Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the potential beneficial effect of immunomodulation therapy on the thromboembolic risk in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Methods: We searched PubMed and Scopus for randomized trials reporting the outcomes of venous thromboembolism (VTE), ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, myocardial infarction, any thromboembolic event, and all-cause mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with immunomodulatory agents. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using the Mantel–Haenszel random effects method. Results: Among 8499 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 4638 were treated with an immunomodulatory agent, 3861—with usual care only. Among the patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents, there were 1.77 VTEs per 100 patient-months compared to 2.30 among those treated with usual care (OR: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.61–1.16; I2: 0%). Among the patients who received an interleukin 6 (IL-6) antagonist, VTEs were reported in 12 among the 1075 patients compared to 20 among the 848 receiving the usual care (OR: 0.52, 95% CI: 0.22–1.20; I2: 6%). Immunomodulators as an add-on to usual care did not reduce the risk of stroke or systemic embolism (OR: 1.10, 95% CI: 0.50–2.40; I2: 0%) or of myocardial infarction (OR: 1.06, 95% CI: 0.47–2.39; I2: 0%) and there was a nonsignificant reduction in any thromboembolic event (OR: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.65–1.14; I2: 0%). Conclusions: We did not identify a statistically significant effect of immunomodulation on prevention of thromboembolic events in COVID-19. However, given the large effect estimate for VTE prevention, especially in the patients treated with IL-6 antagonists, we cannot exclude a potential effect of immunomodulation.
1. Introduction
Soon after the emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and its associated COVID-19 disease, a high prevalence of thrombotic events, mostly consisting of venous thromboembolism (VTE), were observed in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Meta-analyses of observational studies identified VTE prevalence ranging from 23.9% up to 40.3% in the patients who had undergone ultrasound screening [1,2]. Such thrombotic events occurred mainly in patients with severe disease, although they were also observed in mildly symptomatic or asymptomatic patients. It was postulated that thrombotic complications associated with COVID-19 were attributable, at least in part, to immune mechanisms that led to a hypercoagulable state [3,4,5].
Several proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL) 1β and chemotactic cytokines (e.g., IL-8 and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)) are upregulated during COVID-19, leading to a sustained increase in IL-6 levels [6,7,8,9,10]. The latter seems to play a major role in the maintenance of the virus-driven inflammatory process. Alongside this inflammatory process, a prothrombotic effect was postulated through multiple mechanisms that include endothelial inflammation, destabilization of atherosclerotic plaques, release of the von Willebrand factor, and upregulation of coagulation and complement pathways [11]. These pathogenic mechanisms could lead to the formation of microthrombi in various vascular beds and, eventually, the development of clinically overt venous and arterial thrombosis.
Several immunomodulatory agents targeting IL-6 and IL-1 blockade were proposed as potential therapeutic options for severe COVID-19 to inhibit the proinflammatory effect and its consequences on pulmonary and other organ function [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Our group recently showed in the SAVE study that early soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR)-guided anakinra use decreased the severe respiratory failure but did not affect the thromboembolic risk [16]. Recent meta-analyses of randomized and observational studies exploring the effect of anakinra and tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 showed a favorable effect on clinical outcomes, including mortality risk [22,23,24,25,26]. However, the impact of immunomodulation treatments on the occurrence of thromboembolic events in COVID-19 patients remains uncertain, representing a clinically important gap in knowledge given the biologically plausible association between COVID-19-mediated inflammation and thrombosis.
Against this background, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to investigate the effect of immunomodulatory agents on thromboembolic events in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Inclusion Criteria
We searched PubMed and Scopus until 16 October 2021 for RCTs of immunomodulatory agents in COVID-19 reporting thromboembolic events. We used search items “hydroxychloroquine, corticosteroids, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone, interleukin-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab, sarilumab, siltuximab, interleukin-1 inhibitor, canakinumab, anakinra, complement inhibitor, vilobelimab, JAK-2 inhibitors, baricitinib, IVIG, TNFa inhibitor, interferon gamma, GM-CSF” and “coronavirus or COVID-19 or severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)” and “trial or randomized”. In addition, we searched the references of the related letters, reviews, and editorials to identify other potentially eligible studies. To be eligible for the analysis, the studies should have been RCTs, published as full-text articles in English, and provided data on venous and arterial thromboembolic events in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. RCTs of several other immunomodulatory agents not providing data on the incidence of thromboembolic events and pre-prints were not included in the analysis. This work was performed according to the PRISMA statement [27] and was submitted in PROSPERO (ID: CRD42021230346).
2.2. Outcomes, Data Extraction, and Assessment of the Risk of Bias
The following outcomes were assessed: venous thromboembolism (i.e., pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis), myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, and the composite outcome of any thromboembolic event (TE) as reported in individual studies. Among the included studies, we assessed by means of a sensitivity analysis the outcome of mortality to explore potential correlations between thromboembolic events and mortality. In order to overcome the potential effect of hydroxychloroquine or corticosteroids which have been used as usual care in some studies, we prespecified one sensitivity analysis excluding hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids treatment. Additionally, we assessed the outcome of pulmonary embolism among patients with VTE. Eligible studies were assessed independently by two authors (M.F. and P.T.), and the data were extracted using prespecified criteria and collection methods. An assessment of the risk of bias was performed by the same investigators with the use of the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool focusing on sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding, addressing incomplete outcome data, selective reporting and presence of other bias. Any discrepancy or uncertainty was resolved by consensus or discussion among all authors.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed on an intention-to-treat basis. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated for each outcome using the Mantel–Haenszel random effects method. Heterogeneity between trials was assessed by measuring inconsistency using the I2 index which measures the proportion of the variability in effect estimates that can be attributed to heterogeneity rather than chance. I2 was calculated as follows: I2 = 100% × (Q − df)/Q, where Q is the Cochran heterogeneity statistic and df is the degree of freedom. A value of 0% indicates no observed heterogeneity, and larger values show increasing heterogeneity [28]. The median follow-up duration was calculated using the follow-up duration reported in each trial.
We prespecified a subgroup analysis based on the immunomodulatory agent used in each study. Differences in pooled effect sizes between the subgroups were compared with a test of interaction (Cochran’s Q test).
All the analyses were performed with Review Manager 5 (RevMan) version 5.3 (Copenhagen, Denmark: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011).
3. Results
The initial literature search yielded 1875 potentially eligible articles, of which 22 met the inclusion criteria [12,13,14,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. The flow diagram of study selection is presented in Supplementary Figure S1. The main characteristics of the included trials are summarized in Table 1. Overall, we did not identify the major risk of bias, except in two studies where we identified high risk of bias in allocation concealment and blinding of participants [12,14] (Supplementary Figures S2 and S3).

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of included studies.
Among 8499 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 4635 were treated with an immunomodulatory agent as an add-on to usual care, and 3,861 were treated with usual care only. The median (IQR) follow-up period of the included studies was 28 (21–28) days.
3.1. Venous Thromboembolic Events
Among the 7873 patients from 18 trials [12,29,30,31,32,33,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47] who were included in the analysis of the outcome of VTE comprising deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, during a median follow-up period of 28 (IQR: 21–28) days, the outcome occurred in 170 patients during the overall follow-up period of 8435 patient-months (2.01 per 100 patient-months). There were 81 VTE events among the COVID-19 patients prescribed an immunomodulatory agent (1.77 per 100 patient-months) and 88 among the placebo-assigned patients (2.30 per 100 patient-months) (OR: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.61–1.16; I2: 0%) (Figure 1). This effect remained consistent after excluding hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroid treatment (OR: 0.88, 95% CI: 0.61–1.27, I2: 3%). In the subgroup analysis of trials of IL-6 antagonists, there were 12 VTE events among the 1075 patients prescribed an IL-6 antagonist compared to 20 among the 848 patients in the placebo group (OR: 0.52, 95% CI: 0.22–1.20, RRR: 52%, ARR: 1.2%, NNT: 80) without heterogeneity (I2: 6%). In the sensitivity analysis of the outcome of pulmonary embolism, neither the overall immunomodulatory agents nor IL-6 antagonists significantly reduced the risk of pulmonary embolism (Supplementary Figure S4).
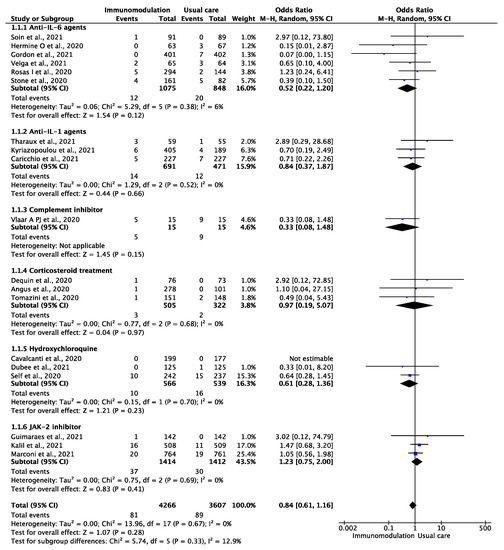
Figure 1.
Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals for the occurrence of venous thromboembolic events among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents as an add-on to usual care vs. usual care only. Boxes represent the OR and lines represent the 95% CIs for individual studies. The diamonds and their width represent the pooled ORs and the 95% CIs, respectively. CI, confidence interval for the Mantel–Hansen estimator, I2: heterogeneity.
3.2. Ischemic Stroke or Systemic Embolism
Among the 4352 patients from nine trials [13,32,34,35,36,37,38,41,46] who were included in the analysis of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, during a median follow-up period of 28 (IQR: 28–29) days, the outcome occurred in 26 patients during the follow-up period of 4663 patient-months (0.56 per 100 patient-months). There were 16 ischemic strokes or systemic embolic events among the patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents (0.63 per 100 patient-months) and 10 among the patients treated with SOC (0.46 per 100 patient-months) (OR: 1.10, 95% CI: 0.50–2.40; I2: 0%) (Figure 2). This effect remained consistent after excluding hydroxychloroquine treatment (OR: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.46–2.31, I2: 0%).
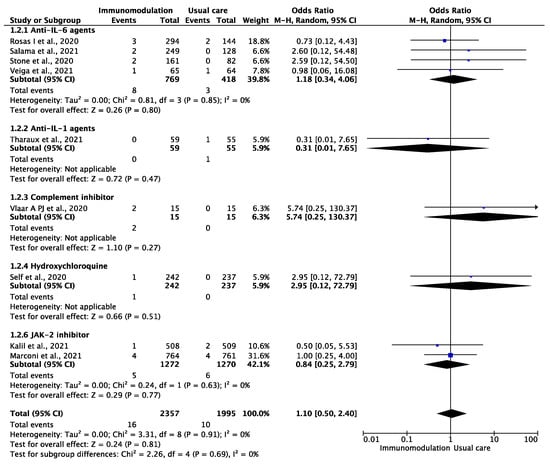
Figure 2.
Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals for the occurrence of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents as an add-on to usual care vs. usual care only. Boxes represent the OR and lines represent the 95% CIs for individual studies. The diamonds and their width represent the pooled ORs and the 95% CIs, respectively. CI, confidence interval for the Mantel–Hansen estimator, I2: heterogeneity.
3.3. Myocardial Infarction
Among the 5438 patients from nine trials [13,31,32,33,34,35,39,40,46] who were included in the analysis of myocardial infarction, during a median follow-up period of 28 (IQR: 21–28) days, this outcome occurred in 23 patients during the overall follow-up period of 5826 patient-months (0.39 per 100 patient-months). There were 14 myocardial infarction events among the patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents (0.45 per 100 patient-months) and nine among the patients treated with usual care (0.33 per 100 patient-months) (OR: 1.06, 95% CI: 0.47–2.39; I2: 0%) (Figure 3). This effect remained consistent after excluding hydroxychloroquine treatment (OR: 0.99, 95% CI: 0.43–2.29, I2: 0%).
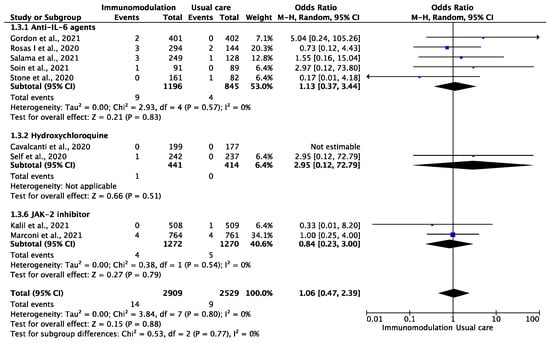
Figure 3.
Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals for the occurrence of myocardial infarction among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents as an add-on to SOC vs. SOC only. Boxes represent the OR and lines represent the 95% CIs for individual studies. The diamonds and their width represent the pooled ORs and the 95% CIs, respectively. CI, confidence interval for the Mantel–Hansen estimator, I2: heterogeneity.
3.4. Any Thromboembolic Event and All-Cause Mortality
Among the 8499 patients from 22 trials [12,13,14,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] who were included in the analysis of the composite outcome of any thromboembolic event, the outcome occurred in 224 patients during the follow-up period of 9106 patient-months (2.46 per 100 patient-months). There were 112 thromboembolic events among the patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents (2.25 per 100 patient-months) and 112 among the patients treated with the standard of care (2.71 per 100 patient-months) (OR: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.65–1.14; I2: 0%) (Figure 4). This effect remained consistent after excluding hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroid treatment (OR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.66–1.22, I2: 0%). In the analysis of all-cause mortality, immunomodulation significantly reduced the risk of all-cause mortality in the included studies (OR: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.66–0.86, I2: 9%) (Supplementary Figure S5). In the sensitivity analysis excluding the effect of hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroid treatment, the results remained consistent (OR: 0.74, 95% CI: 0.64–0.87, I2: 18%).
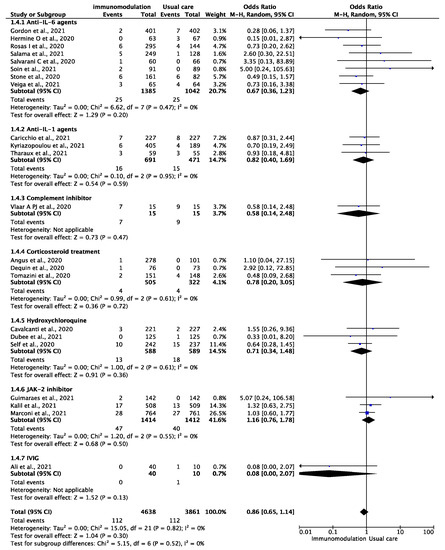
Figure 4.
Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals for the occurrence of any thromboembolic event among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents as an add-on to SOC vs. SOC only. Boxes represent the OR and lines represent the 95% CIs for individual studies. The diamonds and their width represent the pooled ORs and the 95% CIs, respectively. CI, confidence interval for the Mantel–Hansen estimator, I2: heterogeneity.
4. Discussion
This meta-analysis did not identify a statistically significant effect of immunomodulation on the prevention of thromboembolic events in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. However, given the large effect estimate for the prevention of VTE, especially in patients treated with IL-6 antagonists, we cannot exclude an effect of immunomodulation on VTE occurrence. The effect of immunomodulation therapy on any thromboembolism, driven largely by VTE events, was a nonsignificant reduction in this outcome.
The potency of SARS-CoV-2 to trigger a proinflammatory cascade leading to a pulse of proinflammatory cytokines is the first step towards a vicious cycle of hyper-inflammation and cytokine release syndrome [6,7,8,9,10,48]. During this phase, TNF-α and IL-1β facilitate a sustained increase of IL-6. Furthermore, recent histopathological data suggest sustained systemic activation of the complement pathway in the microvascular network [49]. Moreover, locally activated platelets were shown to induce the release of neutrophil extracellular traps covered with the tissue factor, which in turn activates the extrinsic coagulation cascade leading to thrombin formation [50]. This cross-talk between innate immunity, platelets, and endothelial cells in the maladaptive host immune system can lead to the development of microvascular immune-mediated thrombosis and hypercoagulability [51]. Towards this direction, the effects of several immunomodulatory agents in COVID-19 are being investigated in ongoing randomized trials (Supplementary Table S1). In this context, it can be hypothesized that the administration of immunomodulatory agents such as IL-6 or IL-1 antagonists, complement inhibitors, corticosteroids, IVIG, and hydroxychloroquine acting on these pathogenic pathways could potentially mitigate the development of microvascular thrombosis with a corresponding reduction of VTE. Although our results did not confirm this hypothesis, we identified a trend towards fewer VTEs among patients treated with IL-6 inhibitors. Although this effect was not statistically significant, a potential effect of IL-6 antagonists on VTE risk cannot be excluded given the large effect estimate. We should not oversee that these results represent a potential additive effect of these agents on the antithrombotic effect of low-molecular-weight heparin, which was used in these studies. This was driven by RCTs of IL-6 inhibitors, but it should be noted that the number of events and patients in the IL-1-antagonist trials was low, and therefore a positive association cannot be excluded.
On the other hand, we did not identify any effect of these agents on arterial thromboembolic events comprising ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, and myocardial infarction. Compared to VTE, stroke is a heterogeneous syndrome comprising various pathophysiological mechanisms (e.g., atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, patent foramen ovale, dissection, small vessel disease), which frequently overlap [52,53,54,55,56]. This complexity may explain why immunomodulatory agents did not show any decrease in the risk of stroke or systemic embolism in the COVID-19 patients in our analysis.
Despite the potential myocardial injury which frequently occurs in patients with COVID-19 either due to myocardial infarction or because of inflammatory injury to the myocardial cells [57,58], we did not identify any effect of immunomodulatory agents on the risk of myocardial infarction. Although recently the RESCUE trial reported a marked reduction in inflammation and thrombosis biomarkers with a novel IL-6 inhibitor [59] and previous studies showed a beneficial effect of immunomodulatory agents in cardiovascular outcomes [60,61], this effect was not identified in our analysis of patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Currently, the effects of several immunomodulatory agents in COVID-19 are being investigated in ongoing randomized trials (Supplementary Table S1).
Strengths of this meta-analysis include the conduct and report of the analysis according to the PRISMA recommendations for reviews evaluating randomized trials [27]. In addition, our analysis did not consider observational studies, but focused only on RCTs characterized by their prospective design, which minimizes recall errors and selection bias, and the rigorous blind assessment of pre-defined and adjudicated outcome events, especially in this patient population, reduced the possible confounding effect of antithrombotic treatment.
There are potential limitations of this meta-analysis. Firstly, apart from the variations in the definitions of comorbidities used across trials, differences in patient selection criteria and differences in the length of follow-up across trials, the included immunomodulatory agents had highly distinctive immunological properties, which may have affected the outcomes of this study. Even though thromboembolic events and especially VTE were not systematically investigated in the included studies, most COVID-19-related thromboembolic events occur during the most severe, in-hospital period of the disease, and thus it is unlikely that these events were undocumented. Moreover, as these events were objectively diagnosed across treatment arms, no discrepancy would be likely to affect the observed treatment effects. Second, we acknowledge that the studies included in this meta-analysis were not designed to investigate the effect of immunomodulatory agents on thromboembolic events. As a result, the studies did not provide detailed data of thromboembolic events related to patient comorbidities and characteristics; thus, we were not able to perform further analyses, while the patients’ cardiovascular comorbidities may have affected the incidence of thromboembolic events in each arm. Additionally, the studies did not include extensive reports on antithrombotic treatment modalities used in these patients, and the outcomes were not independently adjudicated. However, since these events typically require objective diagnostic testing for confirmation and immunomodulation treatments are not known to have antithrombotic properties, it is unlikely that diagnostic suspicion bias may have affected detection of such events across the treatment arms. Lastly, as a significant number of clinical trials did not report results on thromboembolic events, some immunomodulatory agents were underrepresented in the analysis, potentially affecting the results of the study. Due to the increased research interest and publication rate related to COVID-19, additional RCTs may become available in the future and provide further insights in the effect of immunomodulation on the thromboembolic risk of COVID-19 patients.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we did not identify a statistically significant effect of immunomodulation on the prevention of thromboembolic events in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. However, given the large effect estimate for the prevention of VTE, especially in patients treated with IL-6 antagonists, we cannot exclude an effect of immunomodulation on VTE occurrence. The effect of immunomodulation on thromboembolic risk warrants further research.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm10225366/s1, Figure S1: Flow diagram of the studies identified, screened, and included in the meta-analysis, Figure S2: (A) Risk of bias graph: review of the authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all the included studies; (B) risk of bias summary: review of the authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study, Figure S3: Diagnostic plots for each outcome based on the use of immunomodulatory agents or placebo. Panel (A): venous thromboembolism, Panel (B): ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, Panel (C): myocardial infarction, Panel (D): Any thromboembolic event, Figure S4: Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals for the occurrence of pulmonary embolism among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents as an add-on to SOC vs. SOC only. Boxes represent the OR and lines represent the 95% CIs for individual studies. The diamonds and their width represent the pooled ORs and the 95% CIs, respectively. CI, confidence interval for the Mantel–Hansen estimator, I2: heterogeneity, Figure S5: Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals for the occurrence of all-cause mortality in the included studies among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents as an add-on to SOC vs. SOC only. Boxes represent the OR and lines represent the 95% CIs for individual studies. The diamonds and their width represent the pooled ORs and the 95% CIs, respectively. CI, confidence interval for the Mantel–Hansen estimator, I2: heterogeneity; Table S1: Studies of immunomodulatory agents for COVID-19.
Author Contributions
D.S.: study design, acquisition of data, analysis, interpretation, and preparation of the manuscript; M.F.: study design, acquisition of data, analysis, interpretation, and preparation of the manuscript; P.T.: acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation; E.K.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; N.G.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; E.J.G.-B.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; H.M.: analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; J.D.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; A.C.S.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; G.D.: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content; G.N.: study concept and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation, preparation of the manuscript, study supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable. No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Dimitrios Sagris: nothing to disclose. Matilda Florentin: nothing to disclose. Panagiotis Tasoudis: nothing to disclose. Eleni Korompoki has received speaker’s honoraria from Amgen and BMS/Pfizer, travel grants from Bayer, contributed to the advisory board of BMS/Pfizer. Nikolaos Gatselis: nothing to disclose. Evangelos J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis has received honoraria from Abbott CH, bioMérieux, Brahms GmbH, GSK, InflaRx GmbH, and XBiotech Inc; independent educational grants from Abbott CH, AxisShield, bioMérieux Inc, InflaRx GmbH, Johnson & Johnson, and XBiotech Inc.; and funding from the Horizon2020 Marie-Curie Project European Sepsis Academy (granted to the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens), and the Horizon 2020 European Grants ImmunoSep and RISKinCOVID (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis). Haralampos Milionis declares receiving honoraria, consulting fees, and nonfinancial support from healthcare companies including Amgen, Bayer, Mylan, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Servier. James Douketis discloses consulting fees from Janssen, BMS, and Servier and speaking fees from Bayer, BMS, Pfizer, Sanofi, Leo Pharma. Monies from these sources are deposited into university- or hospital foundation-based research accounts. Alex C Spyropoulos discloses consulting fees and research support from Janssen and Boehringer Ingelheim and consulting fees from Bayer, BMS, Portola, Sanofi, the ATLAS Group. George N Dalekos is an advisor or lecturer for Ipsen, Pfizer, Genkyotex, Novartis, Sobi, received research grants from Abbvie, Gilead and has served as PI in studies for Abbvie, Novartis, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Genkyotex, Regulus Therapeutics Inc, Tiziana Life Sciences, Bayer, Astellas, Pfizer, Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, CymaBay Therapeutics Inc., Sobi, and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. George Ntaios discloses speaker fees/participation in the advisory board/research support from Abbott, Amgen, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Pfizer, Sanofi. All fees are paid to his institution (University of Thessaly).
References
- Nopp, S.; Moik, F.; Jilma, B.; Pabinger, I.; Ay, C. Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Lee, J.J.; Jamil, A.; Gunnam, V.; Najafi, H.; Memar Montazerin, S.; Shojaei, F.; Marszalek, J. Venous Thromboembolism among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 Undergoing Thromboprophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxley, T.J.; Mocco, J.; Majidi, S.; Kellner, C.P.; Shoirah, H.; Singh, I.P.; De Leacy, R.A.; Shigematsu, T.; Ladner, T.R.; Yaeger, K.A.; et al. Large-Vessel Stroke as a Presenting Feature of Covid-19 in the Young. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.S.; Kunichoff, D.; Adhikari, S.; Ahuja, T.; Amoroso, N.; Aphinyanaphongs, Y.; Cao, M.; Goldenberg, R.; Hindenburg, A.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Prevalence and Outcomes of D-Dimer Elevation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Netea, M.G.; Rovina, N.; Akinosoglou, K.; Antoniadou, A.; Antonakos, N.; Damoraki, G.; Gkavogianni, T.; Adami, M.E.; Katsaounou, P.; et al. Complex Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Respiratory Failure. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 992–1000.e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.-H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.C.K.; Meydan, C.; Kim, J.; Foox, J.; Butler, D.; Mason, C.E.; Shapira, S.D.; Noursadeghi, M.; Pollara, G. Transcriptional response modules characterize IL-1β and IL-6 activity in COVID-19. iScience 2021, 24, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Wong, P.; Klein, J.; Castro, T.B.R.; Silva, J.; Sundaram, M.; Ellingson, M.K.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Israelow, B.; et al. Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19. Nature 2020, 584, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abers, M.S.; Delmonte, O.M.; Ricotta, E.E.; Fintzi, J.; Fink, D.L.; de Jesus, A.A.A.; Zarember, K.A.; Alehashemi, S.; Oikonomou, V.; Desai, J.V.; et al. An immune-based biomarker signature is associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e144455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, A.; Havervall, S.; Meijenfeldt, F.v.; Hisada, Y.; Aguilera, K.; Grover, S.P.; Lisman, T.; Mackman, N.; Thålin, C. Patients with COVID-19 Have Elevated Levels of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Tissue Factor Activity That Is Associated with Severity and Mortality—Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermine, O.; Mariette, X.; Tharaux, P.-L.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Porcher, R.; Ravaud, P.; Group, C.-C. Effect of Tocilizumab vs Usual Care in Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19 and Moderate or Severe Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, C.; Han, J.; Yau, L.; Reiss, W.G.; Kramer, B.; Neidhart, J.D.; Criner, G.J.; Kaplan-Lewis, E.; Baden, R.; Pandit, L.; et al. Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Dolci, G.; Massari, M.; Merlo, D.F.; Cavuto, S.; Savoldi, L.; Bruzzi, P.; Boni, F.; Braglia, L.; Turrà, C.; et al. Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, G.; Larcher, A.; Tomelleri, A.; Campochiaro, C.; Della-Torre, E.; De Luca, G.; Farina, N.; Boffini, N.; Ruggeri, A.; Poli, A.; et al. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 inhibition compared with standard management in patients with COVID-19 and hyperinflammation: A cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e253–e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazopoulou, E.; Panagopoulos, P.; Metallidis, S.; Dalekos, G.N.; Poulakou, G.; Gatselis, N.; Karakike, E.; Saridaki, M.; Loli, G.; Stefos, A.; et al. An open label trial of anakinra to prevent respiratory failure in COVID-19. eLife 2021, 10, e66125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narain, S.; Stefanov, D.G.; Chau, A.S.; Weber, A.G.; Marder, G.; Kaplan, B.; Malhotra, P.; Bloom, O.; Liu, A.; Lesser, M.L.; et al. Comparative Survival Analysis of Immunomodulatory Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Cytokine Storm. Chest 2021, 159, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalekos, G.N.; Stefos, A.; Georgiadou, S.; Lygoura, V.; Michail, A.; Ntaios, G.; Samakidou, A.; Giannoulis, G.; Gabeta, S.; Vlychou, M.; et al. Lessons from pathophysiology: Use of individualized combination treatments with immune interventional agents to tackle severe respiratory failure in patients with COVID-19. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 88, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aomar-Millán, I.F.; Salvatierra, J.; Torres-Parejo, Ú.; Faro-Miguez, N.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Ceballos-Torres, Á.; Cruces-Moreno, M.T.; Gómez-Jiménez, F.J.; Hernández-Quero, J.; Anguita-Santos, F. Anakinra after treatment with corticosteroids alone or with tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and moderate hyperinflammation. A retrospective cohort study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontali, E.; Volpi, S.; Signori, A.; Antonucci, G.; Castellaneta, M.; Buzzi, D.; Montale, A.; Bustaffa, M.; Angelelli, A.; Caorsi, R.; et al. Efficacy of early anti-inflammatory treatment with high doses of intravenous anakinra with or without glucocorticoids in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Antorán, B.; Sancho-López, A.; Torres, F.; Moreno-Torres, V.; de Pablo-López, I.; García-López, P.; Abad-Santos, F.; Rosso-Fernández, C.M.; Aldea-Perona, A.; Montané, E.; et al. Combination of Tocilizumab and Steroids to Improve Mortality in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Spanish, Multicenter, Cohort Study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.A.; Stewart, I.; Fabbri, L.; Moss, S.; Robinson, K.; Smyth, A.R.; Jenkins, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis of anakinra, sarilumab, siltuximab and tocilizumab for COVID-19. Thorax 2021, 76, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Haghbin, H.; Abu Sitta, E.; Nawras, Y.; Fatima, R.; Sharma, S.; Lee-Smith, W.; Duggan, J.; Kammeyer, J.A.; Hanrahan, J.; et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, L.; Cavalli, G.; Navalesi, P.; Sella, N.; Landoni, G.; Yavorovskiy, A.G.; Likhvantsev, V.V.; Zangrillo, A.; Dagna, L.; Monti, G. Anakinra for patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of non-randomized cohort studies. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 86, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tleyjeh, I.M.; Kashour, Z.; Damlaj, M.; Riaz, M.; Tlayjeh, H.; Altannir, M.; Altannir, Y.; Al-Tannir, M.; Tleyjeh, R.; Hassett, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in COVID-19 patients: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malgie, J.; Schoones, J.W.; Pijls, B.G. Decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with Tocilizumab: A rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e742–e749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, W264–W269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators Investigators. Effect of Hydrocortisone on Mortality and Organ Support in Patients with Severe COVID-19: The REMAP-CAP COVID-19 Corticosteroid Domain Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dequin, P.-F.; Heming, N.; Meziani, F.; Plantefève, G.; Voiriot, G.; Badié, J.; François, B.; Aubron, C.; Ricard, J.-D.; Ehrmann, S.; et al. Effect of Hydrocortisone on 21-Day Mortality or Respiratory Support Among Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, A.B.; Zampieri, F.G.; Rosa, R.G.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Veiga, V.C.; Avezum, A.; Damiani, L.P.; Marcadenti, A.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Lisboa, T.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, W.H.; Semler, M.W.; Leither, L.M.; Casey, J.D.; Angus, D.C.; Brower, R.G.; Chang, S.Y.; Collins, S.P.; Eppensteiner, J.C.; Filbin, M.R.; et al. Effect of Hydroxychloroquine on Clinical Status at 14 Days in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.C.; Mouncey, P.R.; Al-Beidh, F.; Rowan, K.M.; Nichol, A.D.; Arabi, Y.M.; Annane, D.; Beane, A.; van Bentum-Puijk, W.; Berry, L.R.; et al. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.O.; Bräu, N.; Waters, M.; Go, R.C.; Hunter, B.D.; Bhagani, S.; Skiest, D.; Aziz, M.S.; Cooper, N.; Douglas, I.S.; et al. Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Frigault, M.J.; Serling-Boyd, N.J.; Fernandes, A.D.; Harvey, L.; Foulkes, A.S.; Horick, N.K.; Healy, B.C.; Shah, R.; Bensaci, A.M.; et al. Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, V.C.; Prats, J.; Farias, D.L.C.; Rosa, R.G.; Dourado, L.K.; Zampieri, F.G.; Machado, F.R.; Lopes, R.D.; Berwanger, O.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; et al. Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2021, 372, n84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharaux, P.-L.; Pialoux, G.; Pavot, A.; Mariette, X.; Hermine, O.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Porcher, R.; Ravaud, P.; Bureau, S.; Dougados, M.; et al. Effect of anakinra versus usual care in adults in hospital with COVID-19 and mild-to-moderate pneumonia (CORIMUNO-ANA-1): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaar, A.P.J.; de Bruin, S.; Busch, M.; Timmermans, S.A.M.E.G.; van Zeggeren, I.E.; Koning, R.; ter Horst, L.; Bulle, E.B.; van Baarle, F.E.H.P.; van de Poll, M.C.G.; et al. Anti-C5a antibody IFX-1 (vilobelimab) treatment versus best supportive care for patients with severe COVID-19 (PANAMO): An exploratory, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e764–e773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soin, A.S.; Kumar, K.; Choudhary, N.S.; Sharma, P.; Mehta, Y.; Kataria, S.; Govil, D.; Deswal, V.; Chaudhry, D.; Singh, P.K.; et al. Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazini, B.M.; Maia, I.S.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Berwanger, O.; Rosa, R.G.; Veiga, V.C.; Avezum, A.; Lopes, R.D.; Bueno, F.R.; Silva, M.V.A.O.; et al. Effect of Dexamethasone on Days Alive and Ventilator-Free in Patients with Moderate or Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19: The CoDEX Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, A.C.; Patterson, T.F.; Mehta, A.K.; Tomashek, K.M.; Wolfe, C.R.; Ghazaryan, V.; Marconi, V.C.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Hsieh, L.; Kline, S.; et al. Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Uddin, S.M.; Shalim, E.; Sayeed, M.A.; Anjum, F.; Saleem, F.; Muhaymin, S.M.; Ali, A.; Ali, M.R.; Ahmed, I.; et al. Hyperimmune anti-COVID-19 IVIG (C-IVIG) treatment in severe and critical COVID-19 patients: A phase I/II randomized control trial. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 36, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubée, V.; Roy, P.M.; Vielle, B.; Parot-Schinkel, E.; Blanchet, O.; Darsonval, A.; Lefeuvre, C.; Abbara, C.; Boucher, S.; Devaud, E.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine in mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019: A placebo-controlled double blind trial. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchio, R.; Abbate, A.; Gordeev, I.; Meng, J.; Hsue, P.Y.; Neogi, T.; Arduino, R.; Fomina, D.; Bogdanov, R.; Stepanenko, T.; et al. Effect of Canakinumab vs Placebo on Survival without Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in Patients Hospitalized with Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazopoulou, E.; Poulakou, G.; Milionis, H.; Metallidis, S.; Adamis, G.; Tsiakos, K.; Fragkou, A.; Rapti, A.; Damoulari, C.; Fantoni, M.; et al. Early treatment of COVID-19 with anakinra guided by soluble urokinase plasminogen receptor plasma levels: A double-blind, randomized controlled phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, V.C.; Ramanan, A.V.; de Bono, S.; Kartman, C.E.; Krishnan, V.; Liao, R.; Piruzeli, M.L.B.; Goldman, J.D.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; de Cassia Pellegrini, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): A randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P.O.; Quirk, D.; Furtado, R.H.; Maia, L.N.; Saraiva, J.F.; Antunes, M.O.; Kalil Filho, R.; Junior, V.M.; Soeiro, A.M.; Tognon, A.P.; et al. Tofacitinib in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICD10. Cytokine Release Syndrome 2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D89.83. Available online: https://www.icd10data.com/ICD10CM/Codes/D50-D89/D80-D89/D89-/D89.83 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Magro, C.; Mulvey, J.J.; Berlin, D.; Nuovo, G.; Salvatore, S.; Harp, J.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Laurence, J. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: A report of five cases. Transl. Res. 2020, 220, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skendros, P.; Mitsios, A.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mastellos, D.C.; Metallidis, S.; Rafailidis, P.; Ntinopoulou, M.; Sertaridou, E.; Tsironidou, V.; Tsigalou, C.; et al. Complement and tissue factor-enriched neutrophil extracellular traps are key drivers in COVID-19 immunothrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6151–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gencer, S.; Lacy, M.; Atzler, D.; van der Vorst, E.P.C.; Döring, Y.; Weber, C. Immunoinflammatory, Thrombohaemostatic, and Cardiovascular Mechanisms in COVID-19. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1629–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntaios, G.; Wintermark, M.; Michel, P. Supracardiac atherosclerosis in embolic stroke of undetermined source: The underestimated source. Eur. Heart J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaios, G.; Pearce, L.A.; Veltkamp, R.; Sharma, M.; Kasner, S.E.; Korompoki, E.; Milionis, H.; Mundl, H.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Connolly, S.J.; et al. Potential Embolic Sources and Outcomes in Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source in the NAVIGATE-ESUS Trial. Stroke 2020, 51, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntaios, G. Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaios, G.; Perlepe, K.; Lambrou, D.; Sirimarco, G.; Strambo, D.; Eskandari, A.; Karagkiozi, E.; Vemmou, A.; Koroboki, E.; Manios, E.; et al. Prevalence and Overlap of Potential Embolic Sources in Patients with Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntaios, G.; Hart, R.G. Embolic Stroke. Circulation 2017, 136, 2403–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bangalore, S.; Sharma, A.; Slotwiner, A.; Yatskar, L.; Harari, R.; Shah, B.; Ibrahim, H.; Friedman, G.H.; Thompson, C.; Alviar, C.L.; et al. ST-Segment Elevation in Patients with Covid-19—A Case Series. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2478–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, G.G.; Montorfano, M.; Trabattoni, D.; Andreini, D.; Ferrante, G.; Ancona, M.; Metra, M.; Curello, S.; Maffeo, D.; Pero, G.; et al. ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Patients with COVID-19. Circulation 2020, 141, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Devalaraja, M.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Engelmann, M.D.M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Ivkovic, M.; Lo, L.; Kling, D.; Pergola, P.; Raj, D.; et al. IL-6 inhibition with ziltivekimab in patients at high atherosclerotic risk (RESCUE): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardif, J.-C.; Kouz, S.; Waters, D.D.; Bertrand, O.F.; Diaz, R.; Maggioni, A.P.; Pinto, F.J.; Ibrahim, R.; Gamra, H.; Kiwan, G.S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Low-Dose Colchicine after Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).