Characteristics and Risk Factors for Intensive Care Unit Cardiac Arrest in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19—A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population, Design and Ethics
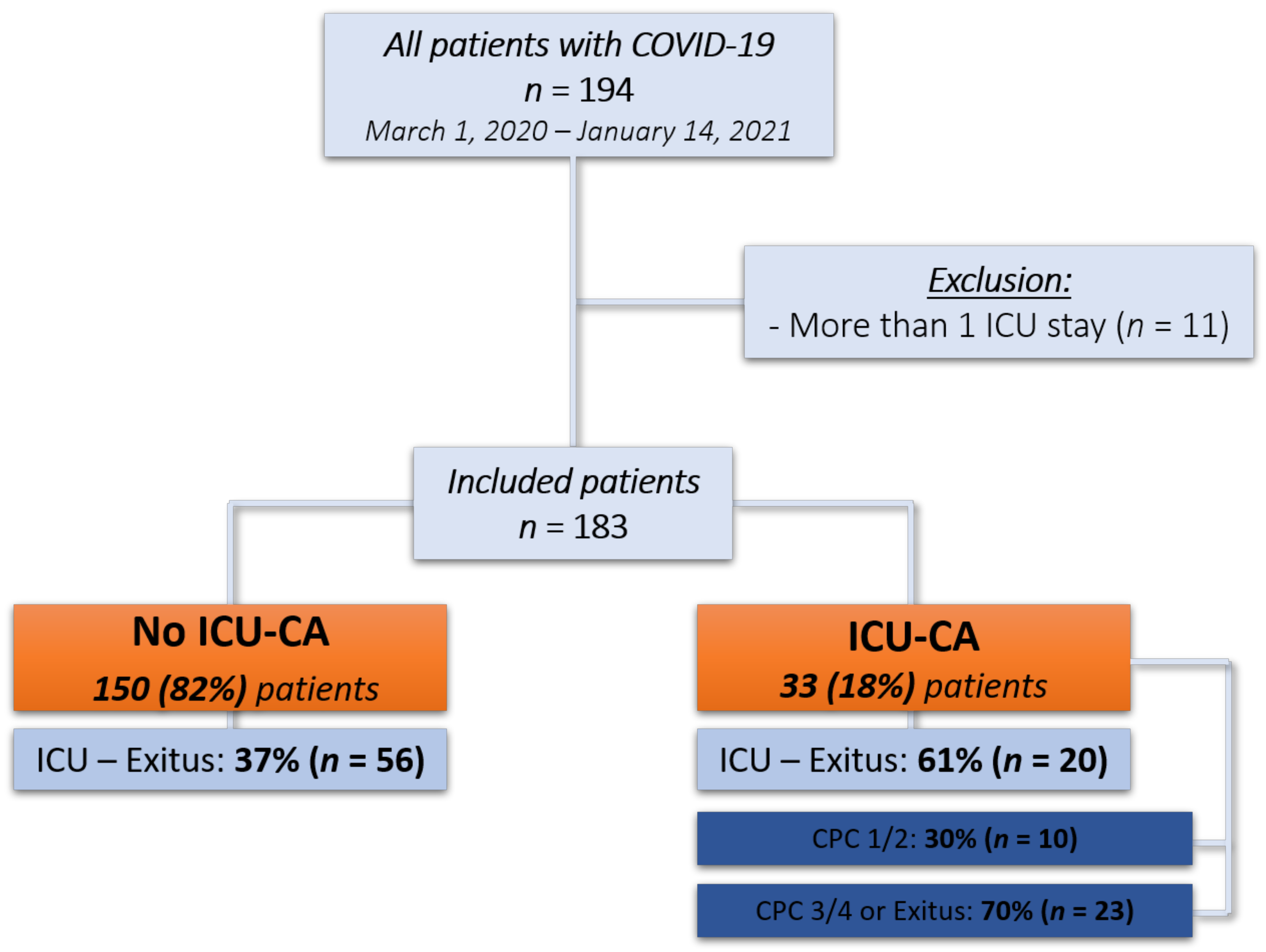
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Definitions and Patient Management
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Baseline and ICU Characteristics of the Study Populations
3.3. Characteristics of Intensive Care Unit Cardiac Arrest
3.4. Survival, Functional Outcome and Risk Factors for ICU-CA
3.5. Factors Associated with Unfavorable Outcome in Patients with ICU-CA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO—World Map—COVID-19. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Roedl, K.; Jarczak, D.; Thasler, L.; Bachmann, M.; Schulte, F.; Bein, B.; Weber, C.F.; Schäfer, U.; Veit, C.; Hauber, H.P.; et al. Mechanical ventilation and mortality among 223 critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicentric study in Germany. Aust. Crit. Care Off. J. Confed. Aust. Crit. Care Nurses 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, E.; Sechi, G.M.; Mare, C.; Canevari, F.; Brancaglione, A.; Primi, R.; Klersy, C.; Palo, A.; Contri, E.; Ronchi, V.; et al. Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest during the Covid-19 Outbreak in Italy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijon, E.; Karam, N.; Jost, D.; Perrot, D.; Frattini, B.; Derkenne, C.; Sharifzadehgan, A.; Waldmann, V.; Beganton, F.; Narayanan, K.; et al. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest during the COVID-19 pandemic in Paris, France: A population-based, observational study. Lancet Public Health 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanian, P.; Lundgren, P.; Strömsöe, A.; Aune, S.; Bergström, G.; Hagberg, E.; Hollenberg, J.; Lindqvist, J.; Djärv, T.; Castelheim, A.; et al. Cardiac arrest in COVID-19: Characteristics and outcomes of in- and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. A report from the Swedish Registry for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. Eur. Heart J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roedl, K.; Söffker, G.; Fischer, D.; Müller, J.; Westermann, D.; Issleib, M.; Kluge, S.; Jarczak, D. Effects of COVID-19 on in-hospital cardiac arrest: Incidence, causes, and outcome—A retrospective cohort study. Scand. J. TraumaResusc. Emerg. Med. 2021, 29, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Xu, S.; Ma, X.; Xu, Z.; Lyu, J.; Ng, M.; Cui, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; et al. In-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes among patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Resuscitation 2020, 151, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.-W.; Lu, T.-C.; Fang, C.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Chen, W.-J.; Chen, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-L. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department services acuity and possible collateral damage. Resuscitation 2020, 153, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, V.; Chishti, I.; Rothman, A.; Redlener, M.; Liang, J.; Pan, D.; Mathew, J. Outcomes of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Patients with COVID-19 in New York City. Resuscitation 2020, 155, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, S.S.; Brenner, S.K.; Azam, T.U.; Shadid, H.R.; Anderson, E.; Berlin, H.; Pan, M.; Meloche, C.; Feroz, R.; O’Hayer, P.; et al. In-hospital cardiac arrest in critically ill patients with covid-19: Multicenter cohort study. BMJ 2020, 371, m3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Smith, H.; Olarewaju, A.; Jani, Y.; Cobb, A.; Owens, J.; Moore, J.; Chenna, A.; Hess, D. Is Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Futile in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Experiencing In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest? Crit. Care Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, O.J.L.; Yuriditsky, E.; Johnson, N.J.; Doran, O.; Buckler, D.G.; Neefe, S.; Seethala, R.R.; Motov, S.; Moskowitz, A.; Lee, J.; et al. In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Patients with Coronavirus 2019. Resuscitation 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efendijev, I.; Nurmi, J.; Castrén, M.; Skrifvars, M.B. Incidence and outcome from adult cardiac arrest occurring in the intensive care unit: A systematic review of the literature. Resuscitation 2014, 85, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Kane, C.; Oglesby, F.; Barnard, K.; Soar, J.; Thomas, M. The incidence of cardiac arrest in the intensive care unit: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Care Soc. 2019, 20, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemiale, V.; Dumas, F.; Mongardon, N.; Giovanetti, O.; Charpentier, J.; Chiche, J.D.; Carli, P.; Mira, J.P.; Nolan, J.; Cariou, A. Intensive care unit mortality after cardiac arrest: The relative contribution of shock and brain injury in a large cohort. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedl, K.; Jarczak, D.; Blohm, R.; Winterland, S.; Müller, J.; Fuhrmann, V.; Westermann, D.; Söffker, G.; Kluge, S. Epidemiology of intensive care unit cardiac arrest: Characteristics, comorbidities, and post-cardiac arrest organ failure—A prospective observational study. Resuscitation 2020, 156, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, J.P.; Soar, J.; Cariou, A.; Cronberg, T.; Moulaert, V.R.M.; Deakin, C.D.; Bottiger, B.W.; Friberg, H.; Sunde, K.; Sandroni, C. European Resuscitation Council and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine Guidelines for Post-resuscitation Care 2015: Section 5 of the European Resuscitation Council Guidelines for Resuscitation 2015. Resuscitation 2015, 95, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, C. Biomarkers after resuscitation: Relevance in daily clinical practice for prognosis estimation and definition of therapeutic goals. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notf. 2019, 114, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, J.P.; Berg, R.A.; Andersen, L.W.; Bhanji, F.; Chan, P.S.; Donnino, M.W.; Lim, S.H.; Ma, M.H.; Nadkarni, V.M.; Starks, M.A.; et al. Cardiac Arrest and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Outcome Reports: Update of the Utstein Resuscitation Registry Template for In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Consensus Report From a Task Force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian and New Zealand Council on Resuscitation, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa, Resuscitation Council of Asia). Resuscitation 2019, 144, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmann, V.; Jäger, B.; Zubkova, A.; Drolz, A. Hypoxic hepatitis—Epidemiology, pathophysiology and clinical management. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2010, 122, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, S.; Janssens, U.; Welte, T.; Weber-Carstens, S.; Marx, G.; Karagiannidis, C. German recommendations for critically ill patients with COVID-19. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notf. 2020, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, J.R.; Lemeshow, S.; Saulnier, F. A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA 1993, 270, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efendijev, I.; Raj, R.; Reinikainen, M.; Hoppu, S.; Skrifvars, M.B. Temporal trends in cardiac arrest incidence and outcome in Finnish intensive care units from 2003 to 2013. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, S.; Ewer, M.S.; Price, K.J.; Feeley, T.W. Outcome and cost implications of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the medical intensive care unit of a comprehensive cancer center. Supportive Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Supportive Care Cancer 2002, 10, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leloup, M.; Briatte, I.; Langlois, A.; Cariou, A.; Lesieur, O. Unexpected cardiac arrests occurring inside the ICU: Outcomes of a French prospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.A.F.; Redfern, O.C.; Hatch, R.; Young, J.D.; Tarassenko, L.; Watkinson, P.J. Trajectories of vital signs in patients with COVID-19. Resuscitation 2020, 156, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covino, M.; Sandroni, C.; Santoro, M.; Sabia, L.; Simeoni, B.; Bocci, M.G.; Ojetti, V.; Candelli, M.; Antonelli, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Predicting intensive care unit admission and death for COVID-19 patients in the emergency department using early warning scores. Resuscitation 2020, 156, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.B.; Kakar, T.S.; Mayer, C.; Khanal, D. Clinical Outcomes of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedl, K.; Spiel, A.O.; Nurnberger, A.; Horvatits, T.; Drolz, A.; Hubner, P.; Warenits, A.M.; Sterz, F.; Herkner, H.; Fuhrmann, V. Hypoxic liver injury after in- and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Risk factors and neurological outcome. Resuscitation 2019, 137, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geri, G.; Guillemet, L.; Dumas, F.; Charpentier, J.; Antona, M.; Lemiale, V.; Bougouin, W.; Lamhaut, L.; Mira, J.P.; Vinsonneau, C.; et al. Acute kidney injury after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Risk factors and prognosis in a large cohort. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, I.; Monchi, M.; Chiche, J.D.; Joly, L.M.; Spaulding, C.; Bourgeois, B.; Cariou, A.; Rozenberg, A.; Carli, P.; Weber, S.; et al. Reversible myocardial dysfunction in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, B.W.; Kilgannon, J.H.; Chansky, M.E.; Mittal, N.; Wooden, J.; Parrillo, J.E.; Trzeciak, S. Multiple organ dysfunction after return of spontaneous circulation in postcardiac arrest syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2013, 41, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedl, K.; Wallmuller, C.; Drolz, A.; Horvatits, T.; Rutter, K.; Spiel, A.; Ortbauer, J.; Stratil, P.; Hubner, P.; Weiser, C.; et al. Outcome of in- and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survivors with liver cirrhosis. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumar, R.W.; Nolan, J.P.; Adrie, C.; Aibiki, M.; Berg, R.A.; Böttiger, B.W.; Callaway, C.; Clark, R.S.B.; Geocadin, R.G.; Jauch, E.C.; et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication. A consensus statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, Australian and New Zealand Council on Resuscitation, European Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Asia, and the Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa); the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; and the Stroke Council. Circulation 2008, 118, 2452–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Alwan, A.; Ehlenbach, W.J.; Menon, P.R.; Young, M.P.; Stapleton, R.D. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation among mechanically ventilated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigoriyan, A.; Vazquez, R.; Palvinskaya, T.; Bindelglass, G.; Rishi, A.; Amoateng-Adjepong, Y.; Manthous, C.A. Outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation for patients on vasopressors or inotropes: A pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2009, 24, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Kaufman, D.A.; Zarich, S.; Chan, P.S.; Ong, P.; Amoateng-Adjepong, Y.; Manthous, C.A. Outcomes of critically ill patients who received cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedl, K.; Jarczak, D.; Drolz, A.; Wichmann, D.; Boenisch, O.; de Heer, G.; Burdelski, C.; Frings, D.; Sensen, B.; Nierhaus, A.; et al. Severe liver dysfunction complicating course of COVID-19 in the critically ill: Multifactorial cause or direct viral effect? Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, L.; Jordan, B.; Druml, W.; Bauer, P.; Metnitz, P.G. Incidence and prognosis of early hepatic dysfunction in critically ill patients—A prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med. 2007, 35, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrifvars, M.B.; Varghese, B.; Parr, M.J. Survival and outcome prediction using the Apache III and the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) score in patients treated in the intensive care unit (ICU) following out-of-hospital, in-hospital or ICU cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | All Patients | ICU-CA | No ICU-CA | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 183) | (n = 33) | (n = 150) | ||
| Demographics | ||||
| Age, years median (IQR) | 63 (55–73) | 64 (55–75) | 62 (55–73) | 0.627 |
| Gender, male n (%) | 120 (66) | 20 (61) | 100 (67) | 0.507 |
| Height, cm median (IQR) | 175 (168–180) | 172 (166–180) | 175 (169–180) | 0.238 |
| Weight, kg median (IQR) | 85 (73–100) | 85 (72–100) | 84 (73–100) | 0.947 |
| BMI, kg/m2 median (IQR) | 27 (24–32) | 29 (24–33) | 27 (24–32) | 0.398 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Charlson comorbidity index, pts.; median (IQR) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 0.801 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 105 (57) | 22 (67) | 83 (55) | 0.233 |
| Coronary heart disease, n (%) | 34 (19) | 7 (21) | 27 (18) | 0.534 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 28 (15) | 3 (9) | 25 (17) | 0.274 |
| Chronic respiratory disease, n (%) | 27 (15) | 5 (15) | 22 (15) | 0.943 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 60 (33) | 12 (36) | 48 (32) | 0.259 |
| Malignant condition, n (%) | 45 (25) | 9 (27) | 36 (24) | 0.693 |
| COVID-19 | ||||
| Positive test to ICU, days median (IQR) | 5 (1–12) | 8 (3–17) | 5 (1–11) | 0.032 |
| Cough, n (%) | 82 (44) | 16 (48) | 66 (44) | 0.613 |
| Shortness of breath, n (%) | 111 (61) | 19 (58) | 92 (61) | 0.689 |
| Fever, n (%) | 81 (44) | 13 (39) | 68 (45) | 0.534 |
| Fatigue, n (%) | 24 (13) | 4 (12) | 20 (13) | 0.852 |
| Myalgia, n (%) | 9 (5) | 2 (6) | 7 (5) | 0.737 |
| Disease Severity on admission | ||||
| SAPS II (pts.) median (IQR) | 40 (33–48) | 44 (37–52) | 39 (32–45) | 0.016 |
| SOFA (pts.) median (IQR) | 7 (3–12) | 12 (6–13) | 7 (3–11) | 0.004 |
| ICU Procedures | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 133 (73) | 32 (97) | 101 (67) | 0.001 |
| HFNC, n (%) | 67 (37) | 8 (24) | 59 (39) | 0.103 |
| NIV, n (%) | 49 (27) | 9 (27) | 40 (27) | 0.943 |
| ECMO, n (%) | 52 (28) | 17 (52) | 35 (23) | 0.001 |
| Vasopressor, n (%) | 145 (79) | 32 (97) | 113 (75) | 0.006 |
| RRT, n (%) | 87 (48) | 22 (67) | 65 (43) | 0.015 |
| ARDS and Management | ||||
| ARDS | 124 (68) | 30 (91) | 94 (63) | 0.002 |
| -Mild | 7 (4) | 1(3) | 6 (4) | 0.314 |
| -Moderate | 24 (13) | 2 (6) | 22 (15) | 0.037 |
| -Severe | 93 (51) | 27(82) | 66 (44) | 0.049 |
| Inhaled vasodilator | 57 (31) | 15 (45) | 42 (28) | 0.05 |
| Prone positioning | 95 (52) | 17 (52) | 78 (52) | 0.96 |
| Neuromuscular blockade | 42 (23) | 9 (27) | 33 (22) | 0.514 |
| Steroid therapy | 118 (64) | 23 (70) | 95 (63) | 0.489 |
| Complications | ||||
| Heart failure, n (%) | 8 (4) | 2 (6) | 6 (4) | 0.6 |
| Pulmonary embolism, n (%) | 13 (7) | 2 (6) | 11 (7) | 0.797 |
| Deep vein thrombosis, n (%) | 15 (8) | 1 (3) | 14 (9) | 0.232 |
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 7 (4) | 3 (9) | 4 (3) | 0.082 |
| Septic shock, n (%) | 80 (44) | 20 (61) | 60 (40) | 0.035 |
| Outcome | ||||
| ICU mortality, n (%) | 76 (42) | 20 (61) | 56 (37) | 0.014 |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 78 (43) | 20 (61) | 58 (39) | 0.021 |
| Length of stay—ICU, days median (IQR) | 13 (5–25) | 21 (8–32) | 12 (5–24) | 0.159 |
| Parameters | All Patients | ICU-CA Favorable | ICU-CA Unfavorable | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 33) | (n = 10) | (n = 23) | ||
| Cardiac arrest Characteristics | ||||
| Initial rhythm shockable (VT/VF), n (%) | 3 (9) | 2 (20) | 1 (4) | 0.151 |
| Defibrillation, n (%) | 5 (15) | 1 (10) | 4 (17) | 0.586 |
| Sustained ROSC, n (%) | 31 (94) | 10 (100) | 21 (91) | 0.336 |
| Cardiac re-arrest, n (%) | 7 (21) | 0 (0) | 7 (30) | 0.049 |
| Presumed non-cardiac cause, n (%) | 28 (85) | 8 (80) | 20 (87) | 0.609 |
| Epinephrine median (IQR) | 1 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 1 (1–2.3) | 0.501 |
| Ischemic time, min; median (IQR) | ||||
| -No-flow | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.363 |
| -Total resuscitation time | 3 (1–5) | 2 (0.8–4.5) | 4 (1–6) | 0.354 |
| Targeted temperature management, n (%) | 16 (48) | 3 (30) | 13 (57) | 0.161 |
| Use of mechanical compression system, n (%) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0.697 |
| E-CPR, n (%) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0.503 |
| VV-ECMO—before CA, n (%) | 8 (24) | 3 (30) | 5 (22) | 0.611 |
| ICU characteristics | ||||
| Severity of illness | ||||
| SAPS II (pts.) median (IQR) | 44 (37–52) | 40.5 (35–53) | 47 (38–52) | 0.472 |
| SOFA—before CA (pts.) median (IQR) | 12 (10–15) | 9 (6–12) | 13 (12–15.5) | 0.038 |
| SOFA—after CA (pts.) median (IQR) | 15 (12–16) | 12 (9–13) | 16 (13.5–17) | 0.01 |
| SOFA—24 h after CA (pts.) median (IQR) | 14 (10–17) | 8 (7–13) | 16 (13.5–17) | 0.002 |
| Lab values—post CA median (IQR) | ||||
| Lactate—highest after CA, mmol/l | 4.6 (3.1–8.3) | 3.4 (1.4–4.5) | 6.1 (4.2–12.7) | 0.016 |
| pH—lowest after CA | 7.2 (7.12–7.3) | 7.4 (7.18–7.46) | 7.2 (7.06–7.25) | 0.034 |
| Horowitz Index median (IQR) | 114 (80–154) | 93 (65–174) | 97 (67–140) | 0.685 |
| Procedures/complications during ICU | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 32 (97) | 10 (100) | 22 (96) | 0.503 |
| Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, n (%) | 17 (53) | 6 (60) | 11 (48) | 0.52 |
| Vasopressor therapy, n (%) | 32 (97) | 9 (90) | 23 (100) | 0.503 |
| Renal replacement therapy, n (%) | 22 (67) | 5 (50) | 17 (74) | 0.181 |
| Coronary angiography—post CA, n (%) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0.891 |
| Hypoxic liver injury, n (%) | 7 (21) | 2 (20) | 5 (22) | 0.911 |
| Cholestasis–Bilirubin >2 mg/dl, n (%) | 15 (45) | 1 (10) | 14 (61) | 0.007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roedl, K.; Söffker, G.; Wichmann, D.; Boenisch, O.; de Heer, G.; Burdelski, C.; Frings, D.; Sensen, B.; Nierhaus, A.; Westermann, D.; et al. Characteristics and Risk Factors for Intensive Care Unit Cardiac Arrest in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19—A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102195
Roedl K, Söffker G, Wichmann D, Boenisch O, de Heer G, Burdelski C, Frings D, Sensen B, Nierhaus A, Westermann D, et al. Characteristics and Risk Factors for Intensive Care Unit Cardiac Arrest in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19—A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(10):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102195
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoedl, Kevin, Gerold Söffker, Dominic Wichmann, Olaf Boenisch, Geraldine de Heer, Christoph Burdelski, Daniel Frings, Barbara Sensen, Axel Nierhaus, Dirk Westermann, and et al. 2021. "Characteristics and Risk Factors for Intensive Care Unit Cardiac Arrest in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19—A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 10: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102195
APA StyleRoedl, K., Söffker, G., Wichmann, D., Boenisch, O., de Heer, G., Burdelski, C., Frings, D., Sensen, B., Nierhaus, A., Westermann, D., Kluge, S., & Jarczak, D. (2021). Characteristics and Risk Factors for Intensive Care Unit Cardiac Arrest in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19—A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(10), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102195






