Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Asthma and Obesity Two Diseases on the Rise and Linked
2.1. Asthma
2.2. Obesity
2.3. Asthma and Obesity: Two Linked Diseases
2.4. Severe Asthma Is Associated with Obesity
3. Asthma and Obesity Two Diseases Bridged by Inflammation
3.1. Asthma and Inflammation
3.1.1. Eosinophilic Asthma
3.1.2. Non-Eosinophilic Asthma
3.2. Obesity and Inflammation
3.2.1. Adipose Tissue Expansion and Inflammation
3.2.2. Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems
3.2.3. Adipokines
3.2.4. Inflammasome
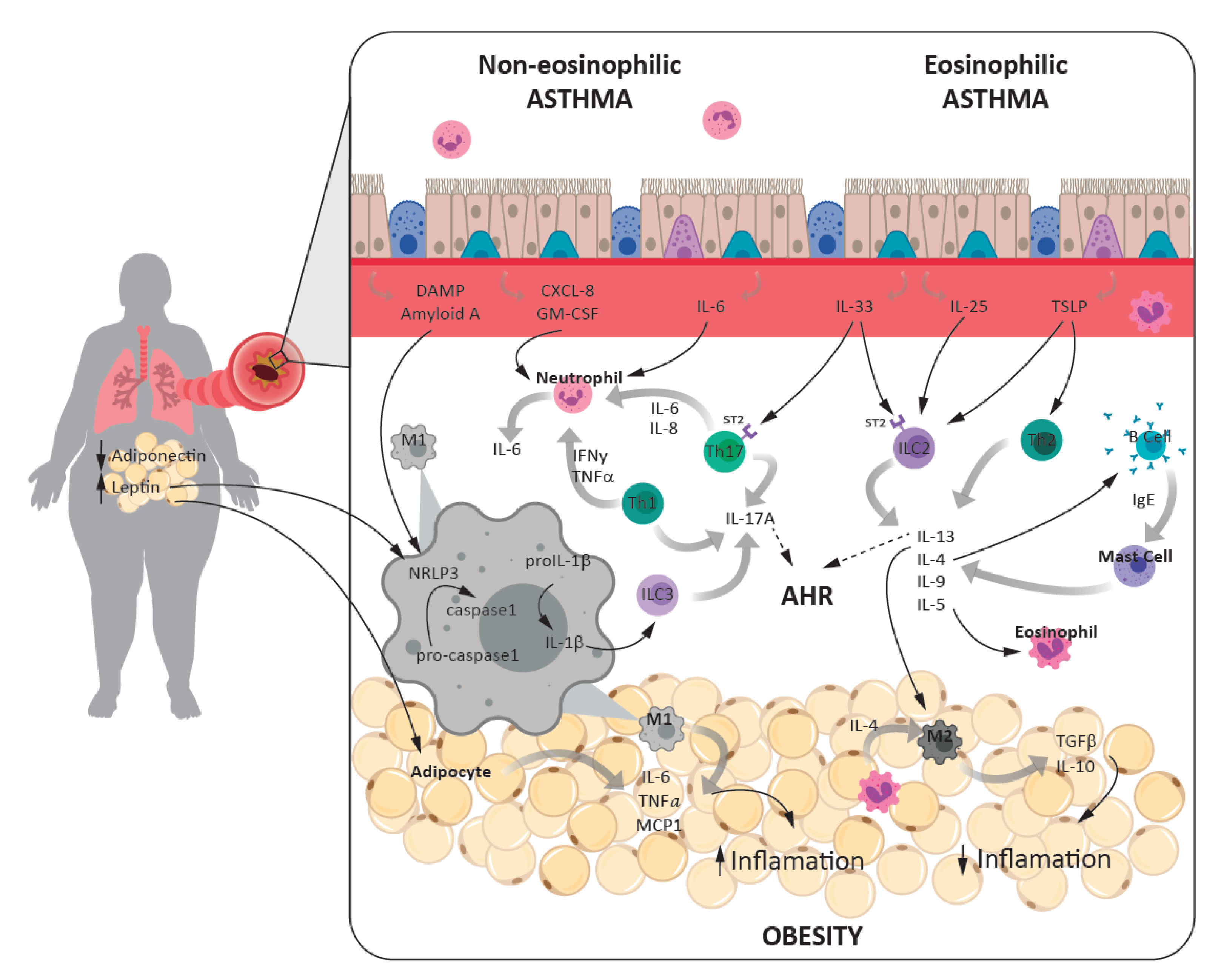
3.3. Inflammatory Links between Asthma and Obesity
3.3.1. Cells and Cytokines
3.3.2. Inflammasome Role in Asthma-Obesity Phenotype
3.3.3. Adipokines
4. Association of Obesity and Asthma: Genetics
5. Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Asthma
6. Effects of Weight Loss on Asthma and Inflammation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Z.; Pei, X.; Xia, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, R.; Hu, C.; Imam, M.U.; Chen, Y.; Imam, M.U.; Liu, L. Anthropometric indices as surrogates for estimating abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue: A meta-analysis with 16,129 participants. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Gallagher, D. Assessment methods in human body composition. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Mendes, F.; Paciência, I.; Rufo, J.C.; Silva, D.; Cunha, P.; Farraia, M.; Delgado, L.; Moreira, P.; Moreira, A. Asthma and body mass definitions affect estimates of association: Evidence from a community-based cross-sectional survey. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, P.; Moreira, A.; Moreira, P.; Delgado, L. Dietary diversity and childhood asthma—Dietary acid load, an additional nutritional variable to consider. Allergy 2020, 75, 2418–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limaye, S.; Salvi, S. Obesity and Asthma: The role of environmental pollutants. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2014, 34, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciência, I.; Rufo, J.C.; Silva, D.; Martins, C.; Mendes, F.C.; Farraia, M.; Delgado, L.; Fernandes, E.D.O.; Padrão, P.; Moreira, P.; et al. Exposure to indoor endocrine-disrupting chemicals and childhood asthma and obesity. Allergy 2019, 74, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permaul, P.; Gaffin, J.M.; Petty, C.R.; Baxi, S.N.; Lai, P.S.; Sheehan, W.J.; Camargo, C.A.; Gold, D.R.; Phipatanakul, W. Obesity may enhance the adverse effects of NO2 exposure in urban schools on asthma symptoms in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 813–820.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abera, S.F.; Agrawal, A.; Ahmed, M.B.; Aichour, A.N.; Aichour, I.; Aichour, M.T.E.; Alam, K.; et al. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEMA 4.4—Guía Española Para el Manejo del Asma. 2019. Available online: https://www.semg.es/index.php/consensos-guias-y-protocolos/316-gema-4-4-guia-espanola-para-el-manejo-del-asma (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Beasley, R.; Semprini, A.; Mitchell, E.A. Risk factors for asthma: Is prevention possible? Lancet 2015, 386, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbank, A.J.; Sood, A.K.; Kesic, M.J.; Peden, D.B.; Hernandez, M. Environmental determinants of allergy and asthma in early life. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, L.; Williams, E.J.; Scott, H.A.; Berthon, B.S.; Jensen, M.; Wood, L.G. Diet and Asthma: Is It Time to Adapt Our Message? Nutrients 2017, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Akinbami, L.J.; McGuire, L.C.; Blanck, H.M. Association of sugar-sweetened beverage intake frequency and asthma among U.S. adults, 2013. Prev. Med. 2016, 91, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.S.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Oken, E.; Litonjua, A.A.; Gold, D.R. Prenatal and Early Life Fructose, Fructose-Containing Beverages, and Midchildhood Asthma. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrison, L.B.; Brandt, E.B.; Myers, J.B.; Hershey, G.K.K. Environmental exposures and mechanisms in allergy and asthma development. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basterra-Gortari, F.J.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Gea, A.; Martínez-González, M. Prevalencia de obesidad y diabetes en adultos españoles, 1987–2012. Med. Clín. 2017, 148, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wadden, T.A. Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Management of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rahilly, S. Human genetics illuminates the paths to metabolic disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 462, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Zhang, S.; Willett, W.C.; Speizer, F.E. Prospective Study of Body Mass Index, Weight Change, and Risk of Adult-onset Asthma in Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.O.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Montgomery, S.M.; Azima, H. Birth weight, body mass index and asthma in young adults. Thorax 1999, 54, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, W.S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Yu, X.; Iribarren, C.; Williams, O.D. Asthma Is Associated with Weight Gain in Females but Not Males, Independent of Physical Activity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dales, R.; Tang, M.; Krewski, D. Obesity May Increase the Incidence of Asthma in Women but Not in Men: Longitudinal Observations from the Canadian National Population Health Surveys. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Pekkanen, J.; Laitinen, J.; Järvelin, M.-R. Body build from birth to adulthood and risk of asthma. Eur. J. Public Health 2002, 12, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.; Sherrill, D.L.; Bobadilla, A.; Martinez, F.D.; Barbee, R.A. The relation of body mass index to asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Chest 2002, 122, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huovinen, E.; Kaprio, J.; Koskenvuo, M. Factors associated to lifestyle and risk of adult onset asthma. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.S. The epidemiology of obesity and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nystad, W.; Meyer, H.E.; Nafstad, P.; Tverdal, A.; Engeland, A. Body Mass Index in Relation to Adult Asthma among 135,000 Norwegian Men and Women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Behren, J.; Lipsett, M.; Horn-Ross, P.L.; Delfino, R.J.; Gilliland, F.; McConnell, R.; Bernstein, L.; Clarke, C.A.; Reynolds, P. Obesity, waist size and prevalence of current asthma in the California Teachers Study cohort. Thorax 2009, 64, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronander, U.N.; Falkenberg, M.; Zetterström, O. Prevalence and incidence of asthma related to waist circumference and BMI in a Swedish community sample. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antó, J.-M.; Sunyer, J.; Basagaña, X.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Cerveri, I.; De Marco, R.; Heinrich, J.; Janson, C.; Jarvis, D.; Kogevinas, M.; et al. Risk factors of new-onset asthma in adults: A population-based international cohort study. Allergy 2010, 65, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.; Wright, A.L.; Morgan, W.; Sherrill, D.L.; Holberg, C.J.; Martinez, F.D. Persistence of Asthma Symptoms during Adolescence: Role of obesity and age at the onset of puberty. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpsøe, M.C.; Basit, S.; Bager, P.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Benn, C.S.; Nøhr, E.A.; Linneberg, A.; Jess, T. Maternal obesity, gestational weight gain, and risk of asthma and atopic disease in offspring: A study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, O.; Varraso, R.; Gillman, M.W.; Field, A.E.; Camargo, C.A. Longitudinal study of maternal body mass index, gestational weight gain, and offspring asthma. Allergy 2016, 71, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, A.; Lønnebotn, M.; Calciano, L.; Benediktsdóttir, B.; Bertelsen, R.J.; Bråbäck, L.; Dharmage, S.; Franklin, K.A.; Gislason, T.; Holm, M.; et al. Being overweight in childhood, puberty, or early adulthood: Changing asthma risk in the next generation? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 791–799.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Salam, M.T.; Alderete, T.L.; Habre, R.; Bastain, T.M.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.D. Effects of Childhood Asthma on the Development of Obesity among School-aged Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Oriss, T.B.; Wenzel, S.E. Emerging molecular phenotypes of asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L130–L140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sutherland, E.R.; Goleva, E.; King, T.S.; Lehman, E.; Stevens, A.D.; Jackson, L.P.; Stream, A.R.; Fahy, J.V. Cluster Analysis of Obesity and Asthma Phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, P.; Pavord, I.D.; Shaw, D.E.; Berry, M.A.; Thomas, M.; Brightling, C.E.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Green, R.H. Cluster Analysis and Clinical Asthma Phenotypes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.C.; Hastie, A.T.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Busse, W.W.; Jarjour, N.N.; Wenzel, S.E.; Peters, S.P.; Meyers, D.A.; Bleecker, E.R. Sputum neutrophil counts are associated with more severe asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1557–1563.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin, F. Obesity as a risk factor for increased asthma severity and allergic inflammation; cause or effect? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, R.; Moreira, P.; Padrão, P.; Teixeira, V.; Carvalho, P.; Delgado, L. Obesity increases the prevalence and the incidence of asthma and worsens asthma severity. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, J.; Patterson, C.C.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Niven, R.M.; Mansur, A.H.; Bucknall, C.; Chaudhuri, R.; Price, D.; Brightling, C.E.; Heaney, L.G. Comorbidity in severe asthma requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy: Cross-sectional data from the Optimum Patient Care Research Database and the British Thoracic Difficult Asthma Registry. Thorax 2016, 71, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.E.; Poynter, M.E. Mechanisms of Asthma in Obesity. Pleiotropic Aspects of Obesity Produce Distinct Asthma Phenotypes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holguin, F.; Bleecker, E.R.; Busse, W.W.; Calhoun, W.J.; Castro, M.; Erzurum, S.C.; Fitzpatrick, A.M.; Gaston, B.; Israel, E.; Jarjour, N.N.; et al. Obesity and asthma: An association modified by age of asthma onset. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1486–1493.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, E.R.; Goleva, E.; Strand, M.; Beuther, D.A.; Leung, D.Y.M. Body Mass and Glucocorticoid Response in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.C.; Armstrong, S.; D’Silva, L.; Allen, C.J.; Hargreave, F.E.; Parameswaran, K. Effect of obesity on airway inflammation: A cross-sectional analysis of body mass index and sputum cell counts. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, J.V. Type 2 inflammation in asthma—Present in most, absent in many. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumou, H.; Bel, E.H. Improving the diagnosis of eosinophilic asthma. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. The immunology of asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, L.; Elias, J.A.; Chupp, G. Asthma: Mechanisms of Disease Persistence and Progression. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 789–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Polosa, R. Treatment strategies for allergy and asthma. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Tan, W.-P.; Wu, C. Detection of IL-9 producing T cells in the PBMCs of allergic asthmatic patients. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, F.D.; Hogan, S.P.; Hershey, G.K.K.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Wills-Karp, M. Importance of Cytokines in Murine Allergic Airway Disease and Human Asthma. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.-P. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, T.Y.F.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Scanlon, S.T.; Zaghouani, H.; Garbi, N.; Fallon, P.G.; McKenzie, A.N.J. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells license dendritic cells to potentiate memory TH2 cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, T.Y.; Steer, C.A.; Mathä, L.; Gold, M.J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, I.; McNagny, K.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Takei, F. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Are Critical for the Initiation of Adaptive T Helper 2 Cell-Mediated Allergic Lung Inflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Loh, Z.; Gan, W.J.; Zhang, V.; Yang, H.; Li, J.H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Schmidt, A.M.; Armour, C.L.; Hughes, J.M.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products and its ligand high-mobility group box-1 mediate allergic airway sensitization and airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 440–450.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, D.T. Mechanisms by which obesity impacts upon asthma. Thorax 2016, 72, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartemes, K.R.; Kephart, G.M.; Fox, S.J.; Kita, H. Enhanced innate type 2 immune response in peripheral blood from patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 671–678.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, T.Y.; Krauß, R.H.; Sun, A.C.; Takei, F. Lung Natural Helper Cells Are a Critical Source of Th2 Cell-Type Cytokines in Protease Allergen-Induced Airway Inflammation. Immunity 2012, 36, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toki, S.; Goleniewska, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Newcomb, D.C.; Zhou, B.; Kita, H.; Boyd, K.L.; Peebles, R.S. TSLP and IL-33 reciprocally promote each other’s lung protein expression and ILC2 receptor expression to enhance innate type-2 airway inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Préfontaine, D.; Lajoie-Kadoch, S.; Foley, S.; Audusseau, S.; Olivenstein, R.; Halayko, A.J.; Lemière, C.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q. Increased Expression of IL-33 in Severe Asthma: Evidence of Expression by Airway Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5094–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Bi, L.; Liu, S.; Dong, L. IL-33 promotes airway remodeling and is a marker of asthma disease severity. J. Asthma 2014, 51, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, V.; Mjösberg, J. Lipid mediators as regulators of human ILC2 function in allergic diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 179, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata, H.; Moro, K.; Fukunaga, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyata, J.; Masaki, K.; Betsuyaku, T.; Koyasu, S.; Asano, K. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces corticosteroid resistance in natural helper cells during airway inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikotra, A.; Choy, D.F.; Ohri, C.M.; Doran, E.; Butler, C.; Hargadon, B.; Shelley, M.; Abbas, A.R.; Austin, C.D.; Jackman, J.; et al. Increased expression of immunoreactive thymic stromal lymphopoietin in patients with severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 104–111.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Verma, M.; Michalec, L.; Liu, W.; Sripada, A.; Rollins, D.; Good, J.; Ito, Y.; Chu, H.; Gorska, M.M.; et al. Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 257–268.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giacco, S.R.; Bakirtas, A.; Bel, E.; Custovic, A.; Diamant, Z.; Hamelmann, E.; Heffler, E.; Kalayci, Ö.; Saglani, S.; Sergejeva, S.; et al. Allergy in severe asthma. Allergy 2016, 72, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.H.; Brightling, C.E.; Woltmann, G.; Parker, D.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Pavord, I.D. Analysis of induced sputum in adults with asthma: Identification of subgroup with isolated sputum neutrophilia and poor response to inhaled corticosteroids. Thorax 2002, 57, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kufaidy, R.; Vazquez-Tello, A.; Bahammam, A.S.; Al-Muhsen, S.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R. IL-17 enhances the migration of B cells during asthma by inducing CXCL13 chemokine production in structural lung cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 696–699.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halwani, R.; Sultana, A.; Vazquez-Tello, A.; Jamhawi, A.; Al-Masri, A.A.; Al-Muhsen, S. Th-17 regulatory cytokines IL-21, IL-23, and IL-6 enhance neutrophil production of IL-17 cytokines during asthma. J. Asthma 2017, 54, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomb, D.C.; Peebles, R.S. Th17-mediated inflammation in asthma. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ramli, W.; Préfontaine, D.; Chouiali, F.; Martin, J.G.; Olivenstein, R.; Lemiere, C.; Hamid, Q. TH17-associated cytokines (IL-17A and IL-17F) in severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Nanzer, A.M.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Richards, D.F.; Timms, P.M.; Martineau, A.R.; Griffiths, C.J.; Corrigan, C.J.; Hawrylowicz, C.M. Distinct endotypes of steroid-resistant asthma characterized by IL-17Ahigh and IFN-γhigh immunophenotypes: Potential benefits of calcitriol. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 628–637.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, N.; Canelos, P.B.; Essayan, D.M.; Plunkett, B.A.; Myers, A.C.; Huang, S.-K. Interleukin-17F Induces Pulmonary Neutrophilia and Amplifies Antigen-induced Allergic Response. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Melton, A.C.; Chen, C.; Engler, M.B.; Huang, K.E.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Bernstein, X.; Li, J.T.; Atabai, K.; et al. IL-17A produced by αβ T cells drives airway hyper-responsiveness in mice and enhances mouse and human airway smooth muscle contraction. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medoff, B.D.; Okamoto, Y.; Leyton, P.; Weng, M.; Sandall, B.P.; Raher, M.J.; Kihara, S.; Bloch, K.D.; Libby, P.; Luster, A.D. Adiponectin Deficiency Increases Allergic Airway Inflammation and Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 41, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Tato, C.M.; Laurence, A.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Blumenschein, W.M.; McClanahan, T.K.; O’Shea, J.J.; Cua, D.J. The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of interleukin 17–producing effector T helper cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekking, P.-P.W.; Loza, M.J.; Pavlidis, S.; De Meulder, B.; Lefaudeux, D.; Baribaud, F.; Auffray, C.; Wagener, A.H.; Brinkman, P.; Lutter, R.; et al. Pathway discovery using transcriptomic profiles in adult-onset severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-H.; Song, H.J.; Park, C.-S. Role of inflammasome activation in development and exacerbation of asthma. Asia Pac. Allergy 2014, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Simpson, J.L.; Phipps, S.; Baines, K.J.; Oreo, K.M.; Gunawardhana, L.; Gibson, P.G. Elevated expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome in neutrophilic asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 43, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozseker, F.; Buyukozturk, S.; Depboylu, B.; Yilmazbayhan, D.; Karayigit, E.; Gelincik, A.; Genc, S.; Colakoglu, B.; Dal, M.; Issever, H. Serum amyloid A (SAA) in induced sputum of asthmatics: A new look to an old marker. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raundhal, M.; Morse, C.; Khare, A.; Oriss, T.B.; Milosevic, J.; Trudeau, J.B.; Huff, R.; Pilewski, J.M.; Holguin, F.; Kolls, J.K.; et al. High IFN-γ and low SLPI mark severe asthma in mice and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3037–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.A.; Hargadon, B.; Shelley, M.; Parker, D.; Shaw, D.E.; Green, R.H.; Bradding, P.; Brightling, C.E.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Pavord, I.D. Evidence of a Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor α in Refractory Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, M.L.; Trudeau, J.B.; Scheller, E.V.; Mandalapu, S.; Elloso, M.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Wenzel, S.E.; Alcorn, J.F. The complex relationship between inflammation and lung function in severe asthma. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morjaria, J.B.; Chauhan, A.J.; Babu, K.S.; Polosa, R.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T. The role of a soluble TNF receptor fusion protein (etanercept) in corticosteroid refractory asthma: A double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial. Thorax 2008, 63, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.E.; Barnes, P.J.; Bleecker, E.R.; Bousquet, J.; Busse, W.W.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Holgate, S.T.; Meyers, D.A.; Rabe, K.F.; Antczak, A.; et al. A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Blockade in Severe Persistent Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, F.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahi, N.; Paige, E.; Balla, J.; Prudence, E.; Ferreira, R.C.; Southwood, M.; Appleby, S.L.; Bakke, P.; Gulsvik, A.; Litonjua, A.A.; et al. Neutrophil-mediated IL-6 receptor trans-signaling and the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.C.; McGrath, K.W.; Hawkins, G.A.; Hastie, A.T.; Levy, B.D.; Israel, E.; Phillips, B.R.; Mauger, D.T.; Comhair, S.A.; Erzurum, S.C.; et al. Plasma interleukin-6 concentrations, metabolic dysfunction, and asthma severity: A cross-sectional analysis of two cohorts. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevnikar, Z.; Östling, J.; Ax, E.; Calvén, J.; Thörn, K.; Israelsson, E.; Öberg, L.; Singhania, A.; Lau, L.C.; Wilson, S.J.; et al. Epithelial IL-6 trans-signaling defines a new asthma phenotype with increased airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.J.; Bacharier, L.B.; Calatroni, A.; Gill, M.A.; Hu, J.; Liu, A.H.; Wheatley, L.M.; Gern, J.E.; Gruchalla, R.S.; Hershey, G.K.K.; et al. Serum IL-6: A biomarker in childhood asthma? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1701–1704.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morjaria, J.B.; Babu, K.S.; Vijayanand, P.; Chauhan, A.J.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T. Sputum IL-6 concentrations in severe asthma and its relationship with FEV1. Thorax 2010, 66, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.; Edwards, M.J.; Bates, S.; Shaw, D.; Chung, K.F.; Loza, M.J.; James, A.; Van Oosterhout, A.; The U-BIOPRED Study Group. IL-6 pathway upregulation in subgroup of severe asthma is associated with neutrophilia and poor lung function. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Bouter, L.M.; McQuillan, G.M.; Wener, M.H.; Harris, T.B. Low-grade systemic inflammation in overweight children. Pediatrics 2001, 107, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, M.; Haluzik, M. The role of adipose tissue immune cells in obesity and low-grade inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, R113–R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman-Boehm, I.; Bluher, M.; Redel, H.; Sion-Vardy, N.; Ovadia, S.; Avinoach, E.; Shai, I.; Kloting, N.; Stumvoll, M.; Bashan, N.; et al. Macrophage Infiltration into OmentalVersusSubcutaneous Fat across Different Populations: Effect of Regional Adiposity and the Comorbidities of Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexrode, K.M.; Pradhan, A.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. Relationship of total and abdominal adiposity with CRP and IL-6 in women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Park, J.Y.; Yu, R. Relationship of obesity and visceral adiposity with serum concentrations of CRP, TNF-α and IL-6. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005, 69, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, A.; Lemieux, I.; Alméras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Bergeron, J.; Després, J.-P. Visceral Obesity and Plasma Glucose-Insulin Homeostasis: Contributions of Interleukin-6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, H.S.; Prakken, B.; Kalkhoven, E.; Boes, M. Adipose tissue-resident immune cells: Key players in immunometabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cildir, G.; Akıncılar, S.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation: All immune cells on the stage. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-C.; Lee, J. Cellular and molecular players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Takemoto, M.; Irisuna, H.; Koshizaka, M.; Onishi, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Mezawa, M.; He, P.; Honjo, S.; et al. The roles of transforming growth factor-β and Smad3 signaling in adipocyte differentiation and obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brestoff, J.R.; Kim, B.S.; Saenz, S.A.; Stine, R.R.; Monticelli, L.A.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Thome, J.J.; Farber, D.L.; Lutfy, K.; Seale, P.; et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of adipose and limit obesity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 519, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.-P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.B.; Nussbaum, J.C.; Liang, H.-E.; Van Dyken, S.J.; Cheng, L.E.; Mohapatra, A.; Chawla, A.; Locksley, R.M. Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Molofsky, A.B.; Liang, H.-E.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Jouihan, H.A.; Bando, J.K.; Chawla, A.; Locksley, R.M. Eosinophils Sustain Adipose Alternatively Activated Macrophages Associated with Glucose Homeostasis. Science 2011, 332, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calco, G.N.; Fryer, A.D.; Nie, Z. Unraveling the connection between eosinophils and obesity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijhuis, J.; Rensen, S.S.; Slaats, Y.; Van Dielen, F.M.; Buurman, W.A.; Greve, J.W.M. Neutrophil Activation in Morbid Obesity, Chronic Activation of Acute Inflammation. Obesity 2009, 17, 2014–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muc, M.; Todo-Bom, A.; Mota-Pinto, A.; Pereira, S.V.; Loureiro, C. Leptin and resistin in overweight patients with and without asthma. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2014, 42, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, M. Adiponectin: A versatile player of innate immunity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Rumpold, H.; Enrich, B.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin induces the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in human leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, D.I.; Kim, H.Y.; Williams, A.S.; Verbout, N.G.; Tran, J.; Si, H.; Wurmbrand, A.P.; Jastrab, J.; Hug, C.; Umetsu, D.T.; et al. Pulmonary Inflammation Induced by Subacute Ozone Is Augmented in Adiponectin-Deficient Mice: Role of IL-17A. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Chao, C.-L.; Chen, C.-L.; Tai, T.Y.; Chuang, L.-M. Weight Reduction Increases Plasma Levels of an Adipose-Derived Anti-Inflammatory Protein, Adiponectin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3815–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-A.; Choi, H.M.; Lee, S.-H.; Yang, H.-I.; Yoo, M.C.; Hong, S.-J.; Kim, K.S. Synergy between adiponectin and interleukin-1β on the expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and cyclooxygenase-2 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-A.; Ji, H.-I.; Lee, S.-H.; Hong, S.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Yoo, M.C.; Kim, K.S. The role of adiponectin in the production of IL-6, IL-8, VEGF and MMPs in human endothelial cells and osteoblasts: Implications for arthritic joints. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Drai, J.; Fouque, D. Adiponectin and Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Balakrishnan, V.; Madero, M.; Pereira, A.A.; Beck, G.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Collins, A.J.; et al. Adiponectin and Mortality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-Y.; Dini, A.A.; Yang, X.-K.; Li, L.-J.; Wu, G.-C.; Leng, R.-X.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Association between serum/plasma adiponectin levels and immune-mediated diseases: A meta-analysis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chan, J.; Rovin, B.H. Induction of chemokine expression by adiponectin in vitro is isoform dependent. Transl. Res. 2009, 154, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumeier, M.; Weigert, J.; Wehrwein, G.; Wrede, C.; Buechler, C.; Schäffler, A.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Schölmerich, J. Different effects of adiponectin isoforms in human monocytic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Hattori, S.; Tomizawa, A.; Inukai, K.; Kasai, K. High molecular weight adiponectin activates AMPK and suppresses cytokine-induced NF-κB activation in vascular endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T. Narrative Review: The Role of Leptin in Human Physiology: Emerging Clinical Applications. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, J.; Jockers, R. Hunting for the functions of short leptin receptor isoforms. Mol. Metab. 2013, 2, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbæk, C.; Uotani, S.; Da Silva, B.; Flier, J.S. Divergent Signaling Capacities of the Long and Short Isoforms of the Leptin Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32686–32695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, B.; Straface, E.; Quaranta, M.G.; Giordani, L.; Viora, M. Leptin Promotes Differentiation and Survival of Human Dendritic Cells and Licenses Them for Th1 Priming. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6820–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Margalet, V.; Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Najib, S.; Gonzalez-Yanes, C. Role of leptin as an immunomodulator of blood mononuclear cells: Mechanisms of action. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 133, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.H.; Kim, M.-S. Molecular mechanisms of central leptin resistance in obesity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauman, J. Leptin receptor signaling: Pathways to leptin resistance. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 2771–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, J.-P.; Maachi, M.; Lagathu, C.; Kim, M.J.; Caron, M.; Vidal, H.; Capeau, J.; Fève, B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Loffreda, S.; Yang, S.Q.; Lin, H.Z.; Karp, C.L.; Brengman, M.L.; Wang, D.J.; Klein, A.S.; Bulkley, G.B.; Bao, C.; Noble, P.W.; et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, D.; Fraser, S.; Oh, J.; Huber, A.M.; Schulman, Y.; Bhagtani, R.H.; Khan, Z.S.; Tesfa, L.; Hall, C.B.; Macian, F. Inflammation, Metabolic Dysregulation, and Pulmonary Function among Obese Urban Adolescents with Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Gollapudi, S.; Su, H.; Gupta, S. Leptin Activates Human B Cells to Secrete TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 via JAK2/STAT3 and p38MAPK/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrati, M.; Salehi, E.; Razmpoosh, E.; Shoormasti, R.S.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J.; Shidfar, F. Relationship between leptin concentration and body fat with peripheral blood mononuclear cells cytokines among obese and overweight adults. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 186, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Romero, C.; Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Human Leptin Enhances Activation and Proliferation of Human Circulating T Lymphocytes. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 199, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarese, G. Balancing susceptibility to infection and autoimmunity: A role for leptin? Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, G.M.; Matarese, G.; Howard, J.K.; Baker, R.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Lechler, R.I. Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nat. Cell Biol. 1998, 394, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, V.; Procaccini, C.; Calì, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Fontana, S.; Zappacosta, S.; La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. A Key Role of Leptin in the Control of Regulatory T Cell Proliferation. Immunity 2007, 26, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Carbone, F.; Cassano, S.; Greco, D.; Qian, K.; Auvinen, P.; Calì, G.; Stallone, G.; et al. Leptin-Induced mTOR Activation Defines a Specific Molecular and Transcriptional Signature Controlling CD4+ Effector T Cell Responses. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, F.-D.; Zou, H.; Matarese, G.; La Cava, A. Cutting Edge: Leptin-Induced RORγt Expression in CD4+ T Cells Promotes Th17 Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, S.L.; Dunne, A.; Subramanian, S.L.; Hull, R.L.; Tannahill, G.M.; Sharp, F.A.; Becker, C.E.; Franchi, L.; Yoshihara, E.; Chen, Z.; et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by islet amyloid polypeptide provides a mechanism for enhanced IL-1β in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijsse, G.S.; Seys, S.F.; Schelpe, A.S.; Dilissen, E.; Goeminne, P.; Dupont, L.J.; Ceuppens, J.L.; Bullens, D.M. Obese individualswith asthma preferentially have a high IL-5/IL-17A/IL-25 sputum inflammatory pattern. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.A.; Gibson, P.G.; Garg, M.L.; Wood, L.G. Airway inflammation is augmented by obesity and fatty acids in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telenga, E.D.; Tideman, S.W.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Hacken, N.H.T.T.; Timens, W.; Postma, D.S.; Berge, M.V.D. Obesity in asthma: More neutrophilic inflammation as a possible explanation for a reduced treatment response. Allergy 2012, 67, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, Y.-J.; Pichavant, M.; Shore, S.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Iwakura, Y.; Israel, E.; Bolger, K.; Faul, J.; et al. Interleukin-17–producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3 inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.S.; Chen, L.; Kasahara, D.I.; Si, H.; Wurmbrand, A.P.; Shore, S.A. Obesity and airway responsiveness: Role of TNFR2. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 26, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Newby, C.; Symon, F.A.; Haldar, P.; Shah, S.; Gupta, S.; Bafadhel, M.; Singapuri, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Woods, J.; et al. Elevated Sputum Interleukin-5 and Submucosal Eosinophilia in Obese Individuals with Severe Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahi, N.; Loutsios, C.; Tregay, N.; Wright, A.K.; Berair, R.; Lok, L.S.C.; Gillett, D.; Cullum, I.; Simmonds, R.P.; Summers, C.; et al. In vivo imaging reveals increased eosinophil uptake in the lungs of obese asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1659–1662.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiria, L.O.; Martins, M.A.; Saad, M.J.A. Obesity and asthma: Beyond TH2 inflammation. Metabolism 2015, 64, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huisstede, A.; Rudolphus, A.; Van Schadewijk, A.; Cabezas, M.C.; Mannaerts, G.H.H.; Taube, C.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Braunstahl, G.-J. Bronchial and Systemic Inflammation in Morbidly Obese Subjects with Asthma: A Biopsy Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, M.M.; Grun, L.K.; Lavandoski, P.; Alves, L.B.; Bristot, I.J.; Mattiello, R.; Mottin, C.C.; Klamt, F.; Jones, M.H.; Padoin, A.V.; et al. Immunosenescence Induced by Plasma from Individuals with Obesity Caused Cell Signaling Dysfunction and Inflammation. Obesity 2017, 25, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.G.; Garg, M.L.; Gibson, P.G. A high-fat challenge increases airway inflammation and impairs bronchodilator recovery in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.G.; Li, Q.; Scott, H.A.; Rutting, S.; Berthon, B.S.; Gibson, P.G.; Hansbro, P.M.; Williams, E.J.; Horvat, J.; Simpson, J.L.; et al. Saturated fatty acids, obesity, and the nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 143, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideleva, O.; Suratt, B.T.; Black, K.E.; Tharp, W.G.; Pratley, R.E.; Forgione, P.; Dienz, O.; Irvin, C.G.; Dixon, A.E. Obesity and asthma: An inflammatory disease of adipose tissue not the airway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, S.A.; Rivera-Sanchez, Y.M.; Schwartzman, I.N.; Johnston, R.A. Responses to ozone are increased in obese mice. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 95, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.S.; Leung, S.-Y.; Nath, P.; Khorasani, N.M.; Bhavsar, P.; Issa, R.; Mitchell, J.A.; Adcock, I.M.; Chung, K.F. Role of TLR2, TLR4, and MyD88 in murine ozone-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and neutrophilia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaroucha, A.; Daniil, Z.; Malli, F.; Georgoulias, P.; Minas, M.; Kostikas, K.; Bargiota, A.; Zintzaras, E.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Leptin, Adiponectin, and Ghrelin Levels in Female Patients with Asthma during Stable and Exacerbation Periods. J. Asthma 2012, 50, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattan, M.; Kumar, R.; Bloomberg, G.R.; Mitchell, H.E.; Calatroni, A.; Gergen, P.J.; Kercsmar, C.M.; Visness, C.M.; Matsui, E.C.; Steinbach, S.F.; et al. Asthma control, adiposity, and adipokines among inner-city adolescents. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, L.; Kang, D.; Wood, L.G.; Wang, G. Systemic inflammation mediates the detrimental effects of obesity on asthma control. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Leynaert, B.; Dumas, O.; Gil, O.D.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Colomer, M.F.; Le Moual, N.; Pison, C.; Romieu, I.; Siroux, V.; et al. Role of Leptin in the Association Between Body Adiposity and Persistent Asthma: A Longitudinal Study. Obesity 2019, 27, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, F.; Sood, A.; Ma, B.; Takyar, S.; Schuyler, M.; Qualls, C.; Cruz, C.S.D.; Chupp, G.L.; Lee, C.G.; Elias, J.A. Chitinase 3–like-1 Regulates Both Visceral Fat Accumulation and Asthma-like Th2 Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Shi, H.; Liu, C.-L.; Panganiban, R.A.; Chung, W.; O’Connor, L.J.; Himes, B.E.; Gazal, S.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Shared genetic and experimental links between obesity-related traits and asthma subtypes in UK Biobank. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; In, K.H.; Ha, E.S.; Lee, K.J.; Hur, G.Y.; Kang, E.H.; Jung, K.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Asthma-Like Symptoms are Increased in the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Asthma 2009, 46, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuesen, B.H.; Husemoen, L.L.N.; Hersoug, L.-G.; Pisinger, C.; Linneberg, A. Insulin resistance as a predictor of incident asthma-like symptoms in adults. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Prakash, Y.S.; Linneberg, A.; Agrawal, A. Insulin and the Lung: Connecting Asthma and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Allergy 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, L.; Neal, W.A.; Ice, C.; Perez, M.K.; Piedimonte, G. Metabolic Abnormalities in Children with Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias-Júnior, S.A.; Reis, M.; De Carvalho-Pinto, R.M.; Stelmach, R.; Halpern, A.; Cukier, A. Effects of weight loss on asthma control in obese patients with severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenius-Aarniala, B.; Poussa, T.; Kvarnström, J.; Grönlund, E.-L.; Ylikahri, M.; Mustajoki, P. Immediate and long term effects of weight reduction in obese people with asthma: Randomised controlled study. BMJ 2000, 320, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.; Bonini, M.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Bonini, S.; Del Giacco, S.R.; Agache, I.; Fonseca, J.A.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Carlsen, K.; Delgado, L.; et al. Weight loss interventions in asthma: EAACI evidence-based clinical practice guideline (part I). Allergy 2013, 68, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.A.; Gibson, P.; Garg, M.L.; Pretto, J.J.; Morgan, P.; Callister, R.; Wood, L.G. Dietary restriction and exercise improve airway inflammation and clinical outcomes in overweight and obese asthma: A randomized trial. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 43, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, P.D.; Ferreira, P.G.; Silva, A.G.; Stelmach, R.; Carvalho-Pinto, R.M.; Fernandes, F.L.A.; Mancini, M.C.; Sato, M.N.; Martins, M.A.; Carvalho, C.R. The Role of Exercise in a Weight-Loss Program on Clinical Control in Obese Adults with Asthma. A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, P.D.; Silva, A.G.; Ferreira, P.G.; Da Silva, A.; Salge, J.M.; Carvalho-Pinto, R.M.; Cukier, A.; Brito, C.M.; Mancini, M.C.; Carvalho, C.R.R. Exercise Improves Physical Activity and Comorbidities in Obese Adults with Asthma. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.B.; Chapman, L.; O’Brien, P. Marked improvement in asthma after Lap-Band surgery for morbid obesity. Obes. Surg. 1999, 9, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Zedda, A.; Faraone, S.; Cerbone, M.R.; Cristiano, S.; Giardiello, C.; Sofia, M. Weight loss and asthma control in severely obese asthmatic females. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, R.C.; Baptist, A.P.; Fan, Z.; Carlin, A.M.; Birkmeyer, N.J.O. The Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Asthma Severity. Obes. Surg. 2010, 21, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikka, N.; Wegienka, G.; Havstad, S.; Genaw, J.; Carlin, A.M.; Zoratti, E. Respiratory medication prescriptions before and after bariatric surgery. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 104, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huisstede, A.; Rudolphus, A.; Cabezas, M.C.; Biter, L.U.; Van De Geijn, G.-J.; Taube, C.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Braunstahl, G.-J.; Van Schadewijk, A. Effect of bariatric surgery on asthma control, lung function and bronchial and systemic inflammation in morbidly obese subjects with asthma. Thorax 2015, 70, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.E.; Pratley, R.E.; Forgione, P.M.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Whittaker-Leclair, L.A.; Griffes, L.A.; Garudathri, J.; Raymond, D.; Poynter, M.E.; Bunn, J.Y.; et al. Effects of obesity and bariatric surgery on airway hyperresponsiveness, asthma control, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 508–515.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, L.-P.; Turcotte, H.; Martin, J.; Poirier, P. Effect of bariatric surgery on airway response and lung function in obese subjects with asthma. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Zamparelli, A.S.; Vitale, D.F.; Faraone, S.; Molino, A.; Zedda, A.; Motta, A. Long-term effect of weight loss induced by bariatric surgery on asthma control and health related quality of life in asthmatic patients with severe obesity: A pilot study. Respir. Med. 2017, 130, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, G.H.; Svahn, J.; Capella, R.F.; Capella, J.F.; Schmidt, H.J.; Wasielewski, A.; Davies, R.J. Predictors of Prolonged Hospital Stay following Open and Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass for Morbid Obesity: Body Mass Index, Length of Surgery, Sleep Apnea, Asthma and the Metabolic Syndrome. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Plecka-Östlund, M.; Lu, Y.; Mattsson, F.; Lagergren, J. Causes and risk factors for mortality within 1 year after obesity surgery in a population-based cohort study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bantulà, M.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Arismendi, E.; Picado, C. Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020169
Bantulà M, Roca-Ferrer J, Arismendi E, Picado C. Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleBantulà, Marina, Jordi Roca-Ferrer, Ebymar Arismendi, and César Picado. 2021. "Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020169
APA StyleBantulà, M., Roca-Ferrer, J., Arismendi, E., & Picado, C. (2021). Asthma and Obesity: Two Diseases on the Rise and Bridged by Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020169





