Laser Ablation Treatment of Recurrent Lymph Node Metastases from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
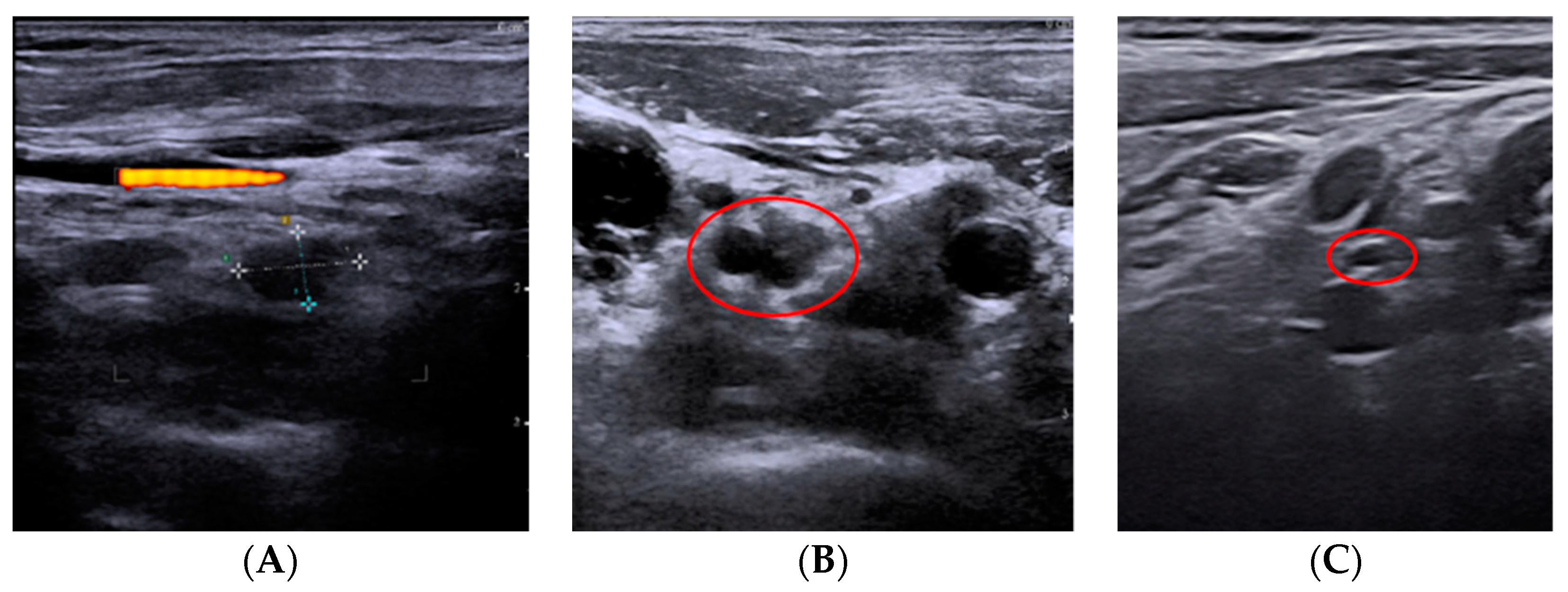
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, H.; Devesa, S.S.; Sosa, J.A.; Check, D.; Kitahara, C.M. Trends in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, 1974–2013. JAMA 2017, 317, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vecchia, C.; Malvezzi, M.; Bosetti, C.; Garavello, W.; Bertuccio, P.; Levi, F.; Negri, E. Thyroid cancer mortality and incidence: A global overview. Int. J. Cancer. 2015, 136, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, G.; Cova, L.; Ierace, T.; Baroli, A.; Di Mauro, E.; Pacella, C.M.; Goldberg, S.N.; Solbiati, L. Treatment of Metastatic Lymph Nodes in the Neck from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Percutaneous Laser Ablation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: What is new and what has changed? Cancer-Am. Cancer Soc. 2017, 123, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Miyauchi, A. Lateral and mediastinal lymph node dissection in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: Indications, benefits, and risks. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenot, T.E.; Deniwar, A.; Bhatia, P.; Al-Qurayshi, Z.; Randolph, G.W.; Kandil, E. Percutaneous ethanol injection vs reoperation for locally recurrent papillary thyroid cancer: A systematic review and pooled analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, E.; Bizzarri, G.; Bianchini, A.; Valle, D.; Misischi, I.; Guglielmi, R.; Salvatori, M.; Solbiati, L.; Crescenzi, A.; Pacella, C.M.; et al. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided laser ablation is effective for treating selected nodal metastases in papillary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E92–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, S. Locoregional control of recurrent papillary thyroid carcinoma by ultrasoundguided percutaneous microwave ablation: A prospective study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ge, M.; Xu, D.; Chen, L.; Qian, C.; Shi, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y. Ultrasonography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for cervical lymph node metastasis from thyroid carcinoma. J. Cancer. Res. 2014, 10, C144–C149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiman, T.H. Optical and microwave-optical experiments in ruby. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1960, 4, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaret, M.M.; Breinin, G.M.; Schmidt, H.; Ripps, H.; Siegel, I.M.; Solon, L.R. Ocular lesions produced by an optical maser (laser). Science 1961, 134, 1525–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, L.; Hornby, P.; Meyer, R.; Goldman, B. Impact of the laser on dental caries. Nature 1964, 25, 203–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P.; Fong, Y. Laser ablation for cancer: Past, present and future. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Goldberg, S.N. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 2011, 258, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S. Pathologic analysis of photothermal and photomechanical effects of laser-tissue interactions. Photochem. Photobiol. 1991, 53, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, S.L. Laser-tissue interactions. Photochemical, photothermal and photomechanical. Surg. Clin. North Am. 1992, 72, 531–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, R.J.; Fuentes, D.; Elliott, A.A.; Weinberg, J.S.; Ahrar, K. Laser-induced thermal therapy for tumor ablation. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solbiati, L.; Giangrande, A.; De Pra, L.; Bellotti, E.; Cantù, P.; Ravetto, C. Percutaneous ethanol injection of parathyroid tumors under US guidance: Treatment for secondary hyperparathyroidism. Radiology 1985, 155, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.E.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, J.H. Radiofrequency and ethanol ablation for the treatment of recurrent thyroid cancers: Current status and challenges. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bown, S.G. Phototherapy in tumors. World J. Surg. 1983, 7, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, D.E.; Monchik, J.M.; Decrea, C.; Pisharodi, L. Radiofrequency ablation of regional recurrence from well-differentiated thyroid malignancy. Surgery 2001, 130, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, W.S.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.J.; Yun, T.J.; Choi, S.H.; Sohn, C.H.; Lee, K.E.; Sung, M.W.; Youn, Y.K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation for treatment of locally recurrent thyroid cancers smaller than 2 cm. Radiology 2015, 276, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ni, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhan, W. Ultrasound-guided laser ablation versus surgery for solitary papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: A retrospective study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Data | Population |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 5 (50%) |
| Female | 5 (50%) |
| Age | 40.2 ± 17.98 |
| FNAC | Positive for malignant cell |
| Eluate Tg | >5000 μg/L |
| Lymph node level | |
| IV | 7 (70%) |
| Vb | 3 (30%) |
| Side | |
| Right | 4 (40%) |
| Left | 6 (60%) |
| Lymph node volume | 1.82 ± 3.45 |
| Fiber optic | 1.01 ± 0.31 |
| Watt | 3.1 ± 0.31 |
| Time in second | 531.86 ± 109.5 |
| Joule | 1256 ± 396 |
| 1-month volume in ml | 1.12 ± 2.18 |
| % reduction at 1 month | 40.12 ± 2.2 |
| 3-months volume in ml | 0.88 ± 1.65 |
| % reduction at 3 months | 49.1 ± 2.13 |
| 6-months volume in ml | 0.706 ± 1.30 |
| % reduction at 6 months | 59.8 ± 3.05 |
| Patient | Gender | Age | FNAC | Eluate Tg (μg/L) | Lymph Node Level | Side | Lymph Node Volume (mL) | Fiber Optic | Watts | Time (Seconds) | Joules |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 20 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Right | 0.7 | 1 | 3 | 270 | 810 |
| 2 | Male | 19 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Right | 0.35 | 1 | 3 | 365 | 1095 |
| 3 | Male | 19 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Right | 0.25 | 1 | 3 | 365 | 1095 |
| 4 | Female | 59 | Positive | >5000 | Vb | Left | 11.58 | 2 | 4 | 340 | 2720 |
| 5 | Female | 59 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Left | 0.46 | 1 | 3 | 335 | 1005 |
| 6 | Female | 63 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Left | 1.27 | 1 | 3 | 420 | 1260 |
| 7 | Male | 28 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Right | 1.32 | 1 | 3 | 400 | 1200 |
| 8 | Female | 35 | Positive | >5000 | VB | Right | 1.05 | 1 | 3 | 395 | 1185 |
| 9 | Female | 48 | Positive | >5000 | VB | Left | 0.79 | 1 | 3 | 325 | 975 |
| 10 | Female | 52 | Positive | >5000 | IV | Left | 0.98 | 1 | 3 | 405 | 1215 |
| Patients | 1 Month Volume (mL) | % Reduction at 1 Month | 3 Months Volume (mL) | % Reduction at 3 Months | 6 Months Volume (mL) | % Reduction at 6-Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 42 | 0.08 | 50 | 0.07 | 60 |
| 2 | 0.22 | 37.2 | 0.19 | 45 | 0.16 | 55 |
| 3 | 0.15 | 40 | 0.13 | 48 | 0.11 | 56 |
| 4 | 7.3 | 37 | 5.56 | 52 | 4.4 | 62 |
| 5 | 0.22 | 43 | 0.2 | 47 | 0.26 | 57 |
| 6 | 0.74 | 42 | 0.62 | 51 | 0.48 | 62 |
| 7 | 0.76 | 42 | 0.64 | 51 | 0.49 | 63 |
| 8 | 0.61 | 41 | 0.53 | 50 | 0.38 | 64 |
| 9 | 0.48 | 39 | 0.4 | 49 | 0.32 | 59 |
| 10 | 0.61 | 38 | 0.51 | 48 | 0.39 | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Offi, C.; Misso, C.; Antonelli, G.; Esposito, M.G.; Brancaccio, U.; Spiezia, S. Laser Ablation Treatment of Recurrent Lymph Node Metastases from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225295
Offi C, Misso C, Antonelli G, Esposito MG, Brancaccio U, Spiezia S. Laser Ablation Treatment of Recurrent Lymph Node Metastases from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225295
Chicago/Turabian StyleOffi, Chiara, Claudia Misso, Giovanni Antonelli, Maria Grazia Esposito, Umberto Brancaccio, and Stefano Spiezia. 2021. "Laser Ablation Treatment of Recurrent Lymph Node Metastases from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225295
APA StyleOffi, C., Misso, C., Antonelli, G., Esposito, M. G., Brancaccio, U., & Spiezia, S. (2021). Laser Ablation Treatment of Recurrent Lymph Node Metastases from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5295. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225295






