Oesophageal pH-Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Validation of General Population Reference Values in Children with Chronic Neurological Impairments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance Protocol
2.3. Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
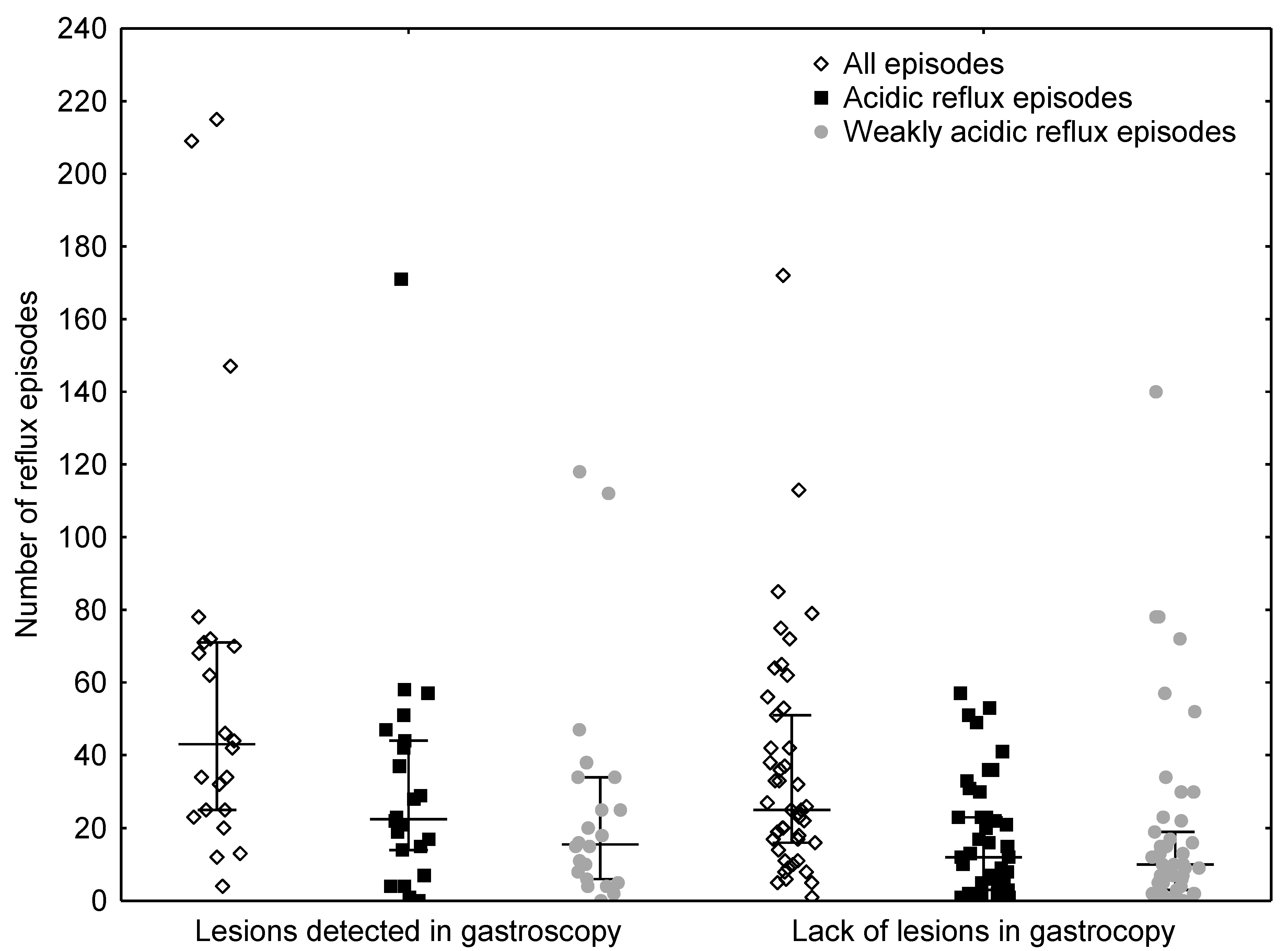
3.1. Comparison of Reflux Numbers
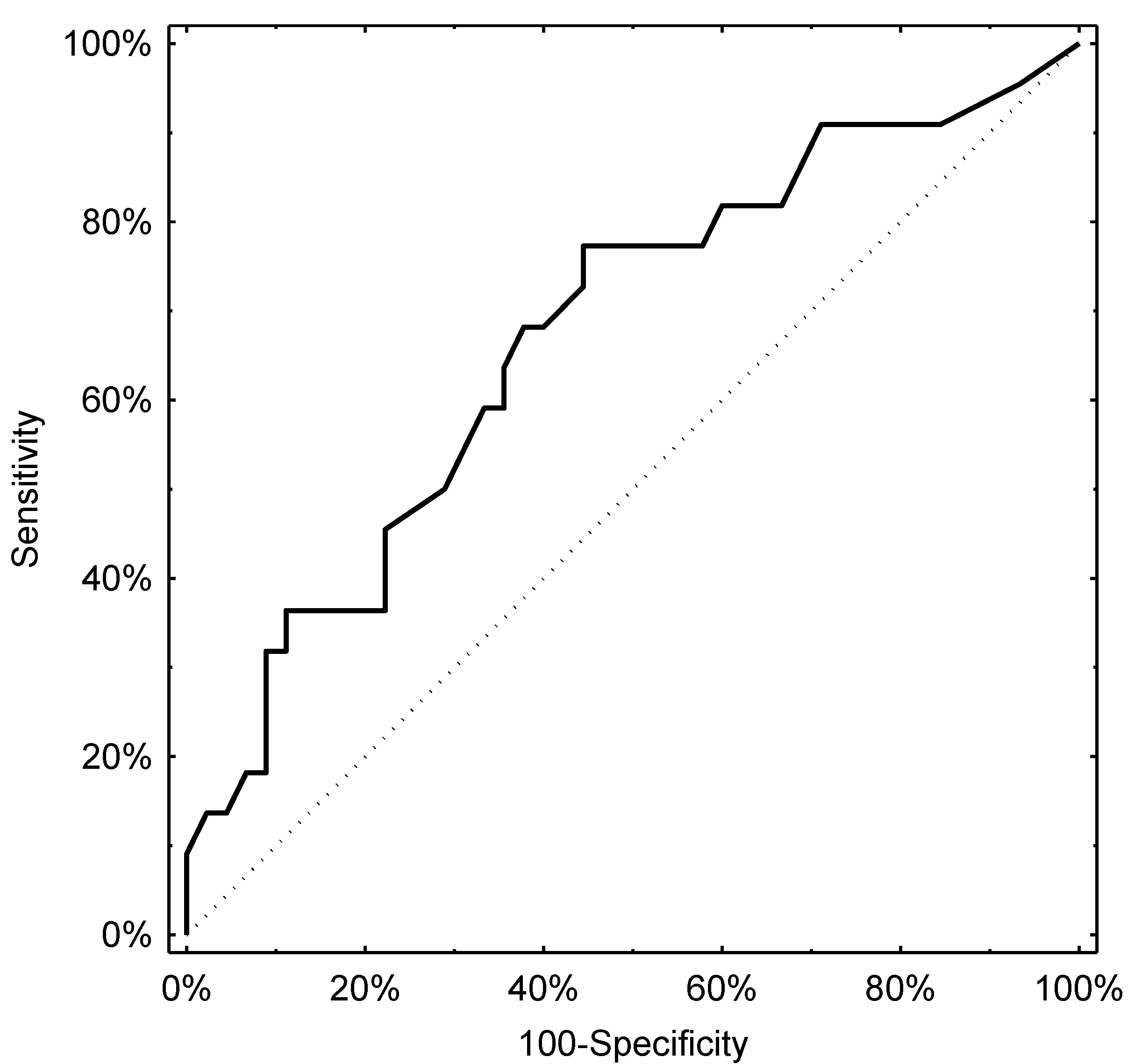
3.2. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Potential of pH-Impedance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosen, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; Singendonk, M.; Cabana, M.; DiLorenzo, C.; Gottrand, F.; Gupta, S.; Langendam, M.; Staiano, A.; Thapar, N.; et al. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 516–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, S.; Tutuian, R.; Sifrim, D.; Vela, M.; Wise, J.; Balaji, N.; Zhang, X.; Adhami, T.; Murray, J.; Peters, J.; et al. Twenty-four hour ambulatory simultaneous impedance and pH monitoring: A multicenter report of normal values from 60 healthy volunteers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silny, J. Intraluminal multiple electric impedance procedure for measurement of gastrointestinal motility. J. Gastrointest Motil. 1991, 3, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzl, T.G.; Benninga, M.A.; Loots, C.M.; Salvatore, S.; Vandenplas, Y. Indications, methodology, and interpretation of combined esophageal impedance-pH monitoring in children: European EURO-PIG Standard Protocol. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zerbib, F.; des Varannes, S.B.; Roman, S.; Pouderouxs, P.; Artigue, F.; Chaput, U.; Mion, F.; Caillol, F.; Verin, E.; Bommelaer, G.; et al. Normal values and day-to-day variability of 24-h ambulatory oesophageal impedance pH-monitoring in a Belgian-French cohort of healthy subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentilin, P.; Iritano, E.; Dulbecco, P.; Bilardi, C.; Savarino, E.; De Conca, S.; Parodi, A.; Reglioni, S.; Vigneri, S.; Savarino, V. Normal values of 24-h ambulatory intraluminal impedance combined with pH-metry in subjects eating a Mediterranean diet. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2006, 38, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalib, M.; Rawat, D.; Lindley, K.; Borrelli, O.; Perring, S.; Auth, M.K.H.; Thapar, N. BSPGHAN Motility Working Group position statement; Paediatric multichannel intraluminal pH impedance monitoring-indications, methods and interpretation. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilic, D.; Hankel, S.; Koerner-Rettberg, C.; Hamelmann, E.; Schmidt-Choudhury, A. The role of baseline impedance as a marker of mucosal integrity in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, M.; Cho, J.; Krishnan, U. Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH measurement in detecting gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, e98–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, S.; Yagi, M.; Ishii, S.; Asagiri, K.; Saikusa, N.; Hashizume, N.; Yoshida, M.; Masui, D.; Komatsuzaki, N.; Higashidate, N.; et al. A baseline impedance analysis in neurogically impaired children: A potent parameter for estimating the condition of esophageal mucosa. Neurogastroenetrol Motil. 2017, 29, e13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojsak, I.; Ivkoviċ, L.; Trbojeviċ, T.; Paviċ, I.; Jadrešin, O.; Mišak, Z.; Kolaček, S. The role of combined 24-h multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring in the evaluation of children with gastrointestinal symptoms suggesting gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Neurogastroenetrol Motil. 2016, 28, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; Walter, S.; Russell, D.; Wood, E.; Galuppi, B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1997, 39, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, C.T.; Byrne, W.J.; Ament, M.E.; Euler, A.R. Correlation of esophageal lengths in children with height: Application to the Tuttle test without prior esophageal manometry. J. Pediatr. 1979, 94, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, H.M.; Rosen, R.; Woodley, F.W.; Orsi, M.; Armas, D.; Faure, C.; Fortunato, J.; O’connor, J.; Skaggs, B.; Nurko, S. Esophageal impedance monitoring for gastroesophageal reflux. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sifrim, D.; Castell, D.; Dent, J.; Kahrilas, P. Gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring review and consensus report on detection and definition of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 2004, 53, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Rudolph, C.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Hassall, E.; Liptak, G.; Mazur, L.; Sondheimer, J.; Staiano, A.; Thomson, M.; Veereman-Wauters, G.; et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: Joint recommendations of the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 498–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, D.; Dent, J.; Reed, W.; Narielvala, F.; Mackinnon, M.; McCarthy, J.; Mitchell, B.; Beveridge, B.; Laurence, B.; Gibson, G. Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology 1988, 95, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://zscore.research.chop.edu/index.php. (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Romano, C.; Dipasquale, V.; Van Winckel, M.; Hulst, J.; Broekaert, I.; Bronsky, J.; Dall’Oglio, L.; Mis, N.F.; Hojsak, I.; Orel, R.; et al. Management of Gastrointestinal and Nutritional Problems in Children With Neurological Impairment: A Survey of Practice. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, e97–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, K.; Nielsen, R.G.; Kruse-Andersen, S.; Fenger, C.; Durup, J.; Husby, S. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and eosinophilic esophagitis in infants and children. A study of esophageal pH, multiple intraluminal impedance and endoscopic ultrasound. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 1029–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P.; Isoldi, S.; Mallardo, S.; Papoff, P.; Rossetti, D.; Dilillo, A.; Oliva, S. Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring is helpful in managing children with suspected gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2018, 50, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Buono, R.; Wenzl, T.G.; Rawat, D.; Thomson, M. Acid and nonacid gastro-oesophageal reflux in neurologically impaired children: Investigation with the multiple intraluminal impedance procedure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toporowska-Kowalska, E.; Gębora-Kowalska, B.; Jabłoński, J.; Fendler, W.; Wąsowska-Królikowska, K. Influence of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy on gastro-oesophageal reflux evaluated by multiple intraluminal impedance in children with neurological impairment. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, H.; Tazuke, Y.; Soh, H.; Usui, N.; Okuyama, H. Characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux in pediatric patients with neurological impairment. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2017, 33, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, S.; Yagi, M.; Ishii, S.; Asagiri, K.; Saikusa, N.; Hashizume, N.; Yoshida, M.; Masiu, D.; Higashidate, N.; Sakamoto, S.; et al. Analyses of the relationship between a ‘number of reflux episodes’ exceeding 70 and the pH index in neurologically impaired children by evaluating esophageal combined pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance measurements. Scand. J. Gastroenetrol. 2018, 53, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Hauser, B.; Devreker, T.; Arrigo, S.; Marino, P.; Citro, C.; Salvatoni, A.; Vandenplas, Y. Esophageal impedance and esophagitis in children: Any correlation? J. Pediatr. Gatsroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresi, F.; Cester, E.A.; Salvatore, S.; De Rose, D.U.; Ripepi, A.; Magistà, A.M.; Fontana, C.; Maggiora, E.; Coscia, A.; Francavilla, R.; et al. Multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring: A step towards pediatric reference values. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilic, D.; Fröhlich, T.; Nöh, F.; Pappas, A.; Schmidt-Choudhury, A.; Köhler, H.; Skopnik, H.; Wenzl, T.G. Detection of gastroesophageal reflux in children using combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH measurement: Data from the German Pediatric Impedance Group. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukahori, S.; Kawahara, H.; Oyama, T.; Saito, T.; Shimono, R.; Tanaka, A.; Noda, T.; Hatori, R.; Fujino, J.; Yagi, M. Japanese Pediatric Impedance Working Group (Japanese-PIG). Standard protocol devised by the Japanese Pediatric Impedance Working Group for combined multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH measurements in children. Surg. Today 2020, 50, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Savarino, E.; Zerbib, F.; Mion, F.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Vaezi, M.; Sifrim, D.; Fox, M.R.; Vela, M.F.; et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut 2018, 67, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopert, R.; Liehr, R.M.; Emde, C.; Riecken, E.O. Reduction of 24 hour gastric acidity by different dietary regimenes: A randomized controlled study in healthy volunteers. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 1989, 13, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Kawashima, Y.; Kondo, A.; Chikumaru, Y.; Matsui, A.; Nagata, I.; Ohno, K. Dysphagia-gastroesophageal reflux complex: Complications due to dysfunction of solitary tract nucleus-mediated vago-vagal reflex. Neuropediatrics 2006, 37, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Koh, H.; Lee, J.S. Gastroesophageal reflux in neurologically impaired children: What are the risk factors? Gut Liver 2017, 11, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farré, R.; Blondeau, K.; Clement, D.; Vicario, M.; Cardozo, L.; Vieth, M.; Mertens, V.; Pauwels, A.; Silny, J.; Jimenez, M.; et al. Evaluation of oesophageal mucosa integrity by the intraluminal impedance technique. Gut 2011, 60, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, S.; Salvatoni, A.; Ummarino, D.; Ghanma, A.; Van der Pol, R.; Rongen, A.; Fuoti, M.; Meneghin, F.; Benninga, M.A.; Vandenplas, Y. Low mean impedance in 24-hour tracings and esophagitis in children: A strong connection. Dis. Esophagus. 2016, 29, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, O.; Salvatore, S.; Mancini, V.; Ribolsi, M.; Gentile, M.; Bizzarri, B.; Cicala, M.; Lindley, K.J.; De’angelis, G.L. Relationship between baseline impedance levels and esophageal mucosal integrity in children with erosive and non-erosive reflux disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 828–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, K.; Nielsen, R.G.; Markoew, S.; Kruse-Andersen, S.; Husby, S. Reproducibility of 24-Hour Combined Multiple Intraluminal Impedance (MII) and pH Measurements in Infants and Children. Evaluation of a Diagnostic Procedure for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| N of Patients | % of Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Diagnosis | ||
| Cerebral palsy | 37 | 55.2 |
| Ceroid lipofuscinosis | 5 | 7.5 |
| Encephalopathy following brain tumour | 2 | 3.0 |
| Encephalopathy congenital | 12 | 17.9 |
| Encephalopathy acquired: post-traumatic, post-inflammatory | 3 | 4.5 |
| Aicardi syndrome | 1 | 1.5 |
| Neurodegenerative disorders due to congenital metabolic defects | 7 | 10.4 |
| Feeding | ||
| Orally fed | 38 | 56.7 |
| Nasogastric tube | 29 | 43.3 |
| Degree of Gross Motor Disability (GMFCS) | ||
| Level IV | 60 | 89.6 |
| Level V | 7 | 10.4 |
| Nutritional Status | ||
| Severe undernutrition (BMI Z-score < −3) | 37 | 55.2 |
| Undernutrition (BMI Z-score > −3 < −1 | 22 | 32.8 |
| Normal nutrition (BMI Z-score 0) | 6 | 9.0 |
| Overnutrition (BMI Z-score > 3) | 2 | 3.0 |
| Indices of MII-pH | Number (Median; Range) |
|---|---|
| reflux events | 2981 (32; 1–215) |
| acidic reflux events | 1437 (15; 0–171) |
| non-acid reflux events: | 1544 (2; 0–140) |
| weakly acidic reflux events | 1432 (11; 0–140) |
| weakly alkaline reflux events | 112 (0; 0–45) |
| Index (Median; Range) | |
| Acid reflux index | 5.75% (2.8%; 0–29.1%) |
| Bolus exposure index | 2.74% (1.5%; 0.2–18.9%) |
| Time (Median; Range) | |
| Mean acid clearance time | 334.36 s (126 s; 0–7177 s) |
| Mean bolus clearance time | 14.39 s (12 s; 2–62 s) |
| Range | Expected | Total | Acidic Reflux | Weakly Acidic Reflux | Alkaline Reflux | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| ≤25% | 16.75 | 25.00 | 26 | 38.81 | 26 | 38.81 | 17 | 25.37 | 46 | 68.66 |
| 25–50% | 16.75 | 25.00 | 18 | 26.87 | 15 | 22.39 | 16 | 23.88 | 13 | 19.40 |
| 50–75% | 16.75 | 25.00 | 5 | 7.46 | 11 | 16.42 | 12 | 17.91 | 5 | 7.46 |
| 75–95% | 13.40 | 20.00 | 9 | 13.43 | 8 | 11.94 | 9 | 13.43 | 1 | 1.49 |
| ≥95% | 3.35 | 5.00 | 9 | 13.43 | 7 | 10.45 | 13 | 19.40 | 2 | 2.99 |
| p level | reference | 0.0160 | 0.1135 | 0.0965 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Total | Acidic Reflux | Weakly Acidic Reflux | Alkaline Reflux | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value range | No lesions | Lesions present | No lesions | Lesions present | No lesions | Lesions present | No lesions | Lesions present |
| ≤25% | 21 (46.67%) | 5 (22.73%) | 21 (46.67%) | 5 (22.73%) | 13 (28.89%) | 4 (18.18%) | 31 (68.89%) | 15 (68.18%) |
| 25–50% | 12 (26.67%) | 6 (27.27%) | 10 (22.22%) | 5 (22.73%) | 12 (26.67%) | 4 (18.18%) | 10 (22.22%) | 3 (13.64%) |
| 50–75% | 3 (6.67%) | 2 (9.09%) | 7 (15.56%) | 4 (18.18%) | 8 (17.78%) | 4 (18.18%) | 3 (6.67%) | 2 (9.09%) |
| 75–95% | 4 (8.89%) | 5 (22.73%) | 4 (8.89%) | 4 (18.18%) | 5 (11.11%) | 4 (18.18%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (4.55%) |
| ≥95% | 5 (11.11%) | 4 (18.18%) | 3 (6.67%) | 4 (18.18%) | 7 (15.56%) | 6 (27.27%) | 1 (2.22%) | 1 (4.55%) |
| p-value | 0.2917 | 0.2684 | 0.6075 | 0.5593 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plocek, A.; Gębora-Kowalska, B.; Fendler, W.; Toporowska-Kowalska, E. Oesophageal pH-Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Validation of General Population Reference Values in Children with Chronic Neurological Impairments. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153351
Plocek A, Gębora-Kowalska B, Fendler W, Toporowska-Kowalska E. Oesophageal pH-Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Validation of General Population Reference Values in Children with Chronic Neurological Impairments. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(15):3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153351
Chicago/Turabian StylePlocek, Anna, Beata Gębora-Kowalska, Wojciech Fendler, and Ewa Toporowska-Kowalska. 2021. "Oesophageal pH-Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Validation of General Population Reference Values in Children with Chronic Neurological Impairments" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 15: 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153351
APA StylePlocek, A., Gębora-Kowalska, B., Fendler, W., & Toporowska-Kowalska, E. (2021). Oesophageal pH-Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Validation of General Population Reference Values in Children with Chronic Neurological Impairments. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(15), 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153351





