Postoperative Olfaction Alteration Following Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.1.1. Test 1: Threshold
2.1.2. Test 2: Discrimination
2.1.3. Test 3: Identification
2.2. Endpoints
2.3. Treatment Protocols
2.4. Ethical Approval
2.5. Statistical Analysis
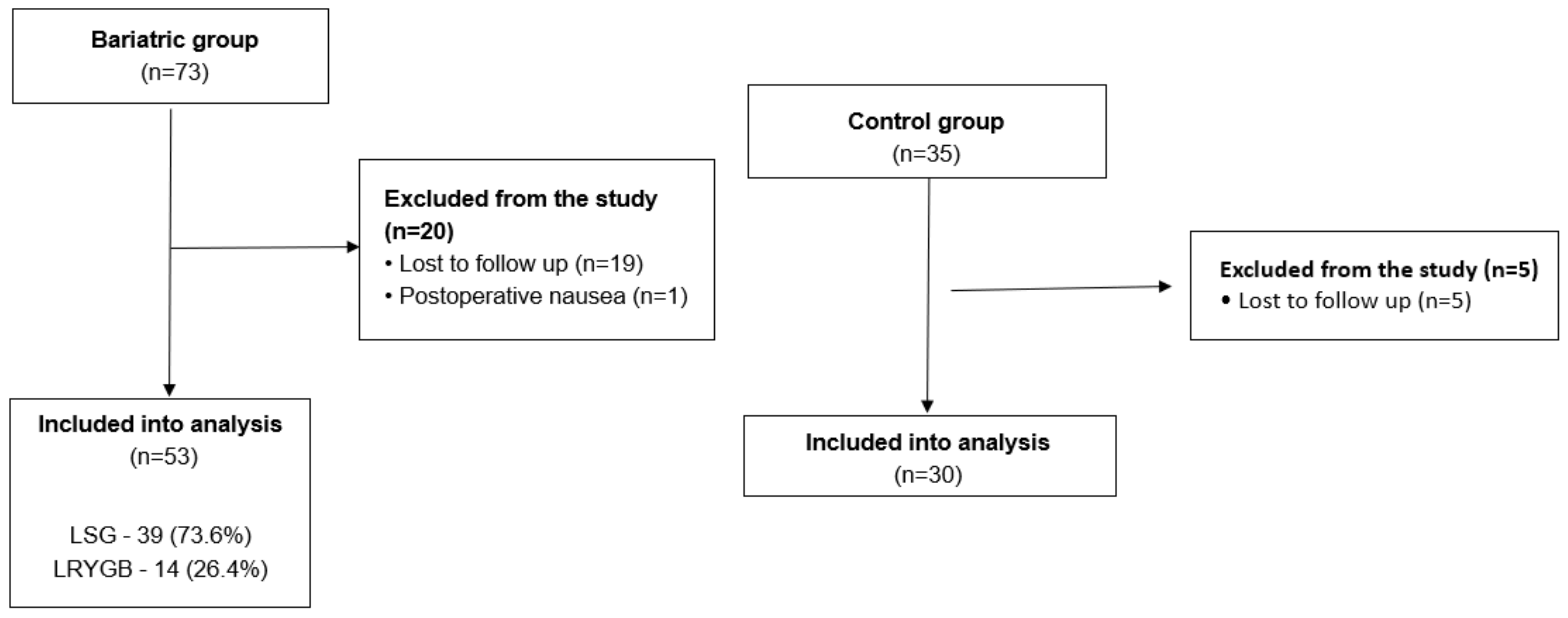
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Group
3.1.1. Bariatric Group
3.1.2. Control Group
3.1.3. Bariatric and Control Group Comparison
3.2. Main Results
3.2.1. Bariatric Group
3.2.2. Control Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Różańska-Walędziak, A.M.; Kowalewski, P.K.; Janik, M.R.; Brągoszewski, J.; Paśnik, K.; Bednarczyk, G.; Wallner, G.; Matłok, M.; Walędziak, M. Present trends in bariatric surgery in Poland. Videosurgery Other Miniinvasive Tech. 2019, 14, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, P.S.; Blundell, J.E.; Mennella, J.A.; Batterham, R.L. Biological control of appetite: A daunting complexity. Obesity 2017, 25, S8–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baly, C.; Aioun, J.; Badonnel, K.; Lacroix, M.C.; Durieux, D.; Schlegel, C.; Salesse, R.; Caillol, M. Leptin and its receptors are present in the rat olfactory mucosa and modulated by the nutritional status. Brain Res. 2007, 1129, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, R.; Batterham, R.L. Potential mechanisms underlying the effect of bariatric surgery on eating behaviour. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2018, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerrweck, C.; Gallardo, V.C.; Calleja, C.; Sepúlveda, E.; Guilber, L. Gross Olfaction Before and After Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2988–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancı, D.; Altun, H.; Altun, H.; Batman, B.; Karip, A.B.; Serin, K.R. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Improves Olfaction Sensitivity in Morbidly Obese Patients. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, C.; Weiss, R.; Keidar, A. Effect of different bariatric operations on food tolerance and quality of eating. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, R.; Huber, O.; Azagury, D.E.; Pichard, C. Twelve key nutritional issues in bariatric surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 805–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzyński, A.; Major, P.; Głuszek, S.; Kaseja, K.; Koszutski, T.; Leśniak, S.; Lewandowski, T.; Lipka, M.; Lisik, W.; Makarewicz, W.; et al. Polskie rekomendacje w zakresie chirurgii bariatrycznej i metabolicznej. Med. Prakt. Chir. 2016, 6, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hummel, T.; Sekinger, B.; Wolf, S.R.; Pauli, E.; Kobal, G. “Sniffin” sticks’. Olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokowska, A.; Hummel, T. Polska wersja testu Sniffin’ Sticks—Adaptacja i normalizacja. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2014, 68, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matłok, M.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Major, P.; Kłęk, S.; Budzyński, P.; Małczak, P. One hundred seventy-nine consecutive bariatric operations after introduction of protocol inspired by the principles of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS®) in bariatric surgery. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Jayaraman, L.; Punhani, D.; Chowbey, P. Enhanced Recovery after Bariatric Surgery in the Severely Obese, Morbidly Obese, Super-Morbidly Obese and Super-Super Morbidly Obese Using Evidence-Based Clinical Pathways: A Comparative Study. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, P.; Wysocki, M.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Pisarska, M.; Dworak, J.; Małczak, P.; Budzyński, A. Risk factors for complications of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 37, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, P.; Stefura, T.; Małczak, P.; Wysocki, M.; Witowski, J.; Kulawik, J.; Wierdak, M.; Pisarska, M.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Budzyński, A. Postoperative Care and Functional Recovery After Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Among Patients Under ERAS Protocol. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, J.G.; Paez, W.; Wolfe, B.M. Vagal nerve function in obesity: Therapeutic implications. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.J.; Bazerbachi, F.; Calderon, G.; Prokop, L.J.; Gomez, V.; Murad, M.H.; Acosta, A.; Camilleri, M.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K. Changes in Time of Gastric Emptying After Surgical and Endoscopic Bariatrics and Weight Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 57–68.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercia, I.; Dutia, R.; Kotler, D.P.; Belsley, S.; Laferrère, B. Gastrointestinal changes after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, C.L.; Lewis, H.B.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Park, A.J. The effect of bariatric surgery on gastrointestinal and pancreatic peptide hormones. Peptides 2016, 77, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miras, A.D.; Le Roux, C.W. Mechanisms underlying weight loss after bariatric surgery. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.A.; Cheskin, L.J.; Furtado, M.; Papas, K.; Schweitzer, M.A.; Magnuson, T.H.; Steele, K.E. Malnutrition in Bariatric Surgery Candidates: Multiple Micronutrient Deficiencies Prior to Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, P.; Małczak, P.; Wysocki, M.; Torbicz, G.; Gajewska, N.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Budzyński, A. Bariatric patients’ nutritional status as a risk factor for postoperative complications, prolonged length of hospital stay and hospital readmission: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 56, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, S.S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Webb, M.; Keidar, A.; Raziel, A.; Sakran, N.; Goitein, D.; Shibolet, O. Nutritional Status Prior to Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.L.; Faria, O.P.; Buffington, C.; de Almeida Cardeal, M.; Ito, M.K. Dietary protein intake and bariatric surgery patients: A review. Obes. Surg. 2011, 21, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J.; Liu, S.I.; Mok, K.T.; Shi, H.Y. Associations of Volume and Thyroidectomy Outcomes: A Nationwide Study with Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Coutts, D.; Wang, T.; Cakmak, Y.O. Systematic review of olfactory shifts related to obesity. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tang, K.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, A. Leptin modulates olfactory discrimination and neural activity in the olfactory bulb. Acta Physiol. 2019, 227, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, B.; Kiyici, S.; Ozmen, S.; Gul, Z.; Sigirli, D.; Cavun, S. The Association Between Olfaction and Taste Functions with Serum Ghrelin and Leptin Levels in Obese Women. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. Taste and Smell Processing in the Brain, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 164, ISBN 9780444638557. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Bariatric Group | Control Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 53 | 30 | - |
| Females, n (%) | 28 (52.8%) | 17 (56.7%) | 0.736 |
| Males, n (%) | 25 (47.2%) | 13 (43.3%) | |
| Mean age, years ± SD | 46.6 ± 9.5 | 48.1 ± 11.2 | 0.519 |
| Mean BMI, kg/m2 ± SD | 45.4 ± 5.1 | 24.9 ± 9.1 | <0.001 |
| Mean Maximal BMI, kg/m2 ± SD | 48.4 ± 6.0 | - | - |
| Type of surgery, n (%) | LSG—39 (73.6%) LRYGB—14 (26.4%) | Cholecystectomy—23 (76.7%) Nissen fundoplication—4 (13.3%) Heller cardiomyotomy—3 (10%) | - |
| Ex-smokers, n (%) | 12 (22.6%) | 8 (26.7%) | 0.680 |
| ASA 2, n (%) | 40 (75.5%) | 26 (86.7%) | 0.225 |
| ASA 3, n (%) | 13 (24.5%) | 4 (13.3%) | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 37 (69.8%) | 22 (73.3%) | 0.734 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 21 (39.6%) | 5 (16.7%) | 0.055 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 12 (22.6%) | 3 (10%) | 0.254 |
| NAFLD, n (%) | 14 (26.4%) | 1 (3.3%) | 0.020 |
| Pulmonary disease, n (%) | 19 (35.9%) | 3 (10%) | 0.021 |
| Mean operative time, min ± SD | 93 ± 32 | 89 ± 36 | 0.603 |
| Parameter | Preoperative Test | Postoperative Test | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bariatric group | |||
| Median Subjective olfactory evaluation, points (IQR) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.3882 |
| Mean Test 1, points ± SD | 9.33 ± 3.88 | 8.19 ± 3.02 | 0.0320 |
| Mean Test 2, points ± SD | 9.40 ± 2.94 | 8.92 ± 2.65 | 0.3588 |
| Mean Test 3, points ± SD | 13.91 ± 1.63 | 13.91 ± 1.88 | 0.7063 |
| Mean total, points ± SD | 32.63 ± 5.47 | 31.02 ± 4.72 | 0.0716 |
| Control group | |||
| Median Subjective olfactory evaluation, points (IQR) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.4722 |
| Mean Test 1, points ± SD | 8.91 ± 3.97 | 8.64 ± 3.59 | 0.5670 |
| Mean Test 2, points ± SD | 9.52 ± 2.99 | 9.01 ± 3.15 | 0.6984 |
| Mean Test 3, points ± SD | 13.98 ± 1.59 | 13.88 ± 1.89 | 0.5409 |
| Mean total, points ± SD | 32.39± 5.47 | 31.53 ± 4.81 | 0.3621 |
| Parameter | Preoperative Test | Postoperative Test | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRYGB | |||
| Median Subjective olfactory evaluation, points (IQR) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.3613 |
| Mean Test 1, points ± SD | 9.85 ± 3.82 | 9.44 ± 3.03 | 0.6496 |
| Mean Test 2, points ± SD | 8.62 ± 3.28 | 8.39 ± 3.2 | 0.8613 |
| Mean Test 3, points ± SD | 13.85 ± 1.68 | 14.15 ± 1.68 | 0.3627 |
| Mean total, points ± SD | 32.31 ± 5.84 | 31.98 ± 4.41 | 0.8613 |
| LSG | |||
| Median Subjective olfactory evaluation, points (IQR) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.9326 |
| Mean Test 1, points ± SD | 9.12 ± 3.97 | 7.75 ± 2.98 | 0.0339 |
| Mean Test 2, points ± SD | 9.74 ± 2.79 | 3.05 ± 2.48 | 0.197 |
| Mean Test 3, points ± SD | 13.97 ± 1.63 | 13.87 ± 1.96 | 0.9142 |
| Mean total, points ± SD | 32.83 ± 5.45 | 30.67 ± 4.88 | 0.0173 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pisarska-Adamczyk, M.; Tylec, P.; Gajewska, N.; Wierzbicka, J.; Przęczek, K.; Małczak, P.; Wysocki, M.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Wierdak, M.; Major, P. Postoperative Olfaction Alteration Following Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081704
Pisarska-Adamczyk M, Tylec P, Gajewska N, Wierzbicka J, Przęczek K, Małczak P, Wysocki M, Pędziwiatr M, Wierdak M, Major P. Postoperative Olfaction Alteration Following Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(8):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081704
Chicago/Turabian StylePisarska-Adamczyk, Magdalena, Piotr Tylec, Natalia Gajewska, Julia Wierzbicka, Krzysztof Przęczek, Piotr Małczak, Michał Wysocki, Michał Pędziwiatr, Mateusz Wierdak, and Piotr Major. 2021. "Postoperative Olfaction Alteration Following Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 8: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081704
APA StylePisarska-Adamczyk, M., Tylec, P., Gajewska, N., Wierzbicka, J., Przęczek, K., Małczak, P., Wysocki, M., Pędziwiatr, M., Wierdak, M., & Major, P. (2021). Postoperative Olfaction Alteration Following Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(8), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081704







