Influence of Coronal Preflaring on the Accuracy of Electronic Working Length Determination: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Population (P): extracted human permanent teeth;
- Intervention (I): coronal preflaring of root canals;
- Comparison (C): unflared root-canals;
- Outcome (O): accuracy of WL determination using EAL;
- Study design (S): laboratory.
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Collection/Extraction Process
2.5. Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias of Individual Studies
2.6. Outcome of Interest
2.7. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of the Studies
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
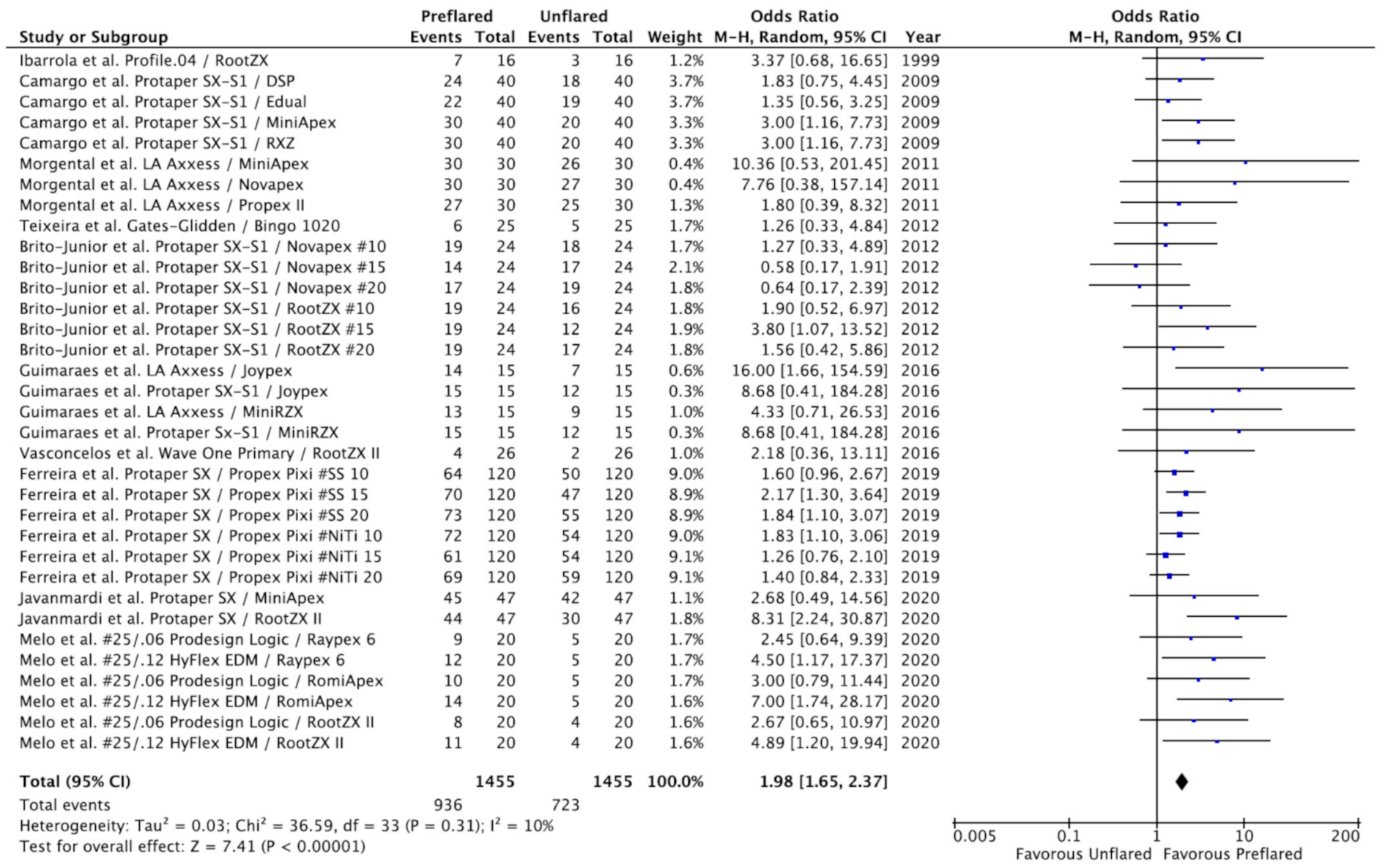
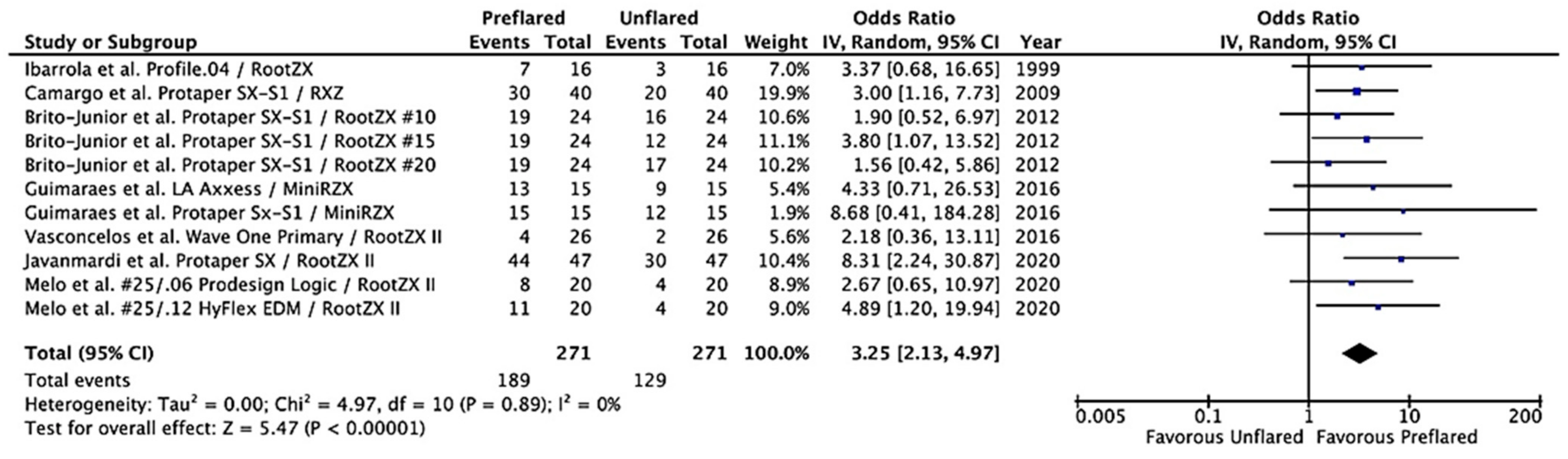
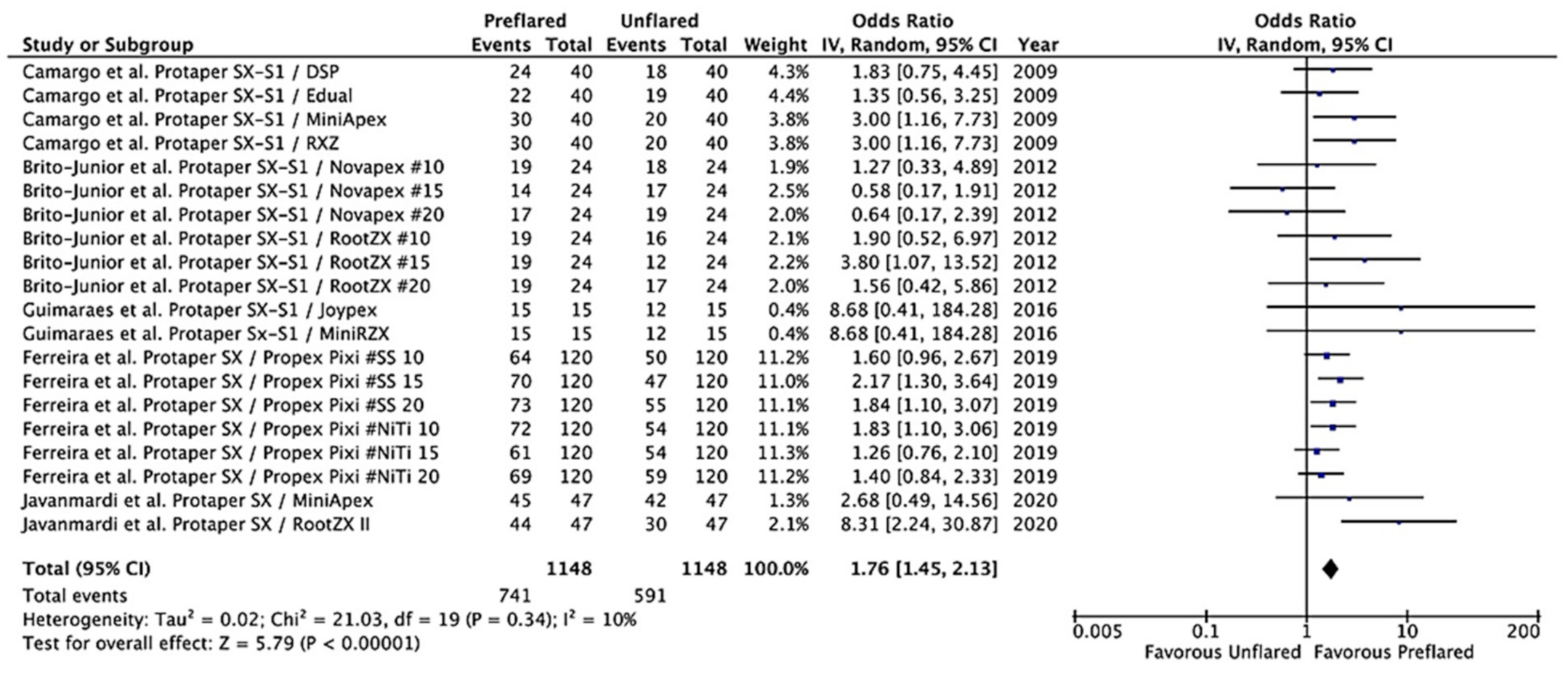
3.3. Outcomes of the Primary Meta-Analysis and Publication Bias
3.4. Additional Analysis
3.5. Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Practice and Research
4.2. Quality Assessment
4.3. Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buchanan, L.S. Cleaning and shaping the root canal system: Negotiating canals to the termini. Dent. Today 1994, 13, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.D. The endodontic glidepath: Secret to rotary safety. Dent. Today 2010, 29, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roland, D.D.; Andelin, W.E.; Browning, D.F.; Hsu, G.H.R.; Torabinejad, M. The effect of preflaring on the rates of separation for 0.04 taper nickel titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotino, G.; Nagendrababu, V.; Bukiet, F.; Grande, N.M.; Veettil, S.K.; De-Deus, G.; Aly Ahmed, H.M. Influence of negotiation, glide path, and preflaring procedures on root canal shaping—Terminology, basic concepts, and a systematic review. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 707–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Falanga, A.; Di Giuseppe, I.L.; Lamorgese, V.; Somma, F. Dentine removal in the coronal portion of root canals following two preparation techniques. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.T.; Messer, H.H. The effect of instrument type and preflaring on apical file size determination. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Marques, D.; Mata, A.; Caramês, J. Clinical efficacy of electronic apex locators: Systematic review. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, I. Use of electronic apex locators may improve determination of working length. Evid. Based Dent. 2014, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean Davis, R.; Gordon Marshal, J.; Craig Baumgartne, J. Effect of early coronal flaring on working length change in curved canals using rotary nickel-titanium versus stainless steel instruments. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moor, R.J.G.; Hommez, G.M.G.; Martens, L.C.; De Boever, J.G. Accuracy of four electronic apex locators: An in vitro evaluation. Dent. Traumatol. 1999, 15, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, K.P.; Walton, R.E.; Rivera, E.M. Straight line access and coronal flaring: Effect on canal length. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Estarli, M.; Barrera, E.S.A.; et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Hum. Y Diet. 2016, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; De Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 26, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.J.N.L.; Rover, G.; Belladonna, F.G.; De-Deus, G.; da Silveira Teixeira, C.; da Silva Fidalgo, T.K. Impact of contracted endodontic cavities on fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth: A systematic review of in vitro studies. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.J.N.L.; Prado, M.C.; Soares, D.N.; Hecksher, F.; Martins, J.N.R.; Fidalgo, T.K.S. The effect of ozone therapy in root canal disinfection: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.; Clarke, M. Forest plots: Trying to see the wood and the trees. BMJ 2001, 322, 1479–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarrola, J.L.; Chapman, B.L.; Howard, J.H.; Knowles, K.I.; Ludlow, M.O. Effect of preflaring on Root ZX apex locators. J. Endod. 1999, 25, 625–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo, É.J.; Zapata, R.O.; Medeiros, P.L.; Bramante, C.M.; Bernardineli, N.; Garcia, R.B.; de Moraes, I.G.; Duarte, M.A.H. Influence of preflaring on the accuracy of length determination with four electronic apex locators. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgental, R.D.; Vier-Pelisser, F.V.; Luisi, S.B.; Cogo, D.M.; Kopper, P.M.P. Preflaring effects on the accuracy of three electronic apex locators. Rev. Odonto Cienc. 2011, 26, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Júnior, M.; Camilo, C.C.; Moreira-Júnior, G.; Pecora, J.D.; Sousa-Neto, M.D. Effect of pre-flaring and file size on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Teixeira, J.M.; Barcellos, M.B.; de Berrêdo Pinho, M.A.; Barbosa, C.A.; Fidel, R.; Fidel, S. Effectiveness of an electronic apex locator used after preflaring of cervical and middle third. RSBO 2012, 9, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, B.M.; Tartari, T.; Fernandes, S.L.; Ferracioli Oda, D.; Bramante, C.M.; Antonio, M.; Duarte, H. Influence of the instrument used for cervical preflaring on the precision of 2 electronic apex locators. Rev. Gaúch. Odontol. 2016, 64, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasconcelos, B.C.; Bastos, L.M.; Oliveira, A.S.; Bernardes, R.A.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Vivacqua-Gomes, N.; Vivan, R.R. Changes in Root canal length determined during mechanical preparation stages and their relationship with the accuracy of Root ZX II. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.; Braga, A.C.; Pina-Vaz, I. The precision of PropEX Pixi with different instruments and coronal preflaring procedures. Eur. Endod. J. 2019, 4, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Javanmardi, S.; Maghaireh, G.; Al Omari, M.; Zeinalddin, M. Accuracy of two different electronic apex locators in treatment and re-treatment cases: An ex-vivo study. Acta Sci. Dent. Sci. 2020, 4, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, A.M.; Vivacqua-Gomes, N.; Bernardes, R.A.; Vivan, R.R.; Duarte, M.A.H.; de Vasconcelos, B.C. Influence of different coronal preflaring protocols on electronic foramen locators precision. Braz. Dent. J. 2020, 31, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinaz, A.C.; Maden, M.; Aydin, C.; Türköz, E. The accuracy of three different electronic root canal measuring devices: An in vitro evaluation. J. Oral Sci. 2002, 44, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Akbar, I.; Al-Omiri, M.K. An in vivo study to determine the effects of early preflaring on the working length in curved mesial canals of mandibular molars. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2013, 14, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Khambete, N.; Patil, S.; Medha, A.; Shetty, R.; Hoshing, U. Working length changes in curved canals after coronal flaring by using rotary files and hand file: An in vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2013, 16, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryantoro, R.; Meidyawati, R.; Suprastiwi, E. The effect of coronal preflaring on the accuracy of two electronic apex locators. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglia-Ferreira, C.; de Almeida Gomes, F.; Ximenes, T.; Neto, M.A.T.; Arruda, T.E.; Ribamar, G.G.; Herculano, L.F.G. Influence of reuse and cervical preflaring on the fracture strength of reciprocating instruments. Eur. J. Dent. 2017, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Elkholy, M.M.A.; Ha, W.N. An arithmetic crown-down dynamic tactile instrumentation technique: A case report of an S-shaped root canal. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Kacker, R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: An update. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2007, 28, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Reasons for Exclusion | Authors and Year |
|---|---|
| Accuracy was not reported/cannot be determined | De Moor et al. 1999 [10] Tinaz et al. 2002 [30] Suryantoro et al. 2017 [33] Maniglia-Ferreira et al. 2017 [34] |
| EAL not used | Iqbal et al. 2013 [31] Kumar et al. 2013 [32] |
| Authors Year | Extracted Teeth Used | Files Used in Preflaring | EAL Used for WL | Reference for WL Accuracy | Accuracy in Unflared Canals (%) | Accuracy in Preflared Canals (%) | Main Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibarrola et al. 1999 | 16 lower molars; 32 mesial canals (Weine III) | Profile 04 sizes 9 to 6 | Root-ZX | Exact apical constriction | RZX—18.8% | RZX—43.8% | Preflaring significantly increased the accuracy of the WL determination with EAL (p = 0.015). |
| Camargo et al. 2009 | 40 lower incisors (Vertucci I) | Protaper SX Protaper S1 | Root-ZX Edual Mini Apex DSP | Exact apical constriction | RZX—50% EduaL—47.5% Mini Apex—50% Apex DSP—45% | RZX—75% Edual—55% Mini Apex—75% Apex DSP—60% | Preflaring significantly increased the precision to determine the real WL with Root ZX and Mini Apex (p > 0.05), but no significant difference was noted for Edual and Apex DSP (p > 0.05). |
| Morgental et al. 2011 | 30 lower incisors | LA Axxess 20/0.06 | Novapex Mini Apex ProPex II | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | Novapex—90% Mini Apex—87% Propex II—83% | Novapex—100% Mini Apex—100% Propex II—90% | Preflaring increased the accuracy of Mini Apex and Propex II (p < 0.05), but no significant difference was noted for Novapex (p > 0.05). |
| Brito-Junior et al. 2012 | 24 upper molars | Protaper SX Protaper S1 | Novapex | Exact apical constriction | #10–75% #15–70% #20–80% | #10–80% #15–60% #20–70% | Coronal preflaring did not increase accuracy in the electronic measurements (p > 0.05). |
| Brito-Junior et al. 2012 | 24 upper molars | Protaper SX Protaper S1 | Root-ZX | Exact apical constriction | #10–65% #15–50% #20–70% | #10–80% #15–80% #20–80% | Coronal preflaring significantly increased accuracy in the electronic measurements (p < 0.05). |
| Teixeira et al. 2012 | 25 lower molars; 50 canals | Gates-Glidden 4-3-2 | Bingo1020 | Exact apical constriction | Bingo1020—21% | Bingo1020—25% | Preflaring with Gates Glidden drills were not able to significantly influence the accuracy of the apex locator in determining the exact working length (p > 0.05). |
| Guimaraes et al. 2016 | 15 lower incisors (Vertucci I) | Protaper SX Protaper S1 | Joypex 5 RZX Mini | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | Joypex 5—80% RZX Mini—80% | Joypex 5—100% RZX Mini—100% | Both EALs presented a higher percentage of exact measurements after preflaring, but differences were not significant (p > 0.05). |
| Guimaraes et al. 2016 | 15 lower incisors (Vertucci I) | LA Axxess 20/0.06 | Joypex 5 RZX Mini | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | Joypex—46.6% RZX Mini—60% | Joypex—93.3% RZX Mini—86.6% | Cervical preparation with LA-Axxes increased the accuracy of the EAL Joypex (p = 0.01), but not of the RZX Mini (p > 0.05). |
| Vasconcelos et al. 2016 | 26 lower molars (Vertucci IV); 52 canals | WaveOne Primary | Root ZX II | Exact apical constriction | RootZX II—7.7% | RootZX II—15.4% | The accuracy of Root ZX II presented no change considering the time interval when the electronic measurement was made. (p > 0.05) |
| Ferreira et al. 2019 | 40 upper anterior teeth (Vertucci I). | Protaper SX | Propex Pixi | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | SS files 10 mm—41.7% 15 mm—39.1% 20 mm—45.9% | SS files 10 mm—53.4% 15 mm—58.3% 20 mm—60.8% | Preflaring procedures increase the accuracy of Propex Pixi regardless of the size of the SS file (p < 0.05). |
| Ferreira et al. 2019 | 40 upper anterior teeth (Vertucci I). | Protaper SX | Propex Pixi | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | NiTi files 10 mm—45% 15 mm—45% 20 mm—49.2% | NiTi files 10 mm—60% 15 mm—50.8% 20 mm—57.5% | Preflaring procedures increase the accuracy of Propex Pixi regardless of the size of the NiTi file (p < 0.05). |
| Javanmardi et al. 2020 | 47 teeth (11 incisors, 10 canines and 26 premolars); 60 canals in total | Protaper SX | Root ZX II | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | RootZX—63.3% | Root ZX—93.3% | Preflaring increases the accuracy of RZX in the determination of WL (p < 0.001). |
| Javanmardi et al. 2020 | 47 teeth (11 incisors, 10 canines and 26 premolars); 60 canals | Protaper SX | Mini Apex Locator | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | Mini Apex—90% | Mini Apex—96.6% | Preflaring does not increase the accuracy of Mini Apex in the determination of WL (p = 0.293). |
| Melo et al. 2020 | 20 lower molars (Vertucci IV) | Prodesign Logic 25/0.06 | Root ZX II Raypex 6 RomiApex A-15 | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | Root ZX—20% Raypex 6—25% RomiApex—25% | Root ZX—40% Raypex 6—42.5% RomiApex—50% | An improvement in the accuracy of EALs after conventional coronal preflaring enlargement was observed (p < 0.05). |
| Melo et al. 2020 | 20 lower molars (Vertucci IV) | HyFlex EDM 25/0.12 | Root ZX II Raypex 6 RomiApex | ±0.5 mm from apical constriction | Root ZX II—20% Raypex 6—25% RomiApex—25% | Root ZX II—55% Raypex 6—57.5% RomiApex—70% | An improvement in the accuracy of EALs after conventional coronal preflaring enlargement was observed (p < 0.05) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León-López, M.; Cabanillas-Balsera, D.; Areal-Quecuty, V.; Martín-González, J.; Jiménez-Sánchez, M.C.; Saúco-Márquez, J.J.; Sánchez-Domínguez, B.; Segura-Egea, J.J. Influence of Coronal Preflaring on the Accuracy of Electronic Working Length Determination: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132760
León-López M, Cabanillas-Balsera D, Areal-Quecuty V, Martín-González J, Jiménez-Sánchez MC, Saúco-Márquez JJ, Sánchez-Domínguez B, Segura-Egea JJ. Influence of Coronal Preflaring on the Accuracy of Electronic Working Length Determination: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(13):2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132760
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-López, María, Daniel Cabanillas-Balsera, Victoria Areal-Quecuty, Jenifer Martín-González, María C. Jiménez-Sánchez, Juan J. Saúco-Márquez, Benito Sánchez-Domínguez, and Juan J. Segura-Egea. 2021. "Influence of Coronal Preflaring on the Accuracy of Electronic Working Length Determination: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 13: 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132760
APA StyleLeón-López, M., Cabanillas-Balsera, D., Areal-Quecuty, V., Martín-González, J., Jiménez-Sánchez, M. C., Saúco-Márquez, J. J., Sánchez-Domínguez, B., & Segura-Egea, J. J. (2021). Influence of Coronal Preflaring on the Accuracy of Electronic Working Length Determination: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(13), 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132760







