Conduction Disorders during Sinus Rhythm in Relation to Atrial Fibrillation Persistence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Mapping Procedure
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
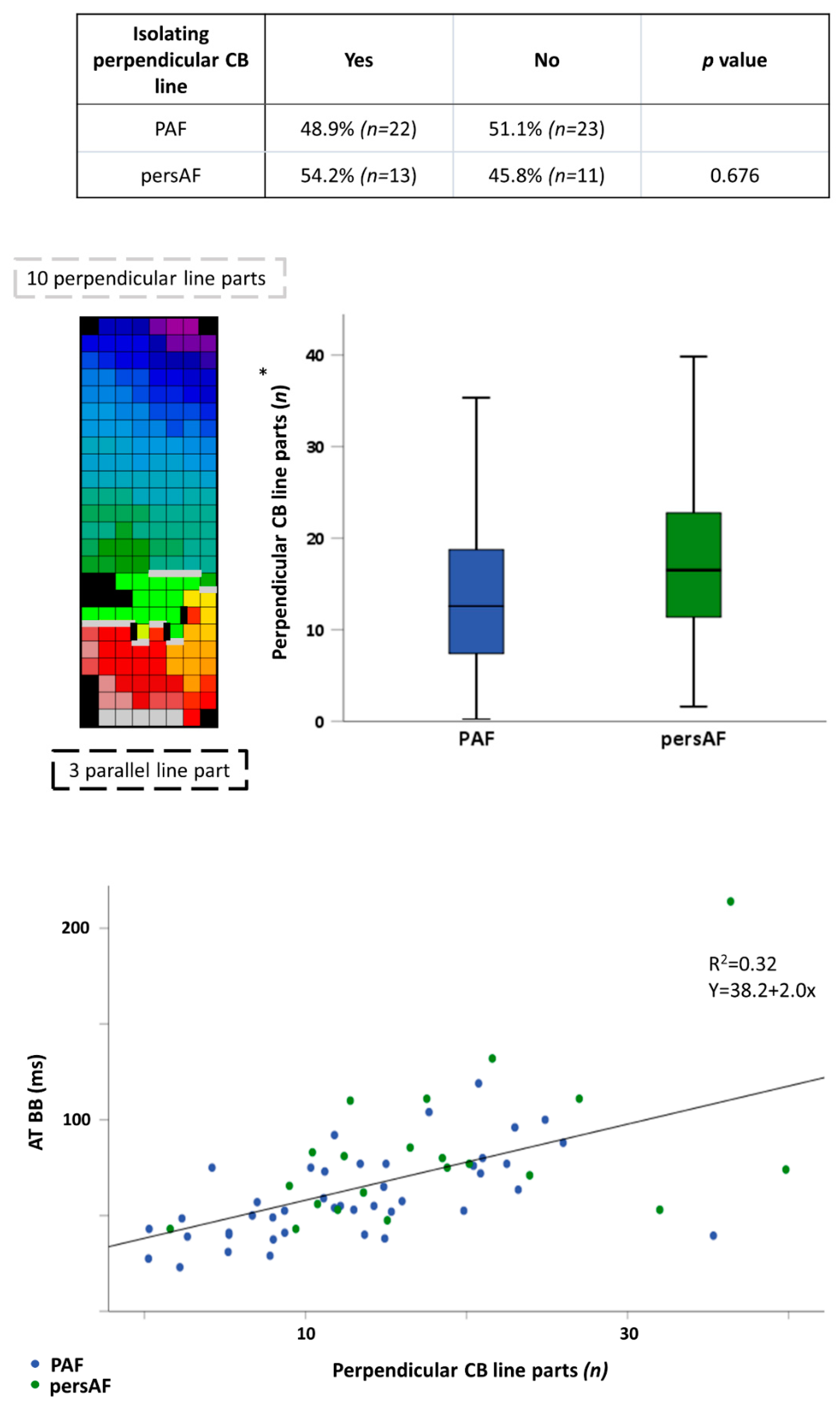
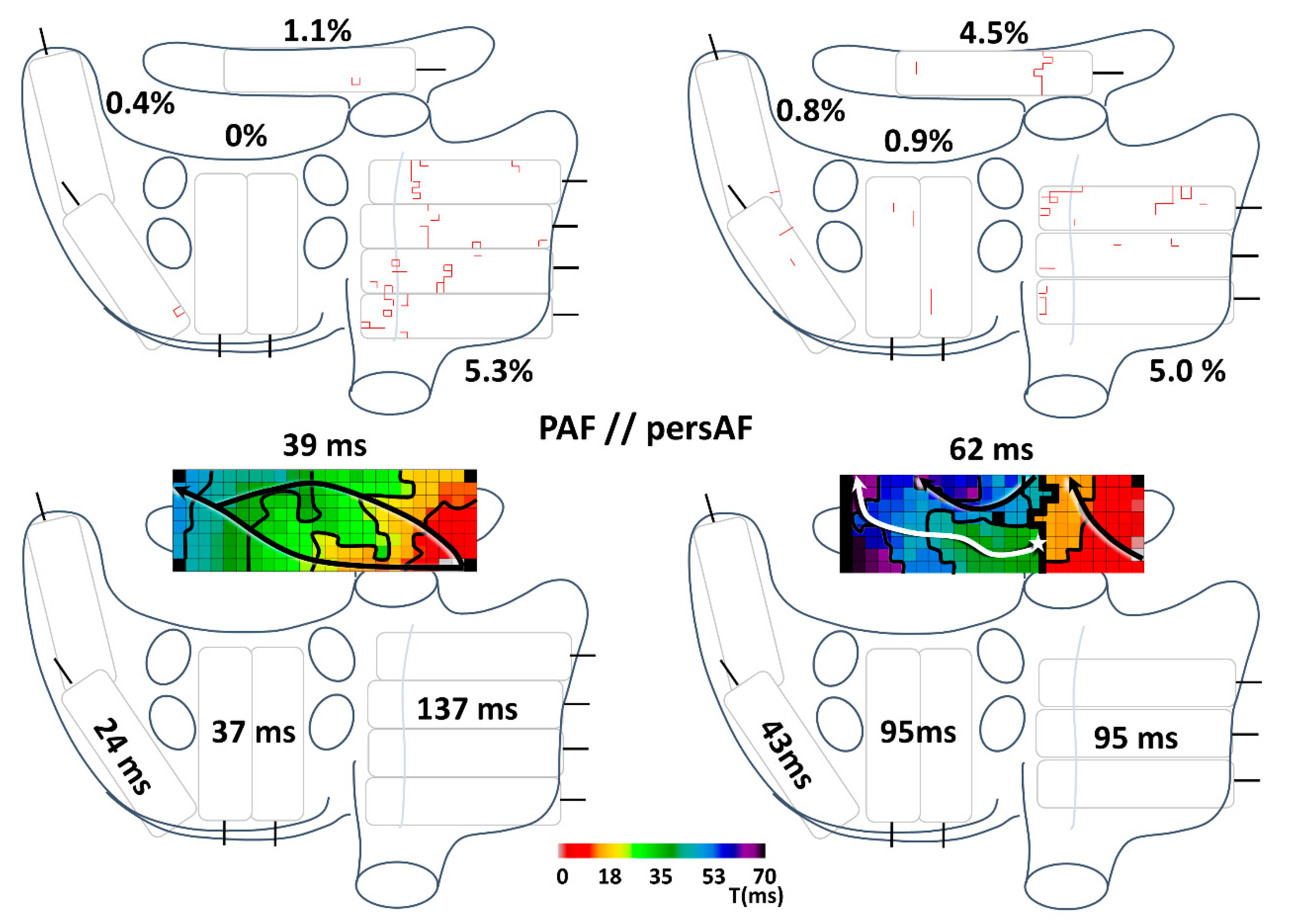
3.2. Conduction Disorders in Paroxysmal and Persistent AF Patients
3.3. Conduction Disorders in Relation to Spontaneous Termination of AF Episodes
3.4. Conduction Disorders in Relation to P-Wave Duration and a-IAB
3.5. Discriminatory Value of Electropathology
3.6. Correlation of Conduction Parameters with HATCH Score
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Clinical Classification of AF
4.3. Conduction Disorders in Relation to AF Classification
4.4. Bachmann’s Bundle in AF
4.5. HATCH Score and Electropathology
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.-C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace 2016, 18, 1609–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilz, R.R.; Heeger, C.-H.; Wick, A.; Saguner, A.M.; Metzner, A.; Rillig, A.; Wohlmuth, P.; Reissmann, B.; Lemeš, C.; Maurer, T.; et al. Ten-Year Clinical Outcome After Circumferential Pulmonary Vein Isolation Utilizing the Hamburg Approach in Patients with Symptomatic Drug-Refractory Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e005250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukkipati, S.R.; Neuzil, P.; Kautzner, J.; Petru, J.; Wichterle, D.; Škoda, J.; Čihák, R.; Peichl, P.; Russo, A.D.; Pelargonio, G.; et al. The durability of pulmonary vein isolation using the visually guided laser balloon catheter: Multicenter results of pulmonary vein remapping studies. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilek, C.; Ullah, W. Pulmonary vein reconnections or substrate in the left atrium: What is the reason for atrial fibrillation re-currences? A dialogue on a pressing clinical situation. EP Eur. 2019, 21, i12–i20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, F.; Dorwarth, U.; Hartl, S.; Brueck, B.; Pongratz, J.; Kosmalla, A.; Wankerl, M.; Hoffmann, E. Benefit of ultra-high-density mapping-guided radiofrequency reablation in pulmonary vein isolation non-responders after initial cryoballoon procedure. EP Eur. 2020, 22, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, D.A.V.I.D.; Bourke, J.P.; Furniss, S.S. Interatrial transseptal electrical conduction: Comparison of patients with atrial fi-brillation and normal controls. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2002, 13, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, A.W.; Kistler, P.M.; Lee, G.; Medi, C.; Heck, P.M.; Spence, S.J.; Sparks, P.B.; Morton, J.B.; Kalman, J.M. Electroanatomic Remodeling of the Left Atrium in Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Patients Without Structural Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 23, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.L.; Tai, C.T.; Lin, Y.J.; Wongcharoen, W.; Lo, L.W.; Tuan, T.C.; Udyavar, A.R.; Chang, S.H.; Tsao, H.M.; Hsieh, M.H.; et al. Biatrial Substrate Properties in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2007, 18, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, B.; Garcia, F.C.; Ju, W.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Li, M.; Gu, K.; Cao, K.; et al. Comparison of left atrial electrophysiologic abnormalities during sinus rhythm in patients with different type of atrial fibrillation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2014, 39, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, K.; Okumura, Y.; Watanabe, I.; Nagashima, K.; Kofune, M.; Mano, H.; Kogawa, R.; Sasaki, N.; Ohkubo, K.; Nakai, T.; et al. Three-Dimensional High-Density Bipolar Contact Mapping of Left Atrial Endocardial Activation During Sinus Rhythm in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Int. Heart J. 2013, 54, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mouws, E.M.; Van Der Does, L.J.M.E.; Kik, C.; Lanters, E.A.H.; Teuwen, C.P.; Knops, P.; Bogers, A.J.; De Groot, N.M. Impact of the arrhythmogenic potential of long lines of conduction slowing at the pulmonary vein area. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, C.B.; Pisters, R.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Prins, M.H.; Tieleman, R.G.; Coelen, R.; van den Heijkant, A.C.; Allessie, M.A.; Crijns, H.J. Progression from Paroxysmal to Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Clinical Correlates and Prognosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luna, A.B.; Baranchuk, A.; Robledo, L.A.E.; van Roessel, A.M.; Martinez-Selles, M. Diagnosis of in-teratrial block. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Does, L.J.M.E.; Yaksh, A.; Kik, C.; Knops, P.; Lanters, E.A.H.; Teuwen, C.P.; Oei, F.B.S.; Van De Woestijne, P.C.; Bekkers, J.A.; Bogers, A.J.J.C.; et al. QUest for the Arrhythmogenic Substrate of Atrial fibRillation in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery (QUASAR Study): Rationale and Design. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2016, 9, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanters, E.A.; Yaksh, A.; Teuwen, C.P.; van der Does, L.J.; Kik, C.; Knops, P.; van Marion, D.M.S.; Brundel, B.; Bogers, A.; Allessie, M.A.; et al. Spatial distribution of conduction disorders during sinus rhythm. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 249, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charitos, E.I.; Purerfellner, H.; Glotzer, T.V.; Ziegler, P.D. Clinical classifications of atrial fibrillation poorly reflect its temporal persistence: Insights from 1,195 patients continuously monitored with implantable devices. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2840–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugihara, C.; Veasey, R.; Freemantle, N.; Podd, S.; Furniss, S.; Sulke, N. The development of AF over time in patients with permanent pacemakers: Objective assessment with pacemaker diagnostics demonstrates distinct patterns of AF. EP Eur. 2015, 17, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Teh, A.W.; Medi, C.; Kistler, P.M.; Morton, J.B.; Kalman, J.M. Atrial remodeling in varying clinical substrates within beating human hearts: Relevance to atrial fibrillation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2012, 110, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheule, S.; Tuyls, E.; Van Hunnik, A.; Kuiper, M.; Schotten, U.; Allessie, M. Fibrillatory Conduction in the Atrial Free Walls of Goats in Persistent and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duytschaever, M.; Danse, P.; Allessie, M. Supervulnerable phase immediately after termination of atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2002, 13, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldo, A.L.; Bush, H.L., Jr.; Gelband, H.; Zorn, G.L., Jr.; Vitikainen, K.J.; Hoffman, B.F. Effects on the canine p wave of discrete lesions in the specialized atrial tracts. Circ. Res. 1971, 29, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, G.; Wong, C.W.; Gong, M.; Wong, W.T.; Bazoukis, G.; Wong, S.H.; Li, G.; Wu, W.K.K.; Tse, L.A.; Lampropoulos, K.; et al. Predictive value of inter-atrial block for new onset or recurrent atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 250, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, K.; Uno, K.; Khrestian, C.; Waldo, A.L. Single site radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Studies guided by simultaneous multisite mapping in the canine sterile pericarditis model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.W.; Self, W.H.; Wasserman, B.S.; McNaughton, C.D.; Darbar, D. Evaluating the hatch score for predicting progression to sustained atrial fibrillation in ed patients with new atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potpara, T.S.; Stankovic, G.R.; Beleslin, B.D.; Polovina, M.M.; Marinkovic, J.M.; Ostojic, M.C.; Lip, G.Y. A 12-year follow-up study of patients with newly diagnosed lone atrial fibrillation: Implications of arrhythmia progression on prognosis: The belgrade atrial fibrillation study. Chest 2012, 141, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Paroxysmal AF (n = 47) | Persistent AF (n = 24) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 72.2 ± 7.3 | 71.0 ± 6.8 | 0.496 |
| Gender: female | 21 (44.7) | 7 (29.2) | 0.206 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 ± 4.4 | 28.7 ± 4.3 | 0.198 |
| Years since diagnosed AF | 1.0 [0.3–5.0] | 1.0 [0.4–5.5] | 0.823 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 12 (25.5) | 5 (20.8) | 0.661 |
| Hypertension | 29 (61.7) | 15 (62.5) | 0.948 |
| Dyslipidemia | 13 (27.7) | 6 (25.0) | 0.811 |
| History of myocardial infarction | 10 (21.3) | 3 (12.5) | 0.521 |
| AADs: Class I Class II Class III Class IV | 1 (2.1) † 27 (57.4) 12 (25.5) 0 | 0 14 (58.3) 6 (25.0) 2 (8.3) † | 0.845 |
| Surgical indication: (i) VHD AVD AVD + CABG MVD MVD + CABG CABG | 32 (68.1) 12 5 10 5 15 (31.9) | 19 (79.2) 6 2 10 1 5 (20.8) | 0.326 ‡ |
| Left ventricular EF: Normal (≥50%) Mild impairment (40–49%) Moderate impairment (30–39%) Severe impairment (≤30%) | 39 (83.0) 5 (10.6) 2 (4.3) 1 (2.1) | 14 (58.3) 6 (25.0) 4 (16.7) 0 | 0.101 |
| LA enlargement § | 32/43 (74.4%) ¶ | 21/24 (87.5%) ¶ | 0.207 |
| LAVI (mL/m2) | 41 (33–56) (n = 31) ¶ | 44 (38–50) (n = 18) ¶ | 0.568 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van der Does, W.F.B.; Heida, A.; van der Does, L.J.M.E.; Bogers, A.J.J.C.; de Groot, N.M.S. Conduction Disorders during Sinus Rhythm in Relation to Atrial Fibrillation Persistence. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132846
van der Does WFB, Heida A, van der Does LJME, Bogers AJJC, de Groot NMS. Conduction Disorders during Sinus Rhythm in Relation to Atrial Fibrillation Persistence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132846
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan der Does, Willemijn F. B., Annejet Heida, Lisette J. M. E. van der Does, Ad J. J. C. Bogers, and Natasja M. S. de Groot. 2021. "Conduction Disorders during Sinus Rhythm in Relation to Atrial Fibrillation Persistence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132846
APA Stylevan der Does, W. F. B., Heida, A., van der Does, L. J. M. E., Bogers, A. J. J. C., & de Groot, N. M. S. (2021). Conduction Disorders during Sinus Rhythm in Relation to Atrial Fibrillation Persistence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132846







