Sleep Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
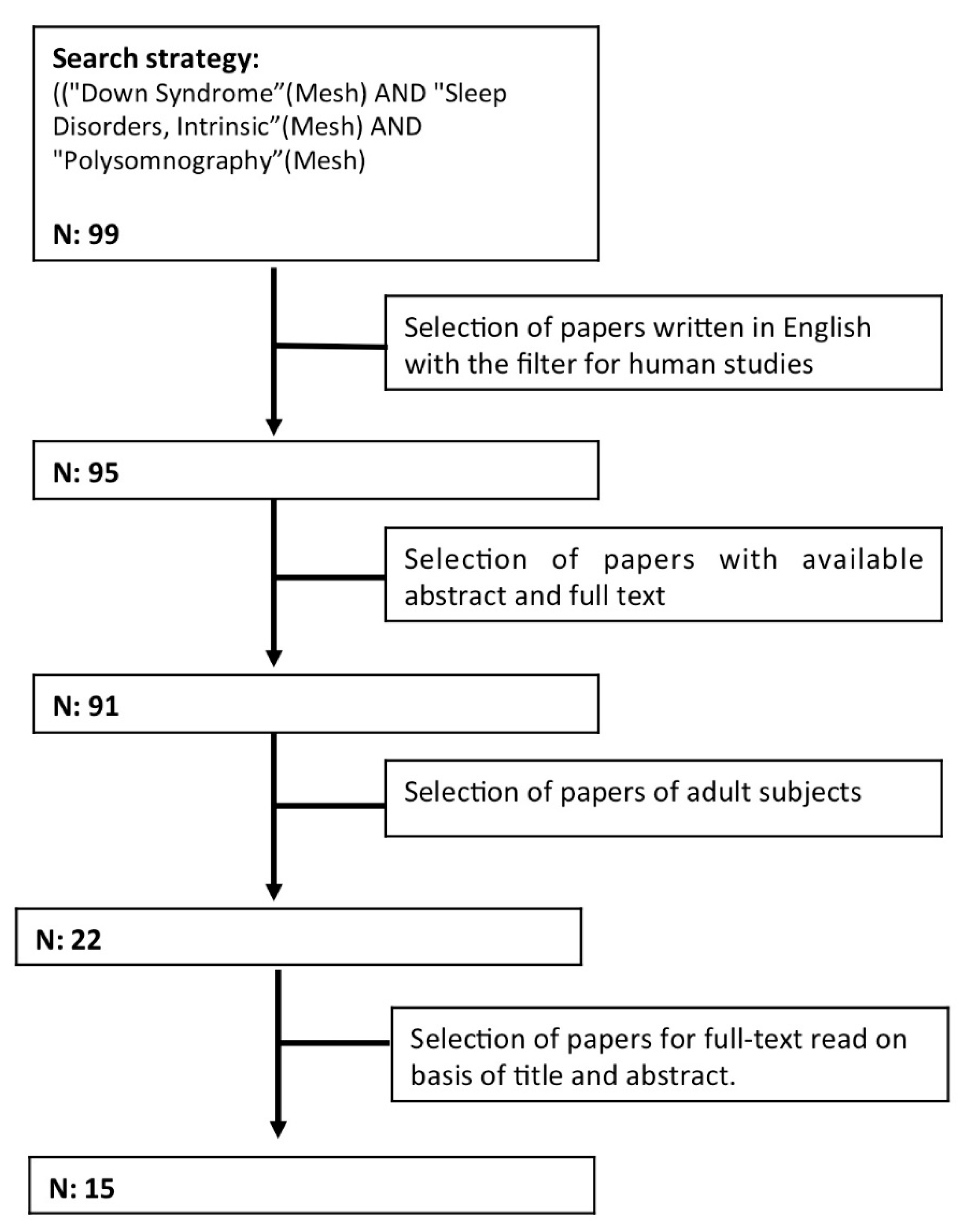
2. Methodology
- Insomnia and behavioral sleep disturbances.
- Sleep breathing disorders.
- Sleep movement disorders.
3. Sleep Disorders
3.1. Insomnia and Behavioral Sleep Disturbances
3.1.1. Diagnosis
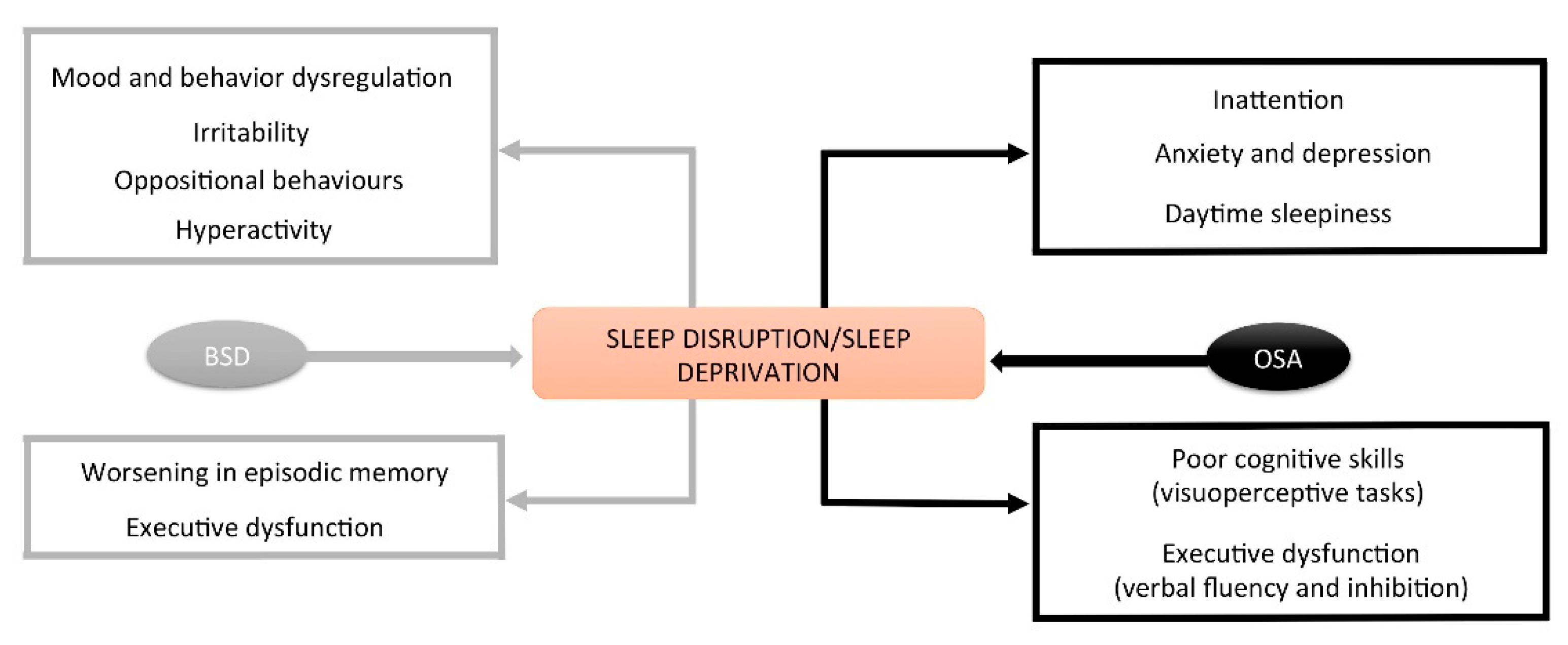
3.1.2. Consequences
3.1.3. Treatment
3.2. Sleep Breathing Disorders
3.2.1. Diagnosis
3.2.2. Treatment
3.2.3. Consequences of OSA
Cognitive
Cardiovascular
3.3. Sleep Movement Disorders
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmire, C.A.; Magyar, C.I.; Connolly, H.V.; Fernandez, I.D.; Van Wijngaarden, E. High Prevalence of Sleep Disorders and Associated Comorbidities in a Community Sample of Children with Down Syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stores, R.J. Sleep Problems in Adults with Down Syndrome and Their Family Carers. J. Appl. Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2019, 32, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.S. Health care management of adults with Down syndrome. Am. Fam. Physician 2001, 64, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.; McCaughey, E.; Annaz, D.; Hill, C.M. Sleep Problems in a Down Syndrome Population. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 94, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, A.J. Sleep Problems and Associated Comorbidities among Adults with Down Syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2016, 60, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stores, G.; Stores, R. Sleep Disorders and Their Clinical Significance in Children with Down Syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 55, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esbensen, A.J.; Hoffman, E.K. Reliability of Parent Report Measures of Sleep in Children with Down Syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2016, 61, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittles, A.H.; Glasson, E.J. Clinical, Social, and Ethical Implications of Changing Life Expectancy in Down Syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 46, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, G.T.; Chicoine, B.; Bulova, P.; Stephens, M.; Hart, S.; Crissman, B.; Videlefsky, A.; Myers, K.; Roizen, N.; Esbensen, A.; et al. Co-Occurring Medical Conditions in Adults with Down Syndrome: A Systematic Review toward the Development of Health Care Guidelines. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 176, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, G.; Wille, M.; Hemels, M.E. Short- and Long-Term Health Consequences of Sleep Disruption. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 2017, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortea, J.; Vilaplana, E.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Benejam, B.; Videla, L.; Barroeta, I.; Fernández, S.; Altuna-Azkargorta, M.; Pegueroles, J.; Montal, V.; et al. Clinical and Biomarker Changes of Alzheimer’s Disease in Adults with Down Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemann, D.; Baglioni, C.; Bassetti, C.; Bjorvatn, B.; Groselj, L.D.; Ellis, J.G.; Espie, C.A.; Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Gjerstad, M.; Gonçalves, M.; et al. European Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Insomnia. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 26, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedernaes, J.; Osorio, R.S.; Varga, A.W.; Kam, K.; Schiöth, H.B.; Benedict, C. Candidate Mechanisms Underlying the Association between Sleep-Wake Disruptions and Alzheimer’s Disease. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 31, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez, S.; Videla, L.; Romero, S.; Benejam, B.; Clos, S.; Fernández, S.; Martínez, M.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Antonijoan, R.M.; Mayos, M.; et al. Prevalence of Sleep Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome: A Comparative Study of Self-Reported, Actigraphic, and Polysomnographic Findings. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, G.; Galanopoulou, C.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Karapetsas, A.; Molyvdas, P. Cognitive Status in Down Syndrome Individuals with Sleep Disordered Breathing Deficits (SDB). Brain Cogn. 2002, 50, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta, O.; Barbaro, M.P.F.; Giliberti, T.; Caratozzolo, G.; Cagnazzo, M.; Scarpelli, F.; Nocerino, M. Sleep Related Breathing Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome. Down Syndr. Res. Pr. 2003, 8, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trois, M.S.; Capone, G.T.; Lutz, J.A.; Melendres, M.C.; Schwartz, A.R.; Collop, N.A.; Marcus, C.L. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults with Down Syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2009, 15, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-C.; Spanò, G.; Edgin, J. The Impact of Sleep Disruption on Executive Function in Down Syndrome. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.A. Obstructivesleep Apnoea/Hypopnea Syndrome in Adults with Down Syndrome. Breathe 2016, 12, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornacchia, M.; Sethness, J.; Alapat, P.; Lin, Y.-H.; Peacock, C. The Prevalence of OSA Among an Adult Population with Down Syndrome Referred to a Medical Clinic. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 124, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, P.; Soriano, J.B.; Aldave, B.; Zamora, E.; Acosta, C.; Erro, M.; Riolobos, C.L.; Ramos, M.I.; Moldenhauer, F.; Ancochea, J. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults with Down Syndrome. Am. J. Med Genet. Part A 2020, 182, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.A.; Amorim, F.F.; Santana, L.A.; Almeida, K.J.Q.; Santana, A.N.C.; Neves, F.A.R. STOP-Bang Question-Naire Should be Used in All Adults with Down Syndrome to Screen Formoderate to Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.A.; Fairley, D.M.; Williams, L.J.; Spanò, G.; Cooper, S.-A.; Riha, R.L. Prospective Trial of CPAP in Community-Dwelling Adults with Down Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cody, K.A.; Piro-Gambetti, B.; Zammit, M.D.; Christian, B.T.; Handen, B.L.; Klunk, W.E.; Zaman, S.; Johnson, S.C.; Plante, D.T.; Hartley, S.L. Association of Sleep with Cognition and Beta Amyloid Accumulation in Adults with Down Syndrome. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 93, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Startin, C.M.; D’Souza, H.; Ball, G.; Hamburg, S.; Hithersay, R.; Hughes, K.M.O.; Massand, E.; Karmiloff-Smith, A.; Thomas, M.S.C.; Consortium, L.; et al. Health Comorbidities and Cognitive Abilities Across the Lifespan in Down Syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, L.C.; Phillips, N.N.; Hoban, T.F.; O’Brien, L.M. Characterization of a Sleep Architectural Phenotype in Children with Down Syndrome. Sleep Breath 2014, 19, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, A.J.; Hoffman, E.K.; Stansberry, E.; Shaffer, R. Convergent Validity of Actigraphy with Polysomnography and Parent Reports when Measuring Sleep in Children with Down Syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2018, 62, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, K.; Reid, G.J.; Morton, J.B. Behavioral Sleep Problems and their Potential Impact on Developing Executive Function in Children. Sleep 2013, 36, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Churchill, S.S.; Kieckhefer, G.M.; Bjornson, K.F.; Herting, J.R. Relationship between Sleep Disturbance and Functional Outcomes in Daily Life Habits of Children with Down Syndrome. Sleep 2015, 38, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukowski, A.F.; Milojevich, H.M. Sleep Problems and Temperament in Young Children with Down Syndrome and Typically Developing Controls. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2016, 61, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, S.; Whittaker, A.; Carroll, D. Parental Stress is Associated with Poor Sleep Quality in Parents Caring for Children with Developmental Disabilities. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2009, 35, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van De Wouw, E.; Evenhuis, H.; Echteld, M. Prevalence, Associated Factors and Treatment of Sleep Problems in Adults with Intellectual Disability: A Systematic Review. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 1310–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, P.J.; Palod, S.; Smith, K.J.; Fife-Schaw, C.; Mirza, N. Interventions for Sleep Difficulties in Adults with an Intellectual Disability: A Systematic Review. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2019, 63, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ward, F.; Nanjappa, M.; Hinder, S.A.J.; Roy, M. Use of Melatonin for Sleep Disturbance in a Large Intellectual Disability Psychiatry Service. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 61, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Punjabi, N.M. Diagnosis and Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simson, R.; Oyekan, A.A.; Ehsan, Z.; Ingram, D.G. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Down Syndrome: Current Perspec-tives. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2018, 10, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maris, M.; Verhulst, S.; Wojciechowski, M.; Van de Heyning, P.; Boudewyns, A. Sleep Problems and Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome, an Overview. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hsueh, W.-Y.; Lin, M.-T.; Kang, K.-T. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D.; Lombardo, A.; Skotko, B.; Davidson, E.J. Parental Perceptions of Sleep Disturbances and Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Children with Down Syndrome. Clin. Pediatr. 2010, 50, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lal, C.; White, D.R.; Joseph, J.E.; van Bakergem, K.; LaRosa, A. Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Down Syndrome. Chest 2015, 147, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Dellavia, C.; Zanotti, G.; Sforza, C. Soft Tissue Facial Anthropometry in Down Syndrome Subjects. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2004, 15, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhood, Z.; Isley, J.W.; Ong, A.A.; Nguyen, S.A.; Camilon, T.J.; LaRosa, A.C.; White, D.R. Adenotonsillectomy Outcomes in Patients with Down Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, L.; Bricout, V.-A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Adults with Down Syndrome: Causes and Consequences. Is It a “Chicken and Egg” Question? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 108, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, N.H. Thyroid disorders in subjects with Down syndrome: An update. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotko, B.G.; Macklin, E.A.; Muselli, M.; Voelz, L.; McDonough, M.E.; Davidson, E.; Allareddy, V.; Jayaratne, Y.; Bruun, R.; Ching, N.; et al. A Predictive Model for Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Down Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J. The Committee on Genetics Health Supervision for Children with Down Syndrome. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.H.; Spruyt, K.; Ward, S.D.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Childhood Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, E.; Fairley, D.M.; McConnell, E.; Morrison, I.; Celmina, M.; Kotoulas, S.-C.; Riha, R.L. Utility of the Pictorial Epworth Sleepiness Scale in the Adult Down Syndrome Population. Sleep Med. 2020, 66, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurvitz, M.S.; Lesser, D.J.; Dever, G.; Celso, J.; Bhattacharjee, R. Findings of Routine Nocturnal Polysomnography in Children with DOWN Syndrome: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Sleep Med. 2020, 76, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizoglu, N.B.; Kiyan, E.; Polat, B.; Ay, P.; Karadag, B.; Ersu, R. Are Home Sleep Studies Useful in Diagnosing Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Down Syndrome? Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Holty, J.E.; Owens, D.K.; Dallas, P.; Starkey, M.; Shekelle, P. Management of obstructive sleep apnea in adults: A clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roche, J.; Isacco, L.; Masurier, J.; Pereira, B.; Mougin, F.; Chaput, J.-P.; Thivel, D. Are Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Sleep Improved in Response to Multidisciplinary Weight Loss Interventions in Youth with Obesity? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rimmer, J.H.; Heller, T.; Wang, E.; Valerio, I. Improvements in Physical Fitness in Adults with Down Syndrome. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 2004, 109, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Espinosa, R.M.; Vila, M.D.M.; García-Galbis, M.R. Evidences from Clinical Trials in Down Syndrome: Diet, Exercise and Body Composition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudoignon, B.; Amaddeo, A.; Frapin, A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Down Syndrome: Benefits of Surgery and Noninva-Sive Respiratory Support. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2017, 173, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, M.; Verhulst, S.; Wojciechowski, M.; Van de Heyning, P.; Boudewyns, A. Outcome of Adenotonsillectomy in Children with Down Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 102, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehme, J.; Laberge, R.; Pothos, M.; Barrowman, N.; Hoey, L.; Kukko, M.; Monsour, A.; Katz, S.L. Treatment and Persistence/Recurrence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Children with Down Syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodson, B.T.; Strohl, K.P.; Soose, R.J.; Gillespie, M.B.; Maurer, J.T.; De Vries, N.; Padhya, T.A.; Badr, M.S.; Lin, H.-S.; Vanderveken, O.M.; et al. Upper Airway Stimulation for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: 5-Year Outcomes. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caloway, C.L.; Diercks, G.R.; Keamy, D.; De Guzman, V.; Soose, R.; Raol, N.; Shott, S.R.; Ishman, S.L.; Hartnick, C.J. Update on Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation in Children with Down Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E263–E267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Boon, M.; Ishman, S.L.; Suurna, M.V. Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation in Three Adults with Down Syndrome and Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, E402–E406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.K.; Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Arevalo, C.; Shults, J.; Beck, S.E.; Marcus, C.L.; Tapia, I.E. Adherence to Positive Airway Pressure for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Developmental Disabilities. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and GRADE Assessment. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cistulli, P.A.; Armitstead, J.; Pépin, J.L.; Woehrle, H.; Nunez, C.M.; Benjafield, A.; Malhotra, A. Short-Term CPAP Adherence in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Big Data Analysis Using Real World Data. Sleep Med. 2019, 59, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Määttä, T.; Määttä, J.; Tervo-Määttä, T.; Taanila, A.; Kaski, M.; Iivanainen, M. Healthcare and guidelines: A population-based survey of recorded medical problems and health surveillance for people with Down syndrome. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 36, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luijks, K.A.; Vandenbussche, N.N.; Pevernagie, D.D.; Overeem, S.S.; Pillen, S. Adherence to Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Adults with an Intellectual Disability. Sleep Med. 2017, 34, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez, S.; Farré, A.; Morante, F.; Videla, L.; Carreras, F.; Benejam, B.; Asensio, A.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Fortuna, A.; Peñacoba, P.; et al. Feasibility of Continuos Airway Pressure Treatment for Sleep Apnea in Adults with Down Syndrome. In Proceedings of the 3rd Internationla Conference Trisomy 21 Reserach Society, Barcelona, Spain, 6–9 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ramar, K.; Dort, L.C.; Katz, S.G.; Lettieri, C.J.; Harrod, C.G.; Thomas, S.M.; Chervin, R.D. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring with Oral Appliance Therapy: An Update for 2015. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 773–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demko, B.G. Oral Appliance Treatment in a Patient with Down Syndrome. J. Dent. Sleep Med. 2014, 1, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannasi, L.C.; Dutra, M.T.S.; Tenguan, V.L.S.; Mancilha, G.P.; Silva, G.R.C.; Fillietaz-Bacigalupo, E.; Da Silva, D.B.; Politti, F.; Nacif, S.R.; De Oliveira, E.F.; et al. Evaluation of the Masticatory Muscle Function, Physiological Sleep Variables, and Salivary Parameters after Electromechanical Therapeutic Approaches in Adult Patients with Down Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Trials 2019, 20, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; McEvoy, C.; Allen, I.E.; Yaffe, K. Association of Sleep-Disordered Breathing with Cognitive Function and Risk of Cognitive Impairment. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, R.S.; Wijayaratne, P.; Nixon, G.M.; Walter, L.M. Sleep and Sleep Disordered Breathing in Children with Down Syn-drome: Effects on Behaviour, Neurocognition and the Cardiovascular System. Sleep Med. Rev. 2019, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, J.; Spanò, G.; Bootzin, R.; Anand, P.; Nadel, L.; Edgin, J. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Cognition in Down Syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, L.J.; Olsen, M.N.; Bacevice, A.M.; Beebe, A.; Konstantinopoulou, S.; Taylor, H.G. Relationship between Sleep, Sleep Apnea, and Neuropsychological Function in Children with Down Syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2014, 19, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, A.; Dimitriou, D. Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Cognitive Functioning in Preschool Children with and without Down Syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2017, 61, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canessa, N.; Castronovo, V.; Cappa, S.F.; Aloia, M.S.; Marelli, S.; Falini, A.; Alemanno, F.; Ferini-Strambi, L. Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Brain Structural Changes and Neurocognitive Function before and after Treatment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benejam, B.; Videla, L.; Vilaplana, E.; Barroeta, I.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Altuna-Azkargorta, M.; Valldeneu, S.; Fernandez, S.; Giménez, S.; Iulita, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Prodromal and Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia in Adults with Down Syndrome Using Neuropsychological Tests. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2020, 12, e12047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, A.E.; Kam, K.; Parekh, A.; Bubu, O.; Osorio, R.S.; Varga, A.W. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Its Treatment in Aging: Effects on Alzheimer’s disease Biomarkers, Cognition, Brain Structure and Neurophysiology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 145, 105054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.A.; Varga, A.W.; Bubu, O.; Pirraglia, E.; Kam, K.; Parekh, A.; Wohlleber, M.; Miller, M.D.; Andrade, A.; Lewis, C.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity Affects Amyloid Burden in Cognitively Normal Elderly. A Longitudinal Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, F.; Edgin, J.O. Poor Sleep as a Precursor to Cognitive Decline in Down Syndrome: A Hypothesis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Park. 2013, 3, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, V.; Rivelli, A.; Bria, K.; Chicoine, B. Heart Disease in Adults with Down Syndrome Between 1996 and 2016. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2020, 33, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Driscoll, D.M.; Horne, R.S.; Davey, M.J.; Hope, S.A.; Anderson, V.; Trinder, J.; Walker, A.M.; Nixon, G.M. Cardiac and Sympathetic Activation are Reduced in Children with Down Syndrome and Sleep Disordered Breathing. Sleep 2012, 35, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinopoulou, S.; Tapia, I.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Radcliffe, J.; Cohen, M.S.; Hanna, B.D.; Pipan, M.; Cielo, C.; Thomas, A.J.; et al. Relationship between Obstructive Sleep Apnea Cardiac Complications and Sleepiness in Children with Down Syndrome. Sleep Med. 2016, 17, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, J.A.; Amon, A.; Abbeduto, L.; Agiovlasitis, S.; Alsaied, T.; Anderson, H.A.; Bain, L.J.; Baumer, N.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Bogunovic, D.; et al. Opportunities, Barriers, and Recommendations in Down Syndrome Research. Transl. Sci. Rare Dis. 2021, 5, 99–129. [Google Scholar]
- Altuna, M.; Giménez, S.; Fortea, J. Epilepsy in Down Syndrome: A Highly Prevalent Comorbidity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannasi, L.; Cruz, M.M.e.; Rezende, T.; Dutra, M.; Nacif, S.; Oliveira, E.; Rode, S.; Nazário, L.; Silvestre, P.; Bacigalupo, E.; et al. 0804 Sleep Bruxism, Awake Bruxism and Sleep Related Breathing Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome. Sleep 2020, 43, A306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D.; Berbert, L.; Weller, E. High Prevalence of Periodic Limb Movements of Sleep in Children with Down Syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, T.J.; Jain, S.V.; Simakajornboon, N. Outcomes of Long-Term Iron Supplementation in Pediatric Restless Legs Syndrome/Periodic Limb Movement Disorder (RLS/PLMD). Sleep Med. 2017, 32, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Citation | Design | Population (Women %) | Age | Sleep Study | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andreu et al. (2002) [15] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 12 (50%) | 21.6 (17–31) y | Polygraphy | OSA associated with worse visuoperceptual skills |
| Resta et al. (2003) [16] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 6 (50%) | 38.6 (28–53) y | PSG | 83% OSA No relation with age neither BMI |
| Trois et al. (2009) [17] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 16 (50%) TD: 48 | 33 (19–56) y | PSG | 94% OSA 69% severe OSA AHI-BMI correlation 62% CPAP (7 h/night) |
| Chen et al. (2013) [18] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 29 (27.6%) | 20.26 (14–31)y | Sleep reports | OSA severity related to executive dysfunction |
| Hill (2016) [19] | Prospective (a) Population-based survey | DS (a) 1100 | >16 y | (a) pEES | (a) 35% OSA self reporting symptoms |
| (b) Sleep center OSAsuspected | (b) 134 | >16 y | (b) home Poligraphy | (b) 42% OSA (AHI > 10) | |
| Esbensen (2016) [5] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 75 (34.7%) | 51.1 (37–65) y | Clinical interview | 22.4% BSD, poorer health 13% OSA, more visits to physicians |
| Giménez et al. (2018) [6] | Prospective Community sample | DS: 54 (38.3%) TD: 35 | 39.6 (20–62) y | PSG, actigraphy, ESS, PSQI, BQ | 74% Sleep disruption 78% OSA (44.1% severe), both undetected by self-reported measures |
| Cornacchia et al. (2019) [20] | Retrospective DS clinic | DS: 125 (39.9%) | 28.8 (18–62) y | PSG | 82.1% OSA 39.1% severe OSA |
| Stores (2019) [2] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 100 (45%) | 28 y (16–61) y | Online survey | 25% OSA, 48% BSD ESS:8.5 Yes: OSA-BMI, osa-ESS58% Caregiver’s sleep affected |
| Landete et al. (2020) [21] | Retrospective Sleep center OSAsuspected | DS: 114 (40.7%) | 36 y | 91% poligraphy 9% PSG | 72.6% OSA (53.5% severe) CPAP use 65% (7 h/day) |
| Carvalho et al. (2020) [22] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 60 (45%) | 27 y | Home polygraphy ESS, PSQI, BQ, SBQ | 100% OSA (38.3% severe) SBQ good sensitivity and OSA specificity |
| Hill et al. (2020) [23] | 1 month prospective CPAP Trial Follow up 1y | DS: 29 (32%) | 28 y | Home PSG pESS; Cognitive measures | 68% use CPAP (2.8 h/night) after 12 months follow up Any differences after 1 m, but after a 12 m |
| Cody et al. (2020) [24] | Prospective DS clinic | DS: 47 (51.1%) | 38.4 (26–56) y | Actigraphy, PIB, PET, Cognitionassessment | Longer awakenings associated with an increase striatal amyloid burden and decreased cognition |
| Clinical Gaps | Practical Recommendations |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Research Gaps | Methodological Research Recommendations |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giménez, S.; Altuna, M.; Blessing, E.; Osorio, R.M.; Fortea, J. Sleep Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143012
Giménez S, Altuna M, Blessing E, Osorio RM, Fortea J. Sleep Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiménez, Sandra, Miren Altuna, Esther Blessing, Ricardo M. Osorio, and Juan Fortea. 2021. "Sleep Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143012
APA StyleGiménez, S., Altuna, M., Blessing, E., Osorio, R. M., & Fortea, J. (2021). Sleep Disorders in Adults with Down Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143012







