Low Muscle Mass in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: Correlations with Vascular Calcification and Vascular Access Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Measurement of the Muscle Mass of Both Lower Extremities Using Bioimpedance Analysis
2.3. Measurement of the Vascular Calcification Score
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Subjects
3.2. Associations of Vascular Calcification with Risk Factors Including Lower Muscle Mass
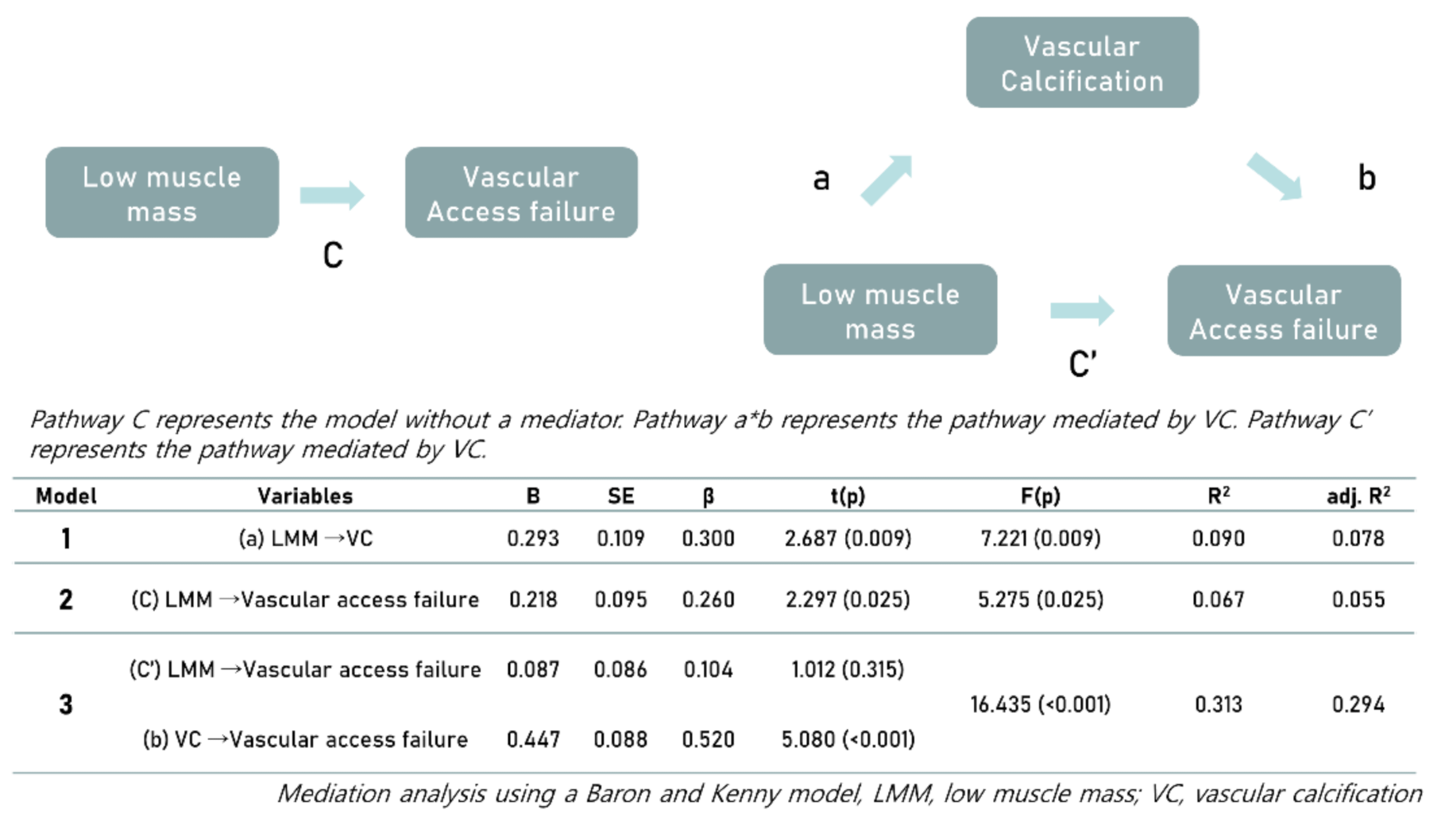
3.3. Associations among Vascular Calcification, Muscle Mass, and the Prevalence of Vascular Access Failure
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Park, S.W.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nevitt, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Visser, M.; Newman, A.B.; et al. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: The health, aging and body composition study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2006, 61, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.-K.; Liu, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.-Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Hsu, P.-S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.-Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Eng. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, G.M.; Guérin, A.P.; Marchais, S.J.; Métivier, F.; Pannier, B.; Adda, H. Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: Impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, B.; Choi, G.; Jin, H.Y.; Jung, H.; Hwang, S.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.; et al. Quantified Vascular Calcification at the Dialysis Access Site: Correlations with the Coronary Artery Calcium Score and Survival Analysis of Access and Cardiovascular Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.J.; Lewis, J.R.; Scott, D.S.; Kiel, D.P.; Schousboe, J.T.; Ebeling, P.R.; Prince, R.L. Aortic Calcification is Associated with Five-Year Decline in Handgrip Strength in Older Women. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 103, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensky, N.E.; Criqui, M.H.; Wright, C.M.; Wassel, C.L.; Alcaraz, J.E.; Allison, M.A. The Association between Abdominal Body Composition and Vascular Calcification. Obesity 2011, 19, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Shin, M.J.; Saini, S.K.; Custodero, C.; Aggarwal, M.; Anton, S.D.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mankowski, R.T. Vascular dysfunction as a potential culprit of sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 145, 111220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlieper, G.; Krüger, T.; Djuric, Z.; Damjanovic, T.; Markovic, N.; Schurgers, L.; Brandenburg, V.M.; Westenfeld, R.; Dimkovic, S.; Ketteler, M.; et al. Vascular access calcification predicts mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.J.; Scott, D.; Khan, B.; Khan, N.; Hodge, A.; English, D.R.; Giles, G.G.; Ebeling, P.R. Low relative lean mass is associated with increased likelihood of abdominal aortic calcification in community-dwelling older Australians. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2016, 99, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boirie, Y. Physiopathological mechanism of sarcopenia. JNHA J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Streeper, T.; Cawthon, P.; Baldwin, K.; Taaffe, D.R.; Harris, T.B. Sarcopenia: Etiology, clinical consequences, intervention, and assessment. Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, S.J.; Yu, L.J. Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1509–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Souza, V.A.; Oliveira, D.; Barbosa, S.R.; Corrêa, J.O.D.A.; Colugnati, F.; Mansur, H.N.; Fernandes, N.; Bastos, M.G. Sarcopenia in patients with chronic kidney disease not yet on dialysis: Analysis of the prevalence and associated factors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176230. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Son, Y.K.; An, W.S. Serum myostatin levels are associated with abdominal aortic calcification in dialysis patients. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 38, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domański, M.; Ciechanowski, K. Sarcopenia: A major challenge in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 754739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moe, S.M.; Chen, N.X. Mechanisms of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vattikuti, R.; Towler, D.A. Metabolism. Osteogenic regulation of vascular calcification: An early perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E686–E696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virchow, R. Cellular Pathology as Based upon Physiological and Pathological Histology; J. B. Lippincott & Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1863. [Google Scholar]
- Abedin, M.; Tintut, Y.; Demer, L.L. Vascular calcification: Mechanisms and clinical ramifications. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Giachelli, C.M. Vascular calcification in CKD-MBD: Roles for phosphate, FGF23, and Klotho. Bone 2017, 100, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, S.M.; Chen, N.X. Pathophysiology of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, J.L.; Joannides, A.J.; Skepper, J.N.; McNair, R.; Schurgers, L.J.; Proudfoot, D.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: A potential mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ketteler, M.J. Fetuin-A and extraosseous calcification in uremia. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2005, 14, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.J.; Raggi, P.; Wolf, M.; Gold, A.M.; Chertow, G.M.; Roe, M.T. Targeting vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, S.; Carmona, A.; Triviño, F.; Rodriguez, M.; Alvarez-Benito, M.; Martín-Malo, A.; Alvarez-Lara, M.-A.; Ramírez, R.; Aljama, P.; Carracedo, J. Endothelial damage and vascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014, 307, F1302–F1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toth, M.J.; Matthews, D.E.; Tracy, R.P.; Previs, M.J. Age-related differences in skeletal muscle protein synthesis: Relation to markers of immune activation. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2005, 288, E883–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, J.M.; Judge, A.R.; Powers, S.K.; Yan, Z. p38 MAPK links oxidative stress to autophagy-related gene expression in cachectic muscle wasting. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 298, C542–C549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, M.G.; Wallis, M.G.; Barrett, E.J.; Vincent, M.A.; Richards, S.M.; Clerk, L.H.; Rattigan, S. Blood flow and muscle metabolism: A focus on insulin action. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2003, 284, E241–E258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ascenzi, F.; Barberi, L.; Dobrowolny, G.; Bacurau, A.V.N.; Nicoletti, C.; Rizzuto, E.; Rosenthal, N.; Scicchitano, B.M.; Musarò, A. Effects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, G.; Frasca, F.; Mineo, R.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors have different biological characteristics depending on the insulin receptor isoform involved. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39684–39695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Ogawa, W.; Sakaue, H.; Hino, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Takata, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Maeda, T.; Konishi, H.; Kikkawa, U.; et al. Requirement for activation of the serine-threonine kinase Akt (protein kinase B) in insulin stimulation of protein synthesis but not of glucose transport. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 3708–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brahmbhatt, A.; Remuzzi, A.; Franzoni, M.; Misra, S. The molecular mechanisms of hemodialysis vascular access failure. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, B.; Banerjee, T.; Scialla, J.J.; Shafi, T.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Powe, N.R.; Parekh, R.S.; Astor, B.C. Vascular calcification markers and hemodialysis vascular access complications. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafronte, N.T.; Diani, L.M.; Vega-Piris, L.; Cuadrado, G.B.; Chiarello, P.G. Comparison between dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and bioelectrical impedance for body composition measurements in adults with chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional, longitudinal, multi-treatment analysis. Nutrition 2021, 82, 111059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, V.; Zerahn, B.; Heaf, J.G. Comparison of Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Bioimpedance in Assessing Body Composition and Nutrition in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2017, 27, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarca, F.; Carrero, J.J.; Rodrigues, J.; Bigogno, F.G.; Fetter, R.L.; Avesani, C.M. Prevalence of sarcopenia in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients: The impact of different diagnostic criteria. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.-J.; Chang, Y.; Jung, H.-S.; Yun, K.E.; Kim, C.-W.; Park, H.S.; Chung, E.C.; Shin, H.; Ryu, S. Relationship Between Low Relative Muscle Mass and Coronary Artery Calcification in Healthy Adults. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Variables | Non-LMM | LMM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 40 (53.3) | 35 (46.7) | |
| Male sex, n (%) | 24 (60.0) | 18 (51.4) | 0.456 |
| Age, years, median [IQR] | 60.5 [51.8, 66.8] | 67.0 [62.5, 76.0] | 0.001 |
| Etiology, n (%) | 0.185 | ||
| Diabetes | 17 (42.5) | 22 (62.9) | |
| HTN | 14 (35.0) | 11 (31.4) | |
| CGN | 1 (2.5) | 0 | |
| PKD | 1 (2.5) | 1 (2.9) | |
| Others | 7 (17.5) | 1 (2.9) | |
| SBP, mmHg, median [IQR] | 150.0 [130.0, 167.5] | 160 [130.0, 170.0] | 0.476 |
| DBP, mmHg, median [IQR] | 70.0 [70.0, 80.0] | 70 [60, 80] | 0.301 |
| Pulse pressure, mmHg, median [IQR] | 70 [60, 87.5] | 80 [60, 90] | 0.057 |
| AVF (vs. AVG), n (%) | 37 (92.5) | 27 (77.1) | 0.061 |
| HD vintage, months, median [IQR] | 48.8 [32.2, 108.4] | 50.5 [25.7, 101.9] | 0.975 |
| UF volume, kg, median [IQR] | 2.2 [1.8, 3.1] | 1.8 [1.3, 2.8] | 0.092 |
| Height, cm, median [IQR] | 164.6 [155.2, 171.2] | 158 [153.1, 167.3] | 0.158 |
| Dry weight, kg, median [IQR] | 61.3 [54.0, 71.4] | 56.5 [47.8, 60.8] | 0.036 |
| BMI, kg/m2, median [IQR] | 22.7 [20.3, 25.7] | 21.5 [20.1, 22.5] | 0.124 |
| spKt/V, median [IQR] | 1.72 [1.56, 2.03] | 2.01 [1.66, 2.24] | 0.132 |
| URR, %, median [IQR] | 75.8 [73.0, 80.5] | 80.6 [74.5, 83.7] | 0.111 |
| Hb, g/dL, median [IQR] | 10.3 [9.8, 11.1] | 10.4 [9.6, 10.9] | 0.762 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 7.1 [6.2, 8.8] | 6.8 [5.9, 7.9] | 0.444 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 123.5 [107.5, 143.5] | 126.0 [107.0,147.0] | 0.920 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 66.0 [50.3, 77.8] | 63.0 [46.5, 84.0] | 0.766 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 103.5 [70.5, 142.0] | 108.0 [85.5, 169.5] | 0.413 |
| Albumin, g/dL, median [IQR] | 3.9 [3.5,4.0] | 3.6 [3.4, 3.9] | 0.096 |
| Ferritin, ng/mL, median [IQR] | 171.4 [83.8, 213.8] | 201.4 [109.3, 300.3] | 0.214 |
| CRP, mg/L, median [IQR] | 0.1 [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 [0.1, 9.0] | 0.003 |
| 25(OH) vitamin D, ng/mL, median [IQR] | 21.9 [15.9, 27.2] | 17.1 [13.4, 22.8] | 0.027 |
| Calcium, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 8.1 [7.6, 8.6] | 8.1 [7.7, 8.5] | 0.710 |
| Phosphorus, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 5.0 [3.8, 5.9] | 4.6 [4.0, 5.6] | 0.679 |
| iPTH, pg/mL, median [IQR] | 347.0 [146.0, 494.8] | 220.0 [134.0, 371.0] | 0.206 |
| Magnesium, mg/dL, median [IQR] | 2.6 [2.4, 2.9] | 2.6 [2.5, 2.8] | 0.928 |
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.900 (0.728–0.459) | 0.190 |
| Age | 0.997 (0.955–1.041) | 0.894 |
| Diabetes | 1.231 (0.484–3.127) | 0.663 |
| SBP | 0.992 (0.973–1.011) | 0.398 |
| DBP | 0.971 (0.934–1.010) | 0.971 |
| Pulse pressure | 0.992 (0.970–1.015) | 0.495 |
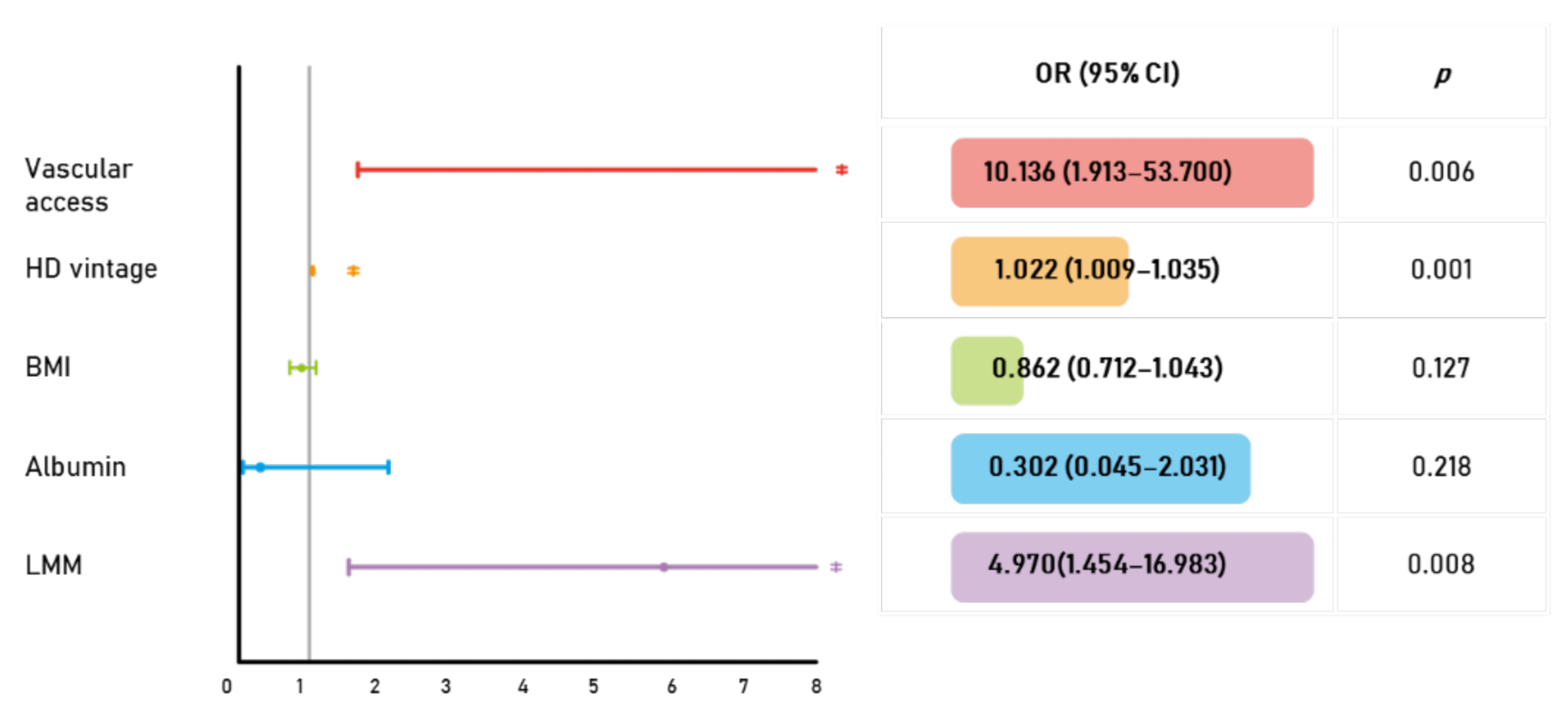
| Vascular access | 5.460 (1.312–22.722) | 0.020 |
| HD vintage | 1.016 (1.006–1.027) | 0.003 |
| UF volume | 1.140 (0.720–1.804) | 0.577 |
| Height | 0.996 (0.947–1.047) | 0.867 |
| Dry weight | 0.963 (0.921–1.006) | 0.093 |
| BMI | 0.842 (0.714–0.993) | 0.041 |
| spKt/V | 2.250 (0.537–9.426) | 0.267 |
| URR | 1.047 (0.963–1.138) | 0.285 |
| Hb | 0.995 (0.636–1.555) | 0.981 |
| Uric acid | 0.894 (0.685–1.169) | 0.414 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.987 (0.971–1.003) | 0.121 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.987 (0.969–1.006) | 0.188 |
| Triglyceride | 0.993 (0.986–1.001) | 0.087 |
| Albumin | 0.139 (0.030–0.651) | 0.012 |
| Ferritin | 0.996 (0.992–1.001) | 0.095 |
| CRP | 0.996 (0.957–1.037) | 0.848 |
| 25(OH) vitamin D | 0.994 (0.944–1.046) | 0.805 |
| Calcium | 1.115 (0.585–2.123) | 0.741 |
| Phosphorus | 1.050 (0.762–1.447) | 0.766 |
| iPTH | 1.001 (0.999–1.003) | 0.290 |
| Magnesium | 1.660 (0.529–5.208) | 0.385 |
| LMM | 3.562 (1.341–9.463) | 0.011 |
| Variables | Non-LMM | LMM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention (PTA or surgery), n (%) | 13 (32.5) | 17 (48.6) | 0.156 |
| Recurrent vascular access failure, n (%) | 5 (12.5) | 12 (34.3) | 0.025 |
| Number of interventions/year, median [IQR] | 0.00 [0.00, 0.18] | 0.00 [0.00, 0.30] | 0.042 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-h.; Choi, G.; Song, Y.; Yoon, H.; Jeong, H.M.; Gu, J.E.; Han, M.; Heo, J.; Yoo, J.-J.; Yoon, J.-w.; et al. Low Muscle Mass in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: Correlations with Vascular Calcification and Vascular Access Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163698
Kim S-h, Choi G, Song Y, Yoon H, Jeong HM, Gu JE, Han M, Heo J, Yoo J-J, Yoon J-w, et al. Low Muscle Mass in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: Correlations with Vascular Calcification and Vascular Access Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163698
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seok-hyung, Gwangho Choi, Youngjin Song, Hojung Yoon, Hae Min Jeong, Jae Eon Gu, Miyeun Han, Jongho Heo, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-woo Yoon, and et al. 2021. "Low Muscle Mass in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: Correlations with Vascular Calcification and Vascular Access Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163698
APA StyleKim, S.-h., Choi, G., Song, Y., Yoon, H., Jeong, H. M., Gu, J. E., Han, M., Heo, J., Yoo, J.-J., Yoon, J.-w., & Kim, H. (2021). Low Muscle Mass in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: Correlations with Vascular Calcification and Vascular Access Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163698






