Autism Spectrum Disorder and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Clinical Case on the Potential Role of the Dystrophin in Autism Neurobiology
Abstract
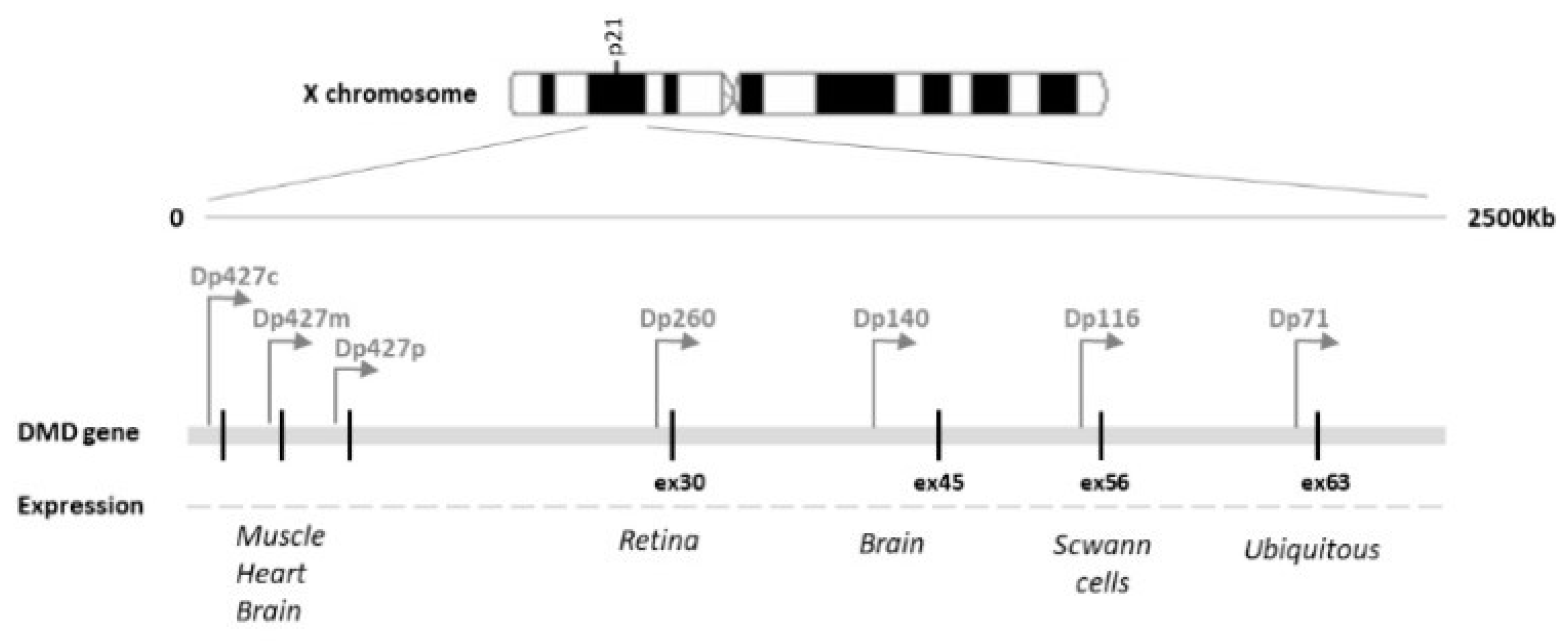
:1. Introduction
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Genetic Landscape of Dystrophin Mutations in Italy: A Nationwide Study—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32194622/ (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Culligan, K.; Ohlendieck, K. Diversity of the Brain Dystrophin-Glycoprotein Complex. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2002, 2, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovolenta, M.; Erriquez, D.; Valli, E.; Brioschi, S.; Scotton, C.; Neri, M.; Falzarano, M.S.; Gherardi, S.; Fabris, M.; Rimessi, P.; et al. The DMD Locus Harbours Multiple Long Non-Coding RNAs Which Orchestrate and Control Transcription of Muscle Dystrophin MRNA Isoforms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dystrophin and Mutations: One Gene, Several Proteins, Multiple Phenotypes—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14636778/ (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Fortunato, F.; Rossi, R.; Falzarano, M.S.; Ferlini, A. Innovative Therapeutic Approaches for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.G.F.; Vles, J.S.H.; Aalbers, M.W.; Chin, R.F.M.; Hendriksen, J.G.M. Brain-Related Comorbidities in Boys and Men with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Descriptive Study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-Y.; Mendell, J.R. Coexisting Muscular Dystrophies and Epilepsy in Children. J. Child. Neurol. 2006, 21, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, F.; Muntoni, F.; Dubowitz, V. Epilepsy in Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophies. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 1997, 1, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Oliviero, A.; Tonali, P.A.; Felicetti, L.; De Marco, M.B.P.; Saturno, E.; Pilato, F.; Pescatori, M.; Dileone, M.; Pasqualetti, P.; et al. Changes in Motor Cortex Excitability in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, M.; Messina, S.; Bruno, C.; D’Amico, A.; Villanova, M.; Brancalion, B.; Sivo, S.; Bianco, F.; Striano, P.; Battaglia, D.; et al. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Epilepsy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2013, 23, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, L.; Di Filippo, T.; Glorioso, P.; La Grutta, S.; Epifanio, M.S.; Roccella, M. Autism Spectrum Disorders in Children Affected by Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Minerva Pediatr. 2018, 70, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotti, V.; Mandy, W.P.L.; Scoto, M.; Pane, M.; Deconinck, N.; Messina, S.; Mercuri, E.; Skuse, D.H.; Muntoni, F. Neurodevelopmental, Emotional, and Behavioural Problems in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy in Relation to Underlying Dystrophin Gene Mutations. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2016, 58, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihani, R.; Smile, S.; Yoon, G.; Dupuis, A.; Mosleh, M.; Snider, A.; McAdam, L. Cognitive and Neurobehavioral Profile in Boys With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Child. Neurol. 2015, 30, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussenot, R.; Amar, M.; Fossier, P.; Vaillend, C. Dp71-Dystrophin Deficiency Alters Prefrontal Cortex Excitation-Inhibition Balance and Executive Functions. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2670–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricotti, V.; Roberts, R.G.; Muntoni, F. Dystrophin and the Brain. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorenweerd, N.; Mahfouz, A.; van Putten, M.; Kaliyaperumal, R.; T’ Hoen, P.A.C.; Hendriksen, J.G.M.; Aartsma-Rus, A.M.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M.; Niks, E.H.; Reinders, M.J.T.; et al. Timing and Localization of Human Dystrophin Isoform Expression Provide Insights into the Cognitive Phenotype of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, R.; Nagapin, F.; Bozon, B.; Laroche, S.; Aubin, T.; Vaillend, C. Altered Social Behavior and Ultrasonic Communication in the Dystrophin-Deficient Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Mol. Autism 2015, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagnamenta, A.T.; Holt, R.; Yusuf, M.; Pinto, D.; Wing, K.; Betancur, C.; Scherer, S.W.; Volpi, E.V.; Monaco, A.P. A Family with Autism and Rare Copy Number Variants Disrupting the Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophy Gene DMD and TRPM3. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2011, 3, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luiz, D.; Faragher, B.; Barnard, A.; Knoesen, N.; Kotras, N.; Burns, L.E.; Challis, D. Griffiths Mental Development Scales–Extended Revised, Two to Eight Years; Hogrefe: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow, S.S.; Balla, D.A.; Cicchetti, D.V.; Harrison, P.L. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales; American Guidance Service: Shoreview, MN, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Schopler, E.; Reichler, L.M.; Marcus, R.L. Psychoeducational Profile: Third Edition (PEP-3); Pro-Ed.: Austin, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; DiLavore, P.; Risi, S.; Gotham, K.; Bishop, S. Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, 2nd ed.; Western Psychological Services: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Association, A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roid GM, M.L. Leiter International Performance Scale-Revised: Examiners Manual; Stoelting Co.: Wood Dale, IL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.J.; Betts, G.A.; Maroulis, S.; Gilissen, C.; Pedersen, R.L.; Mowat, D.R.; Johnston, H.M.; Buckley, M.F. Dystrophin Gene Mutation Location and the Risk of Cognitive Impairment in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.G.F.; Hoogland, G.; Schipper, S.; Hendriksen, J.G.M.; Vles, J.S.H.; Aalbers, M.W. A Possible Role of Dystrophin in Neuronal Excitability: A Review of the Current Literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 51, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajh, M.; Hendriksen, J.; McDermott, M.P.; Martens, W.; Hart, K.A.; Griggs, R.C.; Muscle Study Group and TREAT-NMD. Relationships between DMD Mutations and Neurodevelopment in Dystrophinopathy. Neurology 2019, 93, e1597–e1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelly, J.; Montarras, D.; Pinset, C.; Berwald-Netter, Y.; Kaplan, J.C.; Kahn, A. Quantitative Estimation of Minor MRNAs by CDNA-Polymerase Chain Reaction. Application to Dystrophin MRNA in Cultured Myogenic and Brain Cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 187, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranmolate, A.; Tse, N.; Colognato, H. Myelination Is Delayed during Postnatal Brain Development in the Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darmahkasih, A.J.; Rybalsky, I.; Tian, C.; Shellenbarger, K.C.; Horn, P.S.; Lambert, J.T.; Wong, B.L. Neurodevelopmental, Behavioral, and Emotional Symptoms Common in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torossian, A.; Saré, R.M.; Loutaev, I.; Smith, C.B. Increased Rates of Cerebral Protein Synthesis in Shank3 Knockout Mice: Implications for a Link between Synaptic Protein Deficit and Dysregulated Protein Synthesis in Autism Spectrum Disorder/Intellectual Disability. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 148, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.T.; Darmahkasih, A.J.; Horn, P.S.; Rybalsky, I.; Shellenbarger, K.C.; Tian, C.; Wong, B.L. Neurodevelopmental, Behavioral, and Emotional Symptoms in Becker Muscular Dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, M.; Anthony, K. Dystrophin Dp71 and the Neuropathophysiology of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1748–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagani, M.; Bertero, A.; Liska, A.; Galbusera, A.; Sabbioni, M.; Barsotti, N.; Colenbier, N.; Marinazzo, D.; Scattoni, M.L.; Pasqualetti, M.; et al. Deletion of Autism Risk Gene Shank3 Disrupts Prefrontal Connectivity. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 5299–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Pang, K.; Han, K.; Adamski, C.J.; Wang, W.; He, L.; Lai, J.K.; Bondar, V.V.; Duman, J.G.; Richman, R.; et al. An Autism-Linked Missense Mutation in SHANK3 Reveals the Modularity of Shank3 Function. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2534–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.M.; Kang, Y. Neurexin-Neuroligin Signaling in Synapse Development. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Gu, H.; Luo, X.; Hou, F.; Zhang, J.; Song, R. Neurexin Gene Family Variants as Risk Factors for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An Autism-Associated Mutation Impairs Neuroligin-4 Glycosylation and Enhances Excitatory Synaptic Transmission in Human Neurons—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33268543/ (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Wang, P.; Carrion, P.; Qiao, Y.; Tyson, C.; Hrynchak, M.; Calli, K.; Lopez-Rangel, E.; Andrieux, J.; Delobel, B.; Duban-Bedu, B.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Analysis of 18q12.1-Q12.2 Copy Number Variation in Autism. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 56, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilling, M.; Lauritsen, M.B.; Møller, M.; Henriksen, K.F.; Vicente, A.; Oliveira, G.; Cintin, C.; Eiberg, H.; Andersen, P.S.; Mors, O.; et al. A 3.2 Mb Deletion on 18q12 in a Patient with Childhood Autism and High-Grade Myopia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firth, H.V.; Richards, S.M.; Bevan, A.P.; Clayton, S.; Corpas, M.; Rajan, D.; Van Vooren, S.; Moreau, Y.; Pettett, R.M.; Carter, N.P. DECIPHER: Database of Chromosomal Imbalance and Phenotype in Humans Using Ensembl Resources. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toma, C.; Torrico, B.; Hervás, A.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Tristán-Noguero, A.; Padillo, V.; Maristany, M.; Salgado, M.; Arenas, C.; Puente, X.S.; et al. Exome Sequencing in Multiplex Autism Families Suggests a Major Role for Heterozygous Truncating Mutations. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, E.T.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Sanders, S.J.; Stevens, C.; Sabo, A.; MacArthur, D.G.; Neale, B.M.; Kirby, A.; Ruderfer, D.M.; Fromer, M.; et al. Rare Complete Knockouts in Humans: Population Distribution and Significant Role in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neuron 2013, 77, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cattane, N.; Richetto, J.; Cattaneo, A. Prenatal Exposure to Environmental Insults and Enhanced Risk of Developing Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Focus on Biological Pathways and Epigenetic Mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 117, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, A.M.; Bourgeron, T. Searching for Ways out of the Autism Maze: Genetic, Epigenetic and Environmental Clues. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzi, Y.; Provenzano, G.; Casarosa, S. Neurobiological Bases of Autism-Epilepsy Comorbidity: A Focus on Excitation/Inhibition Imbalance. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sgadò, P.; Dunleavy, M.; Genovesi, S.; Provenzano, G.; Bozzi, Y. The Role of GABAergic System in Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Focus on Autism and Epilepsy. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.L.R.; Merzenich, M.M. Model of Autism: Increased Ratio of Excitation/Inhibition in Key Neural Systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunova, G.; Pallanti, S.; Hollander, E. Excitatory/Inhibitory Imbalance in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Implications for Interventions and Therapeutics. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 17, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatak, S.; Talantova, M.; McKercher, S.R.; Lipton, S.A. Novel Therapeutic Approach for Excitatory/Inhibitory Imbalance in Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 61, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.B.; Valakh, V. Excitatory/Inhibitory Balance and Circuit Homeostasis in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neuron 2015, 87, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peña-Padilla, C.; Romero-Valenzuela, I.; Baldomero-López, A.; Sandoval-Talamantes, A.K.; Castellanos-González, A.; Nagy, P.L.; Kelly, R.R.; Corona-Rivera, J.R. Third Case of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and West Syndrome: Expanding the Spectrum of the DMD Neuropsychiatric Phenotype. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2021, 31, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CLINICAL EVALUATION | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Evaluation | Follow-Up 1 | Follow-Up 2 | Follow-Up 3 | Follow-Up 4 | |
| Age of the patient | 2 years 8 months | 3 years 2 months | 3 years 10 months | 4 years 10 months | 5 years 9 months |
| Developmental/cognitive evaluation | |||||
| GSMD (age-related scores) | |||||
| Motor scale | 22.5 months | 24 months | 19.5 months | 21 months | |
| Social skills | 17 months | 17 months | 16.5 months | 22.5 months | |
| Language | 13 months | 11 months | 14 months | 11 months | |
| Coordination | 19 months | 18 months | 20 months | 20.5 months | |
| Performance | 13.5 months | 15 months | 21 months | 21 months | |
| Total | 17 months | 17 months | 18 months | 18 months | |
| Leiter-R | |||||
| Total IQ | 65 | ||||
| Adaptive functioning | |||||
| VABS (age-related scores) | |||||
| Communication | <1 year 6 months | <1 year 6 months | <1 year 6 months | ||
| Daily living skills | 1 year 8 months | 1 year 8 months | 1 year 8 months | ||
| Social skills | 1 year 7 months | 1 year 8 months | 1 year 6 months | ||
| Motor skills | 1 year 7 months | 1 year 8 months | 1 year 6 months | ||
| Autism Spectrum Disorder | |||||
| ADOS-2 (module 1) | |||||
| Social Interaction score | 14 | ||||
| Stereotype behaviors and restricted interest score | 2 | ||||
| Total score | 16 | ||||
| Level of severity of symptoms | Mild | ||||
| PEP-3 | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Performance subtests | Level of development | ||||
| Verbal/preverbal cognitive | Severe (<12 months) | ||||
| Expressive language | Severe (<12 months) | ||||
| Receptive language | Moderate (<12 months) | ||||
| Fine motor | Severe (<12 months) | ||||
| Gross motor | Severe (<12 months) | ||||
| Visuo-motor imitation | Severe (12 months) | ||||
| Emotional expression | Moderate | ||||
| Social reciprocity | Moderate | ||||
| Characteristic Motor Behavior | Moderate | ||||
| Characteristic Verbal Behavior | Severe | ||||
| Composite subtests | |||||
| Communication | Severe (<12 months) | ||||
| Motricity | Severe (15 months) | ||||
| Impairment in adaptive behavior | Severe | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simone, M.; Margari, L.; Pompamea, F.; De Giacomo, A.; Gabellone, A.; Marzulli, L.; Palumbi, R. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Clinical Case on the Potential Role of the Dystrophin in Autism Neurobiology. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194370
Simone M, Margari L, Pompamea F, De Giacomo A, Gabellone A, Marzulli L, Palumbi R. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Clinical Case on the Potential Role of the Dystrophin in Autism Neurobiology. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194370
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimone, Marta, Lucia Margari, Francesco Pompamea, Andrea De Giacomo, Alessandra Gabellone, Lucia Marzulli, and Roberto Palumbi. 2021. "Autism Spectrum Disorder and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Clinical Case on the Potential Role of the Dystrophin in Autism Neurobiology" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194370
APA StyleSimone, M., Margari, L., Pompamea, F., De Giacomo, A., Gabellone, A., Marzulli, L., & Palumbi, R. (2021). Autism Spectrum Disorder and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Clinical Case on the Potential Role of the Dystrophin in Autism Neurobiology. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194370







