Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, a Comprehensive Review
Abstract
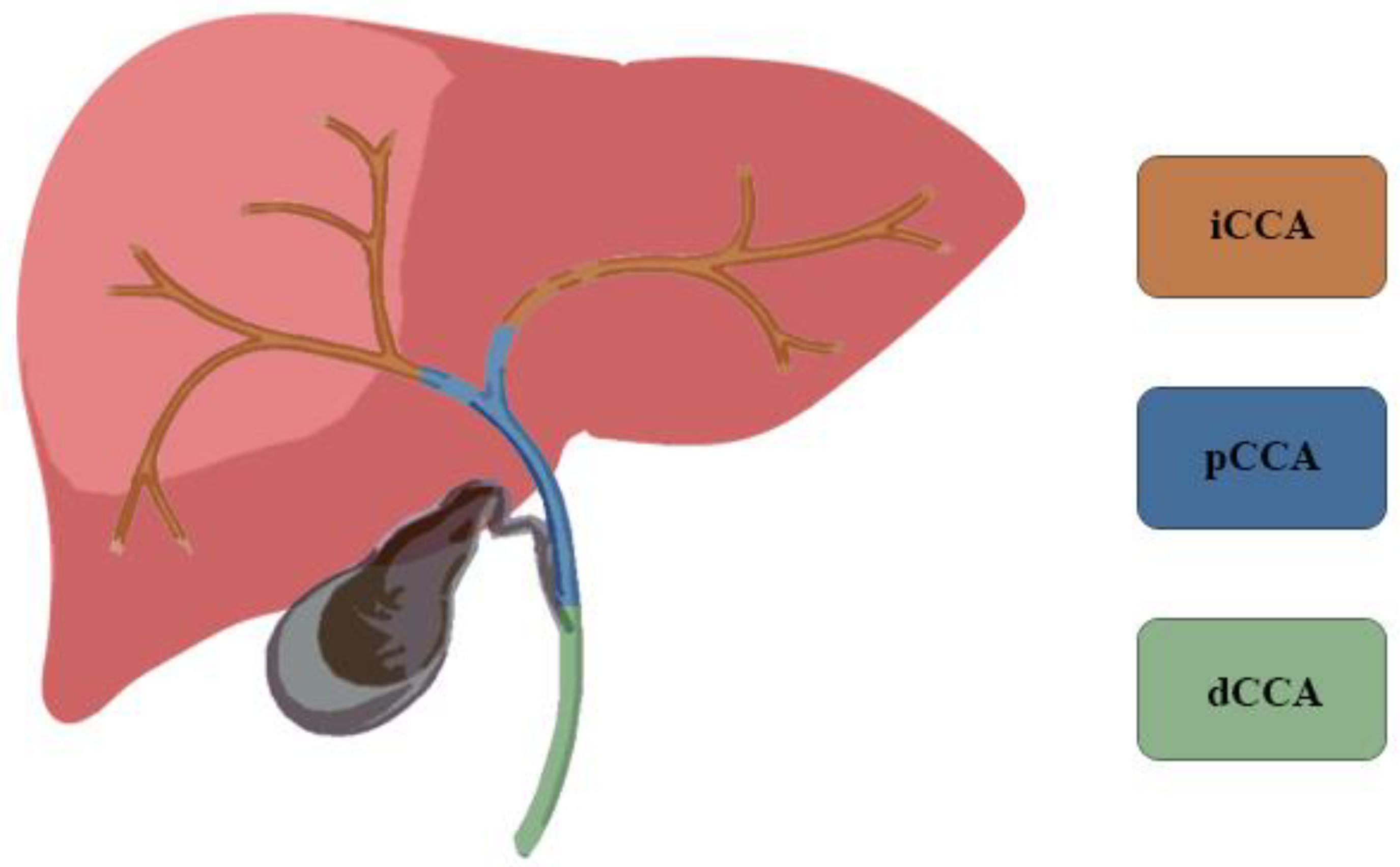
1. Introduction
2. Available Treatments
3. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy
3.1. Rationale
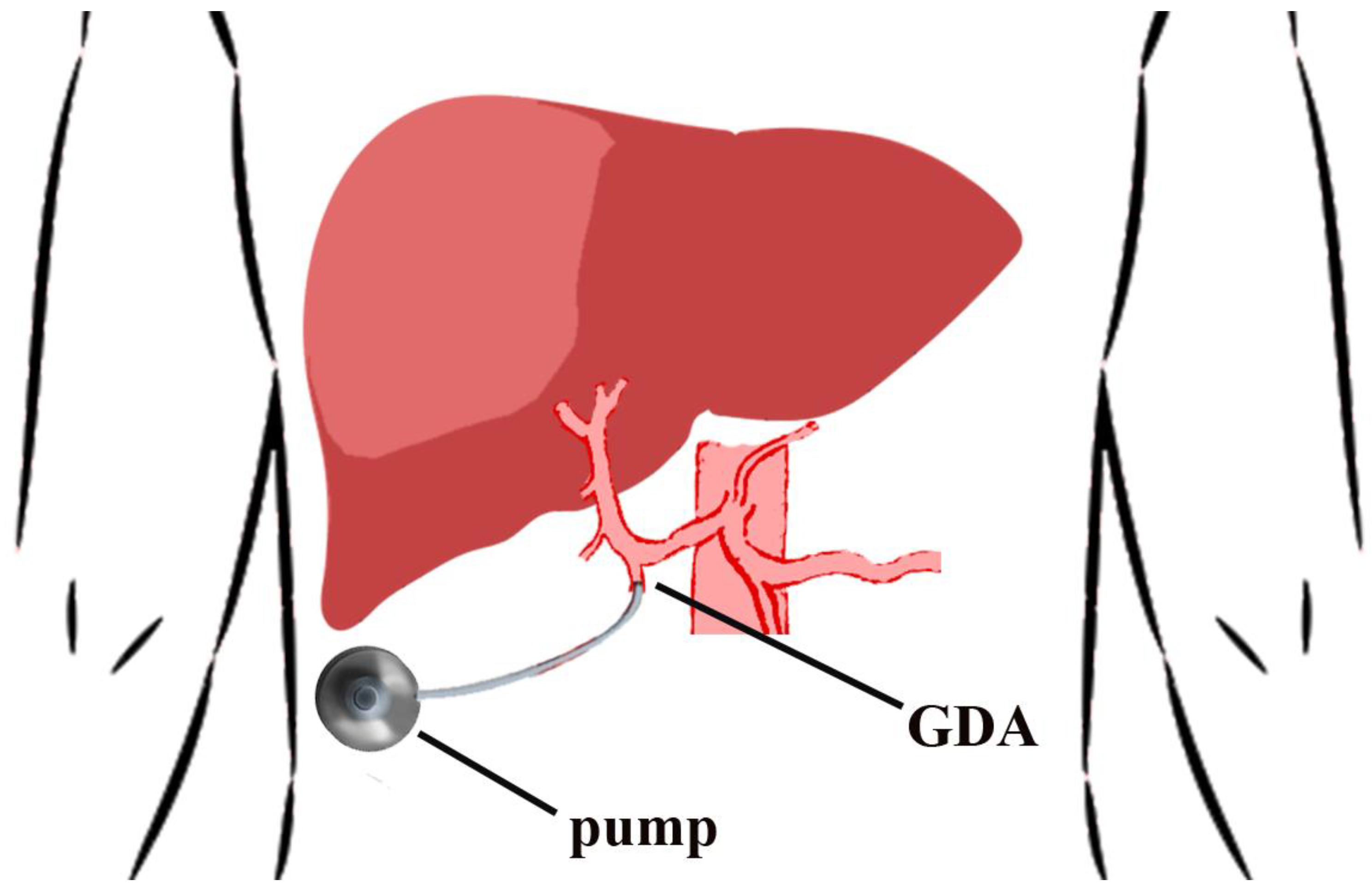
3.2. Port Placement Technique
3.3. Complications
4. Literature Review
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renshaw, K. Malignant neoplasms of the extrahepatic biliary ducts. Ann. Surg. 1922, 76, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.; Gores, G.J. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Folseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Thomas, H.C.; Davidson, B.R.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2005, 366, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvaro, D.; Bragazzi, M.C.; Benedetti, A.; Fabris, L.; Fava, G.; Invernizzi, P.; Marzioni, M.; Nuzzo, G.; Strazzabosco, M.; Stroffolini, T.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma in Italy: A national survey on clinical characteristics, diagnostic modalities and treatment. Results from the ‘Cholangiocarcinoma’ committee of the Italian Association for the Study of Liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Davidson, B.R.; Goldin, R.D.; Heaton, N.; Karani, J.; Pereira, S.P.; Rosenberg, W.M.; Tait, P.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Thillainayagam, A.V.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: An update. Gut 2012, 61, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeOliveira, M.L.; Cunningham, S.C.; Cameron, J.L.; Kamangar, F.; Winter, J.M.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Choti, M.A.; Yeo, C.J.; Schulick, R.D. Cholangiocarcinoma: Thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakeeb, A.; Pitt, H.A.; Sohn, T.A.; Coleman, J.A.; Abrams, R.A.; Piantadosi, S.; Hruban, R.H.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Yeo, C.J.; Cameron, J.L. Cholangiocarcinoma: A spectrum of intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal tumors. Ann Surg. 1996, 224, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljiffry, M.; Walsh, M.J.; Molinari, M. Advances in diagnosis, treatment and palliation of cholangiocarcinoma: 1990–2009. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4240–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebata, T.; Kosuge, T.; Hirano, S.; Unno, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Kokudo, N.; Miyagawa, S.; Takada, T.; Nagino, M. Proposal to modify the International Union Against Cancer staging system for perihilar cholangiocarcinomas. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuccio, P.; Malvezzi, M.; Carioli, G.; Hashim, D.; Boffetta, P.; El-Serag, H.B.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E. Global trends in mortality from intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welzel, T.M.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Gloria, G.; Sakoda, L.C.; Hsing, A.W.; El Ghormli, L.; Olsen, J.H.; McGlynn, K.A. Risk factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in a low-risk population: A nationwide case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahib, L.; Wehner, M.R.; Matrisian, L.M.; Nead, K.T. Estimated Projection of US Cancer Incidence and Death to 2040. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempoux, C.; Jibara, G.; Ward, S.C.; Fan, C.; Qin, L.; Roayaie, S.; Fiel, M.I.; Schwartz, M.; Thung, S.N. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: New insights in Pathology. Semin. Liver Dis. 2011, 31, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, S.; Beretta, G.D.; Labianca, R.; Zampino, M.G.; Gatta, G.; Heinemann, V. Cholangiocarcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2009, 69, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.; Wasan, H.; Palmer, D.H.; Cunningham, D.; Anthoney, A.; Maraveyas, A.; Madhusudan, S.; Iveson, T.; Hughes, S.; Pereira, S.P.; et al. Cisplatin plus Gemcitabine versus Gemcitabine for Biliary Tract Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarca, A.; Palmer, D.H.; Wasan, H.S.; Ross, P.J.; Ma, Y.T.; Arora, A.; Falk, S.; Gillmore, R.; Wadsley, J.; Patel, K.; et al. ABC-06|A randomised phase III, multi-centre, open-label study of active symptom control (ASC) alone or ASC with oxaliplatin / 5-FU chemotherapy (ASC+mFOLFOX) for patients (pts) with locally advanced/metastatic biliary tract cancers (ABC) previously-tr. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, M.A.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Burris, H.A.; Janku, F.; Shroff, R.T.; Cleary, J.M.; Azad, N.S.; Goyal, L.; Maher, E.A.; Gore, L.; et al. Phase I study of AG-120, an IDH1 mutant enzyme inhibitor: Results from the cholangiocarcinoma dose escalation and expansion cohorts. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Macarulla, T.; Javle, M.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Lubner, S.J.; Adeva, J.; Cleary, J.M.; Catenacci, D.V.T.; Borad, M.J.; Bridgewater, J.A.; et al. Final results from ClarIDHy, a global, phase III, randomized, double-blind study of ivosidenib (IVO) versus placebo (PBO) in patients (pts) with previously treated cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) and an isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javle, M.; Lowery, M.; Shroff, R.T.; Weiss, K.H.; Springfeld, C.; Borad, M.J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Goyal, L.; Sadeghi, S.; Macarulla, T.; et al. Phase II Study of BGJ398 in Patients With FGFR-Altered Advanced Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javle, M.M.; Shroff, R.T.; Zhu, A.; Sadeghi, S.; Choo, S.; Borad, M.J.; Lowery, M.A.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Macarulla, T.; Philip, P.A.; et al. A phase 2 study of BGJ398 in patients (pts) with advanced or metastatic FGFR-altered cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) who failed or are intolerant to platinum-based chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Shaib, W.; Rimassa, L.; Harris, W.; Personeni, N.; El-Rayes, B.; Tolcher, A.; Hall, T.; Wang, Y.; Schwartz, B.; et al. PD-019 ARQ 087, an oral pan- fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor, in patients (pts) with advanced and/or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA). Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, ii109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Bahleda, R.; Kelley, R.K.; Hierro, C.; Ahn, D.; Zhu, A.; Javle, M.; Winkler, R.; et al. Efficacy of TAS-120, an irreversible fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor (FGFRi), in patients with cholangiocarcinoma and FGFR pathway alterations previously treated with chemotherapy and other FGFRi’s. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, ix49–ix50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Sahai, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Vaccaro, G.; Melisi, D.; Al-Rajabi, R.; Paulson, A.S.; Borad, M.J.; Gallinson, D.; Murphy, A.G.; et al. FIGHT-202: A phase II study of pemigatinib in patients (pts) with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Patel, M.; Ahn, M.J.; Lee, J.; Bauer, T.M.; Farago, A.F.; Wheler, J.J.; Liu, S.V.; et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of the Multitargeted Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK Inhibitor Entrectinib: Combined Results from Two Phase I Trials (ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1). Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion–Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.K.; Subimerb, C.; Pairojkul, C.; Wongkham, S.; Cutcutache, I.; Yu, W.; McPherson, J.R.; Allen, G.E.; Ng, C.C.; Wong, B.H.; et al. Exome sequencing of liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koay, E.J.; Odisio, B.C.; Javle, M.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Crane, C.H. Management of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: How do we decide among the various liver-directed treatments? Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2017, 6, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepatobiliary Cancer. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 2021; Hepatobiliary Cancer (Version 2.2021). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hepatobiliary.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Nathan, H.; Aloia, T.A.; Vauthey, J.N.; Abdalla, E.K.; Zhu, A.X.; Schulick, R.D.; Choti, M.A.; Pawlik, T.M. A proposed staging system for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensminger, W.D.; Gyves, J.W. Clinical pharmacology of hepatic arterial chemotherapy. Semin. Oncol. 1983, 10, 176–182. [Google Scholar]
- Cercek, A.; Boerner, T.; Tan, B.R.; Chou, J.F.; Gönen, M.; Boucher, T.M.; Hauser, H.F.; Do, R.K.G.; Lowery, M.A.; Harding, J.J.; et al. Assessment of Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Floxuridine in Combination with Systemic Gemcitabine and Oxaliplatin in Patients with Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.P.; Rivkin, S.E. The implanted pump in metastatic colorectal cancer of the liver. Risk versus benefit. Am. J. Surg. 1985, 149, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.R.; Garnick, M.B.; Osteen, R.T.; Steele, G.D.J.; Wilson, R.E.; Schade, D.; Kaplan, W.D.; Boxt, L.M.; Kandarpa, K.; Mayer, R.J. Long-term hepatic arterial infusion of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine for liver metastases using an implantable infusion pump. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1983, 1, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiels, C.A.; D’Angelica, M.I. Hepatic artery infusion pumps. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 122, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.J.; Stojadinovic, A.; Ben-Porat, L.; Gonen, M.; Kooby, D.; Blumgart, L.; Paty, P.; Fong, Y. The management of variant arterial anatomy during hepatic arterial infusion pump placement. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 9, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massani, M.; Nistri, C.; Ruffolo, C.; Bonariol, R.; Pauletti, B.; Bonariol, L.; Caratozzolo, E.; Morana, G.; Bassi, N. Intrahepatic chemotherapy for unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: Review of literature and personal experience. Updates Surg. 2015, 67, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.M.; Higgins, J.; Waltman, A.C.; Athanasoulis, C.; McKusick, K. Effect of ligation of variant hepatic arterial structures on the completeness of regional chemotherapy infusion. Am. J. Surg. 1987, 153, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, A.A.; Kerlan, R.K.; Stagg, R.J.; Price, D.C.; Hohn, D.C. Total hepatic arterial perfusion after occlusion of variant lobar vessels: Implications for hepatic arterial chemotherapy. Surgery 1986, 99, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jolissaint, J.S.; Soares, K.C.; Seier, K.P.; Kundra, R.; Gonen, M.; Shin, P.J.; Boerner, T.; Sigel, C.; Madupuri, R.; Vakiani, E.; et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma with Lymph Node Metastasis: Treatment-Related Outcomes and the Role of Tumor Genomics in Patient Selection. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Lu, D.; Li, W.; Tan, W.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Min, J.; Shang, C.; Chen, Y. Is lymph node dissection necessary for resectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Assoc. 2019, 21, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Chen, Q.; Kimbrough, C.W.; Beal, E.W.; Lv, Y.; Chakedis, J.; Dillhoff, M.; Schmidt, C.; Cloyd, J.; Pawlik, T.M. Lymphadenectomy for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Has Nodal Evaluation Been Increasingly Adopted by Surgeons over Time?A National Database Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. Off. J. Soc. Surg. Aliment. Tract. 2018, 22, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolverato, G.; Bagante, F.; Weiss, M.; Alexandrescu, S.; Marques, H.P.; Aldrighetti, L.; Maithel, S.K.; Pulitano, C.; Bauer, T.W.; Shen, F.; et al. Comparative performances of the 7th and the 8th editions of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging systems for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, F.; Hahn, F.; Müller, L.; Baumgart, J.; Hoppe-Lotichius, M.; Kloeckner, R.; Lang, H. Relevance of suspicious lymph nodes in preoperative imaging for resectability, recurrence and survival of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, M.; Feng, Y. Prognostic Factors and Treatment Strategies for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma from 2004 to 2013: Population-Based SEER Analysis. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloyd, J.M.; Ejaz, A.; Pawlik, T.M. The Landmark Series: Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.M.; Kemeny, N.; Oderman, P.; Botet, J. Long-term hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Anatomic considerations, operative technique, and treatment morbidity. Arch. Surg. 1984, 119, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curley, S.A.; Chase, J.L.; Roh, M.S.; Hohn, D.C. Technical considerations and complications associated with the placement of 180 implantable hepatic arterial infusion devices. Surgery 1993, 114, 928–935. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, S.; Petrowsky, H.; Schwinnen, I.; Staib-Sebler, E.; Gog, C.; El-Ganainy, A.; Gutt, C.; Müller, H.H.; Lorenz, M. Technical complications of continuous intra-arterial chemotherapy with 5-fluorodeoxyuridine and 5-fluorouracil for colorectal liver metastases. Surgery 2003, 133, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, P.J.; Nissan, A.; Picon, A.I.; Kemeny, N.; Dudrick, P.; Ben-Porat, L.; Espat, J.; Stojadinovic, A.; Cohen, A.M.; Fong, Y.; et al. Technical complications and durability of hepatic artery infusion pumps for unresectable colorectal liver metastases: An institutional experience of 544 consecutive cases. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2005, 201, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeny, N.E.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Hollis, D.R.; Lenz, H.-J.; Warren, R.S.; Naughton, M.J.; Weeks, J.C.; Sigurdson, E.R.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Zhang, C.; et al. Hepatic arterial infusion versus systemic therapy for hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: A randomized trial of efficacy, quality of life, and molecular markers (CALGB 9481). J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemeny, M.M.; Battifora, H.; Blayney, D.W.; Cecchi, G.; Goldberg, D.A.; Leong, L.A.; Margolin, K.A.; Terz, J.J. Sclerosing cholangitis after continuous hepatic artery infusion of FUDR. Ann. Surg. 1985, 202, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemeny, N.; Daly, J.; Reichman, B.; Geller, N.; Botet, J.; Oderman, P. Intrahepatic or systemic infusion of fluorodeoxyuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987, 107, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.E.; Schneider, P.D.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Simpson, C.; Culnane, M.; Steinberg, S.M. A prospective randomized trial of regional versus systemic continuous 5-fluorodeoxyuridine chemotherapy in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases. Ann. Surg. 1987, 206, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohn, D.C.; Stagg, R.J.; Friedman, M.A.; Hannigan, J.F.J.; Rayner, A.; Ignoffo, R.J.; Acord, P.; Lewis, B.J. A randomized trial of continuous intravenous versus hepatic intraarterial floxuridine in patients with colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver: The Northern California Oncology Group trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.K.J.; O’Connell, M.J.; Wieand, H.S.; Fitzgibbons, R.J.J.; Mailliard, J.A.; Rubin, J.; Nagorney, D.M.; Tschetter, L.K.; Krook, J.E. Intra-arterial floxuridine vs systemic fluorouracil for hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. A randomized trial. Arch. Surg. 1990, 125, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougier, P.; Laplanche, A.; Huguier, M.; Hay, J.M.; Ollivier, J.M.; Escat, J.; Salmon, R.; Julien, M.; Roullet Audy, J.C.; Gallot, D.; et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of floxuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma: Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 10, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.; Müller, H.H. Randomized, multicenter trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin administered either via hepatic arterial or intravenous infusion versus fluorodeoxyuridine administered via hepatic arterial infusion in patients with nonresectable liver metastases from color. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeny, M.M.; Adak, S.; Gray, B.; Macdonald, J.S.; Smith, T.; Lipsitz, S.; Sigurdson, E.R.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Benson, A.B., 3rd. Combined-modality treatment for resectable metastatic colorectal carcinoma to the liver: Surgical resection of hepatic metastases in combination with continuous infusion of chemotherapy—An intergroup study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.G.; Edwards, M.J.; McMasters, K.M. Morbidity of adjuvant hepatic arterial infusion pump chemotherapy in the management of colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 188, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Ito, H.; Kemeny, N.E.; Gonen, M.; Allen, P.J.; Paty, P.B.; Fong, Y.; Dematteo, R.P.; Blumgart, L.H.; Jarnagin, W.R.; et al. Biliary sclerosis after hepatic arterial infusion pump chemotherapy for patients with colorectal cancer liver metastasis: Incidence, clinical features, and risk factors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, J.; Narayan, R.R.; Kemeny, N.E.; D’Angelica, M.I. Role of Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Treatment of Initially Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2019, 154, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.J.; McArdle, C.S.; Ledermann, J.; Taylor, I.; Sherlock, D.J.; Schlag, P.M.; Buckels, J.; Mayer, D.; Cain, D.; Stephens, R.J. Intrahepatic arterial versus intravenous fluorouracil and folinic acid for colorectal cancer liver metastases: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantore, M.; Mambrini, A.; Fiorentini, G.; Rabbi, C.; Zamagni, D.; Caudana, R.; Pennucci, C.; Sanguinetti, F.; Lombardi, M.; Nicoli, N. Phase II study of hepatic intraarterial epirubicin and cisplatin, with systemic 5-fluorouracil in patients with unresectable biliary tract tumors. Cancer 2005, 103, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarnagin, W.R.; Schwartz, L.H.; Gultekin, D.H.; Gönen, M.; Haviland, D.; Shia, J.; D’Angelica, M.; Fong, Y.; DeMatteo, R.; Tse, A.; et al. Regional chemotherapy for unresectable primary liver cancer: Results of a phase II clinical trial and assessment of DCE-MRI as a biomarker of survival. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeny, N.E.; Schwartz, L.; Gönen, M.; Yopp, A.; Gultekin, D.; D’Angelica, M.; Fong, Y.; Haviland, D.; Gewirtz, A.N.; Allen, P.; et al. Treating primary liver cancer with hepatic arterial infusion of floxuridine and dexamethasone: Does the addition of systemic bevacizumab improve results? Oncology 2011, 80, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, Y.; Arai, Y.; Yamaura, H.; Sato, Y.; Najima, M.; Aramaki, T.; Sone, M.; Kumada, T.; Tanigawa, N.; Anai, H.; et al. Phase I/II study of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with gemcitabine in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (JIVROSG-0301). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Clin. Trials. 2011, 34, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Lorgis, V.; Vincent, J.; Ladoire, S.; Guiu, B. Hepatic arterial infusion of gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin as second-line treatment for locally advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Preliminary experience. Chemotherapy 2014, 59, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, I.T.; Koerkamp, B.G.; Do, R.K.G.; Gönen, M.; Fong, Y.; Allen, P.J.; D’Angelica, M.; Kingham, T.P.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Klimstra, D.S.; et al. Unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Systemic plus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy is associated with longer survival in comparison with systemic chemotherapy alone. Cancer 2016, 122, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, T.; Aramaki, O.; Moriguchi, M.; Nakayama, H.; Midorikawa, Y.; Takayama, T. Arterial infusion of cisplatin plus S-1 against unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Biosci. Trends. 2018, 12, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.W.; Syrigos, K.N.; Katirtzoglou, N.A. S-1: A promising new oral fluoropyrimidine derivative. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Number and Type of Patients | Treatment Regimen | PFS | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cantore et al., 2005 [66] | 30 BTC •25 iCCA •5 gallbladder cancer | 3-week cycle HAI epirubicin 50 mg/m2, CIS 60 mg/m2 as bolus on Day 1 5-FU 200 mg/m2 per day by continuous infusion Day 1 to Day 14 | 7.1 months (C.I. 1.6–19.1) | 13.2 months |
| Jarnagin et al., 2009 [67] | 34 PLC •26 iCCA •8 HCC | 4-week cycle HAI: FUDR (0.16 mg/kg × 20/pump flow rate) and DEXA 25 mg on day 1 for 14-days of each cycle | 7.4 months | 29.5 months |
| Kemeny et al., 2011 [68] | 22 PLC •18 iCCA •4 HCC | 4-week cycle HAI: FUDR (0.16 mg/kg × 30/pump flow rate) and DEXA 25 mg on day 1 for 14-days of each cycle SYS: bevacizumab 5 mg/kg every other week. | 8.45 months (CI 5.53–11.05) | 31.1 months (CI 14.14–33.59) |
| Inaba et al., 2011 [69] | 13 iCCA | 4-week cycle HAI: GEM 1000 mg/m2 30-min infusion on days 1, 8, and 15 for 5 cycles | - | 389 days (CI 158–620) |
| Ghiringhelli et al., 2013 [70] | 12 iCCA | Second-line treatment 2-week cycle HAI: GEM (1000 mg/m2 given over 30 min) followed by OX (100 mg/m2 given over 2 h) | 9.2 months (CI 2.1–29.4) | 20.3 months (CI 13.2–49.7) |
| Massani et al., 2015 [38] | 11 iCCA | 2-week cycle HAI: Day 1: 100 mg/mq of OX Day 2: 5 FU 7 mg/kg at 2 mL/h in CI for 48 h | - | 17.6 months |
| Konstantinidis et al., 2016 [71]. | 104 iCCA •78 HAI/SYS •26 SYS | 4-week cycle HAI: FUDR (0.16 mg/kg × 20/pump flow rate) and DEXA 25 mg on day 1 for 14-days of each cycle SYS: mostly GEM based | HAI/SYS 12 months SYS 7 months | HAI/SYS 30.8 months SYS 18.4 months |
| Higaki et al., 2018 [72] | 12 iCCA | 42-day cycle HAI: CIS 65 mg/m2 2 mL/min on Day 1 SYS: S-1 60 mg/m2 per day 1–28. | - | 10.1 months (CI 3.6–23.2) |
| Cercek A, et al., 2019 [33] | 38 iCCA | 4-week cycle HAI: FUDR (0.12 mg/kg × 30/pump flow rate) and DEXA 30 mg/pump on day 1 for 14-days of each cycle SYS: GEM (800 mg/m2) with OX (85 mg/m2) on Day 1 or 15, every 2 weeks | 11.8 months (1-sided 90% CI, 11.1) | 25.0 months (95% CI, 20.6-not reached) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massani, M.; Bonariol, L.; Stecca, T. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, a Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122552
Massani M, Bonariol L, Stecca T. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, a Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(12):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122552
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassani, Marco, Luca Bonariol, and Tommaso Stecca. 2021. "Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, a Comprehensive Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 12: 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122552
APA StyleMassani, M., Bonariol, L., & Stecca, T. (2021). Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, a Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(12), 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122552






