A Machine Learning Predictive Model for Post-Ureteroscopy Urosepsis Needing Intensive Care Unit Admission: A Case–Control YAU Endourology Study from Nine European Centres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
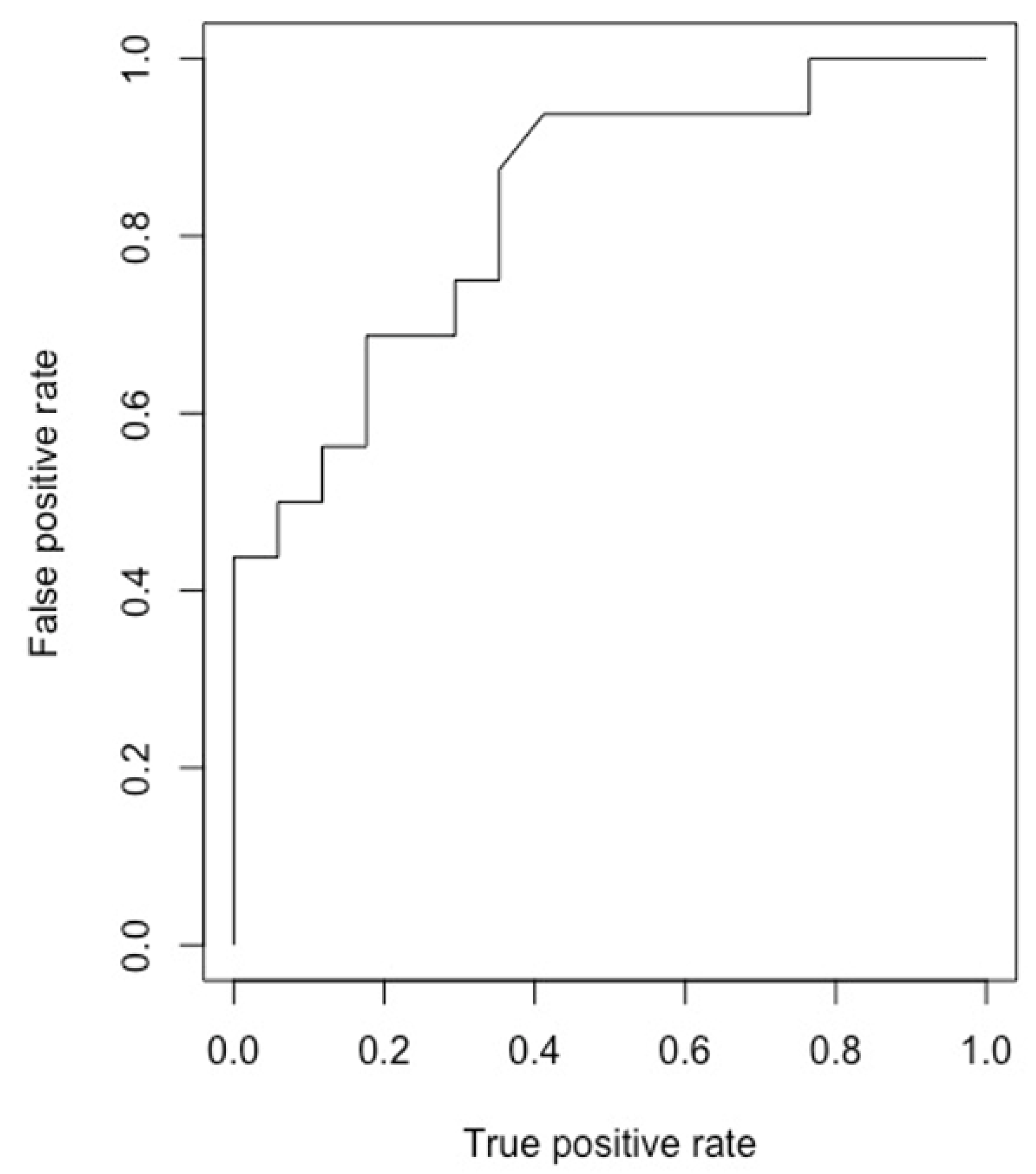
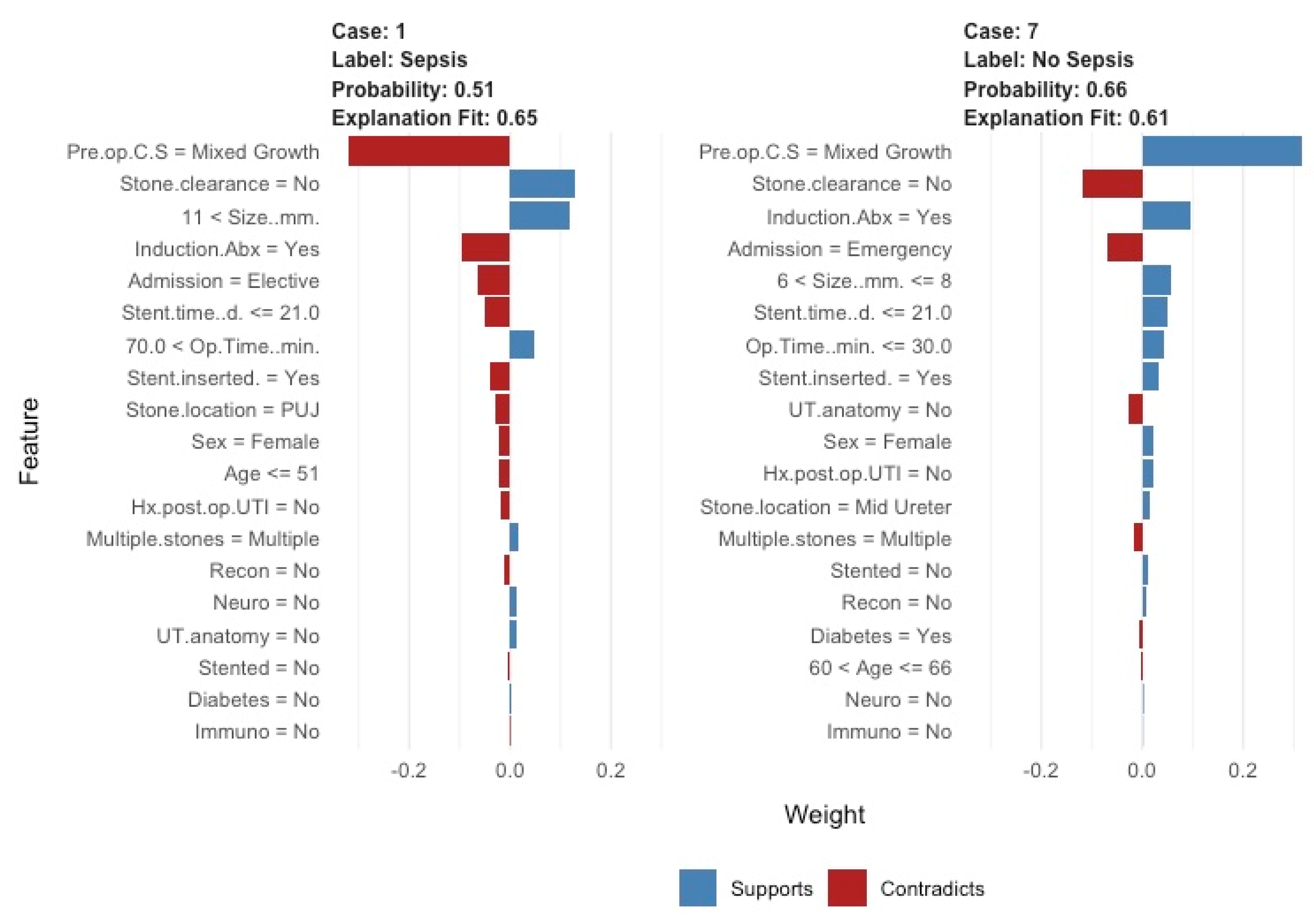
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Meaning of the Study
4.2. Risk Factors of Post-Ureteroscopic Urosepsis from Previous Published Literature
4.3. Comparison with Other ML Studies
4.4. Strengths, Limitations and Areas of Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geraghty, R.M.; Proietti, S.; Traxer, O.; Archer, M.; Somani, B.K. Worldwide impact of warmer seasons on the incidence of renal colic and kidney stone disease: Evidence from a systematic review of literature. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimos, D.; Krambeck, A.; Miller, N.L.; Monga, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nelson, C.P.; Pace, K.T.; Pais, V.M.; Pearle, M.S.; Preminger, G.M.; et al. Surgical management of stones: American Urological Association/Endourological Society guideline, PART I. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, C.; Neisius, A.; Petřík, A.; Seitz, C.; Skolarikos, A.; Somani, B.; Thomas, K.; Gambaro, G. EAU Guidelines on urolithiasis. Eur. Assoc. Urol. 2021. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guideline/urolithiasis/# (accessed on 22 August 2021).
- Pietropaolo, A.; Proietti, S.; Geraghty, R.; Skolarikos, A.; Papatsoris, A.; Liatsikos, E.; Somani, B.K. Trends of ‘urolithiasis: Interventions, simulation, and laser technology’ over the last 16 years (2000–2015) as published in the literature (PubMed): A systematic review from European section of Uro-technology (ESUT). World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkat, G.; Cai, T.; Veeratterapillay, R.; Bruyere, F.; Bartoletti, R.; Pilatz, A.; Köves, B.; Geerlings, S.E.; Pradere, B.; Pickard, R.; et al. Management of Urosepsis in 2018. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenlehner, F.M.; Tandogdu, Z.; Johansen, T.E.B. An update on classification and management of urosepsis. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2017, 27, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Taeb, A.M. SIRS, qSOFA and new sepsis definition. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Liu, V.X.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Rea, T.D.; Scherag, A.; Rubenfeld, G.; Kahn, J.M.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Singer, M.; et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis. JAMA 2016, 315, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Levy, M.M.; Rhodes, A.; Annane, D.; Gerlach, H.; Opal, S.M.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Douglas, I.S.; Jaeschke, R.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 580–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanot, R.; Pietropaolo, A.; Tokas, T.; Kallidonis, P.; Skolarikos, A.; Keller, E.X.; De Coninck, V.; Traxer, O.; Gozen, A.; Sarica, K.; et al. Predictors and Strategies to Avoid Mortality Following Ureteroscopy for Stone Disease: A Systematic Review from European Association of Urologists Sections of Urolithiasis (EULIS) and Uro-technology (ESUT). Eur. Urol. Focus 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, S.; Pietropaolo, A.; Montanari, E.; Sarica, K.; Somani, B.K. Predictors of Urinary Infections and Urosepsis after Ureteroscopy for Stone Disease: A Systematic Review from EAU Section of Urolithiasis (EULIS). Curr. Urol. Rep. 2020, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Southern, J.B.; Higgins, A.M.; Young, A.J.; Kost, K.A.; Schreiter, B.R.; Clifton, M.; Fulmer, B.R.; Garg, T. Risk Factors for Postoperative Fever and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome After Ureteroscopy for Stone Disease. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, A.; Hendry, J.; Kyriakides, R.; Geraghty, R.; Jones, P.; Aboumarzouk, O.; Somani, B.K. Outcomes of Elective Ureteroscopy for Ureteric Stones in Patients with Prior Urosepsis and Emergency Drainage: Prospective Study over 5 yr from a Tertiary Endourology Centre. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martov, A.; Gravas, S.; Etemadian, M.; Unsal, A.; Barusso, G.; D’Addessi, A.; Krambeck, A.; De La Rosette, J.; Clinical Research Office of the Endourological Society Ureteroscopy Study Group. Postoperative infection rates in patients with a negative baseline urine culture undergoing ureteroscopic stone removal: A matched case-control analysis on antibiotic prophylaxis from the CROES URS global study. J. Endourol. 2015, 29, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.G.; Guo, Y.L. Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of BMPER in Patients with Urosepsis following Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8078139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhojani, N.; Miller, L.E.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Cutone, B.; Chew, B.H. Risk Factors for Urosepsis After Ureteroscopy for Stone Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Yu, X.; Qin, C.; Xu, T.; Shen, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Identification of Factors Associated with Postoperative Urosepsis after Ureteroscopy with Holmium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser Lithotripsy. Urol. Int. 2019, 103, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Naik, N.; Somani, B.K.; Hameed, B.Z. Artificial intelligence (AI) in urology-Current use and future directions: An iTRUE study. Turk. J. Urol. 2020, 46 (Suppl. 1), S27–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, C. Comparison of machine learning and logistic regression models in predicting acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2021, 151, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminsharifi, A.; Irani, D.; Tayebi, S.; Jafari Kafash, T.; Shabanian, T.; Parsaei, H. Predicting the Postoperative Outcome of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy with Machine Learning System: Software Validation and Comparative Analysis with Guy’s Stone Score and the CROES Nomogram. J. Endourol. 2020, 34, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, E.S.; Porras, A.R.; Biggs, E.; Tabrizi, P.R.; Sussman, R.D.; Sprague, B.M.; Shalaby-Rana, E.; Majd, M.; Pohl, H.G.; Linguraru, M.G. Early Detection of ureteropelvic junction obstruction using signal analysis and machine learning: A dynamic solution to a dynamic problem. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Yardimci, A.H.; Bektas, C.T.; Turkcanoglu, M.H.; Erdim, C.; Yucetas, U.; Koca, S.B.; Kilickesmez, O. Textural differences between renal cell carcinoma subtypes: Machine learning-based quantitative computed tomography texture analysis with independent external validation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 107, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Rong, P.; Cao, P.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, W.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W. Machine learning-based quantitative texture analysis of CT images of small renal masses: Differentiation of angiomyolipoma without visible fat from renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, Z.; Mason, J.; Gill, K.; Miranda, G.; Gill, I.S.; Kuhn, P.; Newton, P.K. Machine learning models for predicting post-cystectomy recurrence and survival in bladder cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.; Li, H.; Guan, Y. Treatment Stratification of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer by Machine Learning. Iscience 2020, 23, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Opal, S.M. The role of genetics and antibodies in sepsis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Group A, n = 57 | Group B, n = 57 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) ± SD | 60 ± 16 | 60 ± 16 | |
| Male gender, n (%) | 26 (45.6%) | 26 (45.6%) | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 15 (26.3%) | 12 (21.1%) | |
| Immunosuppression/modulation, n (%) | 3 (5.3%) | 1 (1.8%) | |
| Neurological disorder, n (%) | 1 (1.8%) | 1 (1.8%) | |
| Previous urinary tract reconstruction, n (%) | 1 (1.8%) | 0 | |
| Abnormal upper tract anatomy, n (%) | 1 (1.8%) | 5 (8.8%) | |
| History of recurrent UTI, n (%) | 14 (24.6%) | 3 (5.3%) | |
| Emergency admission | 30 (52.6%) | 9 (15.8%) | |
| Presence of pre-operative stent, n (%) | 33 (57.9%) | 26 (45.6%) | |
| Mean stent dwell time (days) ± SD | 52 ± 63 | 30 ± 60 | |
| Number of stones | 1 | 31 | 31 |
| 2 | 20 | 13 | |
| 3 | 3 | 13 | |
| 4 | 2 | 0 | |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | |
| Mean largest stone diameter (mm) ± SD | 10 ± 5 | 8 ± 4 | |
| Location, n | Vesicoureteric junction (VUJ) | 3 | 3 |
| Distal ureter | 7 | 11 | |
| Mid ureter | 8 | 11 | |
| Proximal ureter | 8 | 13 | |
| Renal | 31 | 15 | |
| N/A | 0 | 4 | |
| Positive pre-operative urine culture, n (%) | 15 (26.3%) | 15 (26.3%) | |
| Mean operative time (mins) ± SD | 58 ± 31 | 43 ± 23 | |
| Post-operative stent insertion, n (%) | 36 (46.2%) | 42 (53.8%) | |
| Stone free, n (%) | 34 (48.6%) | 51 (89.5%) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietropaolo, A.; Geraghty, R.M.; Veeratterapillay, R.; Rogers, A.; Kallidonis, P.; Villa, L.; Boeri, L.; Montanari, E.; Atis, G.; Emiliani, E.; et al. A Machine Learning Predictive Model for Post-Ureteroscopy Urosepsis Needing Intensive Care Unit Admission: A Case–Control YAU Endourology Study from Nine European Centres. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173888
Pietropaolo A, Geraghty RM, Veeratterapillay R, Rogers A, Kallidonis P, Villa L, Boeri L, Montanari E, Atis G, Emiliani E, et al. A Machine Learning Predictive Model for Post-Ureteroscopy Urosepsis Needing Intensive Care Unit Admission: A Case–Control YAU Endourology Study from Nine European Centres. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173888
Chicago/Turabian StylePietropaolo, Amelia, Robert M. Geraghty, Rajan Veeratterapillay, Alistair Rogers, Panagiotis Kallidonis, Luca Villa, Luca Boeri, Emanuele Montanari, Gokhan Atis, Esteban Emiliani, and et al. 2021. "A Machine Learning Predictive Model for Post-Ureteroscopy Urosepsis Needing Intensive Care Unit Admission: A Case–Control YAU Endourology Study from Nine European Centres" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173888
APA StylePietropaolo, A., Geraghty, R. M., Veeratterapillay, R., Rogers, A., Kallidonis, P., Villa, L., Boeri, L., Montanari, E., Atis, G., Emiliani, E., Sener, T. E., Al Jaafari, F., Fitzpatrick, J., Shaw, M., Harding, C., & Somani, B. K. (2021). A Machine Learning Predictive Model for Post-Ureteroscopy Urosepsis Needing Intensive Care Unit Admission: A Case–Control YAU Endourology Study from Nine European Centres. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173888








