Prognostic Performance of Existing Scoring Systems among Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Clinical Parameters and Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Prediction of 3-Day and 7-Day Mortality after CRRT
3.3. Prediction of ICU Mortality and In-Hospital Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liangos, O.; Wald, R.; O’Bell, J.W.; Price, L.; Pereira, B.J.; Jaber, B.L. Epidemiology and outcomes of acute renal failure in hospitalized patients: A national survey. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 1, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagshaw, S.M.; Laupland, K.B.; Doig, C.J.; Mortis, G.; Fick, G.H.; Mucenski, M.; Godinez-Luna, T.; Svenson, L.W.; Rosenal, T. Prognosis for long-term survival and renal recovery in critically ill patients with severe acute renal failure: A population-based study. Crit. Care 2005, 9, R700–R709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, B.R.; Liu, K.D.; Teixeira, J.P. Critical Care Nephrology: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins, R.L.; Elseviers, M.M.; Van der Niepen, P.; Hoste, E.; Malbrain, M.L.; Damas, P.; Devriendt, J.; SHARF investigators. Intermittent versus continuous renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury patients admitted to the intensive care unit: Results of a randomized clinical trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2009, 24, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Truche, A.S.; Darmon, M.; Bailly, S.; Clec’h, C.; Dupuis, C.; Misset, B.; Azoulay, E.; Schwebel, C.; Bouadma, L.; Kallel, H.; et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy versus intermittent hemodialysis in intensive care patients: Impact on mortality and renal recovery. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, N.V.; Muirhead, A.W.; Wilkes, S.R.; Fluck, R.J.; Taal, M.W. National trends in acute kidney injury requiring dialysis in England between 1998 and 2013. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.; Jo, H.A.; Han, K.; Kim, Y.; An, J.N.; Joo, K.W.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.; et al. Epidemiology of continuous renal replacement therapy in Korea: Results from the National Health Insurance Service claims database from 2005 to 2016. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 37, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farese, S.; Jakob, S.M.; Kalicki, R.; Frey, F.J.; Uehlinger, D.E. Treatment of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: Lower costs by intermittent dialysis than continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration. Artif. Organs 2009, 33, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, S.; Bellomo, R.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; Gibney, N.; Tolwani, A.; et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy: A worldwide practice survey. The beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (B.E.S.T. kidney) investigators. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metnitz, P.G.; Krenn, C.G.; Steltzer, H.; Lang, T.; Ploder, J.; Lenz, K.; Le Gall, J.R.; Druml, W. Effect of acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy on outcome in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Timsit, J.F.; Montuclard, L.; Colvez, A.; Gattolliat, O.; Philippart, F.; Rigal, G.; Misset, B.; Carlet, J. Decision-making process, outcome, and 1-year quality of life of octogenarians referred for intensive care unit admission. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez Mata, G.; del Mar Jimenez Quintana, M.; Rivera Fernandez, R.; Bravo, M.; Aguayo De Hoyos, E.; Zimmerman, J.; Wagner, D.; Knaus, W. [Severity assessment by APACHE III system in Spain]. Med. Clin. 2001, 117, 446–451. [Google Scholar]
- Von Bierbrauer, A.; Riedel, S.; Cassel, W.; von Wichert, P. [Validation of the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) III scoring system and comparison with APACHE II in German intensive care units]. Anaesthesist 1998, 47, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; de Mendonca, A.; Cantraine, F.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Suter, P.M.; Sprung, C.L.; Colardyn, F.; Blecher, S. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: Results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on “sepsis-related problems” of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raith, E.P.; Udy, A.A.; Bailey, M.; McGloughlin, S.; MacIsaac, C.; Bellomo, R.; Pilcher, D.V.; Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society (ANZICS) Centre for Outcomes and Resource Evaluation (CORE). Prognostic Accuracy of the SOFA Score, SIRS Criteria, and qSOFA Score for In-Hospital Mortality Among Adults with Suspected Infection Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. JAMA 2017, 317, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrillow, S.J. Predictions and outcomes for the critically ill patient with cirrhosis: Is it time to settle on the SOFA and let jaundiced views on outcome MELD away? Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 2259–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Guo, S.B. Use of CRB-65 and quick Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment to predict site of care and mortality in pneumonia patients in the emergency department: A retrospective study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Park, N.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.K.; Chin, H.J.; Na, K.Y.; Joo, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Han, S.S. Development of a new mortality scoring system for acute kidney injury with continuous renal replacement therapy. Nephrology 2019, 24, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lin, M.H.; Lee, C.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, G.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, Y.H. Chang Gung Research Database: A multi-institutional database consisting of original medical records. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.C.; Chan, Y.Y.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Hung, M.J.; Chien, R.N.; Lai, C.C.; Lai, E.C. The Chang Gung Research Database-A multi-institutional electronic medical records database for real-world epidemiological studies in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2019, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aakre, C.; Franco, P.M.; Ferreyra, M.; Kitson, J.; Li, M.; Herasevich, V. Prospective validation of a near real-time EHR-integrated automated SOFA score calculator. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2017, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Bennett, C.; Wiley, B.M.; Murphree, D.H.; Keegan, M.T.; Gajic, O.; Wright, R.S.; Barsness, G.W. Predictive Value of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score for Mortality in a Contemporary Cardiac Intensive Care Unit Population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonnassieux, M.; Duclos, A.; Schneider, A.G.; Schmidt, A.; Benard, S.; Cancalon, C.; Joannes-Boyau, O.; Ichai, C.; Constantin, J.M.; Lefrant, J.Y.; et al. Renal Replacement Therapy Modality in the ICU and Renal Recovery at Hospital Discharge. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, e102–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradari, A.G.; Firouzian, A.; Davanlou, A.; Aarabi, M.; Daneshiyan, M.; Kiakolaye, Y.T. Comparison of Patients’ Admission, Mean and Highest Sofa Scores in Prediction of Icu Mortality: A Prospective Observational Study. Mater. Sociomed. 2016, 28, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khwannimit, B.; Bhurayanontachai, R.; Vattanavanit, V. Comparison of the performance of SOFA, qSOFA and SIRS for predicting mortality and organ failure among sepsis patients admitted to the intensive care unit in a middle-income country. J. Crit. Care 2018, 44, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R. Clinical review: Scoring systems in the critically ill. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minne, L.; Abu-Hanna, A.; de Jonge, E. Evaluation of SOFA-based models for predicting mortality in the ICU: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flaatten, H.; de Lange, D.W.; Artigas, A.; Bin, D.; Moreno, R.; Christensen, S.; Joynt, G.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Sprung, C.L.; Benoit, D.; et al. The status of intensive care medicine research and a future agenda for very old patients in the ICU. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidet, B.; Leblanc, G.; Simon, T.; Woimant, M.; Quenot, J.P.; Ganansia, O.; Maignan, M.; Yordanov, Y.; Delerme, S.; Doumenc, B.; et al. Effect of Systematic Intensive Care Unit Triage on Long-term Mortality Among Critically Ill Elderly Patients in France: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atramont, A.; Lindecker-Cournil, V.; Rudant, J.; Tajahmady, A.; Drewniak, N.; Fouard, A.; Singer, M.; Leone, M.; Legrand, M. Association of Age with Short-term and Long-term Mortality Among Patients Discharged From Intensive Care Units in France. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e193215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

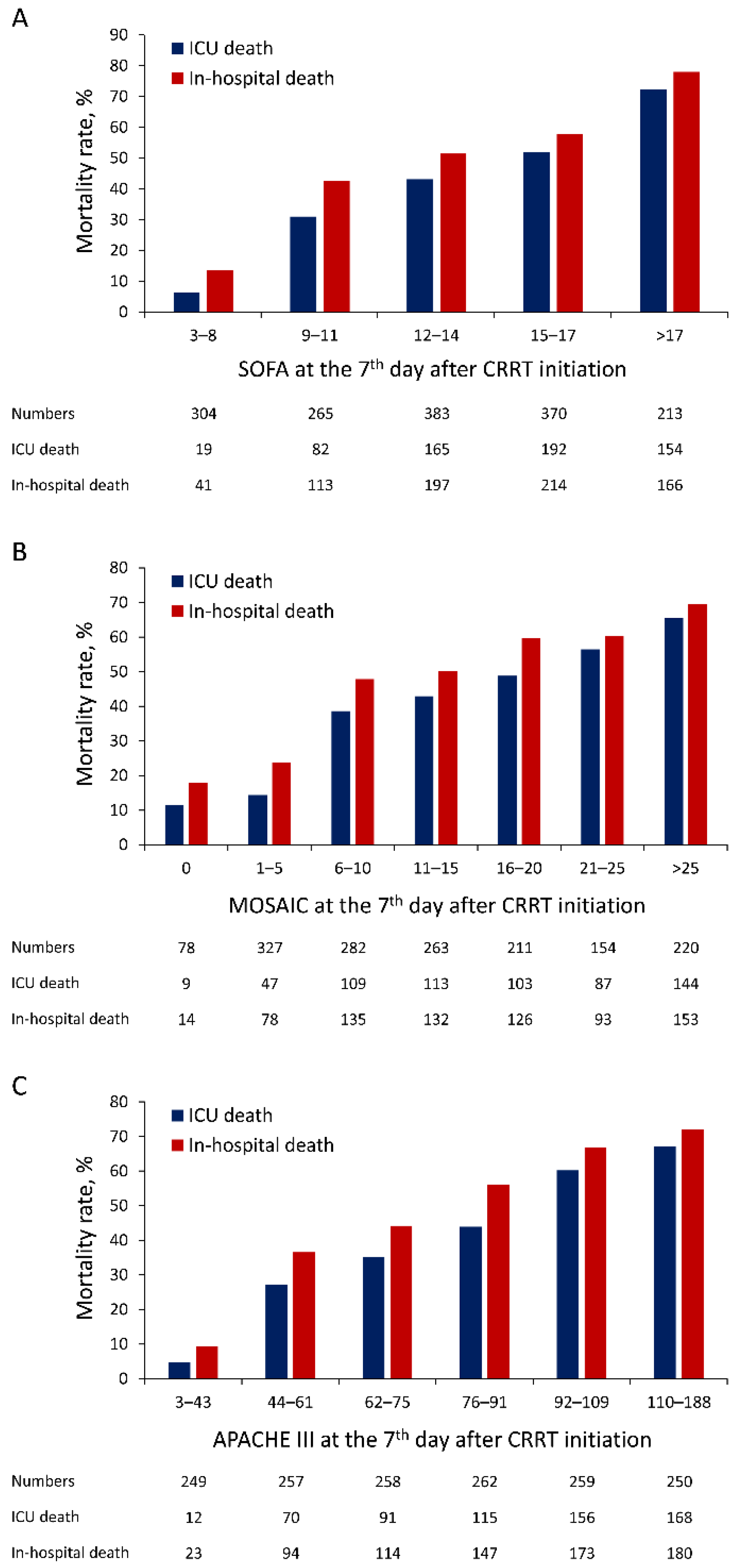
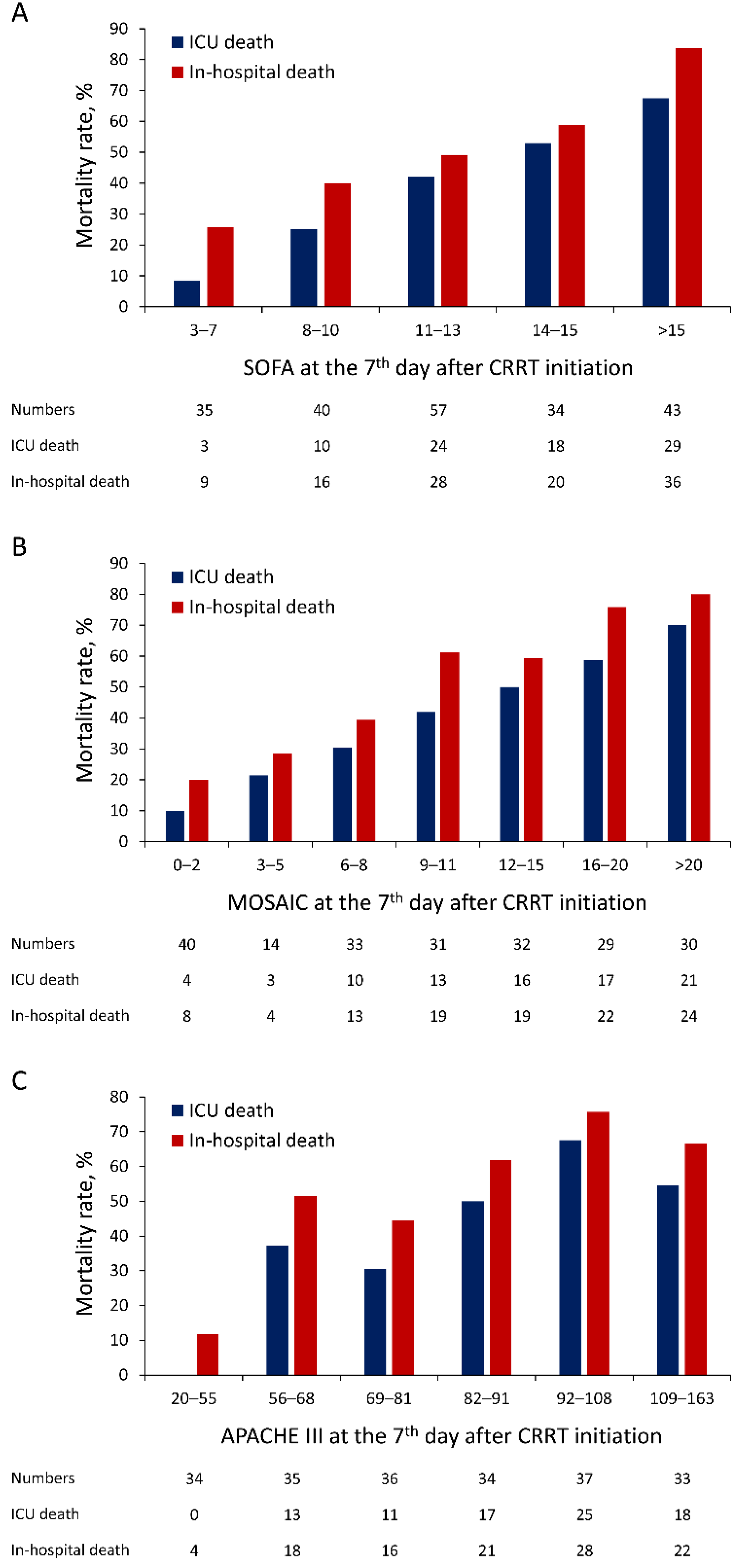
| Variable | Valid Number | Total (n = 3370) | Survivor (n = 946) | Non-Survivor (n = 2424) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||||
| Age, year | 3370 | 64.1 ± 15.7 | 61.8 ± 15.7 | 65.0 ± 15.6 | <0.001 |
| Male | 3370 | 2283 (67.7) | 652 (68.9) | 1631 (67.3) | 0.361 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 2883 | 27.1 ± 25.0 | 27.7 ± 22.0 | 26.9 ± 26.0 | 0.412 |
| Comorbidity | |||||
| Heart failure | 3370 | 834 (24.7) | 217 (22.9) | 617 (25.5) | 0.128 |
| Coronary atrial disease | 3370 | 861 (25.5) | 210 (22.2) | 651 (26.9) | 0.005 |
| Chronic obstruction pulmonary disease | 3370 | 537 (15.9) | 137 (14.5) | 400 (16.5) | 0.150 |
| Asthma | 3370 | 273 (8.1) | 70 (7.4) | 203 (8.4) | 0.351 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 3370 | 638 (18.9) | 128 (13.5) | 510 (21.0) | <0.001 |
| Stroke | 3370 | 350 (10.4) | 94 (9.9) | 256 (10.6) | 0.593 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 3370 | 1177 (34.9) | 344 (36.4) | 833 (34.4) | 0.274 |
| Hypertension | 3370 | 1610 (47.8) | 429 (45.3) | 1181 (48.7) | 0.078 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 3370 | 2268 (67.3) | 579 (61.2) | 1689 (69.7) | <0.001 |
| Malignancy | 3370 | 1179 (35.0) | 292 (30.9) | 887 (36.6) | 0.002 |
| Charlson’s Comorbidity Index score | 3370 | 4.4 ± 3.3 | 3.8 ± 3.3 | 4.6 ± 3.3 | <0.001 |
| Route of ICU | 3370 | 0.003 | |||
| Surgical | 960 (28.5) | 304 (32.1) | 656 (27.1) | ||
| Medical | 2410 (71.5) | 642 (67.9) | 1768 (72.9) | ||
| Laboratory data at initiation of CRRT | |||||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 3332 | 4.0 ± 2.2 | 4.3 ± 2.4 | 3.9 ± 2.2 | <0.001 |
| Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 3296 | 68.6 ± 43.3 | 66.7 ± 42.1 | 69.3 ± 43.7 | 0.123 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 3279 | 9.9 ± 2.5 | 10.1 ± 2.4 | 9.9 ± 2.5 | 0.090 |
| Platelet, count ×103 | 3216 | 111.3 ± 93.4 | 118.7 ± 96.6 | 108.5 ± 92.0 | 0.005 |
| Albumin, mg/dL | 2352 | 2.4 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.4 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| pH | 2900 | 7.27 ± 0.17 | 7.28 ± 0.17 | 7.26 ± 0.17 | 0.014 |
| Treatment at initiation of CRRT | |||||
| Mechanical ventilator | 3370 | 3199 (94.9) | 890 (94.1) | 2309 (95.3) | 0.162 |
| Inotropic agent | 3370 | 3240 (96.1) | 874 (92.4) | 2366 (97.6) | <0.001 |
| Days from ICU admission to CRRT | 3370 | 3 (2,5) | 2 (2, 5) | 3 (2, 6) | 0.023 |
| In-hospital outcome | |||||
| Duration of CRRT, day | 3370 | 3 (2,6) | - | - | - |
| Duration of ICU stay, day | 3370 | 9 (4,19) | - | - | - |
| Duration of hospitalization, day | 3370 | 16 (6,35) | - | - | - |
| Death within 3 days after CRRT | 3370 | 1251 (37.1) | - | - | - |
| Death within 7 days after CRRT | 3370 | 1693 (50.2) | - | - | - |
| Death during ICU admission | 3370 | 2276 (67.5) | - | - | - |
| Day/Score | Total Cohort | Cohort with Octogenarian (Age ≥ 80 Years) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivor (n = 1677) | Non-Survivor (n = 1693) | AUC, % (95% CI) | Survivor (n = 231) | Non-Survivor (n = 327) | AUC, % (95% CI) | |
| Day 1 a (n = 3370) | ||||||
| SOFA | 14.1 ± 3.4 | 14.9 ± 3.3 | 56.5 (54.6–58.4) | 13.0 ± 3.2 | 13.8 ± 3.1 | 55.7 (50.9–60.5) |
| qSOFA | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 56.0 (54.2–57.8) | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 55.0 (50.4–59.6) |
| APACHE III | 97.3 ± 28.7 | 110.8 ± 28.2 | 63.2 (61.3–65.1) | 100.9 ± 27.3 | 111.6 ± 27.1 | 61.6 (56.9–66.3) |
| MOSAIC | 19.2 ± 10.4 | 23.6 ± 11.1 | 61.4 (59.5–63.3) | 16.7 ± 9.9 | 20.1 ± 10.8 | 58.8 (54.0–63.5) |
| Day 3 b (n = 2119) | ||||||
| SOFA | 14.0 ± 3.5 | 15.7 ± 3.0 | 63.9 (61.1–66.7) | 12.7 ± 3.5 | 14.3 ± 3.2 | 63.5 (56.9–70.1) |
| qSOFA | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 68.7 (66.2–71.3) | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 74.3 (68.8–79.7) |
| APACHE III | 87.0 ± 28.6 | 115.4 ± 28.2 | 76.1 (73.6–78.5) | 88.2 ± 24.3 | 119.7 ± 30.1 | 78.9 (73.1–84.8) |
| MOSAIC | 17.5 ± 9.9 | 24.1 ± 10.7 | 67.7 (64.9–70.6) | 14.5 ± 8.4 | 20.1 ± 11.1 | 64.4 (57.3–71.5) |
| Day/Score | Total Cohort | Cohort with Octogenarian (Age ≥ 80 Years) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivor (n = 1094) | Non-Survivor (n = 2276) | AUC (95% CI) | Survivor (n = 151) | Non-Survivor (n = 407) | AUC (95% CI) | |
| Day 1 a (n = 3370) | ||||||
| SOFA | 13.7 ± 3.4 | 14.8 ± 3.3 | 59.2 (57.2–61.2) | 12.6 ± 3.4 | 13.8 ± 3.1 | 59.9 (54.6–65.2) |
| qSOFA | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 55.5 (53.6–57.4) | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 53.4 (48.4–58.5) |
| APACHE III | 95.5 ± 29.4 | 108.2 ± 28.2 | 62.3 (60.3–64.4) | 98.7 ± 27.5 | 110.3 ± 27.1 | 62.3 (57.1–67.6) |
| MOSAIC | 18.8 ± 10.7 | 22.7 ± 11.0 | 60.1 (58.1–62.2) | 16.5 ± 10.1 | 19.5 ± 10.7 | 58.0 (52.6–63.3) |
| Day 3 b (n = 2119) | ||||||
| SOFA | 13.4 ± 3.5 | 15.4 ± 3.1 | 66.1 (63.8–68.5) | 11.8 ± 3.4 | 14.2 ± 3.2 | 69.2 (63.4–75.1) |
| qSOFA | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 61.2 (58.9–63.4) | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 66.3 (60.6–71.9) |
| APACHE III | 83.4 ± 29.5 | 102.5 ± 29.1 | 67.8 (65.5–70.1) | 85.7 ± 24.7 | 106.8 ± 30.2 | 69.9 (64.1–75.8) |
| MOSAIC | 16.9 ± 10.3 | 20.9 ± 10.3 | 61.7 (59.3–64.1) | 13.6 ± 8.5 | 18.2 ± 10.0 | 63.0 (56.7–69.2) |
| Day 7 c (n = 1677) | ||||||
| SOFA | 11.0 ± 4.7 | 14.9 ± 3.4 | 74.1 (71.7–76.5) | 10.2 ± 4.1 | 14.0 ± 3.3 | 75.4 (68.9–81.8) |
| qSOFA | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 66.7 (64.2–69.2) | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 61.6 (54.4–68.8) |
| APACHE III | 65.0 ± 31.7 | 93.1 ± 27.3 | 74.7 (72.3–77.1) | 72.9 ± 28.0 | 94.6 ± 23.0 | 72.6 (65.8–79.3) |
| MOSAIC | 10.6 ± 9.2 | 17.9 ± 10.0 | 71.3 (68.8–73.9) | 8.7 ± 7.2 | 15.5 ± 8.5 | 74.2 (67.5–80.9) |
| Day/Score | Total Cohort | Cohort with Octogenarian (Age ≥ 80 Years) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivor (n = 946) | Non-Survivor (n = 2424) | AUC (95% CI) | Survivor (n = 122) | Non-Survivor (n = 436) | AUC (95% CI) | |
| Day 1 a (n = 3370) | ||||||
| SOFA | 13.7 ± 3.4 | 14.8 ± 3.3 | 58.4 (56.3–60.5) | 12.4 ± 3.2 | 13.8 ± 3.1 | 61.0 (55.5–66.5) |
| qSOFA | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 54.8 (52.8–56.8) | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 50.3 (44.9–55.7) |
| APACHE III | 95.1 ± 29.5 | 107.5 ± 28.3 | 62.1 (60.0–64.2) | 98.3 ± 26.2 | 109.7 ± 27.6 | 62.1 (56.6–67.7) |
| MOSAIC | 18.8 ± 10.6 | 22.4 ± 11.0 | 59.5 (57.4–61.7) | 16.9 ± 10.2 | 19.2 ± 10.6 | 56.0 (50.2–61.7) |
| Day 3 b (n = 2119) | ||||||
| SOFA | 13.4 ± 3.5 | 15.2 ± 3.2 | 64.7 (62.3–67.1) | 11.4 ± 3.2 | 14.1 ± 3.3 | 71.3 (65.5–77.1) |
| qSOFA | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 60.2 (57.9–62.5) | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 67.2 (61.3–73.0) |
| APACHE III | 82.7 ± 29.7 | 100.8 ± 29.4 | 67.0 (64.6–69.3) | 83.6 ± 23.6 | 104.9 ± 30.1 | 70.1 (64.2–76.0) |
| MOSAIC | 16.7 ± 10.4 | 20.6 ± 10.3 | 61.2 (58.8–63.7) | 13.0 ± 8.6 | 17.9 ± 9.7 | 64.3 (57.8–70.7) |
| Day 7 c (n = 1677) | ||||||
| SOFA | 10.8 ± 4.8 | 14.5 ± 3.7 | 71.8 (69.3–74.3) | 10.0 ± 3.9 | 13.4 ± 3.9 | 73.2 (66.5–79.8) |
| qSOFA | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 64.9 (62.4–67.5) | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 59.4 (52.3–66.5) |
| APACHE III | 63.5 ± 32.0 | 90.2 ± 28.0 | 73.5 (71.0–76.0) | 70.8 ± 27.0 | 91.6 ± 25.4 | 70.7 (63.7–77.7) |
| MOSAIC | 10.5 ± 9.3 | 16.8 ± 10.0 | 68.7 (66.1–71.3) | 7.9 ± 7.0 | 14.7 ± 8.4 | 74.7 (67.9–81.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, C.-L.; Fan, P.-C.; Kuo, G.; Lee, C.-C.; Chen, J.-J.; Lee, T.-H.; Tu, Y.-R.; Hsu, H.-H.; Tian, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-H. Prognostic Performance of Existing Scoring Systems among Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194592
Yen C-L, Fan P-C, Kuo G, Lee C-C, Chen J-J, Lee T-H, Tu Y-R, Hsu H-H, Tian Y-C, Chang C-H. Prognostic Performance of Existing Scoring Systems among Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194592
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Chieh-Li, Pei-Chun Fan, George Kuo, Cheng-Chia Lee, Jia-Jin Chen, Tao-Han Lee, Yi-Ran Tu, Hsiang-Hao Hsu, Ya-Chung Tian, and Chih-Hsiang Chang. 2021. "Prognostic Performance of Existing Scoring Systems among Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194592
APA StyleYen, C.-L., Fan, P.-C., Kuo, G., Lee, C.-C., Chen, J.-J., Lee, T.-H., Tu, Y.-R., Hsu, H.-H., Tian, Y.-C., & Chang, C.-H. (2021). Prognostic Performance of Existing Scoring Systems among Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194592






