First Experience in the Control of the Venous Side of the Brain AVM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- To present the novel combination of simultaneous intra-arterial and transvenous approaches, named the hybrid high-pressure nidus embolization (HIPRENE);
- (ii)
- To analyze brain AVM treatment outcomes using an intra-arterial-only approach with high PCT compared to the HIPRENE treatment regime with a double-sided hybrid approach.
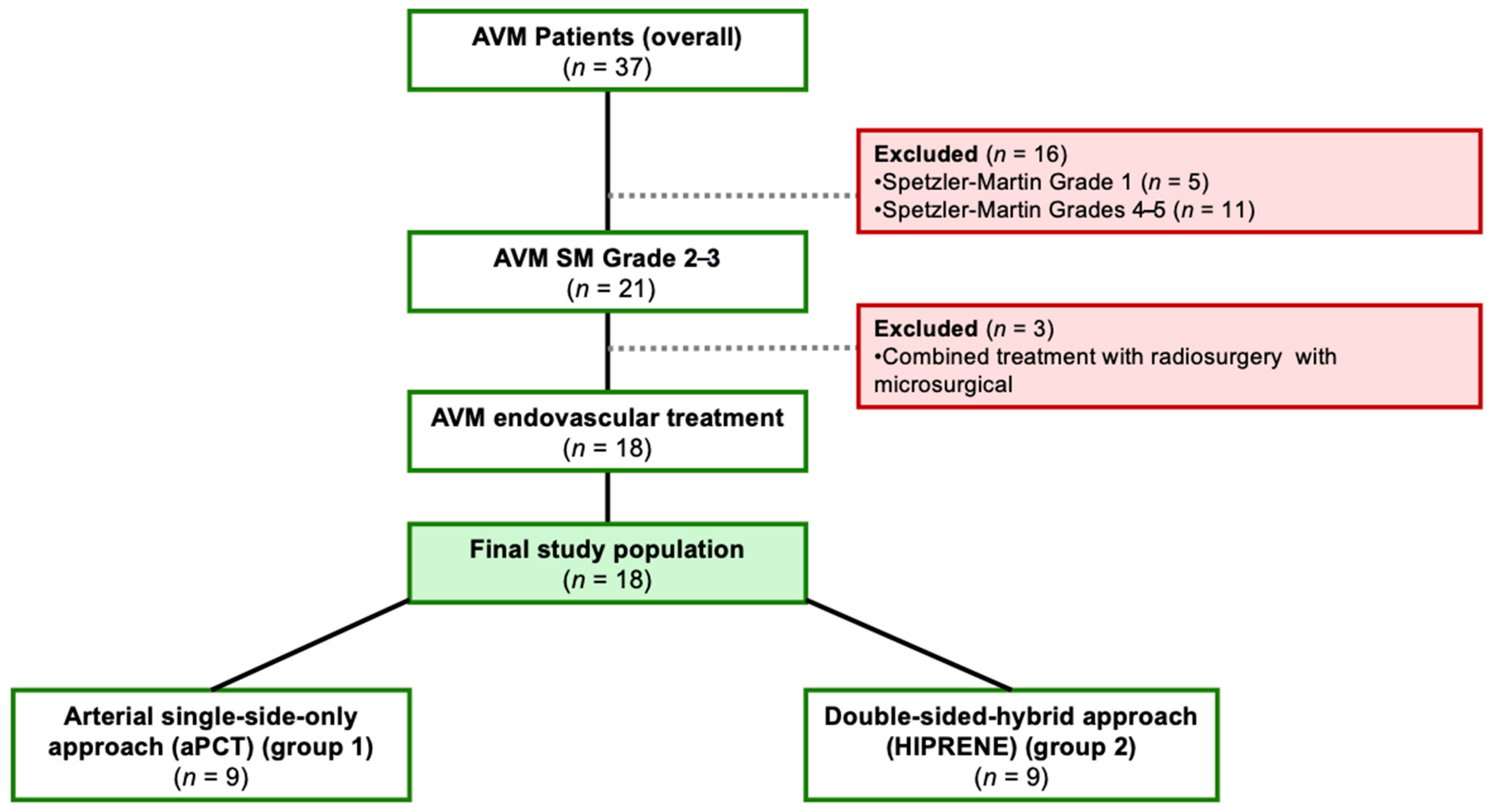
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
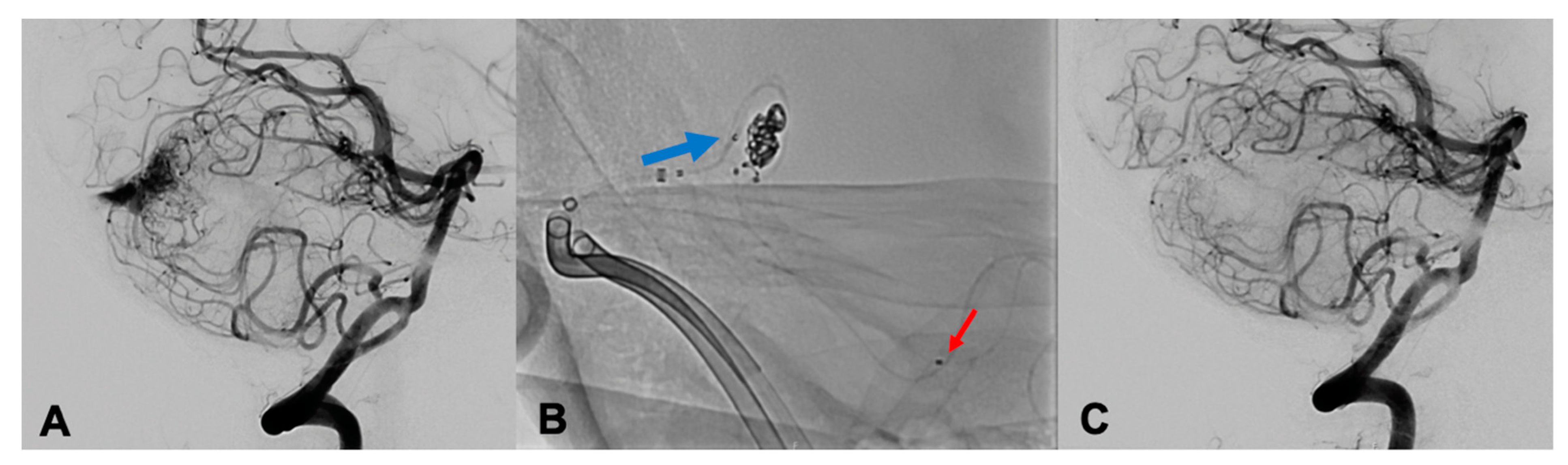
2.3. Embolization Procedure
2.3.1. Arterial Single-Side-Only Approach (aPCT) (Group 1)
2.3.2. Double-Sided Hybrid Approach (HIPRENE) (Group 2)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Arterial Single-Side-Only Approach (aPCT) (Group 1)
3.3. Double-Sided Hybrid Approach (HIPRENE) (Group 2)
3.4. Comparison of Treatment Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AVM | Arteriovenous malformation |
| HIPRENE | Hybrid high-pressure nidus embolization |
| NBCA | N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate |
| PCT | Pressure cooker technique |
| TRENSH | Transvenous retrograde nidus sclerotherapy under controlled hypotension |
References
- Wu, E.M.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; McDougall, C.M.; Aoun, S.; Mehta, N.; Neeley, O.J.; Plitt, A.; Ban, V.S.; Sillero, R.; White, J.A.; et al. Embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with intent to cure: A systematic review. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 132, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollherbst, D.F.; Chapot, R.; Bendszus, M.; Möhlenbruch, M.A. Glue, Onyx, Squid or PHIL? Liquid Embolic Agents for the Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senturk, C. Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. In Vascular Malformations of the Central Nervous System; Gürer, B., Kuru Bektaşoğlu, P., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- van Rooij, W.J.; Sluzewski, M.; Beute, G.N. Brain AVM embolization with Onyx. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 172–177; discussion 178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elsenousi, A.; Aletich, V.A.; Alaraj, A. Neurological outcomes and cure rates of embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with n-butyl cyanoacrylate or Onyx: A meta-analysis. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2016, 8, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapot, R.; Stracke, P.; Velasco, A.; Nordmeyer, H.; Heddier, M.; Stauder, M.; Schooss, P.; Mosimann, P.J. The Pressure Cooker Technique for the treatment of brain AVMs. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 41, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhar, L.N.; Biswas, A.; Hallam, D.; Kim, L.J.; Douglas, J.; Ghodke, B. Neuroendovascular Management of Tumors and Vascular Malformations of the Head and Neck. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 20, 453–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-J.; Norat, P.; Ding, D.; Mendes, G.A.C.; Tvrdik, P.; Park, M.S.; Kalani, M.Y. Transvenous embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations: A review of techniques, indications, and outcomes. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 45, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massoud, T.F.; Hademenos, G.J. Transvenous Retrograde Nidus Sclerotherapy under Controlled Hypotension (TRENSH): A Newly Proposed Treatment for Brain Arteriovenous Malformations-Concepts and Rationale. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, X.; Song, C.; He, H.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y. Transvenous retrograde AVM embolization: Indications, techniques, complications and outcomes. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2017, 23, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, A.; Renieri, L.; Nappini, S.; Limbucci, N.; Mangiafico, S. Endovascular Treatment of Deep Hemorrhagic Brain Arteriovenous Malformations with Transvenous Onyx Embolization. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, W.; He, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, T.; Xu, Y. Endovascular transvenous treatment for superficial intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J. Intervig. Med. 2019, 2, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, D.C.; de Castro-Afonso, L.H.; Nakiri, G.S.; Monsignore, L.M.; Trivelato, F.P.; Colli, B.O.; Abud, D.G. Extending the indications for transvenous approach embolization for superficial brain arteriovenous malformations. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2017, 9, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Bai, W.; Li, T.; Hui, F.K.; He, Y.; Xu, B. Curative Transvenous Embolization for Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Single-Center Experience from China. World Neurosurg. 2018, 116, e421–e428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyanagi, M.; Mosimann, P.J.; Nordmeyer, H.; Heddier, M.; Krause, J.; Narata, A.-P.; El Serwi, A.; Stracke, C.P.; Chapot, R. The transvenous retrograde pressure cooker technique for the curative embolization of high-grade brain arteriovenous malformations. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2021, 13, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranvinh, E.; Heit, J.J.; Hacein-Bey, L.; Provenzale, J.; Wintermark, M. Contemporary Imaging of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosif, C.; Mendes, G.A.C.; Saleme, S.; Ponomarjova, S.; Silveira, E.P.; Caire, F.; Mounayer, C. Endovascular transvenous cure for ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations in complex cases with high Spetzler-Martin grades. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Group 1 (n = 9) | Group 2 (n = 9) | |
|---|---|---|
| Males (n/%) | 5/55.6 | 3/33.3 |
| Age/years (median) | 54 | 45 |
| Spetzler–Martin grade II (n/%) | 6/66.5 | 5/55.6 |
| Spetzler–Martin grade III (n/%) | 3/33.5 | 4/44.4 |
| Nidus diameter/mm (median) | 26 | 25 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-procedural hemorrhaging (%) | 66.7% | 33.3% | p = 0.169 |
| Number of treatment sessions to nidus occlusion (Ø) | 1.7 | 1.2 | p = 0.136 |
| Nidus occlusion rate after initial treatment session (%) | 44.4% | 77.7% | p = 0.167 |
| Neuromonitoring event rate (%) | 44.4% | 22.2% | p = 0.310 |
| Diffusion weighted lesions in post-operative MRI (%) | 55.6% | 33.3% | p = 0.319 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waldeck, S.; Chapot, R.; von Falck, C.; Froelich, M.F.; Brockmann, M.; Overhoff, D. First Experience in the Control of the Venous Side of the Brain AVM. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5771. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245771
Waldeck S, Chapot R, von Falck C, Froelich MF, Brockmann M, Overhoff D. First Experience in the Control of the Venous Side of the Brain AVM. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(24):5771. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245771
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaldeck, Stephan, Rene Chapot, Christian von Falck, Matthias F. Froelich, Marc Brockmann, and Daniel Overhoff. 2021. "First Experience in the Control of the Venous Side of the Brain AVM" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 24: 5771. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245771
APA StyleWaldeck, S., Chapot, R., von Falck, C., Froelich, M. F., Brockmann, M., & Overhoff, D. (2021). First Experience in the Control of the Venous Side of the Brain AVM. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(24), 5771. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245771





