multicentre randomized clinical trial. Pain 2014, 155, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slangen, R.; Schaper, N.C.; Faber, C.G.; Joosten, E.A.; Dirksen, C.D.; van Dongen, R.T.; Kessels, A.G.; van Kleef, M. Spinal cord stimulation and pain relief in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A prospective two-center randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 3016–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruccu, G.; Garcia-Larrea, L.; Hansson, P.; Keindl, M.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; Paulus, W.; Taylor, R.; Tronnier, V.; Truini, A.; Attal, N. EAN guidelines on central neurostimulation therapy in chronic pain conditions. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 10-kHz High-Frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation for Adults With Chronic Noncancer Pain: A Health Technology Assessment. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2020, 20, 1–109.
- Chakravarthy, K.; Richter, H.; Christo, P.J.; Williams, K.; Guan, Y. Spinal Cord Stimulation for Treating Chronic Pain: Reviewing Preclinical and Clinical Data on Paresthesia-Free High-Frequency Therapy. Neuromodulation 2018, 21, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D. Current experience of spinal neuromodulation in chronic pain: Is there a role in children and young people? Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2017, 21, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, W.S.; Ding, Y.R.; Kurtom, K.H. Delayed upper extremity paresthesia post permanent implantation of five lead spinal cord stimulator for low back and lower extremity pain: A case report. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 134, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvanendran, A.; Young, A.C. Spinal epidural hematoma after spinal cord stimulator trial lead placement in a patient taking aspirin. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2014, 39, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnumpurath, S.; Srinivasagopalan, R.; Vadivelu, N. Spinal cord stimulation: Principles of past, present and future practice: A review. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2009, 23, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayek, S.M.; Veizi, E.; Hanes, M. Treatment-Limiting Complications of Percutaneous Spinal Cord Stimulator Implants: A Review of Eight Years of Experience From an Academic Center Database. Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodulation Soc. 2015, 18, 603–608, discussion 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendersky, D.; Yampolsky, C. Is spinal cord stimulation safe? A review of its complications. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, E.; Kurt, K.N.; Yousem, D.M.; Christo, P.J. Spinal cord stimulators: Typical positioning and postsurgical complications. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, J.V.; Varhabhatla, N.C.; Bebic, Z.; Kaye, A.D.; Yong, R.J.; Urman, R.D.; Merkow, J.S. Spinal Cord Stimulation for Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuwissen, K.P.V.; van der Toorn, A.; Gu, J.W.; Zhang, T.C.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Joosten, E.A.J. Active Recharge Burst and Tonic Spinal Cord Stimulation Engage Different Supraspinal Mechanisms: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study in Peripherally Injured Chronic Neuropathic Rats. Pain Pract. Off. J. World Inst. Pain 2020, 20, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, E.A.; Franken, G. Spinal cord stimulation in chronic neuropathic pain: Mechanisms of action, new locations, new paradigms. Pain 2020, 161, S104–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombovy-Johnson, M.L.; Hunt, C.L.; Morrow, M.M.; Lamer, T.J.; Pittelkow, T.P. Current evidence lacking to guide clinical practice for spinal cord stimulation in the treatment of neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury: A review of the Literature and a Proposal for Future Study. Pain Pract. 2020, 20, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapural, L.; Yu, C.; Doust, M.W.; Gliner, B.E.; Vallejo, R.; Sitzman, B.T.; Amirdelfan, K.; Morgan, D.M.; Brown, L.L.; Yearwood, T.L.; et al. Novel 10-kHz High-frequency Therapy (HF10 Therapy) Is Superior to Traditional Low-frequency Spinal Cord Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Back and Leg Pain: The SENZA-RCT Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology 2015, 123, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Flamer, D.; Shah, P.S. Perineural steroids for trauma and compression-related peripheral neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Anaesth./J. Can. D’anesthesie 2015, 62, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Bicket, M.C.; Jamison, D.; Wilkinson, I.; Rathmell, J.P. Epidural steroids: A comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2013, 38, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, R.; Hashimoto, R.; Friedly, J.; Fu, R.; Bougatsos, C.; Dana, T.; Sullivan, S.D.; Jarvik, J. Epidural Corticosteroid Injections for Radiculopathy and Spinal Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, T.D.; Salinas, F.S.; Narayana, S.; Fox, P.T.; Mogul, D.J. Computational and experimental analysis of TMS-induced electric field vectors critical to neuronal activation. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomjai, W.; Katz, R.; Lackmy-Vallée, A. Basic principles of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and repetitive TMS (rTMS). Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enticott, P.G.; Barlow, K.; Guastella, A.J.; Licari, M.K.; Rogasch, N.C.; Middeldorp, C.M.; Clark, S.R.; Vallence, A.-M.; Boulton, K.A.; Hickie, I.B. Protocol: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in autism spectrum disorder: Protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled clinical trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e046830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.-P.; André-Obadia, N.; Antal, A.; Ayache, S.S.; Baeken, C.; Benninger, D.H.; Cantello, R.M.; Cincotta, M.; de Carvalho, M.; De Ridder, D. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 2150–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strafella, A.P.; Paus, T.; Fraraccio, M.; Dagher, A. Striatal dopamine release induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex. Brain A J. Neurol. 2003, 126, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, C.V.; Nelson, A.J. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation to Assess Exercise-Induced Neuroplasticity. Front. Neuroergonomics 2021, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, C.; Pommier, B.; Fauchon, C.; Bradley, C.; Créac’h, C.; Murat, M.; Vassal, F.; Peyron, R. New procedure of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for central neuropathic pain: A placebo-controlled randomized crossover study. Pain 2020, 161, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; Poindessous-Jazat, F.; De Chauvigny, E.; Quesada, C.; Mhalla, A.; Ayache, S.S.; Fermanian, C.; Nizard, J.; Peyron, R.; Lefaucheur, J.-P. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for neuropathic pain: A randomized multicentre sham-controlled trial. Brain 2021, 144, 3328–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J. The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurophysiol. Clin./Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 36, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ostilio, K.; Magis, D. Invasive and Non-invasive Electrical Pericranial Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Primary Headaches. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2016, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P. Cortical neurostimulation for neuropathic pain: State of the art and perspectives. Pain 2016, 157 (Suppl. S1), S81–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Antal, A.; Ayache, S.S.; Benninger, D.H.; Brunelin, J.; Cogiamanian, F.; Cotelli, M.; De Ridder, D.; Ferrucci, R.; Langguth, B.; et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 56–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccard, S.G.; Pereira, E.A.; Aziz, T.Z. Deep brain stimulation for chronic pain. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2015, 22, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keifer, O.P., Jr.; Riley, J.P.; Boulis, N.M. Deep brain stimulation for chronic pain: Intracranial targets, clinical outcomes, and trial design considerations. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 671–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Barry, P.; Reken, S.; Baker, M. Pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in non-specialist settings: Summary of NICE guidance. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2010, 340, c1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sire, A.; Ammendolia, A.; Lippi, L.; Farì, G.; Cisari, C.; Invernizzi, M. Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (PENS) as a Rehabilitation Approach for Reducing Mixed Chronic Pain in Patients with Musculoskeletal Disorders. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavronsky, S.; Koeniger-Donohue, R.; Steller, J.; Hawkins, J.W. Postoperative pain: Acupuncture versus percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2012, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Carnero, J. Effectiveness of Dry Needling with Percutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation of High Frequency Versus Low Frequency in Patients with Myofascial Neck Pain. Pain Physician 2021, 24, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, M.A.; White, P.F.; Craig, W.F.; Ghoname, E.; Ahmed, H.E.; Proctor, T.J.; Noe, C.E.; Vakharia, A.S.; Gajraj, N. Percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: A novel analgesic therapy for diabetic neuropathic pain. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozani, S.N. Remote Analgesic Effects Of Conventional Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation: A Scientific And Clinical Review With A Focus On Chronic Pain. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 3185–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krames, E.S. The role of the dorsal root ganglion in the development of neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2014, 15, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.A.; Slavin, K.V. Peripheral nerve/field stimulation for chronic pain. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, L.; Russo, M.; Huygen, F.J.; Van Buyten, J.P.; Smet, I.; Verrills, P.; Cousins, M.; Brooker, C.; Levy, R.; Deer, T.; et al. One-year outcomes of spinal cord stimulation of the dorsal root ganglion in the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain. Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodulation Soc. 2015, 18, 41–48, discussion 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.C.; Nguyen, C.D.; Newman, D.P. Cryoablation of the Infrapatellar Branch of the Saphenous Nerve Identified by Non-Invasive Peripheral Nerve Stimulator for the Treatment of Non-Surgical Anterior Knee Pain: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hao, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, D.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Low-temperature plasma radiofrequency ablation in phantom limb pain: A case report. Brain Circ. 2018, 4, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, V.; Osborn, J.; Chaturvedi, R.; Shah, V.; Chakravarthy, K. Advances in the interventional management of neuropathic pain. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.E.; Grechushkin, V.; Chaudhry, A.; Bhattacharji, P.; Durkin, B.; Moore, W. Cryoneurolysis in Patients with Refractory Chronic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.M.; Vesuna, S.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Huynh, K.; Young, S.; Berndt, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Gorini, C.J.; Deisseroth, K.; Delp, S.L. Optogenetic and chemogenetic strategies for sustained inhibition of pain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoy, D.; Sternson, S.M. Chemogenetic Tools for Causal Cellular and Neuronal Biology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, D.J.; Roth, B.L. DREADDs (designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs): Chemogenetic tools with therapeutic utility. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damez-Werno, D.M.; Kenny, P.J. Using Opioid Receptors to Expand the Chemogenetic and Optogenetic Toolbox. Neuron 2015, 86, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yi, M.-H.; Liu, Y.U.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Bosco, D.B.; Zheng, J.; Xie, M.; Zhou, L.; Qu, W.; Wu, L.-J. Chemogenetic manipulation of microglia inhibits neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain in mice. bioRxiv 2020, 92, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca-Torralba, M.; Suárez-Pereira, I.; Bravo, L.; Camarena-Delgado, C.; Garcia-Partida, J.A.; Mico, J.A.; Berrocoso, E. Chemogenetic silencing of the locus coeruleus–basolateral amygdala pathway abolishes pain-induced anxiety and enhanced aversive learning in rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.M.; Montgomery, K.L.; Towne, C.; Lee, S.Y.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Deisseroth, K.; Delp, S.L. Virally mediated optogenetic excitation and inhibition of pain in freely moving nontransgenic mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Harris, A.R.; Kapsa, R.M. Controlling brain cells with light: Ethical considerations for optogenetic clinical trials. AJOB Neurosci. 2014, 5, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M. New approach for investigating neuropathic allodynia by optogenetics. Pain 2019, 160, S53–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcelli, P.A. Applications of optogenetic and chemogenetic methods to seizure circuits: Where to go next? J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 2345–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Park, E.; Kim, T.; Kim, T.; Kang, M.; Lee, K.S.; Park, S.M. Effectiveness of electrical stimulation on nerve regeneration after crush injury: Comparison between invasive and non-invasive stimulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y. Microbubbles and Nanobubbles with Ultrasound for Systemic Gene Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kugelman, T.; Buch, A.; Herman, M.; Han, Y.; Karakatsani, M.E.; Hussaini, S.A.; Duff, K.; Konofagou, E.E. Non-invasive, Focused Ultrasound-Facilitated Gene Delivery for Optogenetics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puranik, N.; Yadav, D.; Chauhan, P.S.; Kwak, M.; Jin, J.-O. Exploring the Role of Gene Therapy for Neurological Disorders. Curr. Gene Ther. 2021, 21, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Menezes, M.E.; Bhatia, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Gene Therapies for Cancer: Strategies, Challenges and Successes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedon, J.-M.G.; Wu, S.; Zheng, X.; Churchill, C.C.; Glorioso, J.C.; Liu, C.-H.; Liu, S.; Vulchanova, L.; Bekker, A.; Tao, Y.-X. Current gene therapy using viral vectors for chronic pain. Mol. Pain 2015, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksh, T.L.; Fisher, C.J.; Hockman, T.M.; Wiese, A.J. Current and Future Issues in the Development of Spinal Agents for the Management of Pain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 232–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujedo, B.M. Current evidence for spinal opioid selection in postoperative pain. Korean J. Pain 2014, 27, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, A.; Kuwahara, H.; Mayra, A.; Kubodera, T.; Hirai, T.; Sunaga, F.; Tajiri, M.; Hirai, Y.; Shimada, T.; Mizusawa, H. Intraperitoneal administration of AAV9-shRNA inhibits target gene expression in the dorsal root ganglia of neonatal mice. Mol. Pain 2013, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fischer, G.; Hogan, Q.H. AAV-Mediated Gene Transfer to Dorsal Root Ganglion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1382, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, X.; Yi, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, S.; Izenwasser, S.; Lemmon, V.; Roy, S.; Hao, S. Viral vector-mediated gene therapy for opioid use disorders. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 341, 113710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xu, G.Y.; Wu, P.; Li, G.W.; Huang, L.Y. Adeno-associated viral transfer of opioid receptor gene to primary sensory neurons: A strategy to increase opioid antinociception. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6204–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Chavez, R.A.; Landry, R.; Fry, M.; Green-Fulgham, S.M.; Coulson, J.D.; Collins, S.D.; Glover, D.K.; Rieger, J.; Forsayeth, J.R. Targeted interleukin-10 plasmid DNA therapy in the treatment of osteoarthritis: Toxicology and pain efficacy assessments. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 90, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Cui, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Lv, B.; Li, M.; Zhao, W.; et al. pUDK-HGF Gene Therapy to Relieve CLI Rest Pain and Ulcer: A Phase II, Double-Blind, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorioso, J.C.; Fink, D.J. Herpes vector–mediated gene transfer in the treatment of chronic pain. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternak, G.W.; Pan, Y.X. Mu opioids and their receptors: Evolution of a concept. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 1257–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Gooding, S.W.; Lewis, E.; Felth, L.C.; Gaur, A.; Whistler, J.L. Pharmacological and genetic manipulations at the µ-opioid receptor reveal arrestin-3 engagement limits analgesic tolerance and does not exacerbate respiratory depression in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, M.; Treadwell, J.R.; Tregear, S.J.; Coates, V.H.; Wiffen, P.J.; Akafomo, C.; Schoelles, K.M. Long-term opioid management for chronic noncancer pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD006605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, Z.; He, X.; Liu, W. Development of viral vectors for gene therapy for chronic pain. Pain Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 968218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J. IL-10 and IL-1β mediate neuropathic-pain like behavior in the ventrolateral orbital cortex. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Huang, W.; Liu, S.; Levitt, R.C.; Candiotti, K.A.; Lubarsky, D.A.; Hao, S. IL-10 mediated by herpes simplex virus vector reduces neuropathic pain induced by HIV gp120 combined with ddC in rats. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortmann, K.L.M.; Chattopadhyay, M. Decrease in neuroimmune activation by HSV-mediated gene transfer of TNFα soluble receptor alleviates pain in rats with diabetic neuropathy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 41, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bobinski, F.; Teixeira, J.M.; Sluka, K.A.; Santos, A.R.S. Interleukin-4 mediates the analgesia produced by low-intensity exercise in mice with neuropathic pain. Pain 2018, 159, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Liu, D.; Chhoa, M.; Li, C.-M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lehto, S.G.; Immke, D.C.; Moyer, B.D. Voltage-gated sodium channel function and expression in injured and uninjured rat dorsal root ganglia neurons. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, S.G.; Zamponi, G.W. Regulating excitability of peripheral afferents: Emerging ion channel targets. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goaillard, J.-M.; Marder, E. Ion channel degeneracy, variability, and covariation in neuron and circuit resilience. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 44, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.C. Multi-targeting sodium and calcium channels using venom peptides for the treatment of complex ion channels-related diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Cohen, C.J.; Dehnhardt, C.M. Inhibitors of voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1. 7: Patent applications since 2010. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2014, 3, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.; Cummins, T. Chapter Eighteen-Unusual Voltage-Gated Sodium Currents as Targets for Pain. Curr. Top. Membr. 2016, 78, 599–638. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tang, B.; Jiang, H. Primary erythromelalgia: A review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbs, G.R.; Posson, D.J.; Goldstein, P.A. Voltage-Gated Ion Channels in the PNS: Novel Therapies for Neuropathic Pain? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, G.W.; Han, C.; Waxman, S.G. Voltage-Gated Ion Channels as Molecular Targets for Pain. In Translational Neuroscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 415–436. [Google Scholar]
- Kushnarev, M.; Pirvulescu, I.P.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Neuropathic pain: Preclinical and early clinical progress with voltage-gated sodium channel blockers. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altier, C.; Zamponi, G.W. Targeting Ca 2+ channels to treat pain: T-type versus N-type. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratté, S.; Prescott, S.A. Afferent hyperexcitability in neuropathic pain and the inconvenient truth about its degeneracy. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, S.; Murugan, S.; Kumar, D.P.; Kesturu, G.S.; Arul, A.B. Regulatory Action of Calcium Channels in Pain Pathway. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarini, E.; Coppi, E.; Micheli, L.; Parisio, C.; Vona, A.; Cherchi, F.; Pugliese, A.M.; Pedata, F.; Failli, P.; Palomino, S. Acute visceral pain relief mediated by A3AR agonists in rats: Involvement of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Pain 2020, 161, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, B.; Page, K.M.; Kadurin, I.; Ho, S.; Nieto-Rostro, M.; Dolphin, A.C. Thrombospondin-4 reduces binding affinity of [3H]-gabapentin to calcium-channel α2δ-1-subunit but does not interact with α2δ-1 on the cell-surface when co-expressed. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.; Lillesaar, C.; Theodorsson, E.; Hildebrand, C. Hypoglycaemic neuropathy: Occurrence of axon terminals in plantar skin and plantar muscle of diabetic BB/Wor rats treated with insulin implants. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 99, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.; Wilce, J. Venom as a source of useful biologically active molecules. Emerg. Med. 2001, 13, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Cai, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Vallecillo, T.G.M.; Serafini, M.J.; Thomas, A.M.; Pham, N.Y.N.; Bellampalli, S.S.; Moutal, A. Reversal of peripheral neuropathic pain by the small-molecule natural product Physalin F via block of CaV2. 3 (R-type) and CaV2. 2 (N-type) voltage-gated calcium channels. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2939–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Guan, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Tiwari, V.; Hoffman, P.N.; Li, M.; Tao, Y.-X. Impaired neuropathic pain and preserved acute pain in rats overexpressing voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv1. 2 in primary afferent neurons. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busserolles, J.; Tsantoulas, C.; Eschalier, A.; García, J.A.L. Potassium channels in neuropathic pain: Advances, challenges, and emerging ideas. Pain 2016, 157, S7–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Rong, L.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, M.; Ren, X. Epigenetic restoration of voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1. 2 alleviates nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. J. Neurochem. 2021, 156, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elsayed, A.; Jackson, M.; Gu, S.L.; Fiala, K.; Gu, J. Neuropathic pain and Kv7 voltage-gated potassium channels: The potential role of Kv7 activators in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919864256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Class of Drug | Nature of Action | Undesired Effects | Contraindication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tricyclic antidepressants (Nortriptyline, Desipramine) | Inhibition of serotonin as well as norepinephrine reuptake, sodium channel blockade, anticholinergic | Sleeplessness, anticholinergic effects (e.g., xerostomia or ischuria, obesity) | Cardiovascular disease, epilepsy, glaucoma | [43] |
| Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (Duloxetine, Venlafaxine) | Inhibition of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake | Nausea | Hepatic malfunction, impaired renal function, alcohol use disorder | [45] |
| Calcium channel α2-δ ligands (Gabapentin, Pregabalin) | Diminishes the release of glutamate, norepinephrine as well as substance P, with α2-δ subunit ligands of voltage-gated calcium channel | Somnolence, lightheadedness, peripheral edema | Impaired renal function | [55] |
| Opioid agonist (Morphine) | Agonist action on μ-receptor | Nausea, emesis, improper bowel movement, vertigo | History of substance abuse increased suicidal risk | [51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinu, P.; Morsy, M.A.; Nair, A.B.; Mouslem, A.K.A.; Venugopala, K.N.; Goyal, M.; Bansal, M.; Jacob, S.; Deb, P.K. Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Potential and Pitfalls. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113002
Shinu P, Morsy MA, Nair AB, Mouslem AKA, Venugopala KN, Goyal M, Bansal M, Jacob S, Deb PK. Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Potential and Pitfalls. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113002
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinu, Pottathil, Mohamed A. Morsy, Anroop B. Nair, Abdulaziz K. Al Mouslem, Katharigatta N. Venugopala, Manoj Goyal, Monika Bansal, Shery Jacob, and Pran Kishore Deb. 2022. "Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Potential and Pitfalls" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113002
APA StyleShinu, P., Morsy, M. A., Nair, A. B., Mouslem, A. K. A., Venugopala, K. N., Goyal, M., Bansal, M., Jacob, S., & Deb, P. K. (2022). Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Potential and Pitfalls. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113002