Complement Factor C5a Inhibits Apoptosis of Neutrophils—A Mechanism in Polytrauma?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Neutrophil Isolation for In Vitro Characterization
2.3. Neutrophil Cultivation and Induction of Apoptosis
2.4. Quantification of Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
2.5. PMN Surface FasR and FasL Expression
2.6. PMN Surface C3aR and C5aR1 Expression
2.7. Serum FasL and sFasR ELISA
2.8. Caspase 3/7 Activity Quantification
2.9. Apoptosis Array
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
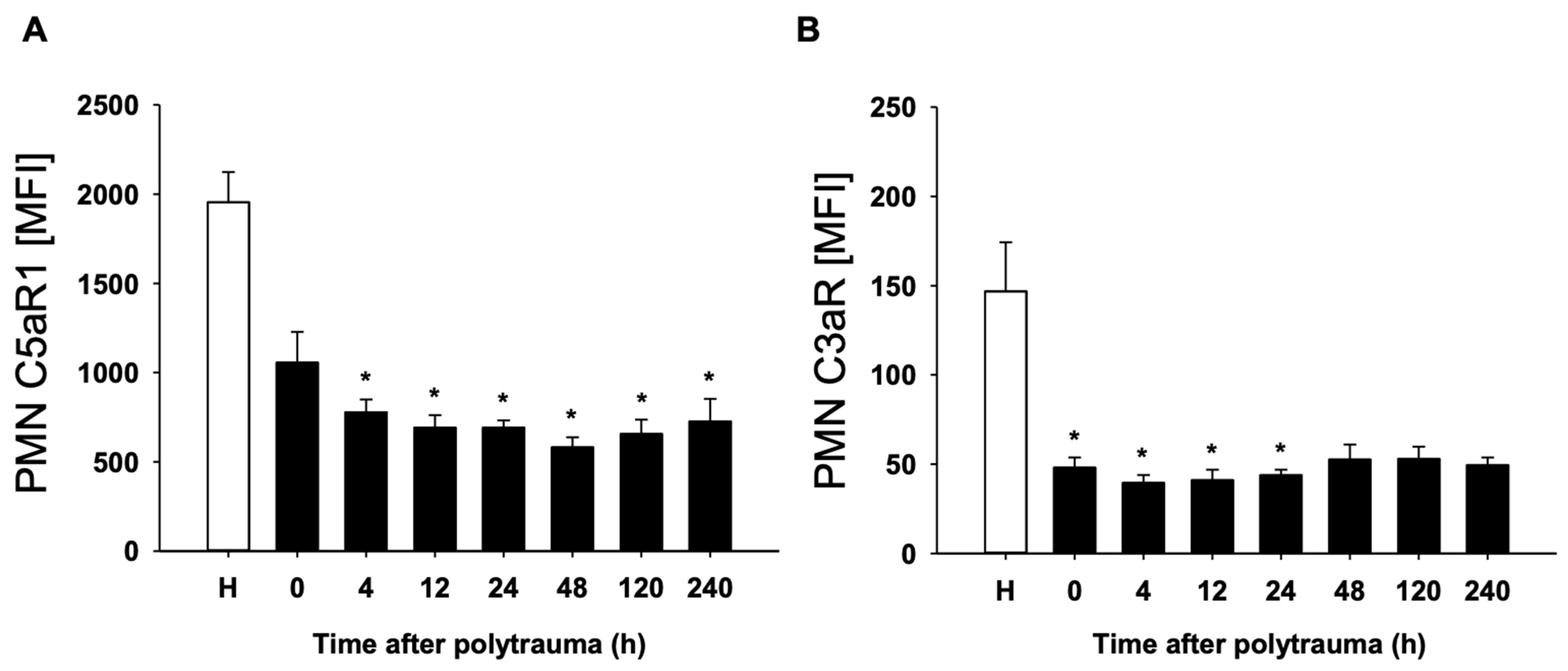
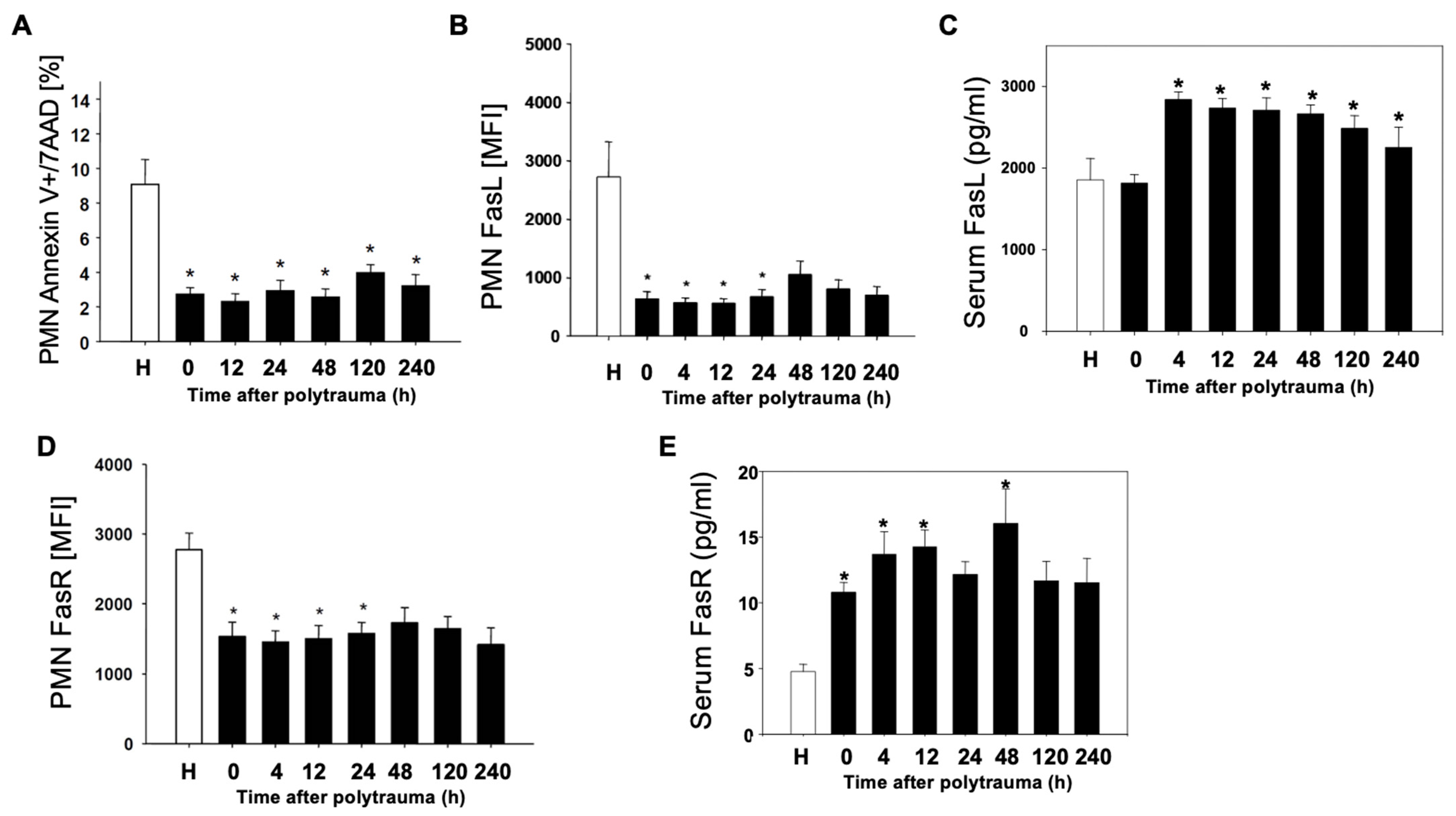
3.1. Decreased Apoptosis of PMN and Alterations of the FasL–FasR–Axis after Polytrauma
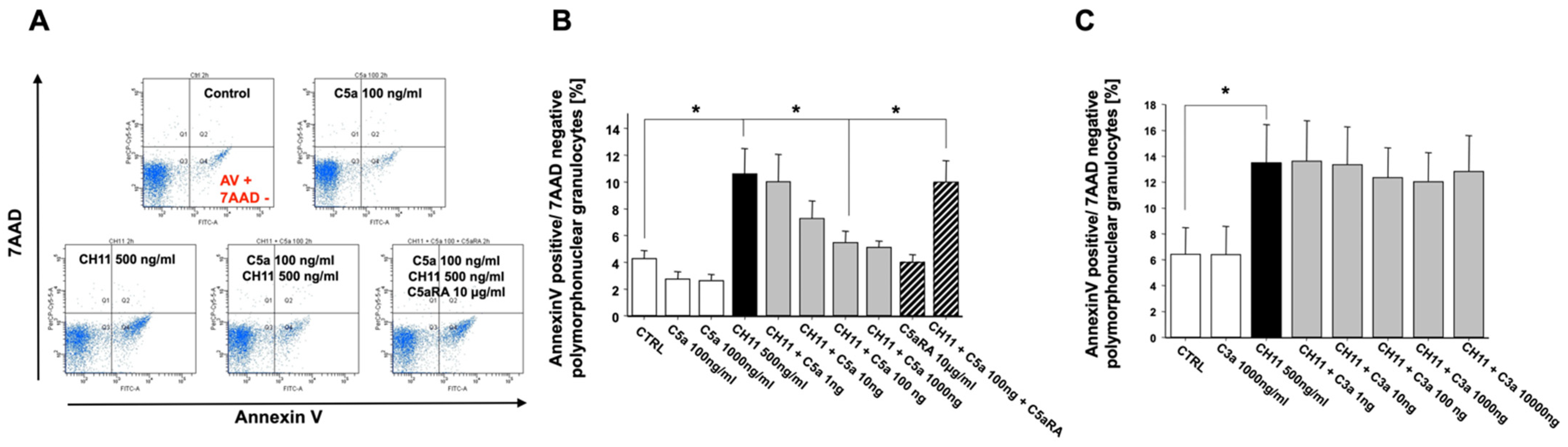
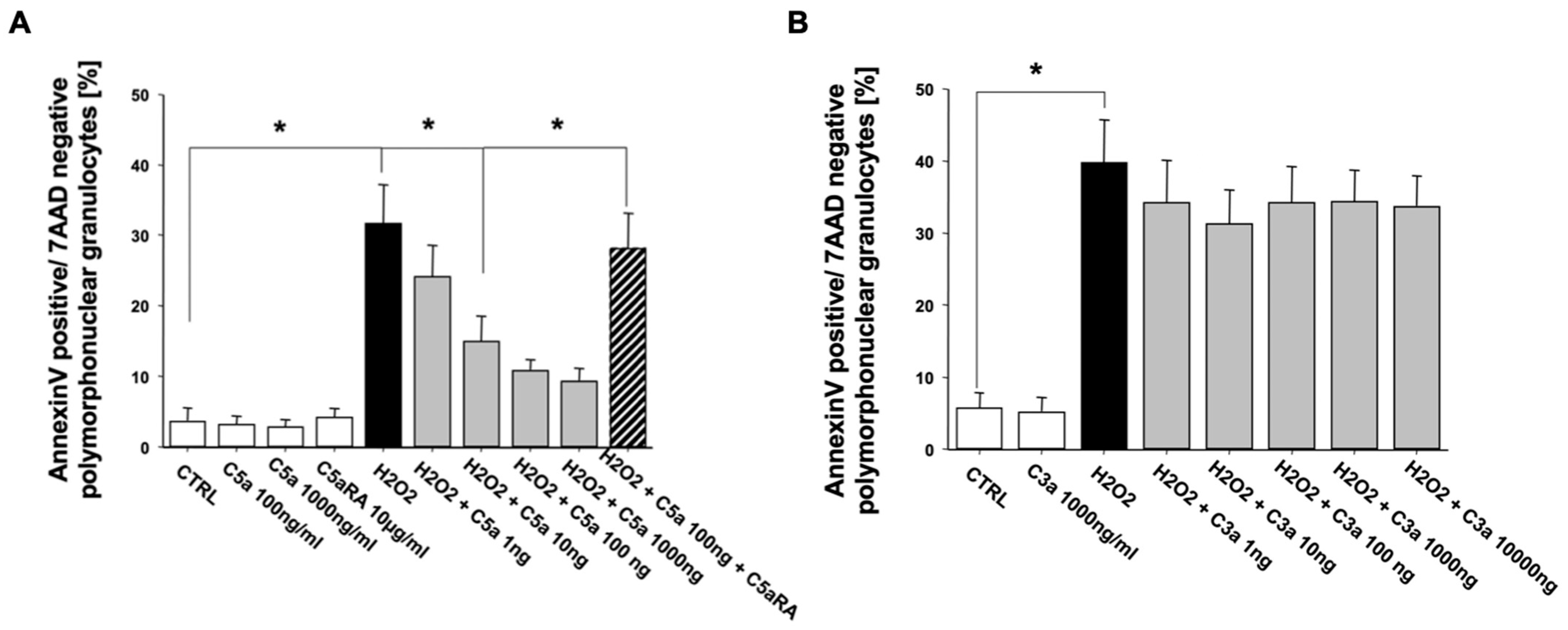
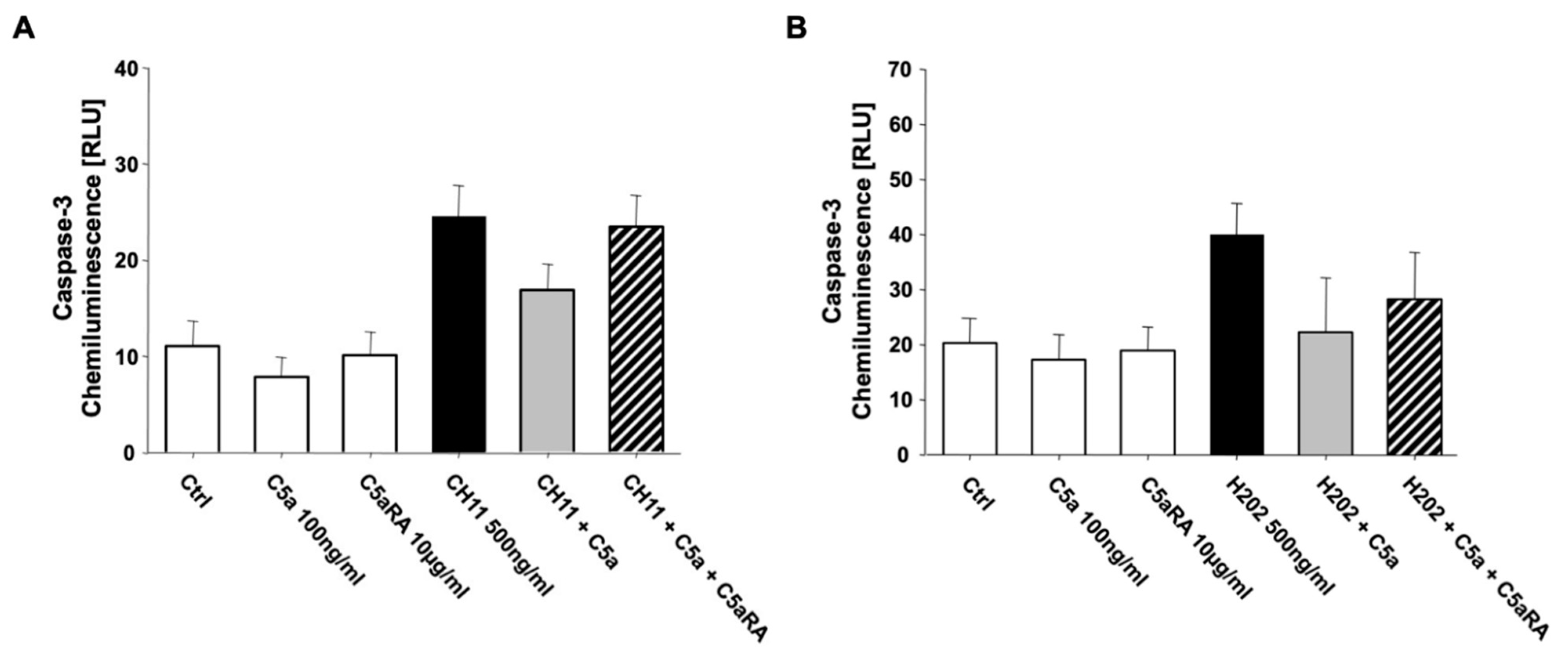
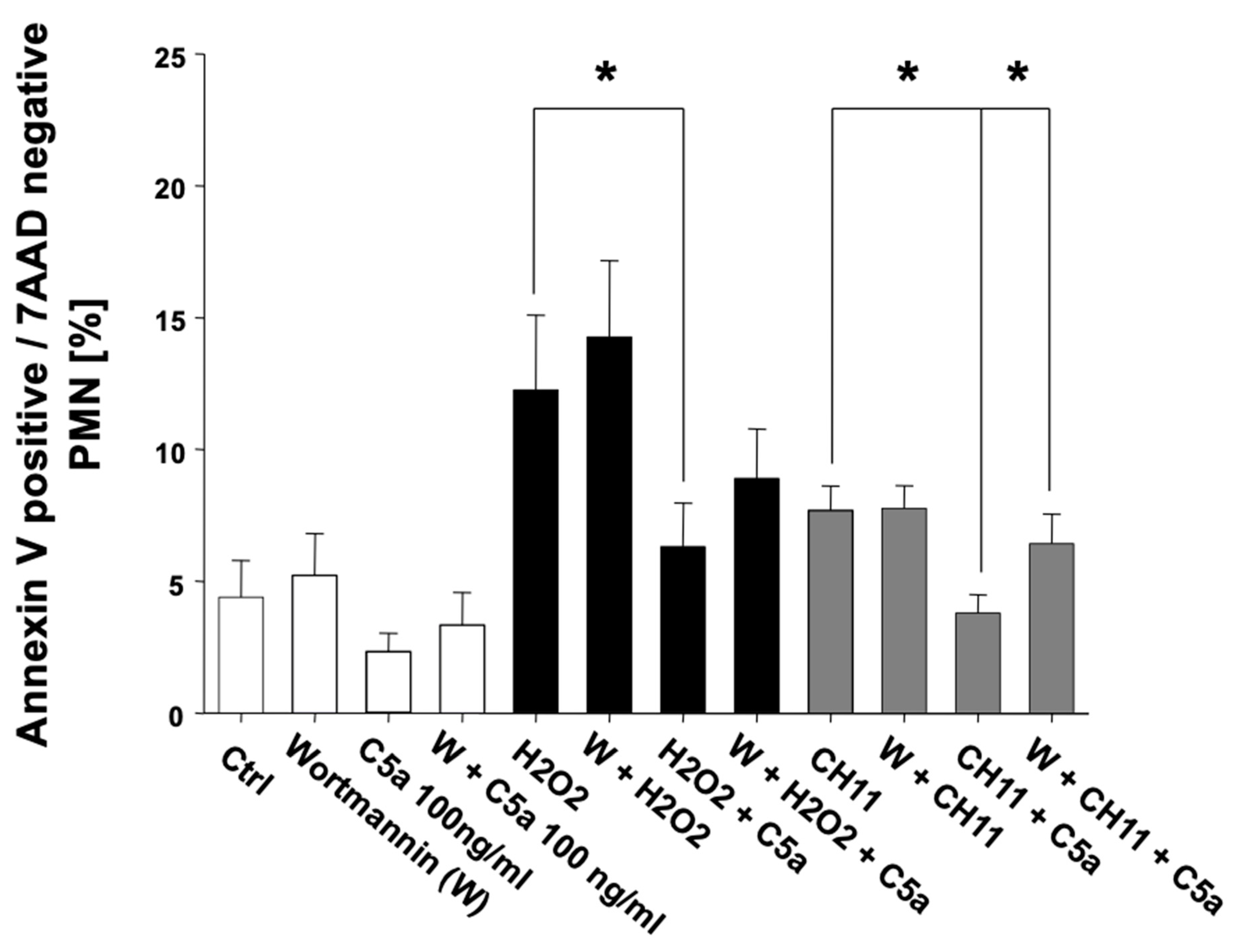
3.2. Anaphylatoxin C5a Inhibits PMN Apoptosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kohl, J. The role of complement in danger sensing and transmission. Immunol. Res. 2006, 34, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Lambris, J.; Ward, P.A. Innate immune responses to trauma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Karl, I.E. The Pathophysiology and Treatment of Sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrnthaller, C.; Ignatius, A.; Gebhard, F.; Huber-Lang, M. New Insights of an Old Defense System: Structure, Function, and Clinical Relevance of the Complement System. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.S.; Rittirsch, D.; Neff, T.A.; McGuire, S.R.; Lambris, J.; Warner, R.L.; Flierl, M.A.; Hoesel, L.M.; et al. Generation of C5a in the absence of C3: A new complement activation pathway. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecke, F.; Schmidt, U.; Kola, A.; Bautsch, W.; Klos, A.; Koehl, J. Circulating complement proteins in multiple trauma patients-Correlation with injury severity, development of sepsis, and outcome. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 25, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, J.; Hugli, T.E.; Smedegård, G. Microvascular effects of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, P.A. The dark side of C5a in sepsis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, W.R. Serum Complement Levels in Bacteremia Due to Gram-Negative Organisms. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973, 288, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, P.H. CD95’s deadly mission in the immune system. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 407, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Golstein, P. The Fas death factor. Science 1995, 267, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, S.J.; Wei, M.C.; Saito, M.; Weiler, S.; Oh, K.J.; Schlesinger, P.H. Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID, which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegezdi, E.; Fitzgerald, U.; Samali, A. Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: The story so far. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1010, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Zallen, G.; Johnson, J.L.; Gabriel, J.; Offner, P.J.; Silliman, C.C. Neutrophils are primed for cytotoxicity and resist apoptosis in injured patients at risk for multiple organ failure. Surgery 1999, 126, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.F.; Watson, R.W.G.; Parodo, J.; Evans, D.; Foster, D.; Steinberg, M.; Rotstein, O.D.; Marshall, J.C. Dysregulated Expression of Neutrophil Apoptosis in the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. Arch. Surg. 1997, 132, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunel-Görgülü, A.; Kirichevska, T.; Lögters, T.; Windolf, J.; Flohe, S. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Delayed Apoptosis in Neutrophils from Multiple Trauma Patients with and without Sepsis. Mol. Med. 2011, 18, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, M.; Denk, S.; Kalbitz, M.; Huber-Lang, M. Granzyme B: A New Crossroad of Complement and Apoptosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 946, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.-F.; Sun, L.; Gao, H.; Shi, K.X.; Rittirsch, D.; Sarma, V.J.; Zetoune, F.S.; Ward, P.A. In vivo regulation of neutrophil apoptosis by C5a during sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, A.-M.; Martin, M.; Flierl, M.A.; Rittirsch, D.; Helm, M.; Lampl, L.; Bruckner, U.; Stahl, G.; Blom, A.; Perl, M.; et al. Early Complementopathy after Multiple Injuries in Humans. Shock 2012, 37, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, S.; Neher, M.D.; Messerer, D.A.; Wiegner, R.; Nilsson, B.; Rittirsch, D.; Nilsson-Ekdahl, K.; Weckbach, S.; Ignatius, A.; Kalbitz, M.; et al. Complement C5a Functions as a Master Switch for the pH Balance in Neutrophils Exerting Fundamental Immunometa-bolic Effects. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4846–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnewehr, H.; Rittirsch, D.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.; Flierl, M.A.; Perl, M.; Denk, S.; Weiss, M.; Schneider, M.E.; Monk, P.; et al. Changes and Regulation of the C5a Receptor on Neutrophils during Septic Shock in Humans. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunel-Görgülü, A.; Zörnig, M.; Lögters, T.; Altrichter, J.; Rabenhorst, U.; Cinatl, J.; Windolf, J.; Scholz, M. Mcl-1-Mediated Impairment of the Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathway in Circulating Neutrophils from Critically Ill Patients Can Be Overcome by Fas Stimulation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6198–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckbach, S.; Hohmann, C.; Braumueller, S.; Denk, S.; Klohs, B.; Stahel, P.F.; Gebhard, F.; Huber-Lang, M.S.; Perl, M. Inflammatory and apoptotic alterations in serum and injured tissue after experimental polytrauma in mice: Distinct early response compared with single trauma or “double-hit” injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013, 74, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabhai, T.; Peter, C.; Bär, A.-K.; Windolf, J.; Relja, B.; Wesselborg, S.; Wahlers, T.; Paunel-Görgülü, A. Serum α-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) antagonizes intrinsic apoptosis induction in neutrophils from patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mica, L.; Härter, L.; Trentz, O.; Keel, M. Endotoxin reduces CD95-induced neutrophil apoptosis by cIAP-2-mediated caspase-3 degradation. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2004, 199, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianayagam, M.C.; Balakrishnan, V.; King, A.J.; Pereira, B.J.; Jaber, B.L. C5a delays apoptosis of human neutrophils by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-signaling pathway. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perianayagam, M.C.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Pereira, B.J.G.; Jaber, B.L. C5a delays apoptosis of human neutrophils via an extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Bad-mediated signalling pathway. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 34, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianayagam, M.C.; Madias, N.E.; Pereira, B.J.G.; Jaber, B.L. CREB transcription factor modulates Bcl2 transcription in response to C5a in HL-60-derived neutrophils. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 36, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Lang, M.S.; Ignatius, A.; Köhl, J.; Mannes, M.; Braun, C.K. Complement in trauma—Traumatised complement? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2863–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elward, K.; Griffiths, M.; Mizuno, M.; Harris, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Morgan, P.; Gasque, P. CD46 Plays a Key Role in Tailoring Innate Immune Recognition of Apoptotic and Necrotic Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36342–36354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.-F.; Huber-Lang, M.; Wang, X.; Sarma, V.; Padgaonkar, V.A.; Craig, R.A.; Riedemann, N.C.; McClintock, S.D.; Hlaing, T.; Shi, M.M.; et al. Protective effects of anti-C5a in sepsis-induced thymocyte apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brint, E.; O’Callaghan, G.; Houston, A. Life in the Fas lane: Differential outcomes of Fas signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4085–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messer, M.P.; Kellermann, P.; Weber, S.J.; Hohmann, C.; Denk, S.; Klohs, B.; Schultze, A.; Braumüller, S.; Huber-Lang, M.S.; Perl, M. Silencing of Fas, Fas-Associated via Death Domain, or Caspase 3 Differentially Affects Lung Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Development of Trauma-Induced Septic Acute Lung Injury. Shock 2013, 39, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunel-Görgülü, A.; Flohé, S.; Scholz, M.; Windolf, J.; Lögters, T. Increased serum soluble Fas after major trauma is associated with delayed neutrophil apoptosis and development of sepsis. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiura, H.; Nonaka, H.; Revollo, I.S.; Semba, U.; Li, Y.; Ota, Y.; Irie, A.; Harada, K.; Kehrl, J.; Yamamoto, T. Pro- and anti-apoptotic dual functions of the C5a receptor: Involvement of regulator of G protein signaling 3 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wardle, D.J.; Burgon, J.; Sabroe, I.; Bingle, C.D.; Whyte, M.K.B.; Renshaw, S.A. Effective Caspase Inhibition Blocks Neutrophil Apoptosis and Reveals Mcl-1 as Both a Regulator and a Target of Neutrophil Caspase Activation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrann, C.D.; Tabriz, N.A.; Barkhausen, T.; Klos, A.; van Griensven, M.; Pape, H.C.; Kendoff, D.O.; Guo, R.; Ward, P.A.; Krettek, C.; et al. The Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling Pathway Exerts Protective Effects during Sepsis by Controlling C5a-Mediated Activation of Innate Immune Functions. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5940–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Reis, E.S.; Lambris, J.D. Complement in disease: A defence system turning offensive. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.C.; Brittan, M.; Wilkinson, T.S.; McAuley, D.F.; Antonelli, J.; McCulloch, C.; Barr, L.C.; McDonald, N.A.; Dhaliwal, K.; Jones, R.O.; et al. C5a-mediated neutrophil dysfunction is RhoA-dependent and predicts infection in critically ill patients. Blood 2011, 117, 5178–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Sarma, J.V.; Rittirsch, D.; Schreiber, H.; Weiss, M.; Flierl, M.; Younkin, E.; Schneider, M.; Suger-Wiedeck, H.; Gebhard, F.; et al. Changes in the Novel Orphan, C5a Receptor (C5L2), during Experimental Sepsis and Sepsis in Humans. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Pan, J.; Mamtilahun, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Venkatesh, A.; Shi, R.; Tu, X.; Jin, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. Microglia exacerbate white matter injury via complement C3/C3aR pathway after hypoperfusion. Theranostics 2020, 10, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ehrnthaller, C.; Braumüller, S.; Kellermann, S.; Gebhard, F.; Perl, M.; Huber-Lang, M. Complement Factor C5a Inhibits Apoptosis of Neutrophils—A Mechanism in Polytrauma? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143157
Ehrnthaller C, Braumüller S, Kellermann S, Gebhard F, Perl M, Huber-Lang M. Complement Factor C5a Inhibits Apoptosis of Neutrophils—A Mechanism in Polytrauma? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143157
Chicago/Turabian StyleEhrnthaller, Christian, Sonja Braumüller, Stephanie Kellermann, Florian Gebhard, Mario Perl, and Markus Huber-Lang. 2021. "Complement Factor C5a Inhibits Apoptosis of Neutrophils—A Mechanism in Polytrauma?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143157
APA StyleEhrnthaller, C., Braumüller, S., Kellermann, S., Gebhard, F., Perl, M., & Huber-Lang, M. (2021). Complement Factor C5a Inhibits Apoptosis of Neutrophils—A Mechanism in Polytrauma? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143157





