Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Vascular Function: The Concept of Autoimmune Atherosclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
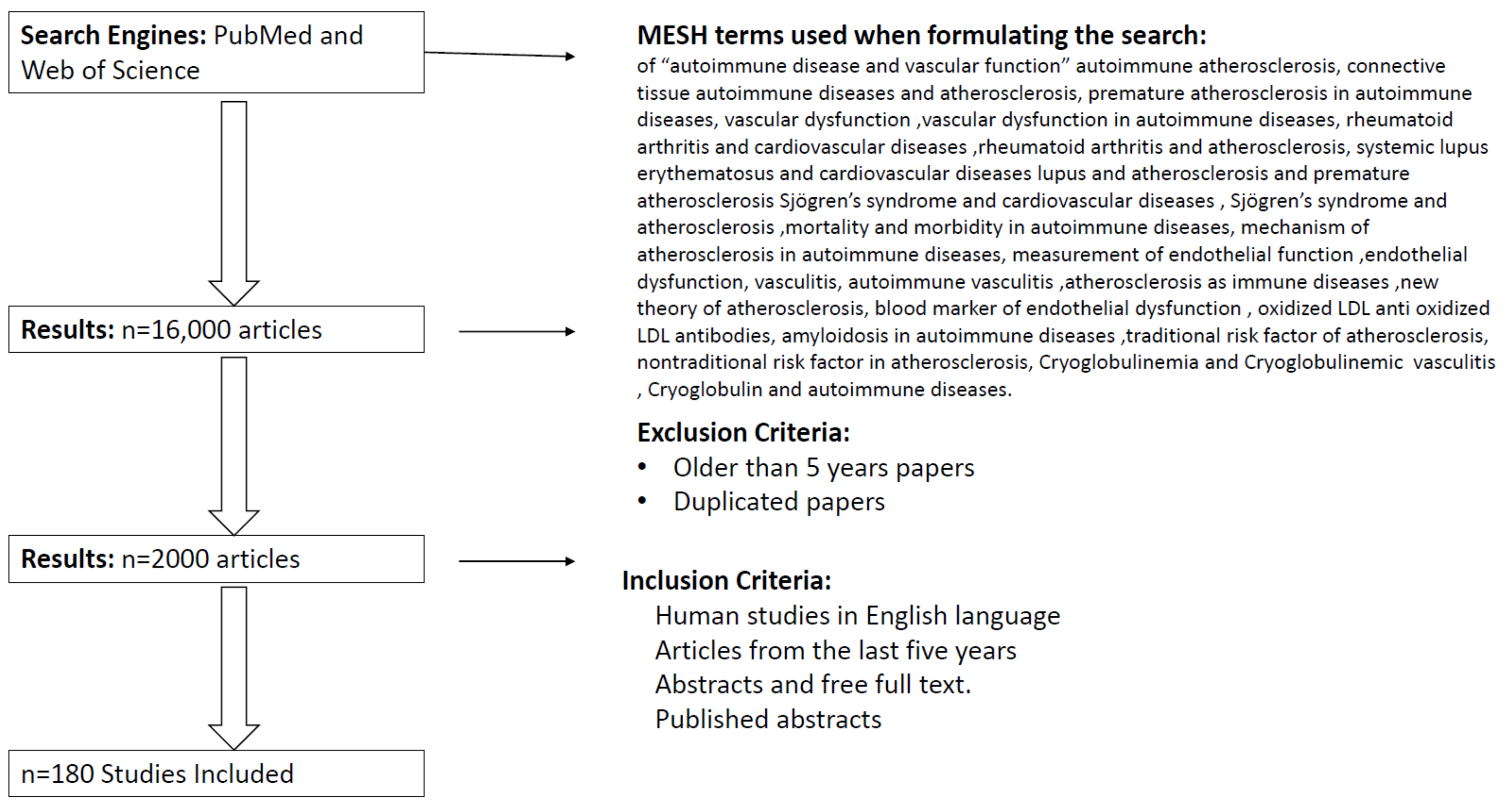
2. Methodology
3. Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases (AIRD)
Pathophysiology of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
4. The Effect of AIRDs on Vascular Function (Premature Atherosclerosis)
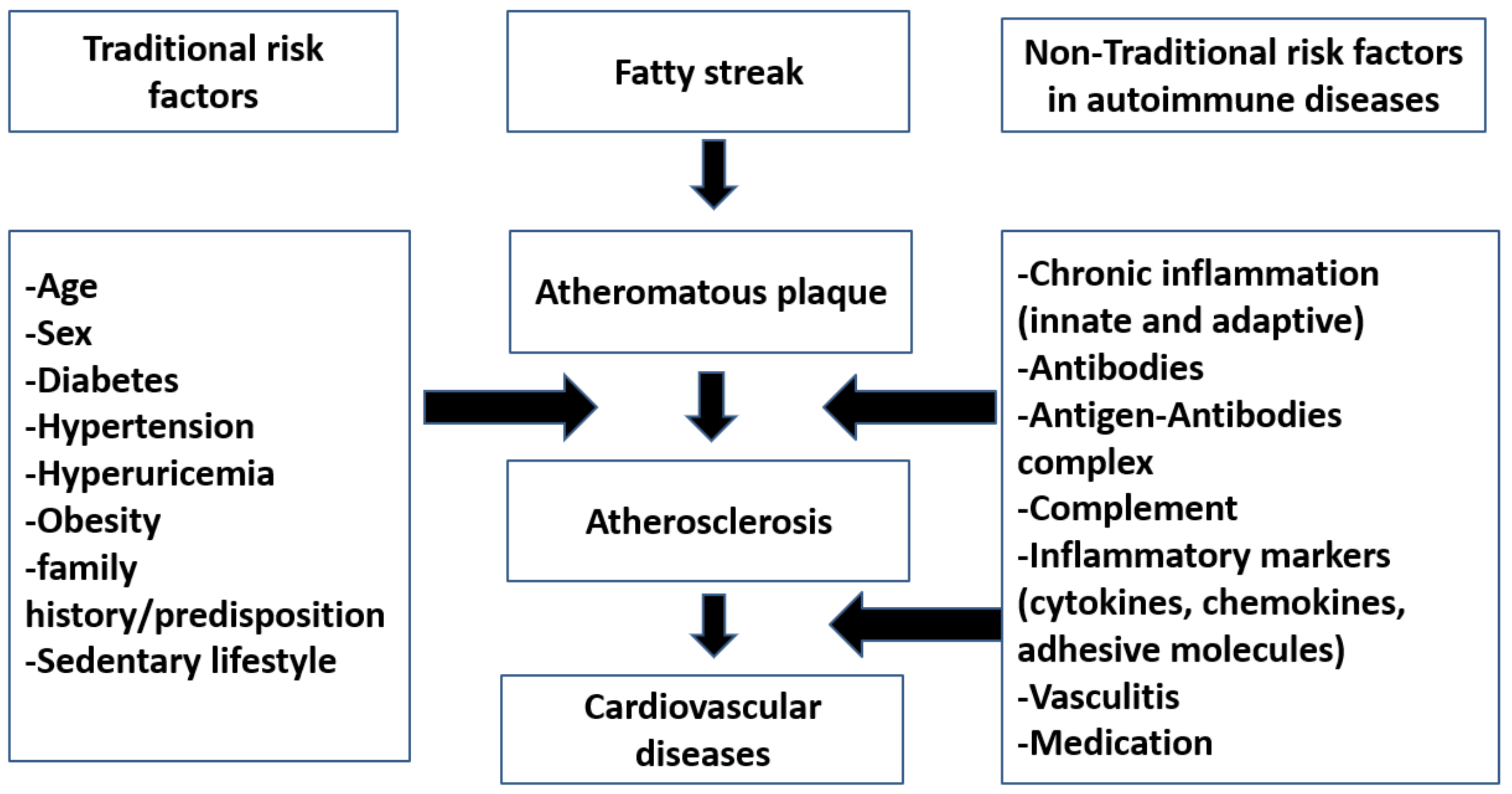
4.1. Traditional Risk Factors in Atherosclerosis
4.2. Nontraditional Risk Factors in Atherosclerosis
4.3. Cardiac Amyloidosis
4.4. Hypertension in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
4.5. Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.6. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
4.7. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome(PSS)
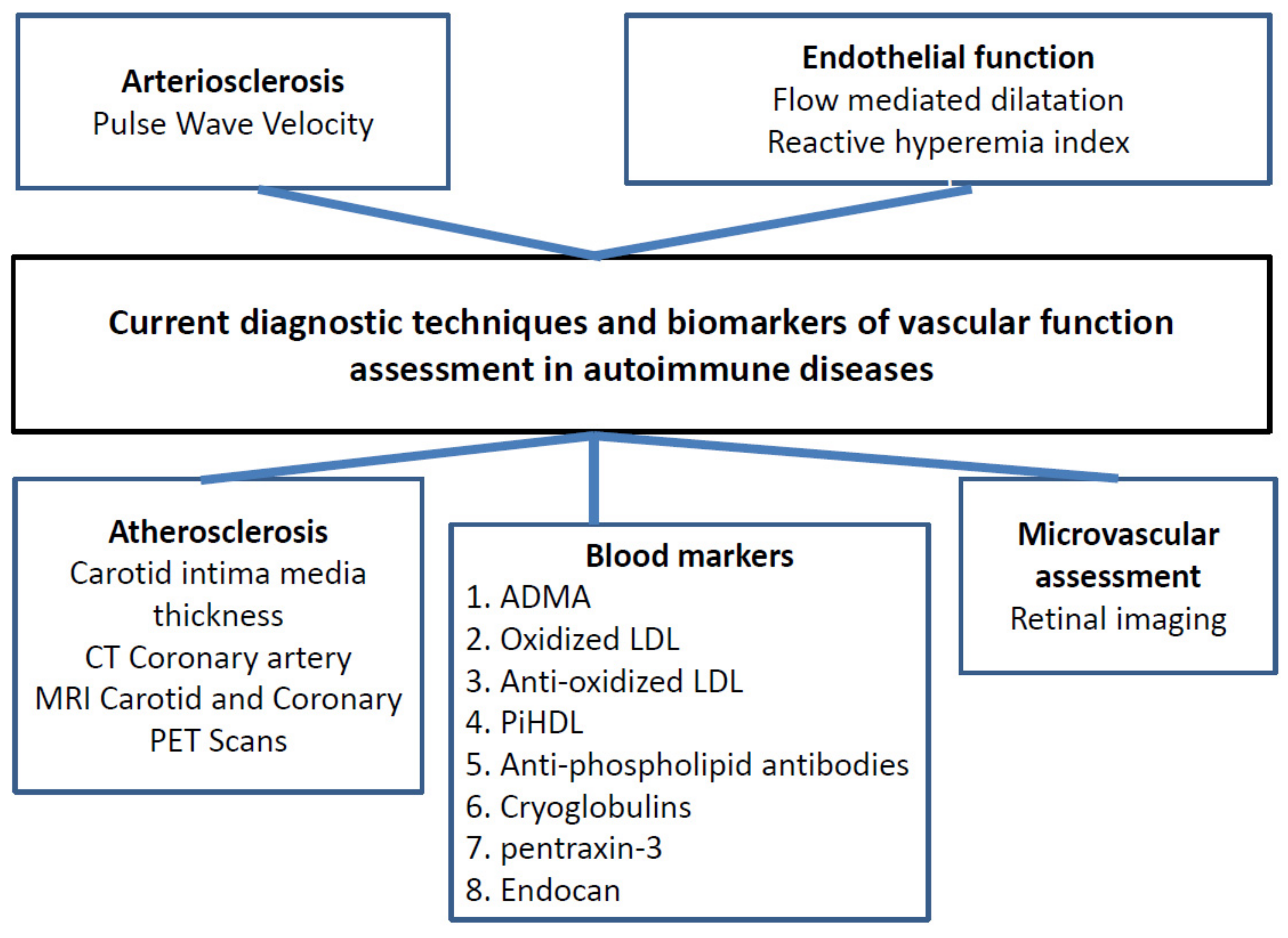
5. Measurements (Assessment) of Vascular Function
5.1. Flow-Mediated Dilation (FMD)
5.2. Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV)
5.3. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness
- Rheumatoid arthritis: All studies regarding the effect of rheumatoid arthritis on flow-mediated dilatation showing impairment in its reactive hyperemia [105,106] and increase in arterial stiffness and carotid intima media thickness showing the evidence of premature atherosclerosis [107,108,109,110,111]. There is no correlation between macrovascular and microvascular endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis (independent of each other) [112].
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: FMD is impaired in lupus erythematosus patients; interestingly, the impairment is mostly found in older age patients with hypertension, diabetes, and renal impairments [125,126]. Arterial stiffness is increased in lupus patients with more relation to age, hypertension, and glucocorticoid use [127,128,129]. Carotid plaque is 21% in patients with lupus under 35 years, and the percentage increased and reached 100% for women over age 65 years [20,130], which may be related to age or disease activity or both.
5.4. Retinal Imaging
5.5. Endo-Pat Test (Peripheral Arterial Tonometry)
5.6. Blood Markers
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frostegård, J. Atherosclerosis in Patients with Autoimmune Disorders. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sima, P.; Vannucci, L.; Vetvicka, V. Atherosclerosis as autoimmune disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmons, D.; Gabriel, S.E. Epidemiology of CVD in rheumatic disease, with a focus on RA and SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, D.; Rose, N.R. Women and Autoimmune Diseases1. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccucci, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Bossù, M.; Giovarruscio, F.; Salucci, A.; Polimeni, A. Autoimmune Diseases and Their Manifestations on Oral Cavity: Diagnosis and Clinical Management. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6061825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.; Lopez, M.; McDevitt, H. Autoimmune diseases: The failure of self-tolerance. Science 1990, 248, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador-Patarroyo, M.J.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A.; Montoya-Ortiz, G. How Does Age at Onset Influence the Outcome of Autoimmune Diseases? Autoimmune Dis. 2011, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Franco, B.L.M.; Lucchino, B.; Spaziante, M.; Iannuccelli, C.; Valesini, G.; Iaiani, G. Lung Infections in Systemic Rheumatic Disease: Focus on Opportunistic Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Forte, A.; Mandell, B.F. Cardiovascular disorders and rheumatic disease. Rev. Española de Cardiol. 2011, 64, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.; Pedro, S.; Ozen, G.; Kalil, A.; Wolfe, F.; Mikuls, T.; Michaud, K. Serious infection risk in rheumatoid arthritis compared with non-inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: A US national cohort study. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, S.; Meilahn, E.N.; Rairie, J.E.; Conte, C.G.; Medsger, T.A.; Jansen-McWilliams, L.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Kuller, L.H. Age-specific Incidence Rates of Myocardial Infarction and Angina in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Comparison with the Framingham Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya-Amaya, J.; Montoya-Sánchez, L.; Rojas-Villarraga, A. Cardiovascular Involvement in Autoimmune Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 367359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buleu, F.; Sirbu, E.; Caraba, A.; Dragan, S. Heart Involvement in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review. Medicina 2019, 55, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekanecz, Z.; Kerekes, G.; Végh, E.; Kardos, Z.; Baráth, Z.; Tamási, L.; Shoenfeld, Y. Autoimmune atherosclerosis in 3D: How it develops, how to diagnose and what to do. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatkhullina, A.R.; Peshkova, I.O.; Koltsova, E.K. The role of cytokines in the development of atherosclerosis. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis—An Inflammatory Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadas, T.N.; Tsokos, G.C.; Tsuboi, N. Mechanisms of Immune Complex–Mediated Neutrophil Recruitment and Tissue Injury. Circulation 2009, 120, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörg, S.; Grohme, D.A.; Erzler, M.; Binsfeld, M.; Haghikia, A.; Müller, D.N.; Linker, R.A.; Kleinewietfeld, M. Environmental factors in autoimmune diseases and their role in multiple sclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4611–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelou, M.; Mavragani, C.P. Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive update. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Tam, L.-S. Novel Insights in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Atherosclerosis. Front. Med. 2018, 4, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar, R. Risk factors for coronary artery disease: Historical perspectives. Heart Views 2017, 18, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuko, K. Rheumatoid Cachexia Revisited: A Metabolic Co-Morbidity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Nutr. 2014, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Baos, S.; Prieto-Potin, I.; Roman-Blas, J.A.; Pernaute, O.S.; Largo, R.; Herrero-Beaumont, G. Mediators and Patterns of Muscle Loss in Chronic Systemic Inflammation. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londhe, P.; Guttridge, D.C. Inflammation induced loss of skeletal muscle. Bone 2015, 80, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaasen, R.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; Gerlag, D.M.; Tak, P.P. Body mass index and clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 63, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Poma, A.; Segami, M.I.; Mora, C.S.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Terrazas, H.N.; Rhor, E.A.; García, E.; Ramos, M.P.; Alva, M.; Castañeda, I.; et al. Obesity is independently associated with impaired quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Resende Guimarães, M.F.B.; Rodrigues, C.E.M.; Gomes, K.W.P.; Machado, C.; Brenol, C.V.; Krampe, S.F.; De Andrade, N.P.B.; Kakehasi, A.M. High prevalence of obesity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Association with disease activity, hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes, a multi-center study. Adv. Rheumatol. 2019, 59, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Van Der Kooij, S.M.; Allaart, C.F.; Toes, R.; Huizinga, T.W.J. A high body mass index has a protective effect on the amount of joint destruction in small joints in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, G.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; González-Gay, M.A.; Seres, I.; Paragh, G.; Kardos, Z.; Baráth, Z.; Tamási, L.; Soltész, P.; Szekanecz, Z. Rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Nelson, K.; Toth, J.; Muscat, J.E. Nicotine dependence as an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis in the National Lung Screening Trial. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Aslani, S.; Fadaei, R.; Jamshidi, A.R. New insights to the mechanisms underlying atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, F.R.; Pecani, A.; Ciciarello, F.; Colasanti, T.; Di Franco, M.; Miranda, F.; Conti, F.; Valesini, G.; Alessandri, C. Association between antibodies to carbamylated proteins and subclinical atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinelli, C.; DI Pino, A.; Ficulle, E.; Marcelli, S.; Feligioni, M. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a Risk Factor and Potential Nutraceutical Target for Certain Pathologies. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzerini, P.E.; Capecchi, P.L.; Selvi, E.; Lorenzini, S.; Bisogno, S.; Galeazzi, M.; Pasini, F.L. Hyperhomocysteinemia, inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. Metabolic syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: The connection. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, I.L.; Vonkeman, H.E.; Van De Laar, M.A. Hyperuricaemia: A marker of increased cardiovascular risk in rheumatic patients: Analysis of the ACT-CVD cohort. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeoch, S.; Bruce, I.N. Atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: Is it all about inflammation? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y. Mechanisms of Disease: Atherosclerosis in autoimmune diseases. Nat. Clin. Pr. Rheumatol. 2006, 2, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobezda, T.; Ghassemi-Nejad, S.; Mikecz, K.; Glant, T.T.; Szekanecz, Z. Of mice and men: How animal models advance our understanding of T-cell function in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengya, Z.; Hanyou, M.; Dong, L.; Xiaohong, L.; Lihua, Z. Th17/Treg imbalance induced by increased incidence of atherosclerosis in patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X. Drugs for Autoimmune Inflammatory Diseases: From Small Molecule Compounds to Anti-TNF Biologics. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, G.; Szekanecz, Z.; Dér, H.; Sándor, Z.; Lakos, G.; Muszbek, L.; Csipö, I.; Sipka, S.; Seres, I.; Paragh, G.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: A multiparametric analysis using imaging techniques and laboratory markers of inflammation and autoimmunity. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 398–406. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, E.; Atzeni, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Turiel, M.; Lopez, L.R.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Is atherosclerosis an autoimmune disease? BMC Med. 2014, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjadi, M.; Sichanie, Z.R.; Totonchi, H.; Karami, J.; Rezaei, R.; Aslani, S. Atherosclerosis and autoimmunity: A growing relationship. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 908–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugatti, S.; Manzo, A.; Montecucco, C.; Caporali, R.F. The Clinical Value of Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerlind, H.; Rönnelid, J.; Hansson, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Mathsson-Alm, L.; Serre, G.; Cornillet, M.; Holmdahl, R.; Jakobsson, P.; Skriner, K.; et al. Anti–Citrullinated Protein Antibody Specificities, Rheumatoid Factor Isotypes, and Incident Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majka, D.S.; Vu, T.-H.T.; Pope, R.M.; Teodorescu, M.; Karlson, E.W.; Liu, K.; Chang, R.W. Association of Rheumatoid Factors With Subclinical and Clinical Atherosclerosis in African American Women: The Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 69, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertovaara, M.; Kähönen, M.; Juonala, M.; Laitinen, T.; Taittonen, L.; Lehtimäki, T.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Raitakari, O.T.; Hurme, M. Autoimmunity and atherosclerosis: The presence of antinuclear antibodies is associated with decreased carotid elasticity in young women. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, K.; Bolko, L.; Giusti, D.; Toquet, S.; Robbins, A.; Antonicelli, F.; Servettaz, A. Autoantibodies Associated With Connective Tissue Diseases: What Meaning for Clinicians? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, P.R.J.; Alves, J.D.; Lopez, L.R.; Gentile, F.; Margarita, A.; Pizzella, L.; Batuca, J.; Scenna, G.; Brancaccio, V.; Matsuura, E. Antibodies Against β2-Glycoprotein I Complexed With an Oxidised Lipoprotein Relate to Intima Thickening of Carotid Arteries in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2006, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinoku, I.; Mavragani, C.P.; Tellis, C.C.; Nezos, A.; Tselepis, A.D.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Autoantibodies to ox-LDL in Sjögren’s syndrome: Are they atheroprotective? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 112), 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, L.R.; Salazar-Paramo, M.; Palafox-Sanchez, C.; Hurley, B.L.; Matsuura, E.; La Torre, I.G.-D. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein and β2-glycoprotein I in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and increased carotid intima-media thickness: Implications in autoimmune-mediated atherosclerosis. Lupus 2006, 15, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciascia, S.; Amigo, M.-C.; Roccatello, D.; Khamashta, M. Diagnosing antiphospholipid syndrome: ’extra-criteria’ manifestations and technical advances. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napodano, C.; Gulli, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Marino, M.; Basile, U. Cryoglobulins: Identification, classification, and novel biomarkers of mysterious proteins. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 104, 299–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragab, G.; Hussein, M.A. Vasculitic syndromes in hepatitis C virus: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filer, A.; Gardner-Medwin, J.M.; Thambyrajah, J.; Raza, K.; Carruthers, D.M.; Stevens, R.J.; Liu, L.; Lowe, S.E.; Townend, J.; Bacon, P.A. Diffuse endothelial dysfunction is common to ANCA associated systemic vasculitis and polyarteritis nodosa. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Carús, M.-E.; Askanase, A.D.; Clancy, R.M.; Di Donato, F.; Chou, T.-M.; Libera, M.R.; Chan, E.K.L.; Buyon, J.P. Anti-SSA/Ro and Anti-SSB/La Autoantibodies Bind the Surface of Apoptotic Fetal Cardiocytes and Promote Secretion of TNF-α by Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5345–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, K.; Rajabally, H.; Ng, W.-F. Anti-Ro antibodies and complete heart block in adults with Sjögren’s syndrome. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 5, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.J.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, Y.-S.; Park, C.-Y.; Choe, J.-Y. Complete Atrioventricular Block in Adult Sjögren’s Syndrome with Anti-Ro Autoantibody. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2011, 26, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schau, T.; Gottwald, M.; Arbach, O.; Seifert, M.; Schöpp, M.; Neuß, M.; Butter, C.; Zänker, M. Increased Prevalence of Diastolic Heart Failure in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Correlates with Active Disease, but Not with Treatment Type. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, Ä.; Holmqvist, M.; Andersson, D.C.; Lund, L.H.; Askling, J. Association Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Risk of Ischemic and Nonischemic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Lin, G.; Oh, J.K.; Crowson, C.S.; Achenbach, S.J.; Therneau, T.M.; Matteson, E.L.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Five-year changes in cardiac structure and function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 240, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, R.H.; Comenzo, R.L.; Skinner, M. The Systemic Amyloidoses. New Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, S.R.; Rison, R.A.; Commins, D. Secondary amyloidosis as a life-ending event in multifocal motor neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stather, D.; Ford, S.; Kisilevsky, R. Sarcoid, amyloid, and acute myocardial failure. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Lyall, D.M.; Mackay, D.F.; Porter, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Sattar, N.; Pell, J.P. Characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis and its association with major comorbid conditions: Cross-sectional study of 502 649 UK Biobank participants. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.P.; Oeser, A.; Solus, J.F.; Avalos, I.; Gebretsadik, T.; Shintani, A.; Raggi, P.; Sokka, T.; Pincus, T.; Stein, C.M. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome is increased in rheumatoid arthritis and is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerli, R.; Sherer, Y.; Vaudo, G.; Schillaci, G.; Gilburd, B.; Giordano, A.; Bocci, E.B.; Allegrucci, R.; Marchesi, S.; Mannarino, E.; et al. Early Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Effects of Smoking on Thickness of the Carotid Artery Intima Media. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2005, 1051, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Robinson, D.W.; Hackett, M.V.; Paramore, L.C.; Fraeman, K.H.; Bala, M.V. Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 2167–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Panoulas, V.F.; Douglas, K.M.J.; Milionis, H.J.; Stavropoulos-Kalinglou, A.; Nightingale, P.; Kita, M.D.; Tselios, A.L.; Metsios, G.S.; Elisaf, M.; Kitas, G.D. Prevalence and associations of hypertension and its control in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.C.; Van Halm, V.P.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic inflammatory joint disorders. Heart 2016, 102, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panoulas, V.F.; Metsios, G.S.; Pace, A.V.; John, H.; Treharne, G.; Banks, M.J.; Kitas, G. Hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvounaris, S.A.; Sidiropoulos, P.I.; Papadakis, J.A.; Spanakis, E.K.; Bertsias, G.K.; Kritikos, H.D.; Ganotakis, E.; Boumpas, D.T. Metabolic syndrome is common among middle-to-older aged Mediterranean patients with rheumatoid arthritis and correlates with disease activity: A retrospective, cross-sectional, controlled, study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 66, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessein, P.H.; Stanwix, A.E.; Joffe, B.I. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis versus osteoarthritis: Acute phase response related decreased insulin sensitivity and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as well as clustering of metabolic syndrome features in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.J.; Moeller, E.; Davis, A.; Paget, S.A.; Crow, M.K.; Lockshin, M.D.; Sammaritano, L.; Devereux, R.B.; Schwartz, J.; Levine, D.M.; et al. Preclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Montagna, G.; Cacciapuoti, F.; Buono, R.; Manzella, D.; Mennillo, G.A.; Arciello, A.; Valentini, G.; Paolisso, G. Insulin resistance is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2007, 4, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Schwartz, J.; Lockshin, M.D.; Paget, S.A.; Davis, A.; Crow, M.K.; Sammaritano, L.; Levine, D.M.; Shankar, B.-A.; et al. Arterial Stiffness in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Hypertension 2005, 46, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Curhan, G.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Karlson, E.W. Cardiovascular risk factors in women with and without rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavathongchai, S.; Bian, A.; Rho, Y.H.; Oeser, A.; Solus, J.F.; Gebretsadik, T.; Shintani, A.; Stein, C.M. Inflammation and Hypertension in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ecobici, M.; Stoicescu, C. Arterial Stiffness and Hypertension—Which Comes First? Maedica 2017, 12, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, V.L.; Ryan, M.J. Autoimmune Disease-Associated Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharir, S.S.; Mustafar, R.; Mohd, R.; Said, M.S.M.; Gafor, H.A.; Said, M.S.M. Persistent hypertension in lupus nephritis and the associated risk factors. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 34, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, I.N.; Urowitz, M.B.; Gladman, D.D.; Ibañez, D.; Steiner, G. Risk factors for coronary heart disease in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: The Toronto Risk Factor Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, J.M.; Vargas-Hitos, J.A.; Navarrete-Navarrete, N.; Mediavilla, J.D.; Jiménez-Jáimez, J.; Díaz-Chamorro, A.; Jiménez-Alonso, J. Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Hypertension in Young and Old Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballocca, F.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Moretti, C.; Omedè, P.; Cerrato, E.; Barbero, U.; Abbate, A.; Bertero, M.T.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Gaita, F. Predictors of cardiovascular events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, J.M.; Vargas-Hitos, J.A.; Martínez-Bordonado, J.; Navarrete-Navarrete, N.; Díaz-Chamorro, A.; Olvera-Porcel, C.; Jiménez-Alonso, J. Cumulated organ damage is associated with arterial stiffness in women with systemic lupus erythematosus irrespective of renal function. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, D.G. The Immune System in Hypertension. Trans. Am. Clin. Clim. Assoc. 2014, 125, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, G.R.; Vinh, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Sobey, C.G. Immune mechanisms of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Agrawal, D.K. Dysregulation of T cell Subsets in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2015, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, B.; Pons, H.; Johnson, R.J. Role of the Immune System in Hypertension. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1127–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, E.; Alunno, A.; Santoboni, G.; Gerli, R. Beneficial cardiovascular effects of low-dose glucocorticoid therapy in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1758–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, E.B.; Wolf, V.L.; Dent, E.; Ryan, M.J. Mechanisms of hypertension in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1897–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerola, A.; Kauppi, M.; Kerola, T.; Nieminen, T. How early in the course of rheumatoid arthritis does the excess cardiovascular risk appear? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowson, C.S.; Rollefstad, S.; Ikdahl, E.; Kitas, G.D.; Van Riel, P.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L.; Kvien, T.K.; Douglas, K.; Sandoo, A.; et al. Impact of risk factors associated with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Monroy, J.C.; Amaya-Amaya, J.; Espinosa-Serna, J.S.; Herrera-Diaz, C.; Anaya, J.-M.; Rojas-Villarraga, A. Cardiovascular Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review in Latin America. Arthritis 2012, 2012, 371909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagopal, P.B.; De Ferranti, S.D.; Cook, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Gidding, S.S.; Hayman, L.L.; McCrindle, B.W.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Steinberger, J. Nontraditional Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanistic, Research, and Clinical Considerations for Youth. Circulation 2011, 123, 2749–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoo, A.; Carroll, D.; Metsios, G.S.; Kitas, G.D.; Van Zanten, J.J.V. The association between microvascular and macrovascular endothelial function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibetoe, G.; Sexton, J.; Ikdahl, E.; Rollefstad, S.; Kitas, G.D.; Van Riel, P.; Gabriel, S.; Kvien, T.K.; Douglas, K.; Sandoo, A.; et al. Prediction of cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis using risk age calculations: Evaluation of concordance across risk age models. Arthritis Res. 2020, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Masedu, F.; Romano, S.; Berardicurti, O.; Liakouli, V.; Carubbi, F.; Di Benedetto, P.; Alvaro, S.; Penco, M.; et al. Increased Cardiovascular Events and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: 1 Year Prospective Single Centre Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, J.H.; Warner, A.; Chipping, J.; Marshall, T.; Lunt, M.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Verstappen, S.M.M. Mortality Trends in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Over 20 Years: Results From the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 66, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L.; Davis, J.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Crowson, C.S. Decreased Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in Recent Years: Dawn of a New Era in Cardiovascular Disease in RA? J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehata, J.C.; Hassell, A.B.; Clarke, S.A.; Mattey, D.L.; Jones, M.A.; Jones, P.W.; Dawes, P.T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: Relationship to single and composite measures of disease activity. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Atzeni, F.; Gerli, R.; Bartoloni, E.; Doria, A.; Barskova, T.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Sitia, S.; Tomasoni, L.; Turiel, M. Cardiac involvement in systemic rheumatic diseases: An update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.S.; Nicola, P.J.M.Z.; Ballman, K.; Jacobsen, S.; Gabriel, S.E. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverner, D.; Paredes, S.; Ferré, R.; Masana, L.; Castro, A.; Vallvé, J.-C. Assessment of arterial stiffness variables in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A mediation analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awalia, A.; Satyadi, S.; Wibisono, S.; Soeroso, J. AB0296 ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS: DO DISEASE ACTIVITY AND DURATION OF ILLNESS MATTER? Abstr. Accept. Publ. 2019, 78, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cem, O.; Askin, A.; Yasar, K.; Ozgul Ucar, E.; Izzet Selcuk, P.; Fulya, D.; Kubilay, S.; Huseyin, T. Clinical significance of aortic stiffness, carotid inti-ma-media thickness and serum osteoprotegerin level in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, Y.; Wu, C.; Shen, B. Impaired brachial artery flow-mediated dilation and increased carotid intima-media thickness in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Chin. Med J. 2012, 125, 832–837. [Google Scholar]
- Adawi, M.; Watad, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Amital, H.; Saaida, G.; Sirchan, R.; Blum, A.; Golan, S.; Rizak, S.; Arnon, B. Endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. QJM Int. J. Med. 2018, 111, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitroulas, T.; Hodson, J.; Sandoo, A.; Smith, J.; Kitas, G.D. Endothelial injury in rheumatoid arthritis: A crosstalk between dimethylarginines and systemic inflammation. Arthritis Res. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.; Oakley, S.P.; Young, L.; Jiang, B.Y.; Wierzbicki, A.; Panayi, G.; Chowienczyk, P.; Kirkham, B. Infliximab improves vascular stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 68, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.A.; Toloza, S.M.; Alarcón, G.S. Impact of Race and Ethnicity in the Course and Outcome of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2014, 40, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiggeri, G.M.; D’Alessandro, M.; Bartolomeo, D.; Degl’Innocenti, M.L.; Magnasco, A.; Lugani, F.; Prunotto, M.; Bruschi, M. An Update on Antibodies to Necleosome Components as Biomarkers of Sistemic Lupus Erythematosus and of Lupus Flares. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mula, R.V.R.; Machiah, D.; Holland, L.; Wang, X.; Parihar, H.; Sharma, A.C.; Selvaraj, P.; Shashidharamurthy, R. Immune Complex-Induced, Nitric Oxide-Mediated Vascular Endothelial Cell Death by Phagocytes Is Prevented with Decoy FcγReceptors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selzer, F.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Fitzgerald, S.; Tracy, R.; Kuller, L.; Manzi, S. Vascular Stiffness in Women With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urowitz, M.B.; Bookman, A.A.; Koehler, B.E.; Gordon, D.A.; Smythe, H.A.; Ogryzlo, M.A. The bimodal mortality pattern of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Med. 1976, 60, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sluis, R.J.; Hoekstra, M. Glucocorticoids are active players and therapeutic targets in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 504, 110728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, C.B.; Appenzeller, S. Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Role of Traditional and Lupus Related Risk Factors. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2008, 4, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviña-Zubieta, J.A.; To, F.; Vostretsova, K.; De Vera, M.; Sayre, E.C.; Esdaile, J.M. Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke in Newly Diagnosed Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A General Population-Based Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 69, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, C.; Eriksson, P.; Zachrisson, H.; Sjöwall, C. High-Frequency Ultrasound of Multiple Arterial Areas Reveals Increased Intima Media Thickness, Vessel Wall Appearance, and Atherosclerotic Plaques in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 581336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.M. Premature morbidity from cardiovascular and cerebro-vascular diseases in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, S.R.; Kasturi, S.; Costenbader, K.H. The epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among patients with SLE: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostopoulou, M.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Parodis, I.; Bertsias, G. Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Recent data on epidemiology, risk factors and prevention. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, E.; Soltesz, P.; Der, H.; Kocsis, Z.; Tarr, T.; Bhattoa, H.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Szegedi, G. Reduced flow-mediated vasodilation as a marker for cardiovascular complications in lupus patients. J. Autoimmun. 2006, 27, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, A.; Kow, N.Y.; Schwarz, H.; Gong, L.; Tay, S.H.; Ling, L.H. Endothelial dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus–a case-control study and an updated meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacre, K.; Escoubet, B.; Pasquet, B.; Chauveheid, M.-P.; Zennaro, M.-C.; Tubach, F.; Papo, T. Increased Arterial Stiffness in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Patients at Low Risk for Cardiovascular Disease: A Cross-Sectional Controlled Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.M.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Ye, Y.; Kang, L.; Pang, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, D.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, S. Accelerated Age-Related Arterial Stiffness in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 22, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Pinto, C.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Molano-González, N.; García-Carrasco, M.; Munguía-Realpozo, P.; Etchegaray-Morales, I.; Morales-Sánchez, H.; Berra-Romani, R.; Cervera, R. Endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2020, 297, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Wildman, R.P.; Kao, A.; Fitzgerald, S.G.; Shook, B.; Tracy, R.P.; Kuller, L.H.; Brockwell, S.; Manzi, S. Progression of carotid intima-media thickness and plaque in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T. Dysfunction of Lacrimal and Salivary Glands in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Nonimmunologic Injury in Preinflammatory Phase and Mouse Model. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauchais, A.-L.; Ouattara, B.; Gondran, G.; Lalloué, F.; Petit, D.; Ly, K.H.; Lambert, M.; Launay, D.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Bezanahari, H.; et al. Articular manifestations in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: Clinical significance and prognosis of 188 patients. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, W.C.; Sanguankeo, A.; Upala, S. Association between primary Sjogren’s syndrome, arterial stiffness, and subclinical atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, M.S.; Karabulut, G.; Gungor, O.; Celtik, A.; Ok, E.; Kabasakal, Y. Is There an Increased Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome? Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Font, J. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome: New clinical and therapeutic concepts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 64, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; Chung, C.-H.; Lin, K.-T.; Lin, C.-S.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Huang, R.-Y.; Wu, C.-T.; Liu, F.-C.; Chien, W.-C. Predictable biomarkers of developing lymphoma in patients with Sjögren syndrome: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50098–50108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Anderson, T.J. Fundamentals of Endothelial Function for the Clinical Cardiologist. Circulation 2002, 105, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, K.E.; Tschakovsky, M.E.; Bandi, E.; Bernareggi, A.; Grandolfo, M.; Mozzetta, C.; Augusti-Tocco, G.; Ruzzier, F.; Lorenzon, P. The relationship between shear stress and flow-mediated dilatation: Implications for the assessment of endothelial function. J. Physiol. 2005, 568, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.K. Linking endothelial dysfunction with endothelial cell activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, R.H. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, an Endogenous Inhibitor of Nitric Oxide Synthase, Explains the “L-Arginine Paradox” and Acts as a Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factor. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2842S–2847S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, G.; Landmesser, U. Endothelial Dysfunction as an Early Sign of Atherosclerosis. Herz 2007, 32, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Goswami, N.; Engwa, G.A.; Sewani-Rusike, C.R.; Mbombela, V.; Webster, I.; de Boever, P.; Kessler, H.H.; Stelzl, E.; Strijdom, H. Relationship between endothelial function, an-tiretroviral treatment and cardiovascular risk factors in HIV patients of African descent in South africa: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Fredriksen, P.M.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Agu, C.; Elias, S.O.; Motaung, K.S.; Brix, B.; Cvirn, G.; Sourij, H.; Stelzl, E.; et al. COVID-19 and its effects on endothelium in HIV-positive patients in sub-Saharan Africa: Cardiometabolic risk, thrombosis and vascular function (ENDOCOVID STUDY). BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Moncada, S.; Vallance, P.; Calver, A.; Collier, J. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet 1992, 339, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, W.; Chen, Z. Vascular Macrophages in Atherosclerosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabe, H.; Obama, T.; Kato, R. The Dynamics of Oxidized LDL during Atherogenesis. J. Lipids 2011, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoni, S.; Bar, I.; Zilberman, L.; George, J. Autoantibodies to Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Patients with Aortic Regurgitation: Association with Aortic Diameter Size. Cardiology 2014, 128, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Wu, R.; Dearing, L.D.; Matsuura, E. Are Anti–Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Antibodies Pathogenic or Protective? Circulation 2004, 110, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, V.J.; Vroegindewey, M.M.; Kardys, I.; Boersma, E.; Haskard, D.; Hartley, A.; Khamis, R. Anti-Oxidized LDL Antibodies and Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charach, G.; Rabinovich, A.; Argov, O.; Weintraub, M.; Charach, L.; Ayzenberg, O.; George, J. Anti-oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibodies in chronic heart failure. World J. Cardiol. 2012, 4, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, Atherosclerosis, and Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimokama, T.; Haraoka, S.; Watanabe, T. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural demon-stration of the lymphocyte-macrophage interaction in human aortic intima. Mod. Pathol. 1999, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, J.J. Association of coronary plaque rupture and atherosclerotic in-flammation. J. Pathol. 1997, 181, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, D.I.; Lee, B.B.; Park, J.E. Prevalence of Foam Cells and Helper–T cells in Atherosclerotic Plaques of Korean Patients with Carotid Atheroma. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2000, 15, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.H.; Polak, J.F.; Wolfson, S.K.; Bond, M.G.; Bommer, W.; Sheth, S.; Psaty, B.M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Manolio, T.A. Use of sonography to evaluate carotid atherosclerosis in the elderly. The Cardiovascular Health Study. CHS Collaborative Research Group. Stroke 1991, 22, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letswalo, B.P.; Schmid-Zalaudek, K.; Brix, B.; Matjuda, E.N.; Klosz, F.; Obernhumer, N.; Gaisl, M.; Engwa, G.A.; Sewani-Rusike, C.; Fredriksen, P.M.; et al. Cardiometabolic risk factors and early indicators of vascular dysfunction: A cross-sectional cohort study in South African adolescents. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e042955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matjuda, E.; Engwa, G.; Anye, S.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.; Goswami, N. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Their Relationship with Vascular Dysfunction in South African Children of African Ancestry. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorogovtsev, V.; Yankevich, D.; Goswami, N. Effects of an Innovative Head-Up Tilt Protocol on Blood Pressure and Arterial Stiffness Changes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, B.; Apich, G.; Ure, C.; Roessler, A.; Goswami, N. Physical therapy affects endothelial function in lymphedema patients. Lymphology 2020, 53, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strijdom, H.; De Boever, P.; Nawrot, T.; Goswami, N. HIV/AIDS: Emerging threat to cardiovascular health in sub-Saharan Africa. South Afr. Med. J. 2016, 106, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaes, A.W.; Spruit, M.A.; Theunis, J.; Goswami, N.; Vanfleteren, L.E.; Franssen, F.M.; Wouters, E.F.; De Boever, P. Endothelial function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review of studies using flow mediated dilatation. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincowitz, C.; Webster, I.; Westcott, C.; Goswami, N.; De Boever, P.; Seidel, G.; Strijdom, H. Vascular health assessment with flow-mediated dilatation and retinal image analysis: A pilot study in an adult population from Cape Town. Cardiovasc. J. Afr 2020, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Louwies, T.; Panis, L.I.; Alders, T.; Bonné, K.; Goswami, N.; Nawrot, T.S.; Dendale, P.; de Boever, P. Microvascular reactivity in rehabilitating car-diac patients based on measurements of retinal blood vessel diameters. Microvasc. Res. 2019, 124, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marincowitz, C.; Genis, A.; Goswami, N.; De Boever, P.; Nawrot, T.; Strijdom, H. Vascular endothelial dysfunction in the wake of HIV and ART. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijdom, H.; De Boever, P.; Walzl, G.; Essop, M.F.; Nawrot, T.S.; Webster, I.; Westcott, C.; Mashele, N.; Everson, F.; Malherbe, S.T.; et al. Cardiovascular risk and endothelial function in people living with HIV/AIDS: Design of the multi-site, longitudinal EndoAfrica study in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Nishiyama, S.K.; Wray, D.W.; Richardson, R.S. Ultrasound Assessment of Flow-Mediated Dilation. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, M.L.; Westerink, J.H.D.M.; Rabelink, T.; De Koning, E.J. Assessment of flow-mediated vasodilatation (FMD) of the brachial artery: Effects of technical aspects of the FMD measurement on the FMD response. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 26, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celermajer, D.; Sorensen, K.; Gooch, V.; Spiegelhalter, D.; Miller, O.; Sullivan, I.; Lloyd, J.; Deanfield, J. Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet 1992, 340, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, R.; Benetos, A.; Topouchian, J.; Laurent, P.; Pannier, B.; Brisac, A.-M.; Target, R.; Levy, B.I. Assessment of Arterial Distensibility by Automatic Pulse Wave Velocity Measurement. Hypertension 1995, 26, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kis, E.; Cseprekál, O.; Kerti, A.; Salvi, P.; Benetos, A.; Tisler, A.; Szabó, A.; Tulassay, T.; Reusz, G.S. Measurement of pulse wave velocity in children and young adults: A comparative study using three different devices. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, R.; Moya, J.L.; García-Lledó, A.; Tomas, J.P.; Ruiz, S.; Megías, A.; Balaguer, J.; Asín, E. Endothelial dysfunction, intima–media thickness and coronary reserve in relation to risk factors and Framingham score in patients without clinical atherosclerosis. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, J.; Shaw, K.; Dasgupta, S.; Ghosh, M.K. Measurement of intima media thickness of carotid artery by B-mode ultrasound in healthy people of India and Bangladesh, and relation of age and sex with carotid artery intima media thickness: An observational study. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Res. 2012, 3, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Hui, Y.N.; Guo, B.; Ma, J.X. Strengthening tight junctions of retinal microvascular endothelial cells by pericytes under normoxia and hypoxia involving angiopoietin-1 signal way. Eye 2007, 21, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.D.; Wong, T.Y.; Witt, N.; Evans, R.; Thom, S.A.M.; Klein, B.E.; Chaturvedi, N.; Klein, R. Determinants of retinal microvascular architecture in normal subjects. Microcirculation 2009, 16, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Meuer, S.M.; Hubbard, L.D. Retinal Vessel Diameters and Their Associations with Age and Blood Pressure. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4644–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, R.; Tielsch, J.; Wang, J.J.; Wong, T.Y.; Mitchell, P.; Tano, Y.; Tominaga, M.; Oizumi, T.; Daimon, M.; Kato, T.; et al. The metabolic syndrome and retinal microvascular signs in a Japanese population: The Funagata study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 92, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Gorur, P.; Pilsl, U.; Anyaehie, B.; Green, D.A.; Bondarenko, O.; Roessler, A.; Hinghofer-Szalkay, H.G. Effect of Orthostasis on Endothelial Function: A Gender Comparative Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenten, B.J.; Hama, S.Y.; De Beer, F.C.; Stafforini, D.M.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; La Du, B.N.; Fogelman, A.M.; Navab, M. Anti-inflammatory HDL becomes pro-inflammatory during the acute phase response. Loss of protective effect of HDL against LDL oxidation in aortic wall cell cocultures. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamozo, S.; Gheitasi, H.; Quartuccio, L.; Kostov, B.; Corazza, L.; Bové, A.; Almirall, A.S.; Gandía, M.; Ramos-Casals, M.; De Vita, S.; et al. Cryoglobulinaemic vasculitis at diagnosis predicts mortality in primary Sjögren syndrome: Analysis of 515 patients. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Funke, A.; Danowski, A.; de Andrade, D.C.O.; Rêgo, J.; Levy, R.A. A importância de reconhecer a síndrome antifosfolípide na medicina vascular. J. Vasc. Bras. 2017, 16, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristagno, G.; Fumagalli, F.; Bottazzi, B.; Mantovani, A.; Olivari, D.; Novelli, D.; Latini, R. Pentraxin 3 in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kali, A.; Shetty, K.R. Endocan: A novel circulating proteoglycan. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balta, S.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Demirkol, S.; Ozturk, C.; Celik, T.; Iyisoy, A. Endocan: A novel inflammatory indicator in cardiovascular disease? Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author(s) | Study Type | Methodology | Results | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kerola, et al., (2012) [93] | Review | Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on FMD as well as atherosclerosis changes in carotid artery in RA |
| Strict control of nontraditional risk factors required to decrease cardiovascular mortality |
| Crowson et al., (2018) [94] | Review | Follow-up of studies for detection of cardiovascular diseases (included 5638 patients without obvious cardiovascular diseases) | 30% of cardiovascular diseases developed are related to RA | Smoking and hypertension are the most important traditional risk factors related to cardiovascular diseases |
| Ruscitti et al., (2017) [99] | Prospective study of 347 patients with RA over one year | Follow-up for detection of cardiovascular diseases via assessment of carotid intima-media thickness and atheromatous plaques | Increased incidence of subclinical atherosclerosis at one year of follow up | Combination of traditional and nontraditional risk factors responsible for premature atherosclerosis |
| Maradit-Kremers et al., (2005) [104] | 603 patients with RA and 603 controls, followed up until death | Follow up in out-patients clinic and hospitalized patients, to assess development of angina, myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death | Rheumatoid arthritis patients have two times more incidence of unrecognized myocardial infarction or sudden cardiac death but not angina as compared to healthy persons | Traditional risk factors alone cannot explain the increased incidence of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis |
| Fan, et al., (2012) [108] | 102 patients with RA and 46 healthy controls | Brachial artery FMD and carotid intima media thickness assessment | FMD was lower in rheumatoid group as compared to that of controls. Higher CIMT values seen in RA patients | No significant correlation between FMD and carotid wall thickness |
| Adawi et al., (2018) [109] | 44 RA patients compared with healthy control | Assessment of FMD in the brachial artery | 86% of the RA patients showed varying degrees of endothelial dysfunction | Early recognition—and monitoring—of endothelial dysfunction and subclinical atherosclerosis are important in follow-ups in RA patients |
| Kiss et al., (2006) [125] | 61 SLE patients and 26 healthy controls | FMD and CIMT measurements carried out | Significant differences between SLE patients and healthy controls: Lower FMD and higher CIMT in SLE | SLE patients should be regularly screened for the development of premature atherosclerosis |
| Mak, et al., (2017) [126] | Case-control study with 71 SLE patients and 71 healthy controls as well as a meta-analysis of 25 case controls studies with 1313 patients and 1012 healthy controls | Endothelial dependent FMD was assessed | Lower FMD was seen in SLE patients as compared to healthy controls | Diabetes, hypertension, and renal disease have greater effect on the atherosclerotic process in SLE patients |
| Sacre et al., (2014) [127] | Cross-sectional controlled study in 41 SLE patients and 35 healthy controls | Carotid-femoral PWV was measured for assessment of arterial stiffness | Increased PWV in SLE patients as compared to healthy persons | Associated hypertension and corticosteroid treatments have an even greater effect on arterial stiffness in SLE patients |
| Thompson et al., (2008) [130] | Prospective study of 217 SLE female patients | Carotid ultrasound at baseline and follow- up for assessment of carotid plaques and CIMT | Accelerated plaque formation in SLE | Traditional and nontraditional risk factors play important roles in the progression of atherosclerosis in SLE |
| Yong, et al., (2019) [133] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 8 studies in 767 PSS patients to assess arterial stiffness and subclinical atherosclerosis | PWV and intima-media thickness assessments carried out in PSS patients | PSS patients have higher PWV and intima-media thickness as compared to healthy controls | PSS patients have premature atherosclerosis. More longitudinal studies are needed to assess the time course of the development of atherosclerosis and risk of cardiovascular diseases |
| Sezis Demirci, et al., (2016) [134] | Arterial stiffness in PSS was assessed in 75 patients and compared with 68 healthy controls | Carotid-femoral PWV measurements were carried out | PWV was higher PSS patients as compared to healthy controls | Arterial stiffness in PSS patients may be due to the associated hypertension, steroidal usage, and hyperlipidemia in these patients, and may not be due to the disease itself |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hedar, A.M.; Stradner, M.H.; Roessler, A.; Goswami, N. Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Vascular Function: The Concept of Autoimmune Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194427
Hedar AM, Stradner MH, Roessler A, Goswami N. Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Vascular Function: The Concept of Autoimmune Atherosclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194427
Chicago/Turabian StyleHedar, Ahmed M., Martin H. Stradner, Andreas Roessler, and Nandu Goswami. 2021. "Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Vascular Function: The Concept of Autoimmune Atherosclerosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194427
APA StyleHedar, A. M., Stradner, M. H., Roessler, A., & Goswami, N. (2021). Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Vascular Function: The Concept of Autoimmune Atherosclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194427






