Comparison of Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility of Sugammadex and Neostigmine in Patients Undergoing Robotic Thyroidectomy: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
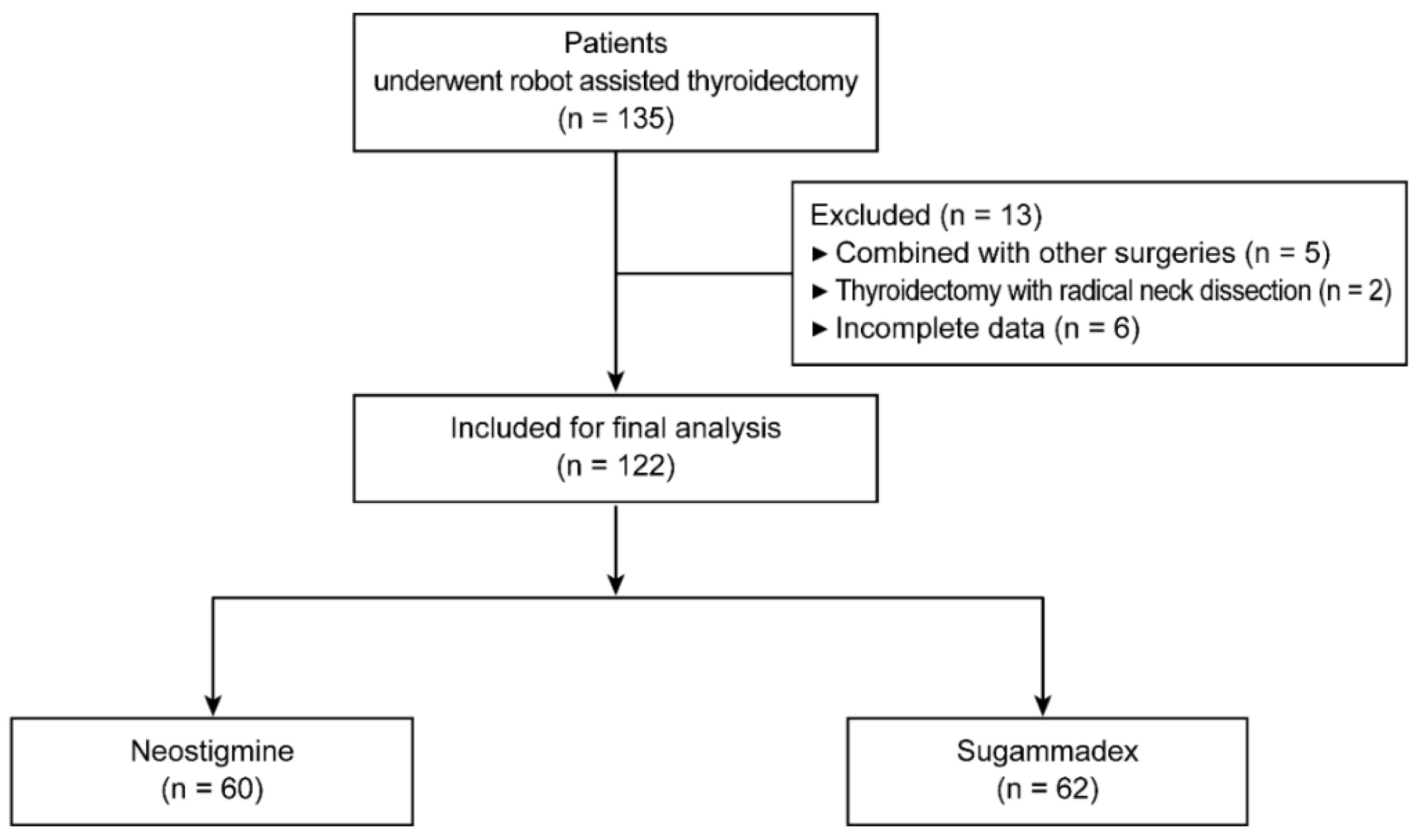
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Practice
2.3. Data Collection and Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsner, J.L.; Smith, J.M.; Ensor, C.R. Intravenous Neostigmine for Postoperative Acute Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction. Ann. Pharmacother. 2012, 46, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad-Gurumeta, A.; Ripolles-Melchor, J.; Casans-Frances, R.; Espinosa, A.; Martinez-Hurtado, E.; Fernandez-Perez, C.; Ramirez, J.M.; Lopez-Timoneda, F.; Calvo-Vecino, J.M. A Systematic Review of Sugammadex vs Neostigmine for Reversal of Neuromuscular Blockade. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacan, O.; White, P.F.; Tufanogullari, B.; Klein, K. Sugammadex Reversal of Rocuronium-Induced Neuromuscular Blockade: A Comparison with Neostigmine-Glycopyrrolate and Edrophonium-Atropine. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesnicky, B.L.; Traill, C.; Marroquin-Harris, F.B. The Effect of Routine Availability of Sugammadex on Postoperative Respiratory Complications: A Historical Cohort Study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2017, 83, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckmann, B.; Sasaki, N.; Grobara, P.; Li, M.K.; Woo, T.; de Bie, J.; Maktabi, M.; Lee, J.; Kwo, J.; Pino, R.; et al. Effects of Sugammadex on Incidence of Postoperative Residual Neuromuscular Blockade: A Randomized, Controlled Study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deljou, A.; Schroeder, D.R.; Ballinger, B.A.; Sprung, J.; Weingarten, T.N. Effects of Sugammadex on Time of First Postoperative Bowel Movement: A Retrospective Analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 3, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.E.; Yates, J.R.; Vega, H.; Heidel, R.E.; Buehler, J.M. Effects on Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility after Neuromuscular Blockade Reversal with Sugammadex versus Neostigmine/Glycopyrrolate in Colorectal Surgery Patients. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 54, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Yoon, S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, W.H.; Jang, J.Y. Effect of Sugammadex on the Recovery of Gastrointestinal Motility after Open Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021, 87, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, E.S.; Grant, A.E.; Torjman, M.C.; McNulty, S.E.; Baratta, J.L.; Viscusi, E.R. The Efficacy of Peripheral Opioid Antagonists in Opioid-Induced Constipation and Postoperative Ileus: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2017, 42, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaparmakov, I.; Erckenbrecht, J.F.; Wienbeck, M. Modulation of the Adrenergic System in the Treatment of Postoperative Bowel Atonia. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1984, 19, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.J.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. Mechanisms of Postoperative Ileus. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. Off. J. Eur. Gastrointest. Motil. Soc. 2004, 16, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.W.; Jeong, J.J.; Nam, K.H.; Chang, H.S.; Chung, W.Y.; Park, C.S. Robot-Assisted Endoscopic Thyroidectomy for Thyroid Malignancies Using a Gasless Transaxillary Approach. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2009, 209, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, R.; Griffiths, C. Acute Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction: A Pharmacological Approach. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1992, 74, 364–367. [Google Scholar]
- Kreis, M.E.; Kasparek, M.; Zittel, T.T.; Becker, H.D.; Jehle, E.C. Neostigmine Increases Postoperative Colonic Motility in Patients Undergoing Colorectal Surgery. Surgery 2001, 130, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiamah, A.; Johnson, S.; Ho, A.; Orbell, J. Neostigmine and Glycopyrronium: A Potential Safe Alternative for Patients with Pseudo-Obstruction without Access to Conventional Methods of Decompression. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, 221249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponec, R.J.; Saunders, M.D.; Kimmey, M.B. Neostigmine for the Treatment of Acute Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, R.G.; Godoy, F.L. Neostigmine for Acute Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2014, 3, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vather, R.; Trivedi, S.; Bissett, I. Defining Postoperative Ileus: Results of a Systematic Review and Global Survey. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Seager, S.J. Gastric Emptying Following Premedication with Glycopyrrolate or Atropine. Br. J. Anaesth. 1983, 55, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Erdivanli, B.; Tomak, Y.; Pergel, A. Reversal of Neuromuscular Blockade with Sugammadex or Neostigmine/Atropine: Effect on Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility. J. Clin. Anesth. 2016, 32, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Noh, H.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Woo, K.; Kim, H. Neuromuscular Blockade Reversal with Sugammadex versus Pyridostigmine/Glycopyrrolate in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Trial of Effects on Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2020, 73, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deljou, A.; Soleimani, J.; Sprung, J.; Schroeder, D.R.; Weingarten, T.N. Effects of Reversal Technique for Neuromuscular Paralysis on Time to Recovery of Bowel Function after Craniotomy. Am. Surg. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.; Djeudji, F.; Leduc, P.; Fanget, F.; Barth, X. Ogilvie’s Syndrome-Acute Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction. J. Visc. Surg. 2015, 152, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, M.J.; Milazkiewicz, R.; Carli, F.; Deacock, A.R. Influence of Neostigmine on Postoperative Vomiting. Br. J. Anaesth. 1988, 61, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeke, A.J.; de Lange, J.J.; van Druenen, B.; Langemeijer, J.J. Effect of Antagonizing Residual Neuromuscular Block by Neostigmine and Atropine on Postoperative Vomiting. Br. J. Anaesth. 1994, 72, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramèr, M.R.; Fuchs-Buder, T. Omitting Antagonism of Neuromuscular Block: Effect on Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting and Risk of Residual Paralysis. A Systematic Review. Br. J. Anaesth. 1999, 82, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løvstad, R.Z.; Thagaard, K.S.; Berner, N.S.; Raeder, J.C. Neostigmine 50 μg kg−1 with Glycopyrrolate Increases Postoperative Nausea in Women after Laparoscopic Gynaecological Surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2001, 45, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelskylä, K.; Yli-Hankala, A.; Soikkeli, A.; Korttila, K. Neostigmine with Glycopyrrolate Does Not Increase the Incidence or Severity of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting in Outpatients Undergoing Gynaecological Laparoscopy. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 81, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sonner, J.M.; Hynson, J.M.; Clark, O.; Katz, J.A. Nausea and Vomiting Following Thyroid and Parathyroid Surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 1997, 9, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Neostigmine (n = 60) | Sugammadex (n = 62) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 39 ± 10 | 37 ± 10 | 0.135 |
| Female sex | 55 (92) | 60 (97) | 0.269 |
| Body mass index, kg m−2 | 22.5 ± 3.2 | 23.1 ± 3.7 | 0.629 |
| ASA physical status | 0.592 | ||
| I | 46 (77) | 50 (81) | |
| II | 14 (23) | 12 (19) | |
| Co-morbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 5 (8) | 1 (2) | 0.111 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 0.492 |
| Liver disease | 2 (3) | 1 (2) | 0.616 |
| Preoperative laboratory value | |||
| T3, pg/mL | 0.90 ± 0.13 | 0.96 ± 0.20 | 0.065 |
| T4, ng/dL | 1.09 ± 0.22 | 1.09 ± 0.17 | 0.521 |
| TSH, mIU/L | 1.67 ± 1.11 | 1.49 ± 0.92 | 0.538 |
| Serum calcium, mg/dL | 9.51 ± 0.32 | 9.54 ± 0.31 | 0.580 |
| Variables | Neostigmine (n = 60) | Sugammadex (n = 62) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of anesthesia, min | 149 ± 39 | 140 ± 31 | 0.120 |
| Sevoflurane/desflurane | 3/57 (5/95) | 4/58 (6/94) | >0.999 |
| Intraoperative administered remifentanil, µg | 494 ± 173 | 471 ± 171 | 0.472 |
| Intraoperative administered rocuronium, mg | 55 ± 8 | 53 ± 13 | 0.287 |
| Intraoperative use of opioid, n | 15 (25) | 27 (44) | 0.031 * |
| Intraoperative total fluid intake, mL | 608 ± 154 | 608 ± 173 | 0.985 |
| Subtotal/total thyroidectomy | 50/10 (83/17) | 54/8 (87/13) | 0.558 |
| Duration of PACU stay, min | 37 ± 11 | 35 ± 9 | 0.193 |
| Additional antiemetics in PACU, n | 2 (3) | 7 (11) | 0.164 |
| Serum calcium at POD 1, mg/dL | 8.69 ± 0.36 | 8.72 ± 0.41 | 0.529 |
| Hypocalcemia at POD 1, n | 10 (22) | 9 (21) | 0.883 |
| Length of postoperative hospital stays, days | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 0.363 |
| Variables | Neostigmine (n = 60) | Sugammadex (n = 62) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients who passed gas > 12 h | 35 (58) | 26 (42) | 0.070 |
| Patients who passed gas ≤ 12 h | 25 (42) | 36 (58) | |
| Patients who passed gas > 24 h | 17 (28) | 6 (10) | 0.008 * |
| Patients who passed gas ≤ 24 h | 43 (72) | 56 (90) | |
| Postoperative constipation | 16 (27) | 9 (15) | 0.097 |
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Group | ||||
| Neostigmine | 1 | 1 | ||
| Sugammadex | 3.69 (1.34–10.15) | 0.012 * | 4.60 (1.59–13.30) | 0.005 * |
| Female sex | 0.71 (0.08–6.16) | 0.752 | ||
| Age, year | 0.99 (0.94–1.03) | 0.520 | ||
| Body mass index, kg m−2 | 1.12 (0.96–1.30) | 0.141 | ||
| ASA physical status | ||||
| I | 1 | |||
| II | 0.55 (0.23–1.34) | 0.188 | ||
| Anesthetic agent | ||||
| Sevoflurane | 1 | |||
| Desflurane | 0.74 (0.52–3.44) | 0.698 | ||
| Remifentanil, 10 µg increase | 1.03 (0.99–1.06) | 0.115 | 1.03 (1.00–1.07) | 0.094 |
| Intraoperative use of opioid | 0.78 (0.31–1.98) | 0.599 | 0.48 (0.17–1.36) | 0.169 |
| Rocuronium, 1 mg increase | 1.02 (0.98–1.07) | 0.379 | ||
| Type of thyroidectomy | ||||
| Subtotal | 1 | |||
| Total | 2.02 (0.43–9.50) | 0.371 | ||
| Total fluid intake, 100 mL increase | 1.08 (0.81–1.44) | 0.591 | ||
| Duration of anesthesia, 5 min increase | 1.00 (0.93–1.06) | 0.904 | ||
| Duration of PACU stay, 5 min increase | 1.02 (0.98–1.06) | 0.376 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.J.; Chun, D.-H.; Kong, H.J.; Shin, H.J.; Yang, S.; Kim, N.Y. Comparison of Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility of Sugammadex and Neostigmine in Patients Undergoing Robotic Thyroidectomy: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102930
Lee MJ, Chun D-H, Kong HJ, Shin HJ, Yang S, Kim NY. Comparison of Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility of Sugammadex and Neostigmine in Patients Undergoing Robotic Thyroidectomy: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(10):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102930
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Min Jeong, Duk-Hee Chun, Hee Jung Kong, Hye Jung Shin, Sunmo Yang, and Na Young Kim. 2022. "Comparison of Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility of Sugammadex and Neostigmine in Patients Undergoing Robotic Thyroidectomy: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 10: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102930
APA StyleLee, M. J., Chun, D.-H., Kong, H. J., Shin, H. J., Yang, S., & Kim, N. Y. (2022). Comparison of Postoperative Gastrointestinal Motility of Sugammadex and Neostigmine in Patients Undergoing Robotic Thyroidectomy: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(10), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11102930






