Thoracic Spine Fractures with Blunt Aortic Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collected and Diagnostic Modalities
2.3. Study End Points
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Incidence of Aortic Injury in Patients with Thoracic Burst Fractures
3.2. Characteristics of Aortic Injury in Patients with Thoracic Burst Fractures
3.3. Risk Factors Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary
4.2. Incidence of BAI
4.3. Study Design
4.4. Risk Factors
4.5. Mechanism
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- VandenBerg, J.; Cullison, K.; Fowler, S.A.; Parsons, M.S.; McAndrew, C.M.; Carpenter, C.R. Blunt Thoracolumbar-Spine Trauma Evaluation in the Emergency Department: A Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy for History, Physical Examination, and Imaging. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 56, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuura, Y.; Osborn, J.M.; Cason, G.W. The epidemiology of thoracolumbar trauma: A meta-analysis. J. Orthop. 2016, 13, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menzer, H.; Gill, G.K.; Paterson, A. Thoracic spine sports-related injuries. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2015, 14, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegl, U.J.A.; Schnake, K.J.; Hartmann, F.; Katscher, S.; Riehle, M.; Scheyerer, M.J.; Schmeiser, G.; Siekmann, H.; Osterhoff, G. Traumatic Fractures of the Thoracic Spine. Z. Orthopädie Unf. 2020, 159, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splendiani, A.; Bruno, F.; Patriarca, L.; Barile, A.; Di Cesare, E.; Masciocchi, C.; Gallucci, M. Thoracic spine trauma: Advanced imaging modality. Radiol. Med. 2016, 121, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, B.D.; Boody, B.S.; Jenkins, T.J.; Hsu, W.K.; Patel, A.A.; Savage, J.W. Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizimungu, R.; Sergio, A.; Baumann, B.M.; Raja, A.S.; Mower, W.R.; Langdorf, M.I.; Medak, A.J.; Hendey, G.W.; Nishijima, D.; Rodriguez, R.M. Thoracic Spine Fracture in the Panscan Era. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2020, 76, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenburg, S.D.; Ravenel, J.G.; Ikonomidis, J.S.; Schonholz, C.; Reeves, S. Acute traumatic aortic injury: Imaging evaluation and management. Radiology 2008, 248, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A.Y.; Broce, M. Review of short-term outcomes for TEVAR after blunt traumatic aortic injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015, 78, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Ramieri, A.; Chiarella, V.; Vigliotta, M.; Domenicucci, M. Thoraco-lumbar fractures with blunt traumatic aortic injury in adult patients: Correlations and management. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cultrera, F.; Gamberini, E.; Iacono, G.; Turicchia, G.U.; Agnoletti, V.; Tosatto, L. Unstable thoracic spine fracture with aortic encroachment: A potentially fatal association and a suggested treatment. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 39, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Morimoto, Y.; Sugimoto, T.; Arase, H.; Araki, K. Blunt Abdominal Aortic Injury Associated with L2 Vertebral Fracture. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 34, 273.e1–273.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, E.; Endo, G.; Furukawa, K.; Shirasaki, Y.; Mori, H. Aortic Pseudoaneurysm due to Simple Vertebral Compression Fracture Treated with Conservative Management. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2016, 9, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, P.G.; Inaba, K.; Barmparas, G.; Georgiou, C.; Toms, C.; Noguchi, T.T.; Rogers, C.; Sathyavagiswaran, L.; Demetriades, D. Blunt thoracic aortic injuries: An autopsy study. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2011, 70, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, J.T.; Hynes, J.T.; Perry, J.F., Jr. Thoracic spinal fractures and aortic rupture: A significant and fatal association. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1990, 50, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, A.R.; Oner, C.; Kepler, C.K.; Dvorak, M.; Schnake, K.; Bellabarba, C.; Reinhold, M.; Aarabi, B.; Kandziora, F.; Chapman, J.; et al. AOSpine thoracolumbar spine injury classification system: Fracture description, neurological status, and key modifiers. Spine 2013, 38, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.A.; Matsumura, J.S.; Mitchell, R.S.; Farber, M.A.; Greenberg, R.K.; Azizzadeh, A.; Murad, M.H.; Fairman, R.M. Endovascular repair of traumatic thoracic aortic injury: Clinical practice guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaccaro, A.R.; Lehman, R.A., Jr.; Hurlbert, R.J.; Anderson, P.A.; Harris, M.; Hedlund, R.; Harrop, J.; Dvorak, M.; Wood, K.; Fehlings, M.G.; et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: The importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine 2005, 30, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, T.T.; Leonard, G.R.; Cepela, D.J. Classifications In Brief: American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) Impairment Scale. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freixinet Gilart, J.; Hernandez Rodriguez, H.; Martinez Vallina, P.; Moreno Balsalobre, R.; Rodriguez Suarez, P.R. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of thoracic traumatism. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2011, 47, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMaire, S.A.; Russell, L. Epidemiology of thoracic aortic dissection. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmerov, A.; DuBose, J.; Azizzadeh, A. Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury: Current Therapies, Outcomes, and Challenges. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2019, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, K.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Finkelstein, J.; Murphy, J.; Brenneman, F.D.; Boulanger, B.R.; Girotti, M. Blunt abdominal aortic trauma in association with thoracolumbar spine fractures. Injury 2001, 32, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, M.J.; Dennis, J.W.; Allmon, J.C.; Gautam, S.; Habib, J. Identification of unique characteristics and the management of blunt traumatic aortic injuries occurring at unusual locations in the descending thoracic aorta. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouawad, N.J.; Paulisin, J.; Hofmeister, S.; Thomas, M.B. Blunt thoracic aortic injury—Concepts and management. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.C.; Liu, K.S.; Chen, H.W.; Huang, Y.K.; Chu, J.J.; Tsai, F.C.; Lin, P.J. Blunt aortic injury: Risk factors and impact of surgical approaches. Surg. Today 2016, 46, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob-Brassard, J.; Salata, K.; Kayssi, A.; Hussain, M.A.; Forbes, T.L.; Al-Omran, M.; de Mestral, C. A systematic review of nonoperative management in blunt thoracic aortic injury. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 1675–1681.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, T.K.; Wee, I.J.Y.; Tseng, F.S.; Syn, N.; Choong, A. A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of nonoperative management of blunt traumatic thoracic aortic injury in 2897 patients. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 941–953.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudko, S.; Kusz, D.; Ziaja, D.; Kusz, B. Laceration of abdominal aorta by a fragment of fractured L2 vertebral body after a low-energy injury: A case report and review of literature. Spine 2012, 37, E1406–E1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Ali Yahia, D.; Bouvier, A.; Nedelcu, C.; Urdulashvili, M.; Thouveny, F.; Ridereau, C.; Tanguy, J.Y.; Picquet, J.; Aube, C.; Willoteaux, S. Imaging of thoracic aortic injury. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2015, 96, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richens, D.; Field, M.; Neale, M.; Oakley, C. The mechanism of injury in blunt traumatic rupture of the aorta. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2002, 21, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
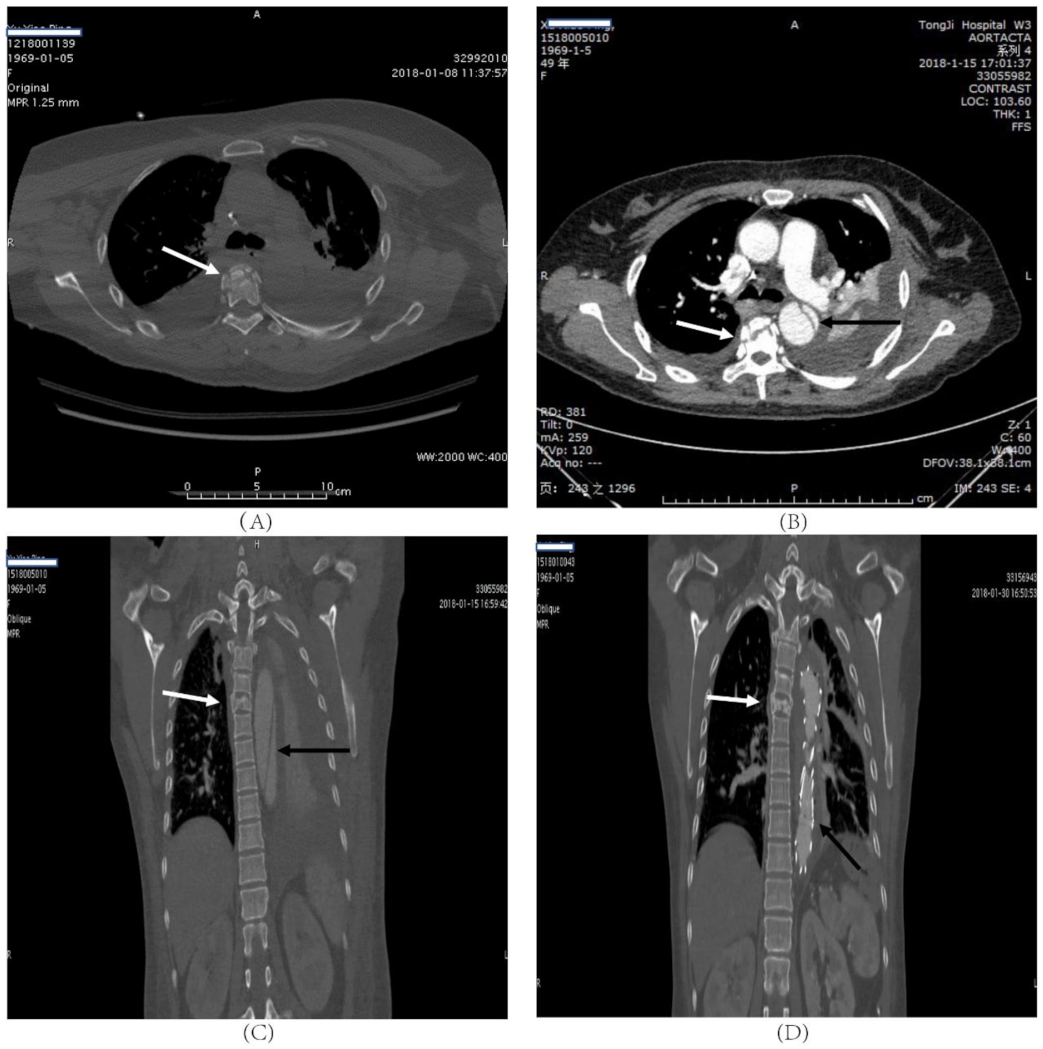
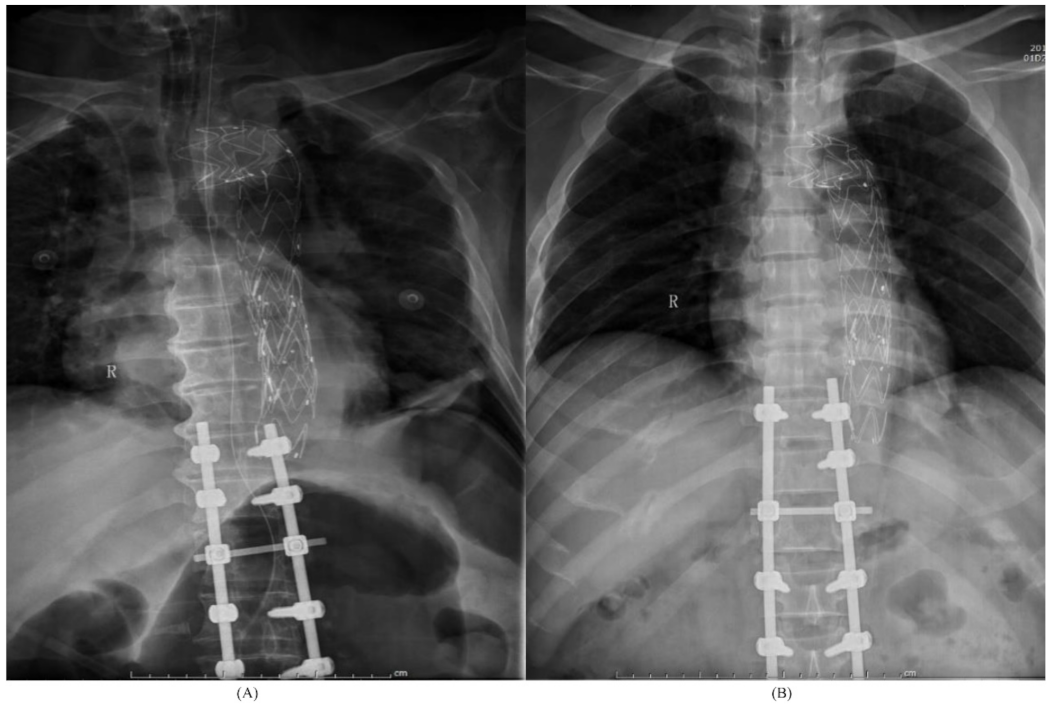
| Patient No. | Sex | Age | Mechanism of Injury | Level of Fracture | AO Classification | TLICS | BAI Grade | Neurological Deficit | Pulmonary Contusion | Hemothorax | Flail Chest | Pelvic Fracture | Extremity Injury |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 58 | Crush | T3/T4 | A3/A1 | 2 | III | + | + | ||||
| 2 | M | 48 | Fall | T11/T12 | A4/A1 | 6 | III | + | + | + | + | ||
| 3 | M | 45 | Fall | T11/T12 | A1/A4 | 6 | II | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 4 | M | 55 | Crush | T2/T6/T7/T8 | A1/A1/A3/A2 | 2 | III | + | + | + | |||
| 5 | M | 54 | Crush | T5/T10 | A3/A4 | 5 | II | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6 | M | 62 | Crush | T11/T12 | A1/A3 | 5 | III | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 7 | M | 54 | Fall | T12 | A3 | 4 | I | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 8 | M | 55 | Crush | T7 | A3 | 2 | III | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 9 | F | 49 | Crush | T5 | A3 | 4 | III | + | + | + | |||
| 10 | M | 51 | Crush | T6-T9/T12 | A1/A1/A1/A3 | 5 | III | + | + | ||||
| 11 | M | 57 | Other | T11/T12 | A4/A3 | 7 | III | + | + | + | + | ||
| 12 | M | 74 | Crush | T12 | A3 | 5 | III | + | + | + | + | ||
| 13 | M | 18 | Fall | T12 | A4 | 4 | III | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 14 | M | 63 | Crush | T4 | A3 | 2 | III | + | + |
| Variable | Non-BAI Patients (n = 110) | BAI Patients (n = 14) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 48 ± 16 | 48 ± 15 | 0.943 |
| Male, n (%) | 81 (73.6%) | 13 (92.9%) | 0.115 |
| ISS, median (IQR) | 27 (18–33) | 38 (29–44.25) | <0.01 |
| Mechanism | |||
| Crush, n (%) | 34 (30.9%) | 9 (64.3%) | 0.014 |
| Falls, n (%) | 58 (52.7%) | 4 (28.6%) | 0.089 |
| Other, n (%) | 18 (16.4%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.369 |
| Multilevel thoracic fractures | 32 (29.1%) | 8 (57.1%) | 0.035 |
| Neurological deficit | 42 (38.2%) | 10 (71.4%) | 0.018 |
| TLICS | 3.5 ± 1.9 | 4.2 ± 1.7 | 0.18 |
| Associated thoracic injuries, n (%) | |||
| Sternum | 14 (12.7%) | 4 (28.6%) | 0.114 |
| Hemothorax | 50 (45.5%) | 10 (71.4%) | 0.067 |
| Rib fractures | 68 (61.8%) | 11 (78.6%) | 0.219 |
| Pulmonary contusion | 49 (44.5%) | 12 (85.7%) | 0.004 |
| Pneumothorax | 10 (9.1%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.81 |
| Hemopneumothorax | 17 (15.5%) | 0 | - |
| Flail chest | 7 (6.4%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0.052 |
| Scapular fracture | 17 (15.5%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.408 |
| Other injuries (AIS ≥ 2), n (%) | |||
| TBI | 49 (44.5%) | 4 (28.6%) | 0.255 |
| Cervical spine injury | 23 (20.9%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0.221 |
| Lumbar spine injury | 39 (35.5%) | 9 (64.3%) | 0.037 |
| Abdominal injury | 15 (13.6%) | 2 (14.3%) | 0.947 |
| Pelvic fracture | 19 (17.3%) | 7 (50%) | 0.005 |
| Extremity injury | 25 (22.7%) | 7 (50%) | 0.029 |
| Risk Factor | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.001 | 0.966–1.038 | 0.942 |
| Sex | 0.215 | 0.027–1.716 | 0.147 |
| ISS | 1.137 | 1.059–1.220 | <0.001 |
| Crush | 4.024 | 1.254–12.907 | 0.019 |
| Fall | 0.359 | 0.106–1.213 | 0.099 |
| Hemothorax | 3 | 0.887–10.149 | 0.077 |
| Pulmonary contusion | 7.469 | 1.596–34.962 | 0.011 |
| Multilevel thoracic fractures | 3.25 | 1.044–10.118 | 0.042 |
| Lumbar spine injury | 3.411 | 1.067–10.898 | 0.038 |
| Neurological deficit | 4.048 | 1.193–13.733 | 0.025 |
| Pelvic fracture | 4.789 | 1.504–12.254 | 0.008 |
| Extremity injury | 3.4 | 1.089–10.616 | 0.035 |
| Flail chest | 4.013 | 0.906–17.78 | 0.067 |
| Hypertension | 2.84 | 0.852–9.468 | 0.089 |
| Diabetes | 1.615 | 0.175–14.918 | 0.672 |
| Osteoproliferation | 0.538 | 0.141–2.048 | 0.363 |
| Atherosclerosis | 2.044 | 0.577–7.242 | 0.268 |
| Alcohol | 3.039 | 0.907–10.185 | 0.072 |
| Risk Factor | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS | 1.184 | 1.072–1.308 | 0.001 |
| Crush | 10.474 | 1.905–57.579 | 0.007 |
| Flail chest | 4.917 | 1.122–21.545 | 0.035 |
| Neurological deficit | 8.299 | 0.999–68.933 | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, H.; Tang, T.-X.; Tang, L.-S.; Chen, D.; Luo, J.-L.; Dong, L.-M.; Gao, S.-H.; Tang, Z.-H. Thoracic Spine Fractures with Blunt Aortic Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Characteristics. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225220
Deng H, Tang T-X, Tang L-S, Chen D, Luo J-L, Dong L-M, Gao S-H, Tang Z-H. Thoracic Spine Fractures with Blunt Aortic Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Characteristics. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(22):5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225220
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Hai, Ting-Xuan Tang, Liang-Sheng Tang, Deng Chen, Jia-Liu Luo, Li-Ming Dong, Si-Hai Gao, and Zhao-Hui Tang. 2021. "Thoracic Spine Fractures with Blunt Aortic Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Characteristics" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 22: 5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225220
APA StyleDeng, H., Tang, T.-X., Tang, L.-S., Chen, D., Luo, J.-L., Dong, L.-M., Gao, S.-H., & Tang, Z.-H. (2021). Thoracic Spine Fractures with Blunt Aortic Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Characteristics. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(22), 5220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10225220








