Low Dose Chest CT and Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Low-Dose Chest CT-Scan
2.1. Latest Developments before COVID-19
2.2. The Diagnosis of COVID-19 Pneumonia with LDCT
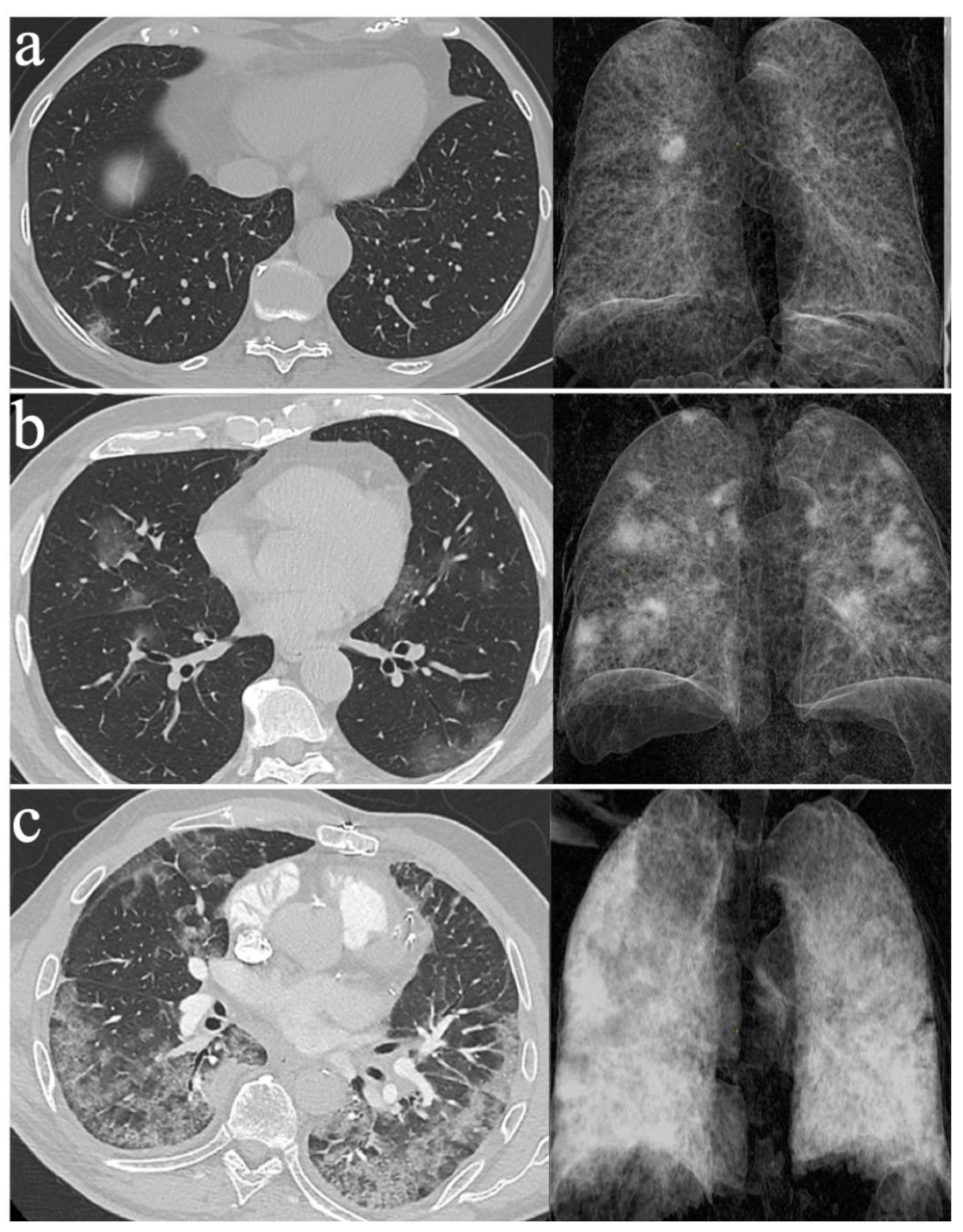
2.3. Assessing the Severity of COVID-19 Pneumonia with LDCT
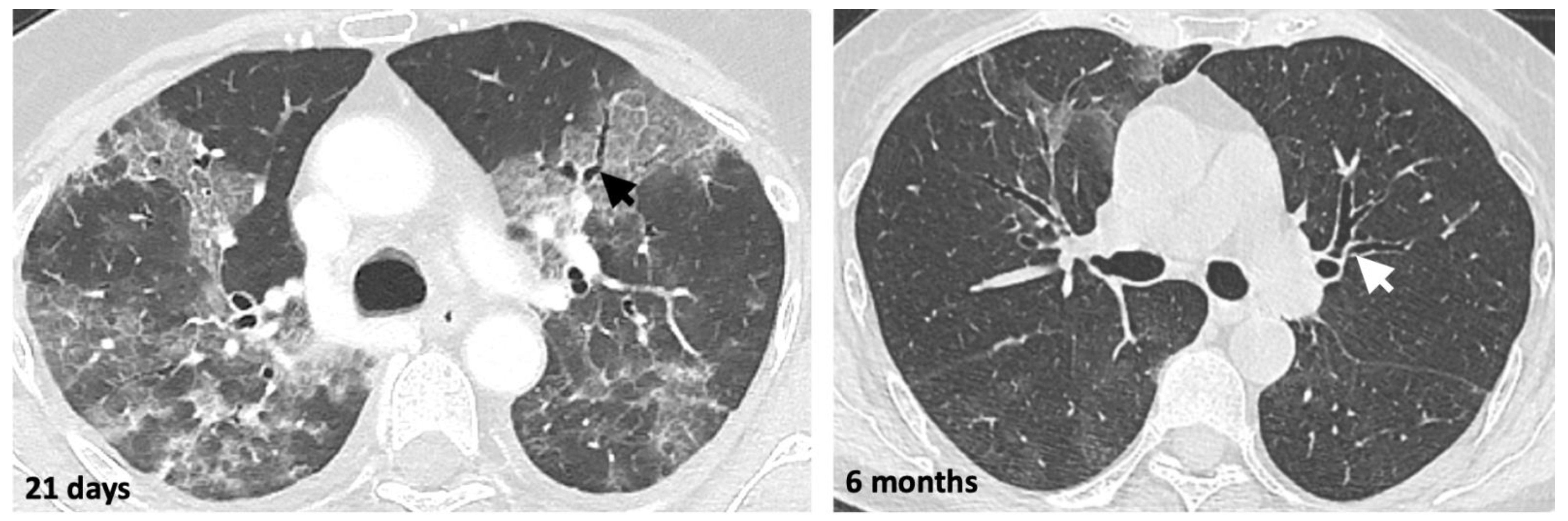
2.4. Monitoring COVID-19 Pneumonia with LDCT
2.5. Limitations of LDCT for the Diagnosis of Pneumonia
3. LUS in Treating COVID-19 Pneumonia
3.1. Use of Lung US before the COVID-19 Epidemic
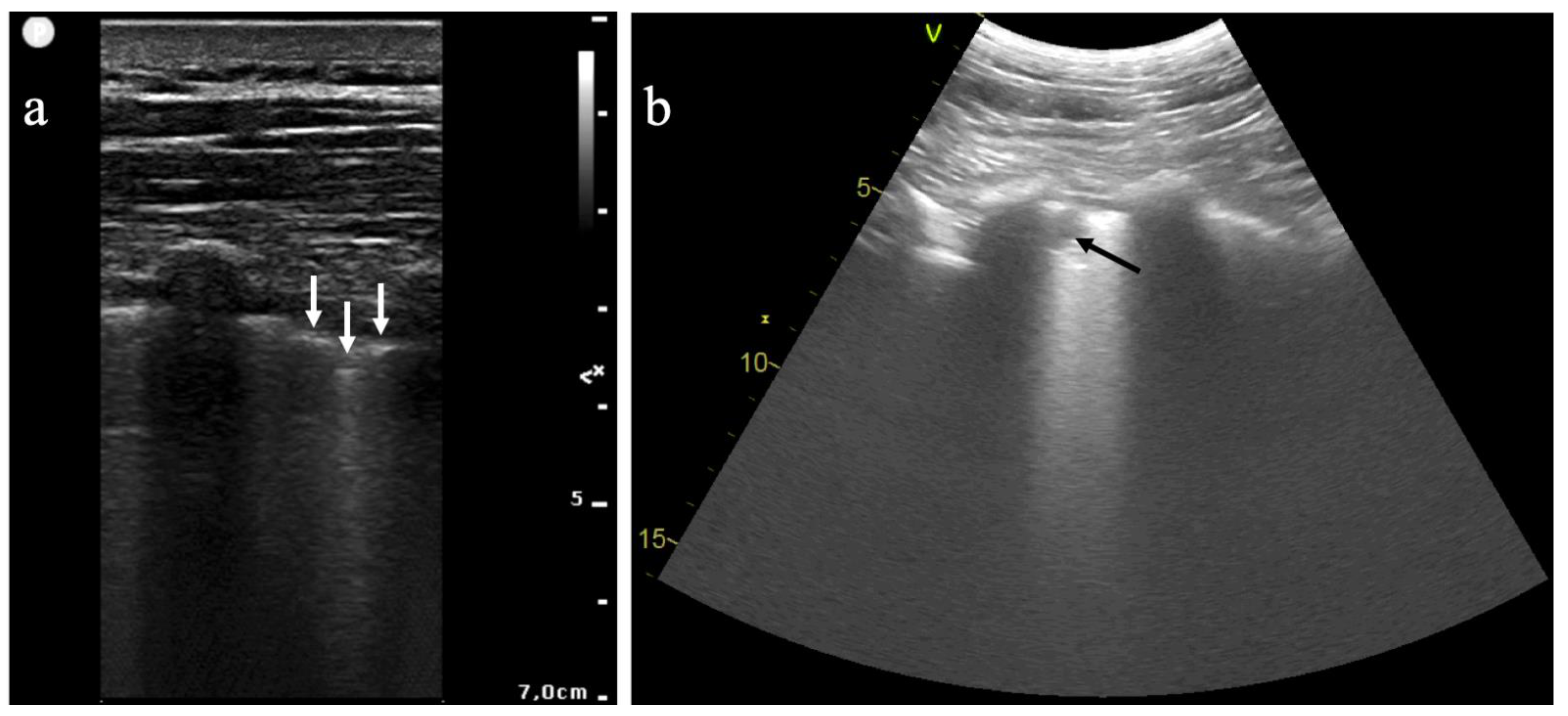
3.2. Using LUS to Diagnose COVID-19 Pneumonia
4. Diagnostic Value of LUS and LDCT for Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 Infections
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, M.; Blasi, F.; Ewig, S.; Garau, J.; Huchon, G.; Ieven, M.; Ortqvist, A.; Schaberg, T.; Torres, A.; van der Heijden, G.; et al. Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections—Full version. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, E1–E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibbons, R.C.; Magee, M.; Goett, H.; Murrett, J.; Genninger, J.; Mendez, K.; Tripod, M.; Tyner, N.; Costantino, T.G. Lung Ultrasound vs. Chest X-Ray Study for the Radiographic Diagnosis of COVID-19 Pneumonia in a High-Prevalence Population. J. Emerg. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, D.A.; Linton, O.W. NCRP Report No. 160, Ionizing Radiation Exposure of the Population of the United States, medical exposure—Are we doing less with more, and is there a role for health physicists? Health Phys. 2009, 97, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenner, D.J. Computed Tomography—An Increasing Source of Radiation Exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Low-Dose Computed Tomographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orso, D.; Guglielmo, N.; Copetti, R. Lung ultrasound in diagnosing pneumonia in the emergency department: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 25, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.C.L.; Hare, S.S.; Edey, A.; Devaraj, A.; Jacob, J.; Johnstone, A.; McStay, R.; Nair, A.; Robinson, G.; Rodrigues, J.; et al. An update on COVID-19 for the radiologist—A British society of Thoracic Imaging statement. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Kalra, M.K.; Gilman, M.D.; Hsieh, J.; Pien, H.H.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Shepard, J.-A.O. Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction Technique for Radiation Dose Reduction in Chest CT: A Pilot Study. Radiology 2011, 259, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffier, J.; Frandon, J.; Larbi, A.; Beregi, J.P.; Pereira, F. CT iterative reconstruction algorithms: A task-based image quality assessment. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidich, D.P.; Marshall, C.H.; Gribbin, C.; Arams, R.S.; McCauley, D.I. Low-dose CT of the lungs: Preliminary observations. Radiology 1990, 175, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neroladaki, A.; Botsikas, D.; Boudabbous, S.; Becker, C.D.; Montet, X. Computed tomography of the chest with model-based iterative reconstruction using a radiation exposure similar to chest X-ray examination: Preliminary observations. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulo, G.; Damilakis, J.; Tsapaki, V.; Schegerer, A.A.; Repussard, J.; Jaschke, W.; Frija, G. Diagnostic Reference Levels based on clinical indications in computed tomography: A literature review. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroft, L.J.M.; van der Velden, L.; Girón, I.H.; Roelofs, J.J.H.; de Roos, A.; Geleijns, J. Added Value of Ultra–low-dose Computed Tomography, Dose Equivalent to Chest X-Ray Radiography, for Diagnosing Chest Pathology. J. Thorac. Imaging 2019, 34, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svahn, T.M.; Sjöberg, T.; Ast, J.C. Dose estimation of ultra-low-dose chest CT to different sized adult patients. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, E.B.; Schininà, V.; Gentile, F.P.; Bibbolino, C. Reduced computed tomography radiation dose in HIV-related pneumonia: Effect on diagnostic image quality. Clin. Imaging 2007, 31, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.K.; et al. The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020, 296, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, H.Y.F.; Lam, H.Y.S.; Fong, A.H.-T.; Leung, S.T.; Chin, T.W.-Y.; Lo, C.S.Y.; Lui, M.M.-S.; Lee, J.C.Y.; Chiu, K.W.-H.; Chung, T.W.-H.; et al. Frequency and Distribution of Chest Radiographic Findings in COVID-19 Positive Patients. Radiology 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7233401/ (accessed on 1 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, M. Temporal Changes of CT Findings in 90 Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Longitudinal Study. Radiology 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7233482/ (accessed on 1 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, S. Recommendation of low-dose CT in the detection and management of COVID-2019. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4356–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagier, J.-C.; Million, M.; Gautret, P.; Colson, P.; Cortaredona, S.; Giraud-Gatineau, A.; Honoré, S.; Gaubert, J.-Y.; Fournier, P.-E.; Tissot-Dupont, H.; et al. Outcomes of 3737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: A retrospective analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 36, 101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, T.; Jacquier, A.; Barral, P.-A.; Castelli, M.; Finance, J.; Lagier, J.-C.; Million, M.; Parola, P.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D.; et al. Low-dose chest CT for diagnosing and assessing the extent of lung involvement of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia using a semi quantitative score. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Goaster, L. HAS Réponses rapides dans le cadre du COVID-19—Indications du scanner thoracique. 2020, 6. Available online: https://www.has-sante.fr/upload/docs/application/pdf/2020-04/reponse_rapide_codid-19_indication_tdm_mel2.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2020).
- Desmet, J.; Biebaû, C.; De Wever, W.; Cockmartin, L.; Viktor, V.; Coolen, J.; Verschakelen, J.; Dubbeldam, A. Performance of Low-Dose Chest CT as a Triage Tool for Suspected COVID-19 Patients. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2021, 105. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7894373/ (accessed on 11 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- Dangis, A.; Gieraerts, C.; De Bruecker, Y.; Janssen, L.; Valgaeren, H.; Obbels, D.; Gillis, M.; Van Ranst, M.; Frans, J.; Demeyere, A.; et al. Accuracy and Reproducibility of Low-Dose Submillisievert Chest CT for the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prokop, M.; Van Everdingen, W.M.; van Rees Vellinga, T.; Van Ufford, H.Q.; Stöger, L.; Beenen, L.; Geurts, B.; Gietema, H.; Krdzalic, J.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.; et al. CO-RADS: A Categorical CT Assessment Scheme for Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19—Definition and Evaluation. Radiology 2020, 296, E97–E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, S.; Panvini, N.; Bellini, D.; Rengo, M.; Ciotola, M.; De Vivo, M.; Gambaretto, C.; Caldon, V.; Panno, S.; Del Borgo, C.; et al. Radiographers and COVID-19 pneumonia: Diagnostic performance using CO-RADS. Radiogr. Lond. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulden, R.; Hoyle, M.-C.; Monis, J.; Railton, D.; Riley, V.; Martin, P.; Martina, R.; Nsutebu, E. qSOFA, SIRS and NEWS for predicting inhospital mortality and ICU admission in emergency admissions treated as sepsis. Emerg. Med. J. 2018, 35, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Q.; Luo, Y.; Gao, C.; Zeng, W. Chest CT Severity Score: An Imaging Tool for Assessing Severe COVID-19. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7233443/ (accessed on 9 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoleriu, M.G.; Gerckens, M.; Obereisenbuchner, F.; Zaimova, I.; Hetrodt, J.; Mavi, S.-C.; Schmidt, F.; Schoenlebe, A.A.; Heinig-Menhard, K.; Koch, I.; et al. Automated quantitative thin slice volumetric low dose CT analysis predicts disease severity in COVID-19 patients. Clin. Imaging 2021, 79, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufuk, F.; Demirci, M.; Sagtas, E.; Akbudak, I.H.; Ugurlu, E.; Sari, T. The prognostic value of pneumonia severity score and pectoralis muscle area on chest CT in adult COVID-19 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 131, 109271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Balestro, E.; Aliberti, S.; Cocconcelli, E.; Biondini, D.; Della Casa, G.; Sverzellati, N.; Maher, T.M. Pulmonary fibrosis secondary to COVID-19: A call to arms? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2213260020302228 (accessed on 17 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Ojo, A.S.; Balogun, S.A.; Williams, O.T.; Ojo, O.S. Pulmonary Fibrosis in COVID-19 Survivors: Predictive Factors and Risk Reduction Strategies. Hindawi 2020, 2020, e6175964. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/pm/2020/6175964/ (accessed on 16 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, B.E.; Lee, S.J.; Ryu, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, J.H. Ultra-Low-Dose CT of the Thorax Using Iterative Reconstruction: Evaluation of Image Quality and Radiation Dose Reduction. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, J.D.; Nazario-Larrieu, J.; Cai, T.; Ledbetter, M.S.; Duran-Mendicuti, M.A.; Judy, P.F.; Rybicki, F.J. Reduced-Dose CT: Effect on Reader Evaluation in Detection of Pulmonary Embolism. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, S.; Fujikawa, A.; Jitsu, M.; Kunishima, N.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Umeda, S.; Uwabe, Y. Chest CT Findings in Cases from the Cruise Ship “Diamond Princess” with Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parekh, M.; Donuru, A.; Balasubramanya, R.; Kapur, S. Review of the Chest CT Differential Diagnosis of Ground-Glass Opacities in the COVID Era. Radiology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS); et al. International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allinovi, M.; Parise, A.; Giacalone, M.; Amerio, A.; Delsante, M.; Odone, A.; Franci, A.; Gigliotti, F.; Amadasi, S.; Delmonte, D.; et al. Lung Ultrasound May Support Diagnosis and Monitoring of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, G.; Lopez, A.; Leone, M.; Zieleskiewicz, L. “No dose” lung ultrasound correlation with “low dose” CT scan for early diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Gargani, L.; Perlini, S.; Spinelli, S.; Barbieri, G.; Lanotte, A.; Casasola, G.G.; Nogué-Bou, R.; Lamorte, A.; Agricola, E.; et al. Lung ultrasound for the early diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia: An international multicenter study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.-Y.; Wang, X.-T.; Zhang, L.-N. Findings of lung ultrasonography of novel corona virus pneumonia during the 2019–2020 epidemic. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 849–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo Giudice, V.; Bruni, A.; Corcioni, E.; Corcioni, B. Ultrasound in the evaluation of interstitial pneumonia. J. Ultrasound 2008, 11, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Testa, A.; Soldati, G.; Copetti, R.; Giannuzzi, R.; Portale, G.; Gentiloni-Silveri, N. Early recognition of the 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) pneumonia by chest ultrasound. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Mathis, G.; Blaivas, M.; Volpicelli, G.; Seibel, A.; Wastl, D.; Atkinson, N.S.S.; Cui, X.-W.; Fan, M.; Yi, D. Lung B-line artefacts and their use. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narinx, N.; Smismans, A.; Symons, R.; Frans, J.; Demeyere, A.; Gillis, M. Feasibility of using point-of-care lung ultrasound for early triage of COVID-19 patients in the emergency room. Emerg. Radiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, E.; Goffi, A.; Tizzani, M.; Locatelli, S.M.; Porrino, J.; Losano, I.; Leone, D.; Calzoari, G.; Vesan, M.; Steri, F.; et al. Lung Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in the Emergency Department. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, Y.; Topilsky, Y.; Taieb, P.; Banai, A.; Hochstadt, A.; Merdler, I.; Oz, A.G.; Vine, J.; Goren, O.; Cohen, B.; et al. Lung ultrasound predicts clinical course and outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieleskiewicz, L.; Markarian, T.; Lopez, A.; Taguet, C.; Mohammedi, N.; Boucekine, M.; Baumstarck, K.; Besch, G.; Mathon, G. Comparative study of lung ultrasound and chest computed tomography scan in the assessment of severity of confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazerian, P.; Vanni, S.; Volpicelli, G.; Gigli, C.; Zanobetti, M.; Bartolucci, M.; Ciavattone, A.; Lamorte, A.; Veltri, A.; Fabbri, A.; et al. Accuracy of Point-of-Care Multiorgan Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism. Chest 2014, 145, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dargent, A.; Chatelain, E.; Kreitmann, L.; Quenot, J.-P.; Cour, M.; Argaud, L.; the COVID-LUS Study Group. Lung ultrasound score to monitor COVID-19 pneumonia progression in patients with ARDS. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, K.; Kagaya, K.; Zarebski, A.; Chowell, G. Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan, 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishiura, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Miyama, T.; Suzuki, A.; Jung, S.-M.; Hayashi, K.; Kinoshita, R.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R.; et al. Estimation of the asymptomatic ratio of novel coronavirus infections (COVID-19). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puylaert, C.A.J.; Scheijmans, J.C.G.; Borgstein, A.B.J.; Andeweg, C.S.; Bartels-Rutten, A.; Beets, G.L.; Henegouwen, M.I.V.B.; Braak, S.J.; Couvreur, R.; Daams, F.; et al. Yield of Screening for COVID-19 in Asymptomatic Patients Before Elective or Emergency Surgery Using Chest CT and RT-PCR (SCOUT). Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, B.; Kou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Wu, D.; Ren, L.; Chen, Z.; Shan, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Application Value of Lung Ultrasound in Asymptomatic Patients with Confirmed COVID-19. Adv. Ultrasound Diagn. Ther. 2020, 4, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafat, E.; Yassa, M.; Koc, A.; Tug, N.; TULIP Collaboration. Utility of lung ultrasound assessment for probable SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy and universal screening of asymptomatic individuals. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.K.; et al. The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement from the Fleischner Society. Chest 2020, 158, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Monteiro, R.A.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Ferraz da Silva, L.F.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Toledo do Nascimento, E.C.; Mauad, T.; do Nascimento Saldiva, P.H.; Dolhnikoff, M. Ultrasound assessment of pulmonary fibroproliferative changes in severe COVID-19: A quantitative correlation study with histopathological findings. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supinski, G.S.; Callahan, L.A. Diaphragm weakness in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Gu, X.; Kang, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; et al. 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: A cohort study. Lancet 2021. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673620326568 (accessed on 12 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Dai, Y.; Ling, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, R.; Ding, X.; Qi, H.; Shi, Y.; et al. Clinical Potential of UTE-MRI for Assessing COVID-19: Patient- and Lesion-Based Comparative Analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Finance, J.; Zieleskewicz, L.; Habert, P.; Jacquier, A.; Parola, P.; Boussuges, A.; Bregeon, F.; Eldin, C. Low Dose Chest CT and Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102196
Finance J, Zieleskewicz L, Habert P, Jacquier A, Parola P, Boussuges A, Bregeon F, Eldin C. Low Dose Chest CT and Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(10):2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102196
Chicago/Turabian StyleFinance, Julie, Laurent Zieleskewicz, Paul Habert, Alexis Jacquier, Philippe Parola, Alain Boussuges, Fabienne Bregeon, and Carole Eldin. 2021. "Low Dose Chest CT and Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 10: 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102196
APA StyleFinance, J., Zieleskewicz, L., Habert, P., Jacquier, A., Parola, P., Boussuges, A., Bregeon, F., & Eldin, C. (2021). Low Dose Chest CT and Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(10), 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102196





