Risk of Reflux-Related Symptoms and Reflux Esophagitis after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment in the Japanese Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Protocol
2.2. H. pylori Eradication Therapy
2.3. Endoscopy and Severity of Gastritis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Endoscopic Reflux Esophagitis after H. pylori Eradication Therapy
3.3. Symptomatic Reflux Esophagitis after H. pylori Eradication Therapy
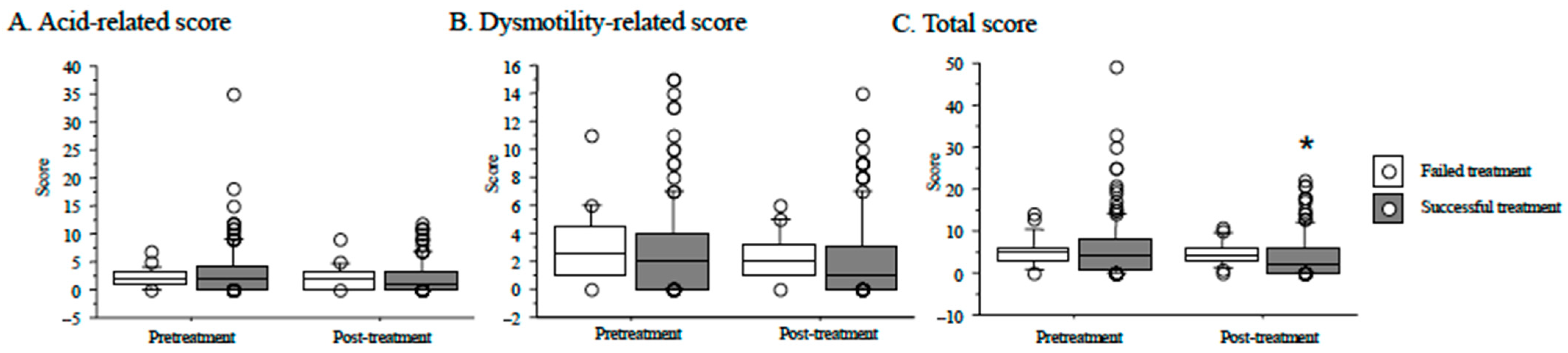
3.4. Reflux Esophagitis after H. pylori Eradication and Outcome of Eradication Therapy
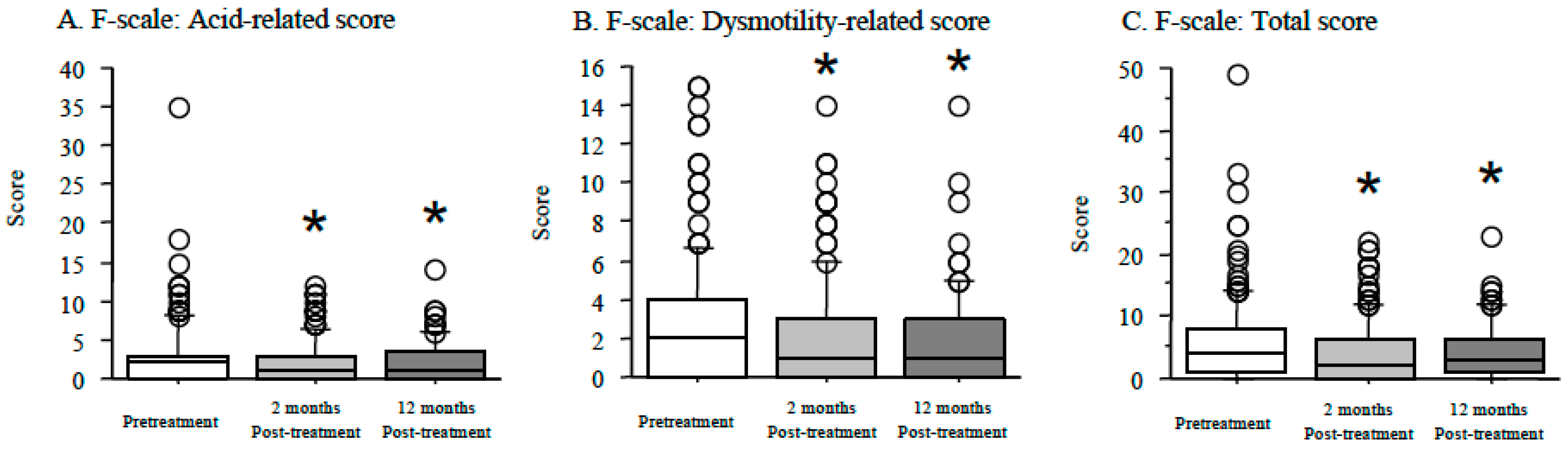
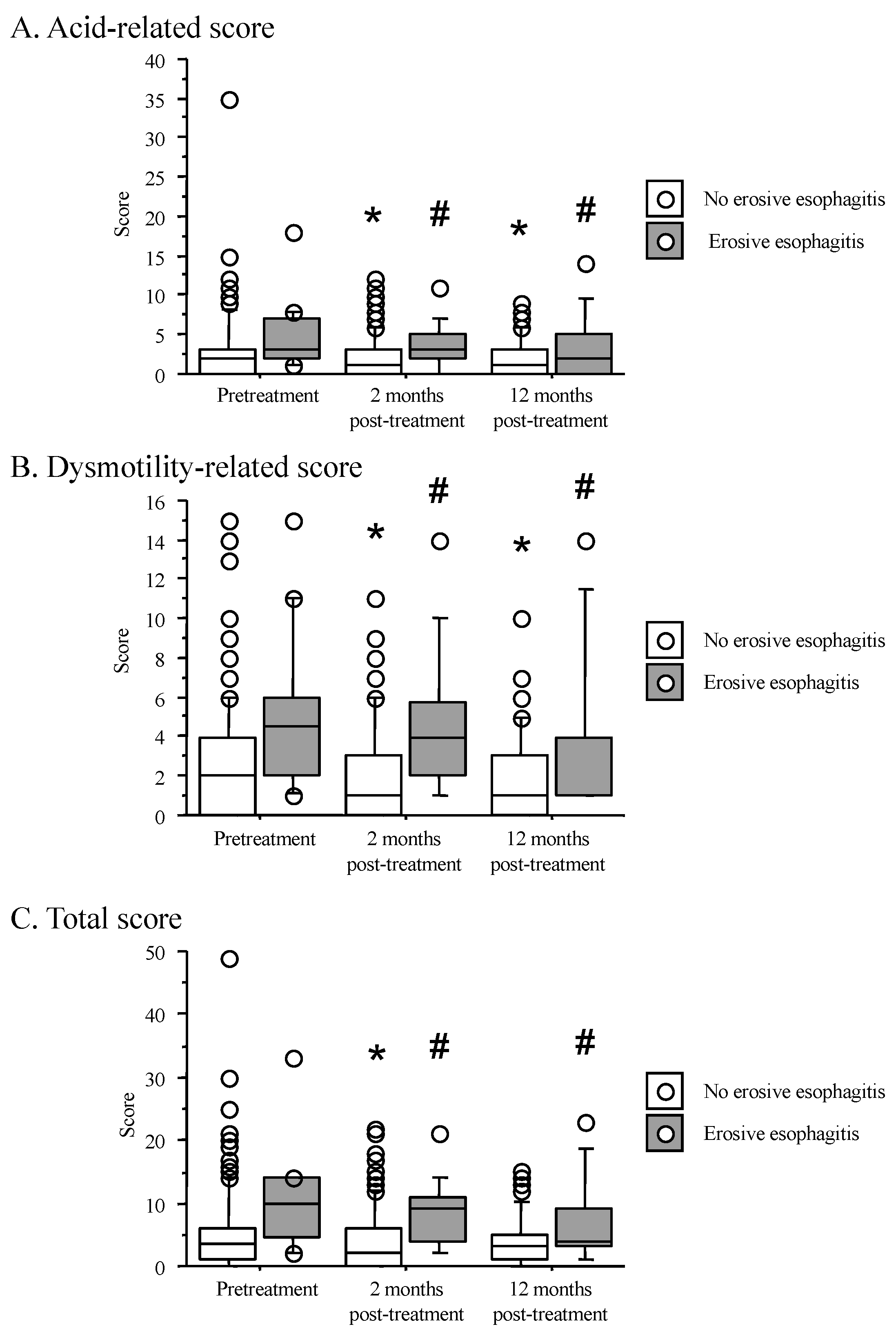
3.5. Time Course of F-Scale Questionnaire Scores between Patients with Non-Erosive and Reflux Esophagitis
3.6. Risk Factors for Reflux Esophagitis after H. pylori Eradication Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heading, R.C. Prevalence of upper gastrointestinal symptoms in the general population: A systematic review. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1999, 231, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Arakawa, T. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of GERD in the Japanese population. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, H.; Minoo, T.; Hojo, M.; Yaginuma, R.; Nagahara, A.; Kawabe, M.; Ohkawa, A.; Asaoka, D.; Kurosawa, A.; Ohkusa, T.; et al. Oesophageal hypersensitivity in Japanese patients with non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20 (Suppl. 1), 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Cui, W.; Ge, J.; Lin, L. The effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy on the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 349, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Ma, S.; Shang, L.; Qian, J.; Zhang, G. Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on gastroesophageal reflux disease. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; El-Omar, E.M.; Xiao, F.; Shirai, N.; Takashima, M.; Sugimura, H.; Sugimurra, H. Interleukin 1beta polymorphisms increase risk of hypochlorhydria and atrophic gastritis and reduce risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence in Japan. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, K.E.; Dickson, A.; El-Nujumi, A.; El-Omar, E.; Kelman, A. Symptomatic benefit 1-3 years after H. pylori eradication in ulcer patients: Impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labenz, J.; Blum, A.L.; Bayerdorffer, E.; Meining, A.; Stolte, M.; Borsch, G. Curing Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer may provoke reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Haruma, K.; Mihara, M.; Kamada, T.; Yoshihara, M.; Sumii, K.; Kajiyama, G.; Kawanishi, M. High incidence of reflux oesophagitis after eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori: Impacts of hiatal hernia and corpus gastritis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Metz, D.C.; Ginsberg, G.G.; Kaplan, D.E.; Goldberg, D.S. Oesophageal and proximal gastric adenocarcinomas are rare after detection of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Murata, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Chemoprevention of gastric cancer development after Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in an East Asian population: Meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1820–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamori, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shiba, M.; Watanabe, T.; Tominaga, K.; Oshitani, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Higuchi, K.; Arakawa, T. Prevalence of symptomatic gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in Japanese patients with peptic ulcer disease after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20 (Suppl. 1), 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, A.M.; Choudhary, A.; Bechtold, M.L. Effect of Helicobacter pylori treatment on gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoobi, M.; Farrokhyar, F.; Yuan, Y.; Hunt, R.H. Is there an increased risk of GERD after Helicobacter pylori eradication?: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.S.; Hungin, A.P.; Wooff, D.; Childs, S. Systematic review: The effect of Helicobacter pylori and its eradication on gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in patients with duodenal ulcers or reflux oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Shiba, M.; Watanabe, T.; Tominaga, K.; Oshitani, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Arakawa, T. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Orito, E.; Mizokami, M.; Gutierrez, O.; Saitou, N.; Kodama, T.; Osato, M.S.; Kim, J.G.; Ramirez, F.C.; Mahachai, V.; et al. Helicobacter pylori in North and South America before Columbus. FEBS Lett. 2002, 517, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Vilaichone, R.K.; Mahachai, V.; Miyajima, H.; Furuta, T.; Yamaoka, Y. Role of Helicobacter pylori cagA EPIYA motif and vacA genotypes for the development of gastrointestinal diseases in Southeast Asian countries: A meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical, A. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria. In Approved Standard, 3rd ed.; CLSI Document M45-A2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, I.; Murakami, K.; Kato, M.; Kato, S.; Azuma, T.; Takahashi, S.; Uemura, N.; Katsuyama, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Haruma, K.; et al. Changing antimicrobial susceptibility epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori strains in Japan between 2002 and 2005. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 4006–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Sahara, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Kagami, T.; Uotani, T.; Furuta, T. High Helicobacter pylori cure rate with sitafloxacin-based triple therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Okimoto, T.; Kodama, M.; Tanahashi, J.; Fujioka, T.; Ikeda, F.; Muraoka, H.; Takigawa, M.; Saika, T.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Sitafloxacin activity against Helicobacter pylori isolates, including those with gyrA mutations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3097–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Ota, H.; Okuda, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Satoh, K.; Shimoyama, T.; Suzuki, H.; Handa, O.; Furuta, T.; Mabe, K.; et al. Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: 2016 Revised Edition. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusano, M.; Shirai, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hongo, M.; Chiba, T.; Kinoshita, Y. It is possible to classify non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) patients into endoscopically normal groups and minimal change groups by subjective symptoms and responsiveness to rabeprazole—A report from a study with Japanese patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 3082–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Nishino, M.; Sahara, S.; Uotani, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Kagami, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Yamato, Y.; Togawa, D.; et al. Improvement of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Japanese patients with spinal kyphotic deformity who underwent surgical spinal correction. Dig. Endosc. 2016, 28, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Role of Vonoprazan in Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy in Japan. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.; Bennett, J.R.; Blum, A.L.; Dent, J.; De Dombal, F.T.; Galmiche, J.P.; Lundell, L.; Margulies, M.; Richter, J.E.; Spechler, S.J.; et al. The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: A progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Ban, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Sahara, S.; Otsuka, T.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Furuta, T.; Andoh, A. Efficacy of the Kyoto Classification of Gastritis in Identifying Patients at High Risk for Gastric Cancer. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, F.; Tominaga, K.; Fujikawa, Y.; Morisaki, T.; Otani, K.; Hosomi, S.; Nagami, Y.; Kamata, N.; Taira, K.; Nakano, A.; et al. Association between Functional Dyspepsia and Gastric Depressive Erosions in Japanese Subjects. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, K.; Adachi, K.; Katsube, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kinoshita, Y. Role of hiatus hernia and gastric mucosal atrophy in the development of reflux esophagitis in the elderly. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Hungin, A.P.; Wooff, D.; Childs, S. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: Systematic review. BMJ 2003, 326, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, K.; Kawami, N.; Sano, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Umezawa, M.; Kotoyori, M.; Hoshihara, Y.; Sakamoto, C. Mechanisms of excessive esophageal acid exposure in patients with reflux esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, K.; Kawami, N.; Sano, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Umezawa, M.; Futagami, S.; Hoshihara, Y.; Sakamoto, C. The effects of nizatidine on transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (TLESRs) and acid reflux in healthy subjects. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2011, 47, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corley, D.A.; Kubo, A.; Levin, T.R.; Block, G.; Habel, L.; Rumore, G.; Quesenberry, C.; Buffler, P.; Parsonnet, J. Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease: A case-control study. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwizer, W.; Thumshirn, M.; Dent, J.; Guldenschuh, I.; Menne, D.; Cathomas, G.; Fried, M. Helicobacter pylori and symptomatic relapse of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2001, 357, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Murata, M.; Mizuno, H.; Iwata, E.; Nagata, N.; Itoi, T.; Kawai, T. Endoscopic Reflux Esophagitis and Reflux-Related Symptoms after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy: Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.C.; Chan, F.K.; Wong, S.K.; Lee, Y.T.; Leung, W.K.; Sung, J.J. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on oesophageal acid exposure in patients with reflux oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.Y.; Choi, I.J.; Ryu, K.H.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, C.G.; Nam, B.H. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on reflux esophagitis and reflux symptoms. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Dent, J.; Zeijlon, L.; Sipponen, P.; Veldhuyzen Van Zanten, S.J.; Burman, C.F.; Lind, T.; Wrangstadh, M.; BayerdOrffer, E.; Lonovics, J. Impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication on heartburn in patients with gastric or duodenal ulcer disease—Results from a randomized trial programme. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayyedi, P.; Deeks, J.; Talley, N.J.; Delaney, B.; Forman, D. An update of the Cochrane systematic review of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in nonulcer dyspepsia: Resolving the discrepancy between systematic reviews. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2621–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Patients (n = 148) | Non-GERD (n = 113) | Redness (n = 32) | Reflux Esophagitis (n = 3) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.5 ± 10.3 | 65.9 ± 10.5 | 64.1 ± 9.8 | 68.7 ± 5.0 | 0.50 |
| Sex (male/female, n/n) | 78/70 | 58/55 | 17/15 | 3/0 | 0.25 |
| Height (cm) | 161.8 ± 7.9 | 161.7 ± 8.1 | 162.0 ± 7.3 | 163.3 ± 6.1 | 0.92 |
| Body weight (kg) | 58.9 ± 10.9 | 59.3 ± 10.8 | 57.5 ± 11.6 | 57.7 ± 6.7 | 0.84 |
| Smoking (no/previous/current, n/n/n) | 85/50/13 | 71/34/8 | 14/14/4 | 0/2/1 | 0.07 |
| Alcohol (no/previous/current) | 71/13/64 | 57/13/43 | 14/0/18 | 0/0/3 | 0.05 |
| Hiatal hernia (−/+) | 128/20 | 98/15 | 27/5 | 3/0 | 0.74 |
| SSBE (−/+) | 106/42 | 85/28 | 19/13 | 2/1 | 0.21 |
| GERD (-/redness/grade A/grade B) | 113/32/2/1 | 113/0/0/0 | 0/32/0/0 | 0/0/2/1 | <0.01 |
| Endoscopic Kyoto classification | |||||
| Atrophy | 2 (0–2) | 2 (0–2) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (2–2) | 0.93 |
| Intestinal metaplasia | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 0.79 |
| Diffuse redness | 2 (0–2) | 2 (0–2) | 2 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 0.16 |
| Total score | 5 (2–7) | 5 (2–7) | 5 (2–7) | 4 (4–7) | 0.26 |
| Eradication history (1st/2nd/3rd) | 107/26/15 | 84/19/10 | 22/7/3 | 1/0/2 | 0.02 |
| F scale | |||||
| Acid-related score | 2 (0–35) | 2 (0–35) | 2 (0–11) | 7 (0–8) | 0.37 |
| Dysmotility-related score | 2 (0–15) | 2 (0–15) | 2 (0–10) | 4 (0–6) | 0.61 |
| Total score | 4 (0–49) | 4 (0–49) | 4 (0–19) | 11 (1–14) | 0.51 |
| All Patients (n = 148) | Non-GERD (n = 106) | Redness (n = 26) | Reflux Esophagitis (n = 16) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GERD (-/redness/grade A/grade B) | 106/26/10/6 | 106/0/0/0 | 0/26/0/0 | 0/0/10/6 | |
| Hiatal hernia (−/+) | 106/42 | 77/29 | 22/4 | 12/4 | 0.31 |
| SSBE (−/+) | 128/20 | 94/12 | 19/7 | 10/6 | 0.69 |
| Endoscopic Kyoto classification | |||||
| Atrophy | 2 (0–2) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (0–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.80 |
| Intestinal metaplasia | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 0.59 |
| Diffuse redness | 2 (0–2) | 2 (0–2) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 0.93 |
| Total score | 5 (2–7) | 5 (2–7) | 4.5 (2–7) | 5 (2–7) | 0.68 |
| Questionnaire | |||||
| F scale | |||||
| Acid-related score | 3.5 (0–14) | 3 (0–8) | 3.5 (0–9) | 5 (0–14) | 0.14 |
| Dysmotility-related score | 1 (0–14) | 1 (0–10) | 2 (0–7) | 1 (0–14) | 0.16 |
| Total score | 3 (0–23) | 3 (0–14) | 7.5 (0–15) | 6 (1–23) | 0.05 |
| Post-Treatment | Non-GERD (n = 106) | Redness (n = 26) | GERD Grade A (n = 10) | GERD Grade B (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pretreatment | ||||
| Non-GERD (n = 113) | 91 | 14 | 5 | 3 |
| Redness (n = 32) | 14 | 12 | 5 | 1 |
| GERD grade A (n = 1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| GERD grade B (n = 2) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Category | Before Eradication Therapy | After eradication Therapy, 12 Months | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | SSBE | Hiatal Hernia | Number | Non-GERD/ GERD (n/n) | F Scale Acid-Related Score | F Scale Dysmotility-Related Score | F Scale Total Score | Number | Non-GERD/GERD (n/n) | F Scale Acid-Related Score | F Scale Dysmotility-Related Score | F Scale Total Score |
| Male | − | − | 47 | 36/11 | 2 (0–10) | 1 (0–7) | 4 (0–17) | 47 | 32/15 | 0 (0–9) | 1 (0–14) | 2 (0–15) |
| Male | − | + | 5 | 5/0 | 0 (0–3) | 1 (0–3) | 1 (0–5) | 5 | 5/0 | 0 (0–0) | 1 (1–1) | 1 (1–1) |
| Male | + | − | 23 | 16/7 | 1 (0–18) | 2 (0–15) | 3 (0–33) | 23 | 16/7 | 1 (0–5) | 1 (0–4) | 2 (0–9) |
| Male | + | + | 3 | 1/2 | 8 (3–12) | 6 (2–13) | 14 (5–25) | 3 | 2/1 | |||
| Female | − | − | 46 | 39/7 | 1 (0–15) | 2 (0–15) | 4 (0–30) | 46 | 37/9 | 1.5 (0–7) | 2 (0–10) | 3 (0–14) |
| Female | − | + | 8 | 5/3 | 4 (1–35) | 3 (0–14) | 6.5 (1–49) | 8 | 3/5 | 4 (3–6) | 3 (0–5) | 9 (3–9) |
| Female | + | − | 12 | 7/5 | 2 (0–9) | 3.5 (0–10) | 5.5 (0–19) | 12 | 9/3 | 3 (0–5) | 2 (0–7) | 5 (0–12) |
| Female | + | + | 4 | 4/0 | 6.5 (4–7) | 6 (2–7) | 13 (6–13) | 4 | 2/2 | 9.5 (5–14) | 7 (5–9) | 16.5 (10–23) |
| p Value | <0.01 | 0.12 | 0.03 | - | - | - | ||||||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | 0.985 | 0.939–1.034 | 0.540 | 0.975 | 0.925–1.028 | 0.356 |
| Sex (male, vs. female) | 2.134 | 0.703–6.482 | 0.181 | 3.499 | 0.987–12.399 | 0.052 |
| Hiatal hernia | 2.417 | 0.695–8.406 | 0.165 | 2.312 | 0.533–10.067 | 0.261 |
| short segment Barrett’s esophagus | 1.600 | 0.542–4.722 | 0.395 | |||
| Smoking | 2.394 | 0.429–13.373 | 0.320 | |||
| Alcohol | 1.496 | 0.523–4.282 | 0.453 | |||
| Kimura–Takemoto (moderate) | 0.398 | 0.064–2.464 | 0.322 | |||
| Kimura–Takemoto (severe) | 0.389 | 0.070–2.163 | 0.389 | |||
| Endoscopic Kyoto classification | ||||||
| Atrophy | 1.094 | 0.248–4.833 | 0.905 | |||
| Intestinal metaplasia | 1.443 | 0.711–2.929 | 0.310 | |||
| Diffuse redness | 1.075 | 0.388–2.977 | 0.890 | |||
| Total score | 1.083 | 0.702–1.672 | 0.718 | |||
| F scale, pretreatment | ||||||
| Acid-related score | 1.085 | 0.989–1.189 | 0.084 | |||
| Dysmotility-related score | 1.200 | 1.055–1.364 | 0.005 | |||
| Total score | 1.069 | 1.009–1.132 | 0.023 | 1.069 | 1.003–1.139 | 0.039 |
| F scale, 2 months after treatment | 1.130 | 1.037–1.233 | 0.006 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugimoto, M.; Murata, M.; Iwata, E.; Nagata, N.; Itoi, T.; Kawai, T. Risk of Reflux-Related Symptoms and Reflux Esophagitis after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment in the Japanese Population. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071434
Sugimoto M, Murata M, Iwata E, Nagata N, Itoi T, Kawai T. Risk of Reflux-Related Symptoms and Reflux Esophagitis after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment in the Japanese Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(7):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071434
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugimoto, Mitsushige, Masaki Murata, Eri Iwata, Naoyoshi Nagata, Takao Itoi, and Takashi Kawai. 2021. "Risk of Reflux-Related Symptoms and Reflux Esophagitis after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment in the Japanese Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 7: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071434
APA StyleSugimoto, M., Murata, M., Iwata, E., Nagata, N., Itoi, T., & Kawai, T. (2021). Risk of Reflux-Related Symptoms and Reflux Esophagitis after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Treatment in the Japanese Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(7), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10071434







