Maternal-Perinatal Variables in Patients with Severe Preeclampsia Who Develop Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, M.A.; Magee, L.A.; Kenny, L.C.; Karumanchi, S.A. International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy (ISSHP). Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension 2018, 72, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Guideline Alliance (UK). Hypertension in Pregnancy: Diagnosis and Management (NG133). 2019. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng133 (accessed on 9 March 2021).
- Sibai, B.M. Publications Committee, Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Evaluation and management of severe preeclampsia before 34 weeks’ gestation. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2011, 205, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Dadelszen, P.; Payne, B.; Li, J.; Ansermino, J.M. Prediction of adverse maternal outcomes in pre-eclampsia: Development and validation of the full PIERS model. PIERS Study Group. Lancet 2011, 377, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucheon, J.A.; Lisonkova, S.; Joseph, K.S. Epidemiology of preeclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 25, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, E.; Cuesta, C.; Grosso, A.L.; Chou, D. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: A systematic review. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 170, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.O.; Mission, J.F.; Caughey, A.B. Hypertensive disease of pregnancy an maternal mortality. Curr. Opin. Obs. Gynecol. 2013, 25, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.S.; Wojdyla, D.; Say, L.; Gülmezoglu, A.M. WHO analysis of causes of maternal death: A systematic review. Lancet 2006, 367, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, A.B.; Saftlas, A.F.; Hsia, J.; Atrash, H.K. Secular trends in the rates of preeclampsia, eclampsia, and gestational hypertension, United States, 1987−2004. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ananth, C.V.; Keyes, K.M.; Wapner, R.J. Pre-eclampsia rates in the United States, 1980−2010: Age-period-cohort analysis. BMJ 2013, 347, f6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umesawa, M.; Kobashi, G. Epidemiology of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy: Prevalence, risk factors, predictors and prognosis. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Suarez, M.L.; Kattah, A.; Grande, J.P.; Garovic, V. Renal disorders in pregnancy: Core curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Ganiger, V.C. Acute kidney injury in pregnancy-specific disorders. Indian J. Nephrol. 2017, 27, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.R.; Conti-Ramsden, F. Acute kidney injury in pregnancy including renal disease diagnosed in pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 57, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X. Pregnancy outcomes in patients with acute kidney injury during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2017, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetzl, L.M. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 222: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 135, 237–260. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.A. National Kidney Foundation. (K/DOQI) clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, S1–S266. [Google Scholar]
- Sibai, B.M. Diagnosis, controversies, and management of the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 103, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campistol, J.M.; Arias, M.; Ariceta, G.; Blasco, M. An update for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome: Diagnosis and treatment. A consensus document. Nefrologia 2013, 33, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, E.; Puri, S.; Varma, V.; Madhyastha, P.R. Pregnancy-related acute kidney injury: An analysis of 165 cases. Indian J. Nephrol. 2017, 27, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Ganiger, V.C.; Prakash, S.; Iqbal, M. Acute kidney injury in pregnancy with special reference to pregnancy specific disorders: A hospital-based study (2014–2016). J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.; Vercel, C.; Frémeaux-Bacchi, V. Obstetric Nephrology: AKI and thrombotic microangiopathies in pregnancy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehrabadi, A.; Liu, S.; Bartholomew, S.; Hutcheon, J.A. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the recent increase in obstetric acute renal failure in Canada: Population based retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2014, 349, g4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callaghan, W.M.; Creanga, A.A.; Kuklina, E.V. Severe maternal morbidity among delivery and postpartum hospitalizations in the United States. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 120, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pankiewicz, K.; Szczerba, E.; Maciejewski, T.; Fijałkowska, A. Non-obstetric complications in preeclampsia. Prz. Menopauzalny. 2019, 18, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.S.; Eggers, P.W.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Cabiddu, G.; Attini, R.; Vigotti, F.N.; Maxia, S.; Lepori, N. Risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkhunaizi, A.; Melamed, N.; Hladunewich, M.A. Pregnancy in advanced chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Arkoub, R.; Xiao, C.W.; Claman, P.; Clark, E.G. Acute kidney injury due to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, D.; Montrief, T.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: A review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Niwas, S.; Parekh, A.; Pandey, L.K. Acute kidney injury in late pregnancy in developing countries. Renal Fail. 2010, 32, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, J.; Pant, P.; Prakash, S.; Sivasankar, M. Changing picture of acute kidney injury in pregnancy: Study of 259 cases over a period of 33 years. Indian J. Nephrol. 2016, 26, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Omani-Samani, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Amini, P. Assisted reproductive technology and the risk of preeclampsia: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omani-Samani, R.; Alizadeh, A.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Mohammadi, M. Risk of preeclampsia following assisted reproductive technology: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 72 cohort studies. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 2826–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomopoulos, C.; Salamalekis, G.; Kintis, K.; Andrianopoulou, I. Risk of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy following assisted reproductive technology: Overview and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chih, H.J.; Elias, F.T.S.; Gaudet, L.; Velez, M.P. Assisted reproductive technology and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goicoechea, M. Ácido úrico y Enfermedad Renal Crónica. Nefrología al Día. Available online: https://www.nefrologiaaldia.org/200 (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Ugwuanyi, R.U.; Chiege, I.M.; Agwu, F.E.; Eleje, G.U. Association between serum uric acid levels and perinatal outcome in women with preeclampsia. Obs. Gynecol. Int. 2021, 6611828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalaxmi, K.; Radhakrishna, N.; Manjula, S. Serum uric acid level in preeclampsia and its correlation to maternal and fetal outcome. Int. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 5, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.M.; Nguyen, L.H.; Phan, N.L.; Le, D.D. Maternal serum uric acid concentration and pregnancy outcomes in women with pre-eclampsia/eclampsia. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019, 144, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakwe, C.R.; Ikpeze, O.C.; Ezebialu, I.U.; Osakwe, J.O. The predictive value of serum uric acid for the occurrence, severity and outcomes of pre-eclampsia among parturients at Nnewi, Nigeria. Niger. J. Med. 2015, 24, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Huang, P.; Fu, J. Serum levels of uric acid may have a potential role in the management of immediate delivery or prolongation of pregnancy in severe preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2020, 39, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F. Pregnancy-related thrombotic microangiopathies: Clues from complement biology. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 54, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meibody, F.; Jamme, M.; Tsatsaris, V.; Provot, F. Post-partum acute kidney injury: Sorting placental and non-placental thrombotic microangiopathies using the trajectory of biomarkers. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswarappa, M.; Rakesh, M.; Sonika, P.; Snigdha, K. Spectrum of renal injury in pregnancy-induced hypertension: Experience from a single center in India. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2017, 28, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ling, G.J.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhai, W.Q.; Chen, Y.J. Effect of HELLP syndrome on acute kidney injury in pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and metaanalysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chen, S. Acute kidney injury during pregnancy and puerperium: A retrospective study in a single center. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chappell, L.C.; Brocklehurst, P.; Green, M.E.; Hunter, R. Planned early delivery or expectant management for late preterm pre-eclampsia (PHOENIX): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, W.A.D.; Varela, C.V.A.; Pinheiro, A.M.; Scherer, P.C. Restrictive versus liberal fluid therapy for post-cesarean acute kidney injury in severe preeclampsia: A pilot randomized clinical trial. Clinics 2020, 75, e1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazda, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Terui, K.; Nagashima, S. Postoperative renal function in parturients with severe preeclampsia who underwent cesarean delivery: A retrospective observational study. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Hur, M.; Kim, W.H. Acute kidney injury in parturients with severe preeclampsia. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, E.F.; Lazdam, M.; Lewandowski, A.J.; Worton, S.A. Cardiovascular risk factors in children and young adults born to preeclamptic pregnancies: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabbali, N.; Tachfouti, N.; Arrayhani, M.; Harandou, M. Outcome assessment of pregnancy-related acute kidney injury in Morocco: A national prospective study. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2015, 26, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, W.R.; Hemmilä, U.K.; Craik, A.L.; Mandula, C.H. Incidence, aetiology and outcomes of obstetric-related acute kidney injury in Malawi: A prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villie, P.; Dommergues, M.; Brocheriou, I.; Piccoli, G.B. Why kidneys fail post-partum: A tubulocentric viewpoint. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, J.; Ling, Z.; Hou, X.; Fan, Y.; Xie, K.; Shen, R. In vitro fertilization is associated with the onset and progression of preeclampsia. Placenta 2020, 89, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, A.M.; Liu, K.; Shariff, S.Z.; Rai, J.G. Characteristics and outcomes of AKI treated with dialysis during pregnancy and the postpartum period. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayansina, D.; Black, C.; Hall, S.J.; Mark, A. Long term effects of gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia on kidney function: Record linkage study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2016, 6, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ayansina, D.; Black, C.; Hall, S. Are women with gestational hypertension or preeclampsia at an increased long term risk of kidney function impairment? Pregnancy Hypertens. 2012, 2, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaze, F.F.; Njukeng, F.A.; Kengne, A.P.; Ashuntantang, G. Post-partum trend in blood pressure levels, renal function and proteinuria in women with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia in Sub-Saharan Africa: A 6-months cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2014, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
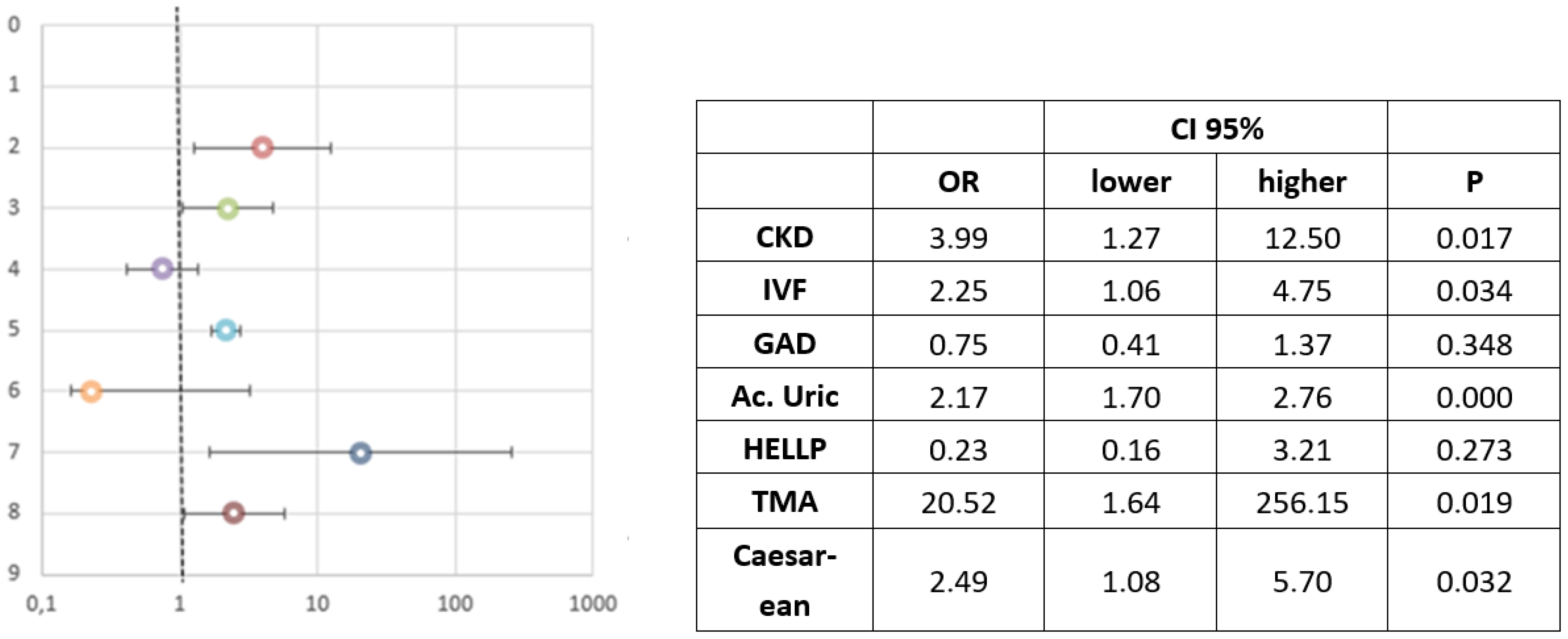
| Total n = 303 | AKI (n = 75) | No AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N; Mean ± S.T | % | Mean ± S.T | % | Mean ± S.T | % | p | |
| Maternal age | 33.94 ± 6.29 | 35.09 ± 6.99 | 33.56 ± 6.02 | 0.068 | |||
| Nationality | 0.570 | ||||||
| Spanish | 179 | 59.1 | 60 | 58.8 | |||
| South American | 91 | 29.6 | 33.3 | 28.9 | |||
| African | 14 | 4.5 | 4 | 4.8 | |||
| European not Spanish | 14 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 5.3 | |||
| Other | 5 | 1.5 | 0 | 2.2 | |||
| HT | 49 | 16.2 | 18.7 | 15.4 | 0.499 | ||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 7 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 0.516 | ||
| Hypothyroidism | 30 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 0.480 | ||
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 26.23 ± 5.27 | 26.05 ± 5.44 | 26.29 ± 5.23 | 0.742 | |||
| Obesity | 66 | 24.0 | 21.1 | 25 | 0.510 | ||
| Overweight | 153 | 56.3 | 53.6 | 57.1 | 0.611 | ||
| Autoimmune disease | 7 | 2.3 | 4 | 1.8 | 0.261 | ||
| CKD | 24 | 7.9 | 17.3 | 4.8 | 0.001 | ||
| CRF | 5 | 1.7 | 5.3 | 0.4 | 0.004 | ||
| Cr baseline serum (mg/dL) | 0.64 ± 0.20 | 0.78 ± 0.31 | 0.60 ± 0.11 | <0.001 | |||
| Pregestational proteinuria | 12 | 4 | 9.3 | 2.2 | 0.006 | ||
| Number of pregnancies | 2.01 ± 1.38 | 1.87 ± 1.31 | 2.06 ± 1.40 | 0.290 | |||
| Nulliparity | 153 | 50.5 | 54.7 | 49.1 | 0.405 | ||
| Abortion History | 107 | 35.3 | 26.7 | 38.2 | 0.071 | ||
| Number of abortions | 0.52 ± 0.87 | 0.44 ± 0.90 | 0.54 ± 0.81 | 0.352 | |||
| History of preeclampsia | 26 | 8.6 | 10.7 | 7.9 | 0.457 | ||
| Family History of HT | 116 | 38.3 | 39.7 | 39.4 | 0.957 | ||
| Family history of preeclampsia | 22 | 7.3 | 4 | 8.3 | 0.210 |
| Total n = 303 | AKI (n = 75) | No AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | p | |
| IVF | 63 | 20.8 | 24 | 32 | 39 | 17.1 | 0.006 |
| Multiple pregnancy | 55 | 18.2 | 19 | 25.3 | 36 | 15.8 | 0.063 |
| HT before 20 weeks of follow-up | 53 | 17.5 | 15 | 20 | 38 | 16.7 | 0.510 |
| Gestational HT | 78 | 25.7 | 14 | 18.7 | 64 | 28.1 | 0.106 |
| Gestational Diabetes | 30 | 9.9 | 8 | 10.7 | 22 | 9.6 | 0.798 |
| Gestational hypothyroidism | 33 | 10.9 | 11 | 14.7 | 22 | 9.6 | 0.480 |
| Proteinuria < 20 weeks | 12 | 4 | 7 | 9.3 | 5 | 2.2 | 0.006 |
| UTI during pregnancy | 97 | 32.1 | 25 | 33.3 | 72 | 31.6 | 0.778 |
| Alphamethyldopa treatment | 59 | 19.5 | 15 | 20 | 44 | 19.3 | 0.894 |
| Calcium antagonist treatment | 11 | 3.6 | 2 | 2.7 | 9 | 3.9 | 0.607 |
| Labetalol treatment | 40 | 13.2 | 18 | 23.5 | 22 | 17 | 0.758 |
| Total n = 303 | AKI (n = 75) | No AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N; Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | p | |
| SBP mmHg | 178.97 ± 16.52 | 179.04 ± 20.13 | 178.95 ± 15.20 | 0.971 | |||
| DBP mmHg | 103.84 ± 11.82 | 102.52 ± 13.81 | 104.28 ± 11.09 | 0.263 | |||
| Gestational age at diagnosis | 34.03 ± 4.37 | 33.31 ± 3.99 | 34.27 ± 4.46 | 0.098 | |||
| Gestational age at diagnosis <28 weeks 28–36.6 weeks ≥37 weeks | 25 175 103 | 8.3 57.8 34 | 8 72 20 | 8.3 53.1 36.6 | 0.010 | ||
| Early initiation of SP | 125 | 41.3 | 49.3 | 38.6 | 0.101 | ||
| Puerperal PE | 66 | 21.8 | 14.7 | 24.1 | 0.085 | ||
| Proteinuria (g/24 h) | 2.8 ± 2.78 | 3.18 ± 2.92 | 2.67 ± 2.72 | 0.170 | |||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.89 ± 0.53 | 1.53 ± 0.73 | 0.68 ± 0.14 | <0.001 | |||
| Urea (mg/dL) | 37.88 ± 21.48 | 58.39 ± 25.83 | 29.68 ± 12.08 | <0.001 | |||
| CrCl (mL/min) | 112.24 ± 42.65 | 81.64 ± 41.58 | 127.39 ± 34.37 | <0.001 | |||
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.80 ± 1.68 | 8.13 ± 1.54 | 6.36 ± 1.48 | <0.001 | |||
| Maximum uric acid level (mg/dL) | 7.37 ± 1.74 | 8.87 ± 1.74 | 6.88 ± 1.45 | <0.001 | |||
| GOT (U/L) | 110.28 ± 298.74 | 220.87 ± 488.14 | 60.880 ± 126.00 | 0.010 | |||
| GPT (U/L) | 68.50 ± 143.03 | 139.63 ± 244.96 | 45.10 ± 73.72 | 0.001 | |||
| Platelets (×103/µL) | 165.25 ± 72.12 | 138.21 ± 78.15 | 174.25 ± 67.15 | <0.001 | |||
| LDH (U/L) | 356.81 ± 340.91 | 534.15 ± 588.81 | 298.47 ± 166.71 | 0.001 | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 10.66 ± 1.76 | 9.89 ± 2.05 | 10.91 ± 1.58 | <0.001 | |||
| Magnesium (mg/dL) | 4.20 ± 2.59 | 5.28 ± 2.47 | 3.77 ± 2.52 | <0.001 | |||
| C3 level (mg/dL) | 141.26 ± 39.46 | 131.59 ± 45.20 | 145.35 ± 36.15 | 0.025 | |||
| C4 level (mg/dL) | 26.34 ± 10.25 | 24.90 ± 11.15 | 26.96 ± 9.81 | 0.156 | |||
| IgG level (mg/dL) | 810.97 ± 283.01 | 756.81 ± 291.17 | 833.81 ± 277.23 | 0.056 | |||
| IgA level (mg/dL) | 202.78 ± 77.91 | 197.15 ± 80.34 | 205.16 ± 76.99 | 0.472 | |||
| IgM level (mg/dL) | 128.06 ± 63.05 | 119.10 ± 60.21 | 131.85 ± 64.02 | 0.157 | |||
| Antiphospholipid 1st | 9 | 3.4 | 4.4 | 3 | 0.575 | ||
| ANA | 16 | 6.7 | 5.6 | 7.1 | 0.670 | ||
| antiDNA | 4 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 0.853 | ||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.41 ± 0.68 | 3.21 ± 0.77 | 3.53 ± 0.60 | 0.004 | |||
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 194.30 ± 94.80 | 227.01 ± 95.35 | 180.80 ± 91.45 | <0.001 | |||
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 247.51 ± 73.28 | 228.27 ± 64.76 | 255.25 ± 75.23 | 0.009 | |||
| Magnesium sulfate treatment | 208 | 68.6 | 82.7 | 64 | 0.003 | ||
| Labetalol treatment | 247 | 81.5 | 82.7 | 81.1 | 0.768 | ||
| Treatment with hydralazine | 98 | 32.3 | 8.9 | 23.4 | 0.435 | ||
| Diuretic treatment | 15 | 5 | 10.7 | 3.1 | 0.009 | ||
| Oliguria | 32 | 10.6 | 34.7 | 2.6 | <0.001 | ||
| HELLP syndrome | 31 | 10.2 | 25.3 | 5.3 | <0.001 | ||
| TMA (includes HELLP) | 35 | 11.6 | 29.3 | 5.7 | <0.001 | ||
| Eclampsia | 10 | 3.3 | 0 | 4.4 | 0.065 |
| Total n = 303 | AKI (n = 75) | Non AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | p | |
| Delivery follow-up | 34.46 ± 3.86 | 33.80 ± 3.60 | 34.68 ± 3.92 | 0.089 | |||
| Gestational age at diagnosis <28 weeks 28–36.6 weeks ≥37 weeks | 16 178 109 | 5.3 58.7 36 | 5.3 73.3 21.3 | 5.3 53.9 40.8 | 0.008 | ||
| Birth initiation method: Spontaneous Induced Elective caesarean section | 25 135 143 | 8.3 44.6 47.2 | 4 38.7 57.3 | 9.6 46.5 43.9 | 0.077 | ||
| Completion of delivery: Vaginal Caesarean | 107 196 | 35.3 64.7 | 17.3 82.7 | 41.2 58.8 | <0.001 | ||
| HT at delivery | 260 | 85.8 | 86.7 | 85.5 | 0.806 | ||
| Transfusion | 30 | 9.9 | 6.9 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Postpartum Labetalol | 292 | 96.4 | 96 | 96.5 | 0.844 | ||
| Postpartum hydralazine | 147 | 48.5 | 56 | 46.3 | 0.143 | ||
| Postpartum Enalapril | 275 | 90.8 | 80 | 94.3 | <0.001 | ||
| ARB II postpartum | 17 | 5.6 | 8.1 | 4.8 | 0.291 | ||
| Postpartum calcium antagonists | 202 | 66.7 | 66 | 70.2 | 0.031 | ||
| Postpartum furosemide | 102 | 33.7 | 44 | 30.3 | 0.082 |
| Total n = 303/351 | AKI (n = 75) | No AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | p | |
| Follow-up at birth | 34.46 ± 3.86 | 33.80 ± 3.60 | 34.68 ± 3.92 | 0.089 | |||
| Lung maturation | 146 | 48.2 | 60 | 44.3 | 0.018 | ||
| Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) | 71 | 20.2 | 18.7 | 25 | 0.261 | ||
| SGA 1st Newborn (non IUGR) | 62 | 17.7 | 10.8 | 23.9 | 0.036 | ||
| Sex 1st Newborn Male Female | 138 165 | 45.5 54.5 | 41.3 58.7 | 46.9 53.1 | 0.399 | ||
| Sex 2nd Newborn Male Female | 20 28 | 41.7 58.3 | 41.2 58.8 | 41.9 58.1 | 0.959 | ||
| Weight 1st Newborn (grams) | 2.128.24 ± 864.29 | 2.023.81 ± 851.33 | 2.162.59 ± 867.61 | 0.228 | |||
| Weight 2nd Newborn (grams) | 1.919.86 ± 504.70 | 2.052.22 ± 433.28 | 1.845.41 ± 532.71 | 0.167 | |||
| Apgar Test value 1st min | 7.52 ± 1.76 | 6.96 ± 1.82 | 7.73 ± 1.67 | 0.002 | |||
| Apgar Test Value 1st min 2nd NB | 7.94 ± 1.23 | 7.72 ± 1.36 | 8.06 ± 1.16 | 0.355 | |||
| Apgar Test Value 5 min 1st NB | 8.44 ± 1.70 | 8.5 ± 1.43 | 9.02 ± 1.18 | 0.006 | |||
| Apgar test value 5 min 2nd NB | 9.16 ± 0.86 | 9.11 ± 0.90 | 9.19 ± 0.85 | 0.768 | |||
| 1st NB cord pH | 7.24 ± 0.09 | 7.23 ± 0.11 | 7.25 ± 0.08 | 0.310 | |||
| 2nd NB cord pH | 7.29 ± 0.08 | 7.28 ± 0.11 | 7.29 ± 0.07 | 0.513 | |||
| Exitus perinatal | 18 | 5.1 | 2.7 | 7 | 0.165 | ||
| Admission to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit | 96 | 27.4 | 42.7 | 28.1 | 0.018 | ||
| Cause of admission Heart disease Distres Intubation difficulty Prematurity IUGR | 15 37 10 13 21 | 15.6 38.5 10.4 13.5 21.9 | 9.4 50.0 15.6 12.5 12.5 | 18.8 32.8 7.8 14.1 26.6 | 0.20 |
| Total n = 303 | AKI (n = 75) | No AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | p | |
| HT | 288 | 95 | 86.7 | 97.8 | <0.001 | ||
| Number of Antihypertensive treatment | |||||||
| 0 1 2 ≥3 | 16 130 132 25 | 5.3 43.9 43.6 8.3 | 13.3 46.7 33.3 6.7 | 2.6 41.7 46.9 8.8 | 0.002 | ||
| Proteinuria | 219 | 72.3 | 71.6 | 75.1 | 0.552 | ||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.68 ± 0.26 | 0.88 ± 0.42 | 0.62 ± 0.12 | <0.001 | |||
| Urea (mg/dL) | 33.15 ± 13.59 | 41.18 ± 18.73 | 29.90 ± 9.07 | <0.001 | |||
| Ccr (mL/min) | 123.49 ± 34.58 | 104.35 ± 37.38 | 130.71 ± 30.61 | <0.001 | |||
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.73 ± 1.44 | 6.21 ± 1.72 | 5.58 ± 1.30 | 0.005 | |||
| Proteinuria (g/24 h) | 1.04 ± 1.17 | 1.36 ± 1.51 | 0.93 ± 1.02 | 0.026 | |||
| GOT (U/L) | 31.87 ± 23.60 | 36.22 ± 27.54 | 29.95 ± 21.46 | 0.075 | |||
| GPT (U/L) | 30.17 ± 25.08 | 39.56 ± 36.01 | 27.08 ± 19.38 | 0.005 | |||
| Platelets at discharge (×103/µL) | 288.45 ± 101.82 | 294.00 ± 115.21 | 286.02 ± 97.18 | 0.574 | |||
| LDH (U/L) | 245.75 ± 82.36 | 268.36 ± 122.88 | 238.28 ± 62.17 | 0.045 | |||
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.22 ± 1.45 | 10.87 ± 1.48 | 11.33 ± 1.43 | 0.016 |
| Total n = 303 | AKI (n = 75) | No AKI (n = 228) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | Mean ± SD | % | p | |
| Persistent hypertension | 72 | 23.8 | 24.3 | 25.8 | 0.797 | ||
| Persistent proteinuria | 31 | 11.1 | 21.4 | 7.6 | 0.001 | ||
| Renal insufficiency | 7 | 2.3 | 9.9 | 0 | <0.001 | ||
| Proteinuria (mg/mg) | 0.19 ± 0.47 | 0.38 ± 0.88 | 0.13 ± 0.21 | 0.032 | |||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.69 ± 0.21 | 0.85 ± 0.35 | 0.65 ± 0.11 | <0.001 | |||
| CrCl (mL/min) | 115.17 ± 29.8 | 99.61 ± 27.57 | 121.68 ± 28.37 | <0.001 | |||
| Evolution Referral to family doctor Referral to Nephrology Loss of follow-up | 203 72 28 | 67 23.8 9.2 | 64 29.3 6.7 | 68 21.9 10.1 | 0.341 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Benitez, P.; Aracil Moreno, I.; Oliver Barrecheguren, C.; Cuñarro López, Y.; Yllana, F.; Pintado Recarte, P.; Arribas, C.B.; Álvarez-Mon, M.; Ortega, M.A.; De Leon-Luis, J.A. Maternal-Perinatal Variables in Patients with Severe Preeclampsia Who Develop Acute Kidney Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235629
Rodríguez-Benitez P, Aracil Moreno I, Oliver Barrecheguren C, Cuñarro López Y, Yllana F, Pintado Recarte P, Arribas CB, Álvarez-Mon M, Ortega MA, De Leon-Luis JA. Maternal-Perinatal Variables in Patients with Severe Preeclampsia Who Develop Acute Kidney Injury. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(23):5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235629
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Benitez, Patrocinio, Irene Aracil Moreno, Cristina Oliver Barrecheguren, Yolanda Cuñarro López, Fátima Yllana, Pilar Pintado Recarte, Coral Bravo Arribas, Melchor Álvarez-Mon, Miguel A. Ortega, and Juan A. De Leon-Luis. 2021. "Maternal-Perinatal Variables in Patients with Severe Preeclampsia Who Develop Acute Kidney Injury" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 23: 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235629
APA StyleRodríguez-Benitez, P., Aracil Moreno, I., Oliver Barrecheguren, C., Cuñarro López, Y., Yllana, F., Pintado Recarte, P., Arribas, C. B., Álvarez-Mon, M., Ortega, M. A., & De Leon-Luis, J. A. (2021). Maternal-Perinatal Variables in Patients with Severe Preeclampsia Who Develop Acute Kidney Injury. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(23), 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235629









