Severity and Duration of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease after Cardiac Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Surgical Procedures and Anesthetic Management
2.3. Data Collection and Study Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reuillard, A.; Garrouste, C.; Pereira, B.; Azarnoush, K.; Souteyrand, G.; Aniort, J.; Innorta, A.; Clerfond, G.; Heng, A.E.; Eschalier, R.; et al. Evolution of chronic kidney disease after surgical aortic valve replacement or transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 112, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Jang, M.J.; Moon, H.R.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, K.H.; Joo, K.W.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Na, K.Y.; et al. Development of model to predict end-stage renal disease after coronary artery bypass grafting: The ACHE score. Medicine 2019, 98, e15789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.K.; Levin, A.; Tonelli, M.; Okpechi, I.G.; Feehally, J.; Harris, D.; Jindal, K.; Salako, B.L.; Rateb, A.; Osman, M.A.; et al. Assessment of Global Kidney Health Care Status. JAMA 2017, 317, 1864–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm-Leen, E.R.; Hall, Y.N.; Tamura, M.K.; Chertow, G.M. Frailty and chronic kidney disease: The Third National Health and Nutrition Evaluation Survey. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 664–671.e662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bellomo, R. Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: Risk factors, pathophysiology and treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, C.E.; Yavas, S.; Segal, M.S.; Schold, J.D.; Tribble, C.G.; Layon, A.J.; Bihorac, A. Acute kidney injury is associated with increased long-term mortality after cardiothoracic surgery. Circulation 2009, 119, 2444–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blitz, J.D.; Shoham, M.H.; Fang, Y.; Narine, V.; Mehta, N.; Sharma, B.S.; Shekane, P.; Kendale, S. Preoperative Renal Insufficiency: Underreporting and Association With Readmission and Major Postoperative Morbidity in an Academic Medical Center. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 123, 1500–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englberger, L.; Suri, R.M.; Greason, K.L.; Burkhart, H.M.; Sundt, T.M., 3rd; Daly, R.C.; Schaff, H.V. Deep hypothermic circulatory arrest is not a risk factor for acute kidney injury in thoracic aortic surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.H.; Grab, J.D.; O’Brien, S.M.; Bridges, C.R.; Gammie, J.S.; Haan, C.K.; Ferguson, T.B.; Peterson, E.D. Bedside tool for predicting the risk of postoperative dialysis in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Circulation 2006, 114, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolari, A.; Pesce, L.L.; Pacini, D.; Mazzanti, V.; Salis, S.; Sciacovelli, C.; Rossi, F.; Alamanni, F. Risk factors for perioperative acute kidney injury after adult cardiac surgery: Role of perioperative management. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 93, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakar, C.V.; Arrigain, S.; Worley, S.; Yared, J.P.; Paganini, E.P. A clinical score to predict acute renal failure after cardiac surgery. JASN 2005, 16, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijeysundera, D.N.; Karkouti, K.; Dupuis, J.Y.; Rao, V.; Chan, C.T.; Granton, J.T.; Beattie, W.S. Derivation and validation of a simplified predictive index for renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery. JAMA 2007, 297, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welten, G.M.; Schouten, O.; Chonchol, M.; Hoeks, S.E.; Feringa, H.H.; Bax, J.J.; Dunkelgrun, M.; van Gestel, Y.R.; van Domburg, R.T.; Poldermans, D. Temporary worsening of renal function after aortic surgery is associated with higher long-term mortality. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2007, 50, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.S.; Eggers, P.W.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, C.A.; Vertosick, E.; Benfante, N.; Tin, A.; Sjoberg, D.; Hakimi, A.A.; Touijer, K.; Montorsi, F.; Eastham, J.; Russo, P.; et al. Impact of Acute Kidney Injury and Its Duration on Long-term Renal Function After Partial Nephrectomy. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legouis, D.; Jamme, M.; Galichon, P.; Provenchere, S.; Boutten, A.; Buklas, D.; Hanouz, J.L.; Hertig, A. Development of a practical prediction score for chronic kidney disease after cardiac surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Kramer, R.S.; Coca, S.G.; Parikh, C.R. Duration of acute kidney injury impacts long-term survival after cardiac surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Park, M.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, H.Y.; Shim, H.S.; Sohn, J.T.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, S.M. Potentially modifiable risk factors for acute kidney injury after surgery on the thoracic aorta: A propensity score matched case-control study. Medicine 2015, 94, e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapsia, V.; Johnson, R.J.; Dass, B.; Shimada, M.; Kambhampati, G.; Ejaz, N.I.; Arif, A.A.; Ejaz, A.A. Elevated uric acid increases the risk for acute kidney injury. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 302.e309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.H.; Lee, S.M.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, J.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Sung, K.I.; Kim, C.S.; Cho, H.S. Simplified clinical risk score to predict acute kidney injury after aortic surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 27, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobey, R.; Cheng, H.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Young, J.N.; Boyd, W.D.; Ji, F.; Liu, H. Postoperative Acute Kidney Injury and Blood Product Transfusion After Synthetic Colloid Use During Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithiran, H.; Kunnath Bonney, G.; Bose, S.; Subramanian, S.; Zhe Yan, Z.N.; Zong En, S.Y.; Papadimas, E.; Chauhan, I.; MacLaren, G.; Kofidis, T. A Score for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery in an Asian Population. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2016, 30, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagny, M.G.; Roediger, L.; Koch, J.N.; Dubois, F.; Senard, M.; Donneau, A.F.; Hubert, M.B.; Hans, G.A. Hydroxyethyl Starch 130/0.4 and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth 2016, 30, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, W.G.; Smith, M.; Bankhead, C.; Matsushita, K.; Stevens, S.; Holt, T.; Hobbs, F.D.; Coresh, J.; Woodward, M. Body-mass index and risk of advanced chronic kidney disease: Prospective analyses from a primary care cohort of 1.4 million adults in England. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.J.; Han, J.; Montez-Rath, M.E.; Kim, S.H.; Cullen, M.R.; Stafford, R.S.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Chertow, G.M. Antidiabetic medication use in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2019, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.E.; Blaine, C.; Dawnay, A.; Devonald, M.A.; Ftouh, S.; Laing, C.; Latchem, S.; Lewington, A.; Milford, D.V.; Ostermann, M. The definition of acute kidney injury and its use in practice. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.R.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Goodrich, C.A.; Bohm, A.R.; Alam, S.S.; Coca, S.G.; McArthur, E.; Garg, A.X.; Parikh, C.R. Are Urinary Biomarkers Better Than Acute Kidney Injury Duration for Predicting Readmission? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, K.W. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Supplments 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Group, K.W. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guidelines for evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Supplments 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Stevens, L.A.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hendriksen, S.; Kusek, J.W.; Van Lente, F. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajulu, U.S.; Spiegelman, D.; Thurston, S.W.; Ganguli, B.; Eisen, E.A. Comparing smoothing techniques in Cox models for exposure-response relationships. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3735–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrleman, S.; Simon, R. Flexible regression models with cubic splines. Stat. Med. 1989, 8, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demler, O.V.; Paynter, N.P.; Cook, N.R. Tests of calibration and goodness-of-fit in the survival setting. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 1659–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B. Multivariable prognostic models: Issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legouis, D.; Galichon, P.; Bataille, A.; Chevret, S.; Provenchere, S.; Boutten, A.; Buklas, D.; Fellahi, J.L.; Hanouz, J.L.; Hertig, A. Rapid Occurrence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients Experiencing Reversible Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, K.; Rosner, M.H.; Haase, M.; Lewington, A.J.P.; O’Donoghue, D.J.; Wilson, F.P.; Nadim, M.K.; Silver, S.A.; Zarbock, A.; Ostermann, M.; et al. Quality Improvement Goals for Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, D.; Katz, N.M.; Fine, D.M.; Ono, M.; Barodka, V.M.; Lester, L.C.; Yenokyan, G.; Hogue, C.W. Defining oliguria during cardiopulmonary bypass and its relationship with cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizota, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hamada, M.; Matsukawa, S.; Shimizu, S.; Kai, S. Intraoperative oliguria predicts acute kidney injury after major abdominal surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, A.M.; Sladen, R.N. Acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 28, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | No AKI | AKI Stage 1, Transient | AKI Stage 1, Persistent | AKI Stage 2 or 3, Transient | AKI Stage 2 or 3, Persistent | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 1357 (67.5) | 388 (19.3) | 143 (7.1) | 58 (2.9) | 63 (3.1) | |
| Demographic data | ||||||
| Age, years | 64 (54–70) | 65 (56–71) | 63 (55–72) | 63 (54–69) | 65 (57–70) | 0.127 |
| Female, n | 350 (25.8) | 88 (22.7) | 46 (32.2) | 24 (41.4) | 21 (33.3) | 0.049 |
| Body-mass index, kg/m2 | 23.9 (21.7–26.2) | 24.0 (21.7–26.2) | 24.4 (22.0–26.8) | 23.3 (21.5–24.9) | 23.8 (21.0–24.7) | 0.150 |
| Surgery type | ||||||
| CABG, n | 626 (46.1) | 152 (39.2) | 48 (33.6) | 11 (19.0) | 11 (17.5) | <0.001 |
| Valvular heart surgery, n | 644 (47.5) | 213 (54.9) | 86 (60.1) | 43 (74.1) | 47 (74.6) | <0.001 |
| Thoracic aortic surgery, n | 33 (2.4) | 14 (3.6) | 4 (2.8) | 3 (5.2) | 2 (3.2) | 0.195 |
| Combined surgery, n | 54 (4.0) | 9 (2.3) | 5 (3.5) | 1 (1.7) | 3 (4.8) | 0.347 |
| Medical history | ||||||
| Hypertension, n | 647 (47.7) | 214 (55.2) | 80 (55.9) | 35 (60.3) | 32 (50.8) | 0.004 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n | 341 (25.1) | 108 (27.8) | 34 (23.8) | 14 (24.1) | 15 (23.8) | 0.926 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n | 166 (12.2) | 70 (18.0) | 22 (15.4) | 12 (20.7) | 14 (22.2) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular accident, n | 132 (9.7) | 38 (9.8) | 21 (14.7) | 14 (24.1) | 9 (14.3) | 0.005 |
| COPD, n | 80 (5.9) | 15 (3.9) | 15 (10.5) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (1.6) | 0.335 |
| Medication | ||||||
| ACEi or ARB, n | 236 (17.4) | 57 (14.7) | 24 (16.8) | 8 (13.8) | 14 (22.2) | 0.741 |
| β-blocker, n | 255 (18.8) | 69 (17.8) | 18 (12.6) | 4 (6.9) | 10 (15.9) | 0.026 |
| Diuretics, n | 167 (12.3) | 49 (12.6) | 20 (14.0) | 10 (17.2) | 8 (12.7) | 0.180 |
| Calcium channel blocker, n | 203 (15.0) | 59 (15.2) | 21 (14.7) | 11 (19.0) | 5 (7.9) | 0.625 |
| Aspirin, n | 677 (49.9) | 210 (54.1) | 87 (39.2) | 19 (32.8) | 20 (31.7) | 0.041 |
| Clopidogrel, n | 255 (18.8) | 72 (18.6) | 27 (18.9) | 6 (10.3) | 8 (12.7) | 0.182 |
| Statins, n | 346 (25.5) | 89 (22.9) | 37 (25.9) | 12 (20.7) | 13 (20.6) | 0.173 |
| Baseline laboratory findings | ||||||
| Hematocrit, % | 38.9 (35.3–42.5) | 37.5 (33.8–41.3) | 37.4 (33.8–40.1) | 36.3 (32.4–40.7) | 38.1 (34.6–40.0) | 0.039 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 0.89 (0.75–1.00) | 0.87 (0.70–1.03) | 0.90 (0.76–1.04) | 0.83 (0.66–0.95) | 0.84 (0.76–0.94) | 0.041 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 87 (75–103) | 90 (74–107) | 85 (78–98) | 91 (72–112) | 89 (79–100) | 0.044 |
| Albumin, mg/dL | 4.1 (3.9–4.4) | 4.1 (3.8–4.4) | 4.1 (3.8–4.4) | 4.0 (3.6–4.3) | 3.9 (3.6–4.3) | 0.094 |
| Operation and anesthesia details | ||||||
| Operation time, hour | 6.0 (5.2–6.9) | 6.3 (5.4–7.6) | 6.6 (5.5–7.7) | 7.1 (6.1–8.5) | 7.1 (5.8–8.7) | 0.005 |
| Crystalloid administration, mL/kg/h | 6.0 (3.8–8.6) | 5.2 (3.1–7.6) | 4.7 (3.1–7.0) | 4.5 (3.6–6.4) | 5.3 (3.6–7.1) | 0.010 |
| Colloid administration, mL/kg/h | 2.1 (0.8–3.9) | 1.9 (0.7–3.6) | 1.7 (0.8–3.1) | 1.9 (1.4–2.4) | 1.7 (0.9–2.6) | 0.040 |
| pRBC transfusion, units | 2 (0–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (0–3) | 2 (0–5) | 2 (1–4) | 0.014 |
| FFP transfusion, units | 0 (0–3) | 0 (0–3) | 2 (0–5) | 3 (0–5) | 2 (0–5) | <0.001 |
| Intraoperative norepinephrine infusion, n | 386 (28.4) | 130 (33.5) | 62 (43.4) | 38 (65.5) | 30 (52.4) | 0.005 |
| Intraoperative epinephrine infusion, n | 71 (5.2) | 31 (8.0) | 17 (11.9) | 6 (10.3) | 10 (15.9) | 0.001 |
| Variable | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, per 10 years | 1.18 | 1.03–1.43 | 0.038 |
| Female | 1.12 | 0.65–1.63 | 0.696 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 1.13 | 1.06–1.33 | 0.001 |
| History of hypertension | 1.05 | 0.92–1.23 | 0.305 |
| History of diabetes mellitus | 1.19 | 1.06–1.41 | 0.045 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 1.03 | 0.55–2.10 | 0.942 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1.20 | 0.66–1.98 | 0.642 |
| Preoperative left ventricle ejection fraction, % | 0.99 | 0.96–1.01 | 0.098 |
| Preoperative hematocrit, % | 0.98 | 0.95–1.01 | 0.175 |
| Preoperative albumin, g/dL | 0.92 | 0.76–1.22 | 0.250 |
| Preoperative estimated glomerular filtration rate, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.85 | 0.83–0.87 | <0.001 |
| Postoperative acute kidney injury | |||
| No acute kidney injury | baseline | ||
| Acute kidney injury stage 1, transient, less than 48 h | 1.95 | 0.83–3.02 | 0.246 |
| Acute kidney injury stage 1, persistent, more than 48 h | 3.11 | 2.62–4.91 | <0.001 |
| Acute kidney injury stage 2 or 3, transient, less than 48 h | 4.07 | 2.98–6.11 | <0.001 |
| Acute kidney injury stage 2 or 3, persistent, more than 48 h | 13.36 | 8.22–18.72 | <0.001 |
| Surgery type | |||
| Valve replacement | baseline | ||
| Coronary artery bypass graft | 1.05 | 0.54–2.36 | 0.901 |
| Aortic surgery | 1.50 | 0.75–3.18 | 0.329 |
| Combined procedures | 2.05 | 0.71–5.18 | 0.152 |
| Operation time, hour | 1.05 | 0.88–1.65 | 0.435 |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time, hour | 1.04 | 0.81–1.79 | 0.357 |
| Intraoperative pRBC transfusion, unit | 1.01 | 0.92–1.15 | 0.247 |
| Intraoperative norepinephrine infusion | 0.98 | 0.77–1.45 | 0.854 |
| Intraoperative epinephrine infusion | 1.09 | 0.84–1.33 | 0.432 |
| Characteristic | No AKI | AKI Stage 1, Transient | AKI Stage 1, Persistent | AKI Stage 2 or 3, Transient | AKI Stage 2 or 3, Persistent | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 1357 (67.5) | 388 (19.3) | 143 (7.1) | 58 (2.9) | 63 (3.1) | |
| AKI duration, days | - | 2 (1–2) | 5 (4–6) * | 2 (2–2) | 6 (5–7) * | <0.001 |
| Hemodialysis during hospital stay, n | - | 2 (0.5) | 13 (9.1) | 22 (37.9) | 34 (54.0) | <0.001 |
| Length of postoperative hospital stay, days | 9 (7–13) | 11 (8–16) | 13 (9–19)* | 15 (11–26) | 18 (12–31) * | <0.001 |
| Length of postoperative ICU stay, days | 6 (3–9) | 7 (4–10) | 7 (4–12) | 9 (7–14) | 12 (6–20) * | <0.001 |
| IABP insertion, n | 70 (5.2) | 24 (6.2) | 15 (10.5)* | 5 (8.6) | 13 (27.1) * | <0.001 |
| Reopen for surgical bleeding, n | 21 (2.0) | 10 (2.6) | 6 (4.2) | 3 (5.2) | 6 (9.5) | 0.021 |
| Respiratory complications, n | 178 (13.1) | 73 (18.8) | 28 (19.6) | 14 (24.1) | 11 (17.5) | 0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality, n | 9 (0.7) | 4 (1.0) | 8 (5.6)* | 2 (3.4) | 12 (19.0) * | <0.001 |
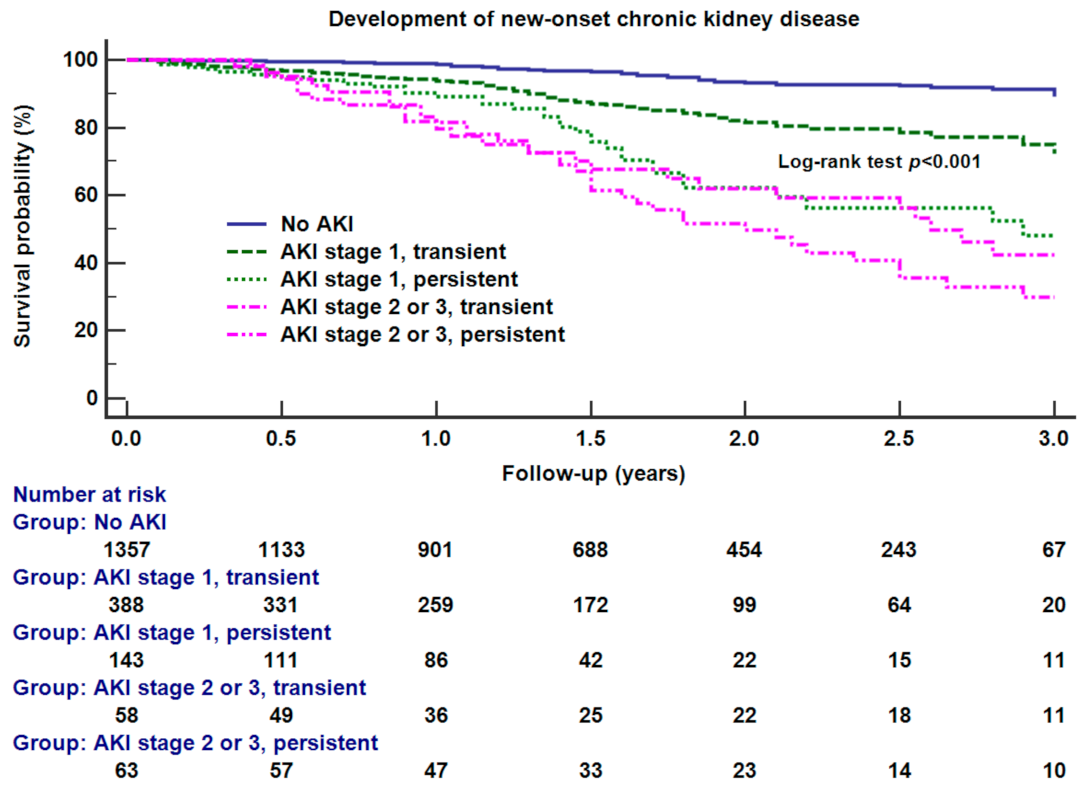
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at 3 months after surgery, n | 43/1167 (3.7) | 81/383 (21.1) | 40/129 (31.0) | 15/52 (28.8) | 20/45 (44.4) * | <0.001 |
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at 3 years after surgery, n | 56/684 (8.2) | 140/348 (40.2) | 76/117 (65.0)* | 17/28 (60.7) | 26/31 (83.8) * | <0.001 |
| Dependence on the hemodialysis at 3 years after surgery, n | 8/684 (1.2) | 10/348 (2.9) | 12/117 (10.3)* | 9/28 (32.1) | 17/31 (54.8) * | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choe, S.H.; Cho, H.; Bae, J.; Ji, S.-H.; Yoon, H.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-T.; Kim, W.H. Severity and Duration of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease after Cardiac Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081556
Choe SH, Cho H, Bae J, Ji S-H, Yoon H-K, Lee H-J, Lee J-H, Kim J-T, Kim WH. Severity and Duration of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease after Cardiac Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(8):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081556
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoe, Suk Hyung, Hyeyeon Cho, Jinyoung Bae, Sang-Hwan Ji, Hyun-Kyu Yoon, Ho-Jin Lee, Ji-Hyun Lee, Jin-Tae Kim, and Won Ho Kim. 2021. "Severity and Duration of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease after Cardiac Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 8: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081556
APA StyleChoe, S. H., Cho, H., Bae, J., Ji, S.-H., Yoon, H.-K., Lee, H.-J., Lee, J.-H., Kim, J.-T., & Kim, W. H. (2021). Severity and Duration of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease after Cardiac Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(8), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081556






