Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Could Predict Outcome in Patients Presenting with Acute Limb Ischemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Preoperative Work-Up and Revascularization Technique
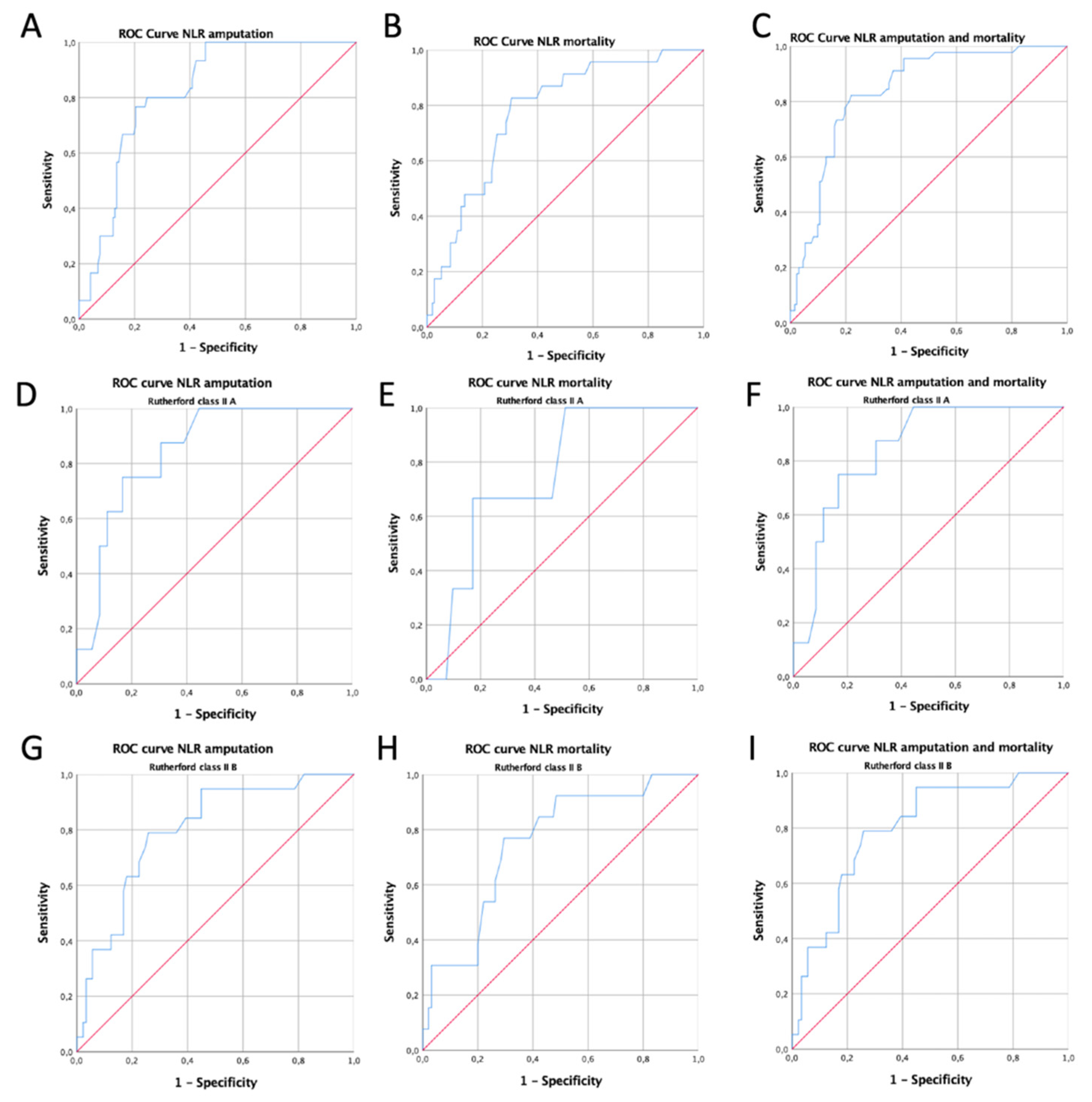
2.4. Study Outcomes
2.5. Ethical Approval
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acar, R.D.; Şahin, M.; Kirma, C. One of the most urgent vascular circumstances: Acute limb ischemia. SAGE Open Med. 2013, 1, 2050312113516110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, R.B.; Baker, J.; Ernst, C.; Johnston, K.; Porter, J.M.; Ahn, S.; Jones, D.N. Recommended standards for reports dealing with lower extremity ischemia: Revised version. J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olinic, D.-M.; Stanek, A.; Tătaru, D.-A.; Homorodean, C.; Olinic, M. Acute Limb Ischemia: An Update on Diagnosis and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Björck, M.; Earnshaw, J.J.; Acosta, S.; Gonçalves, F.B.; Cochennec, F.; Debus, E.; Hinchliffe, R.; Jongkind, V.; Koelemay, M.J.; Menyhei, G.; et al. Editor’s Choice—European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2020 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Acute Limb Ischaemia. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 59, 173–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaffery, Z.; Thornton, S.N.; White, C.J. Acute Limb Ischemia. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 342, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Donato, G.; Setacci, F.; Sirignano, P.; Galzerano, G.; Massaroni, R.; Setacci, C. The combination of surgical embolectomy and endovascular techniques may improve outcomes of patients with acute lower limb ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2013, 59, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, D.K.; Patel, N.H.; Valji, K.; Cardella, J.F.; Brown, D.; Brountzos, E.; Clark, T.W.; Grassi, C.; Meranze, S.; Miller, D.; et al. Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Management of Acute Limb Ischemia. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 16, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spark, J.I.; Sarveswaran, J.; Blest, N.; Charalabidis, P.; Asthana, S. An elevated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio independently predicts mortality in chronic critical limb ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 52, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gary, T.; Pichler, M.; Belaj, K.; Hafner, F.; Gerger, A.; Froehlich, H.; Eller, P.; Pilger, E.; Brodmann, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Its Association with Critical Limb Ischemia in PAOD Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamhane, U.U.; Aneja, S.; Montgomery, D.; Rogers, E.-K.; Eagle, K.A.; Gurm, H.S. Association Between Admission Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 102, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturk, M.; Cakmak, H.A.; Surgit, O.; Celik, O.; Aksu, H.U.; Akgul, O.; Gurdogan, M.; Bulut, U.; Ozalp, B.; Akbay, E.; et al. The predictive value of elevated neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for long-term cardiovascular mortality in peripheral arterial occlusive disease. J. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Porto, F.; Cifani, N.; Proietta, M.; Perrotta, S.; Dito, R.; Di Gioia, C.; Carletti, R.; Rizzo, L.; Orgera, G.; Rossi, M.; et al. Regulatory T CD4 + CD25+ lymphocytes increase in symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Ann. Med. 2016, 49, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.-P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.-C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Fajardo, J.A.; Brizuela-Sanz, J.A.; Aguirre-Gervás, B.; Merino-Díaz, B.; Del Río-Solá, L.; Martín-Pedrosa, M.; Vaquero-Puerta, C. Prognostic Significance of an Elevated Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio in the Amputation-free Survival of Patients with Chronic Critical Limb Ischemia. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 28, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, A.J.; Zargar, H.; Zargar-Shoshtari, K.; Fairey, A.S.; Mertens, L.S.; Dinney, C.P.; Mir, M.C.; Krabbe, L.-M.; Cookson, M.S.; Jacobsen, N.-E.; et al. The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2019, 38, 3.e17–3.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Ma, X.; Liang, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, M. Are pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio useful in predicting the outcomes of patients with small-cell lung cancer? Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37200–37207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, S.; Gao, W.; Guo, S. Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) for Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2020, 16, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahto, E.; Jadric, R.; Pojskic, L.; Kicic, E. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Its Relation with Markers of Inflammation and Myocardial Necrosis in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Med. Arch. 2017, 71, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Arima, H.; Bertmar, C.; Clarke, S.; Herkes, G.; Krause, M. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and early clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 387, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taşoğlu, I.; Çiçek, F.; Lafcı, G.; Kadiroğulları, E.; Sert, D.E.; Demir, A.; Cavus, U.; Colak, N.; Songur, M.; Hodo, B. Usefulness of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Amputation after Embolectomy for Acute Limb Ischemia. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 28, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.M.; Perry, L.A.; Borg, C.; Ramson, D.M.; Campbell, R.; Liu, Z.; Nguyen, J.; Douglas, N.; Kok, J.; Penny-Dimri, J. Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Vascular Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 54, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordzadeh, A.; Malietzis, G.; Browne, T.; Prionidis, I.; Panayiotopoulos, Y.P. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) of five predicts 30-day morbidity in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (rAAA): A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 15, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokgoz, S.; Kayrak, M.; Akpinar, Z.; Seyithanoğlu, A.; Güney, F.; Yürüten, B. Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqui, E.; de Donato, G.; Giannace, G.; Panzano, C.; Alba, G.; Cappelli, A.; Setacci, C.; Palasciano, G. The relation between neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte ratios with mortality and limb amputation after acute limb ischaemia. Vascular 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All Patients | Low-NLR | High-NLR | p (OR; CI95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC I | 6/177 (3.4%) | 6/108 (5.6%) | 0/69 (0%) | <0.001 |
| RC IIA | 44/177 (24.9%) | 32/108 (29.6%) | 12/69 (17.4%) | |
| RC IIB | 108/177 (61%) | 67/108 (62%) | 41/69 (59.4%) | |
| RC III | 19/177 (10.7%) | 3/108 (2.8%) | 16/69 (23.2%) | |
| Male sex | 115/177 (65%) | 67/108 (62%) | 48/69 (69.6%) | 0.305 (0.71; 0.37–1.36) |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 78.9 ± 10.4 | 77.8 ± 11.1 | 80.6 ± 9.3 | 0.065 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 45/177 (25.4%) | 24/108 (22.2%) | 21/69 (30.4%) | 0.22 (0.65; 0.32–1.29) |
| Arterial hypertension | 145/177 (81.9%) | 87/108 (80.6%) | 58/69 (84.1%) | 0.55 (0.78; 0.35–1.75) |
| Dyslipidaemia | 54/177 (30.5%) | 28/108 (25.9%) | 26/69 (37.7%) | 0.09 (0.57; 0.3–1.1) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 70/177 (39.5%) | 38/108 (35.2%) | 32/69 (46.4%) | 0.13 (0.62; 0.33–1.16) |
| ALI aetiology | ||||
| Arterial thrombosis | 90/177 (50.8%) | 56/108 (51.9%) | 34/69 (49.3%) | 0.923 |
| Cardiac embolism | 73/177 (41.3%) | 44/108 (40.7%) | 29/69 (42%) | |
| Graft thrombosis | 14/177 (7.9%) | 8/108 (7.4%) | 6/69 (8.7%) | |
| Performed primary procedure | ||||
| Fogarty embolectomy | 95/177 (53.7%) | 63/108 (58.4%) | 32/69 (46.5%) | 0.053 |
| Fibrinolysis | 62/177 (35%) | 36/108 (33.3%) | 26/69 (37.6%) | |
| By-pass | 9/177 (5.1%) | 5/108 (4.6%) | 4/69 (5.8%) | |
| Mechanical thrombectomy | 6/177 (3.4%) | 4/108 (3.7%) | 2/69 (2.9%) | |
| Major amputation | 5/177 (2.8%) | 0/108 (0%) | 5/69 (7.2%) | |
| Amputation | Mortality | Amputation and Mortality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| low-NLR vs. high-NLR in all enrolled patients | 6/108 (5.5%) vs. 25/69 (36.23%) p < 0.0001 OR:9.65; CI95%:3.7–25.19 | 4/108 (3.7%) vs. 19/69 (27.5%) p = 0.0001 OR:9.88; CI95%:3.19–30.57 | 8/108 (7.4%) vs. 37/69 (53.6%) p < 0.001 OR:14.45; CI95%:6.10–34.21 |
| low-NLR vs. high-NLR in RC IIA patients | 1/32 (3.1%) vs. 4/12 (33.2%) p = 0.02 OR:15.5; CI95%:1.51–158.53 | 1/32 (3.1%) vs. 2/12 (16.6%) p = 0.15 OR:6.2; CI95%:0.50–75.84 | 2/32 (6.2%) vs. 6/12 (50%) p = 0.003 OR:15; CI95%:2.4–93.01 |
| low-NLR vs. high-NLR in RC IIB patients | 3/67 (4.5%) vs. 7/41 (17.1%) p = 0.04 OR:4.39; CI95%:1.06–18.08 | 3/67 (4.5%) vs. 11/41 (26.8%) p = 0.002 OR:7.8; CI95%:2.03–30.1 | 4/67 (6%) vs. 15/41 (36.6%) p = 0.0003 OR:9.08; CI95%:2.75–29.98 |
| low-NLR vs. high-NLR in RC III patients | 2/3 (66.6%) vs. 14/16 (87.5%) p = 0.38 OR:3.5; (CI95%:0.20–58.7) | 0/3 (0%) vs. 6/16 (37.5%) p = 0.35 OR:4.33; CI95%:0.19–98.18 | 2/3 (66.6%) vs. 16/16 (100%) p = 0.001 OR:19.8; CI95%:0.61–633.81 |
| Amputation | Mortality | Amputation and Mortality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | (OR; CI95%) | p | (OR; CI95%) | p | (OR; CI95%) | |
| RC IIA | 0.0020 | 1.91; 0.02–0.42 | 0.2923 | 0.40; 0.07–2.18 | 0.0035 | 1.30; 0.02–0.48 |
| RC IIB | <0.0001 | 2.50; 0.01–0.22 | 0.6662 | 1.74; 0.19–2.86 | 0.0002 | 2.08; 0.02–0.30 |
| Male sex | 0.0748 | 3.09; 0.89–10.71 | 0.6592 | 0.79; 0.28–2.22 | 0.1152 | 2.27; 0.81–6.29 |
| Age > 80 | 0.7787 | 1.16; 0.40–3.35 | 0.9976 | 0.99; 0.36–2.74 | 0.6064 | 0.78; 0.31–1.95 |
| High NLR | 0.0002 | 9.79; 2.99–31.97 | 0.0006 | 7.71; 2.40–24.74 | <0.0001 | 15.09; 5.44–41.84 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.9402 | 0.95; 0.26–3.36 | 0.7911 | 1.16; 0.37–3.56 | 0.7693 | 1.16; 0.41–3.32 |
| Arterial hypertension | 0.9179 | 1.08; 0.23–4.94 | 0.9694 | 1.02; 0.23–4.46 | 0.6756 | 1.31; 0.36–4.83 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.6277 | 1.33; 0.41–4.25 | 0.9732 | 0.98; 0.32–2.95 | 0.8214 | 0.88; 0.31–2.50 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.9060 | 1.06; 0.36–3.11 | 0.6576 | 1.27; 0.43–3.71 | 0.4164 | 1.46; 0.58–3.67 |
| Arterial thrombosis | 0.8647 | 1.17; 0.17–7.80 | 0.9493 | 0.94; 0.15–5.71 | 0.5888 | 0.63; 0.11–3.35 |
| Cardiac embolism | 0.6238 | 0.61; 0.08–4.33 | 0.9304 | 1.08; 0.17–6.71 | 0.3864 | 0.46; 0.08–2.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taurino, M.; Aloisi, F.; Del Porto, F.; Nespola, M.; Dezi, T.; Pranteda, C.; Rizzo, L.; Sirignano, P. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Could Predict Outcome in Patients Presenting with Acute Limb Ischemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194343
Taurino M, Aloisi F, Del Porto F, Nespola M, Dezi T, Pranteda C, Rizzo L, Sirignano P. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Could Predict Outcome in Patients Presenting with Acute Limb Ischemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194343
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaurino, Maurizio, Francesco Aloisi, Flavia Del Porto, Martina Nespola, Tommaso Dezi, Chiara Pranteda, Luigi Rizzo, and Pasqualino Sirignano. 2021. "Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Could Predict Outcome in Patients Presenting with Acute Limb Ischemia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194343
APA StyleTaurino, M., Aloisi, F., Del Porto, F., Nespola, M., Dezi, T., Pranteda, C., Rizzo, L., & Sirignano, P. (2021). Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Could Predict Outcome in Patients Presenting with Acute Limb Ischemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194343








