Influence of Blend Composition and Silica Nanoparticles on the Morphology and Gas Separation Performance of PU/PVA Blend Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
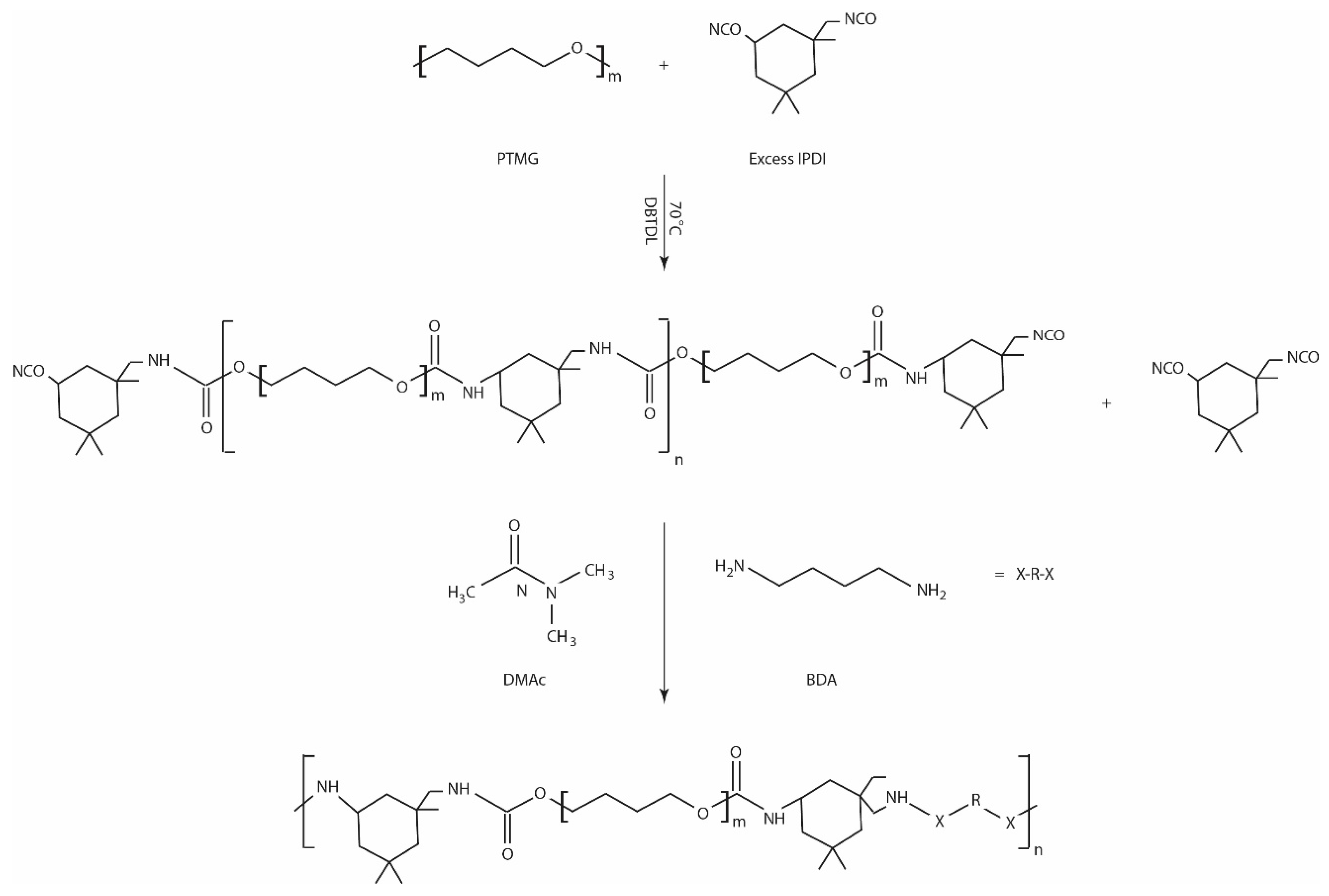
2.2. Polymer Synthesis
2.3. Silica Synthesis
2.4. Membrane Fabrication
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Gas Permeation Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
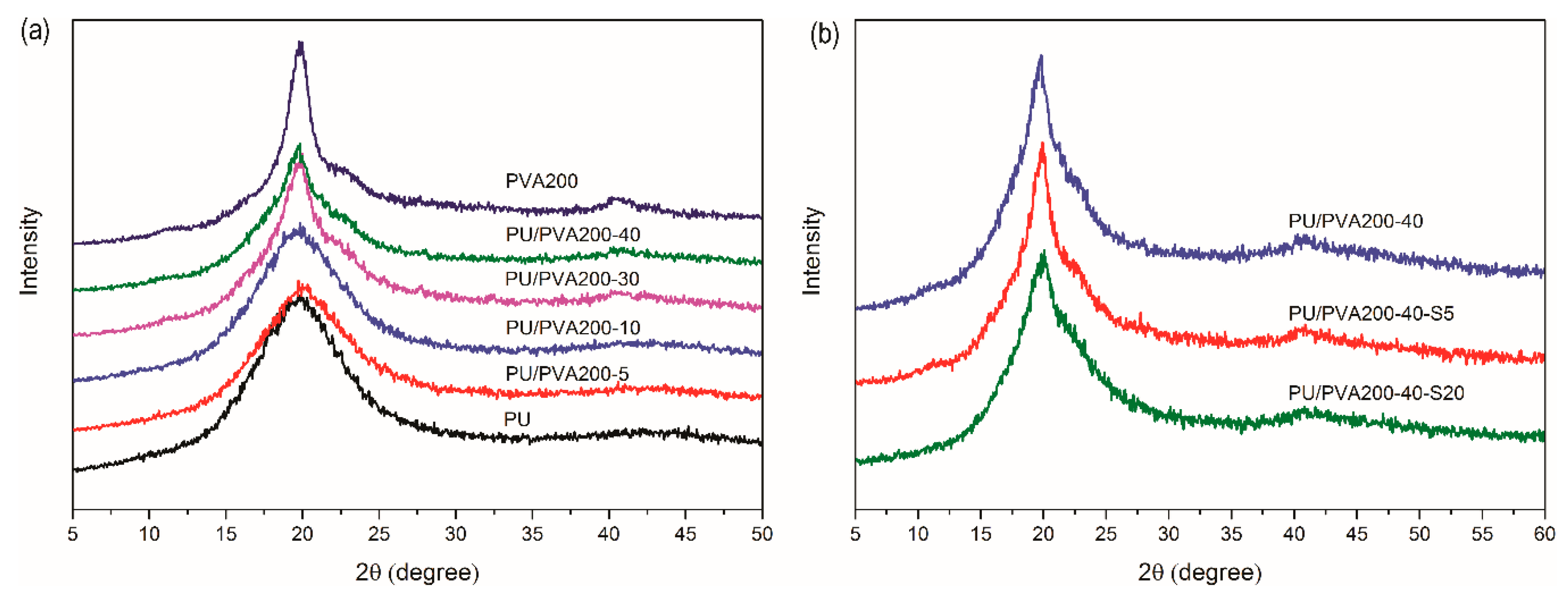
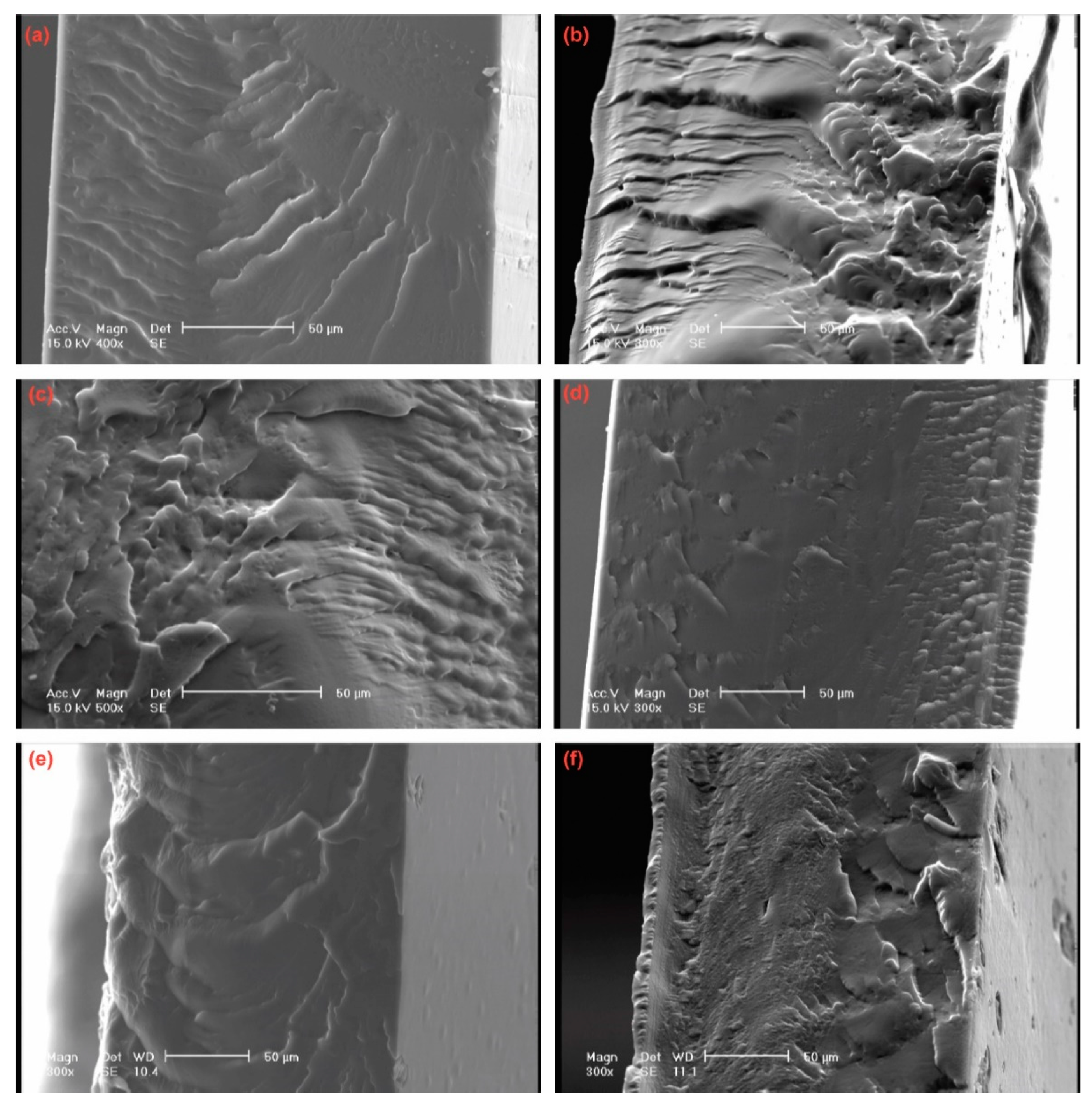
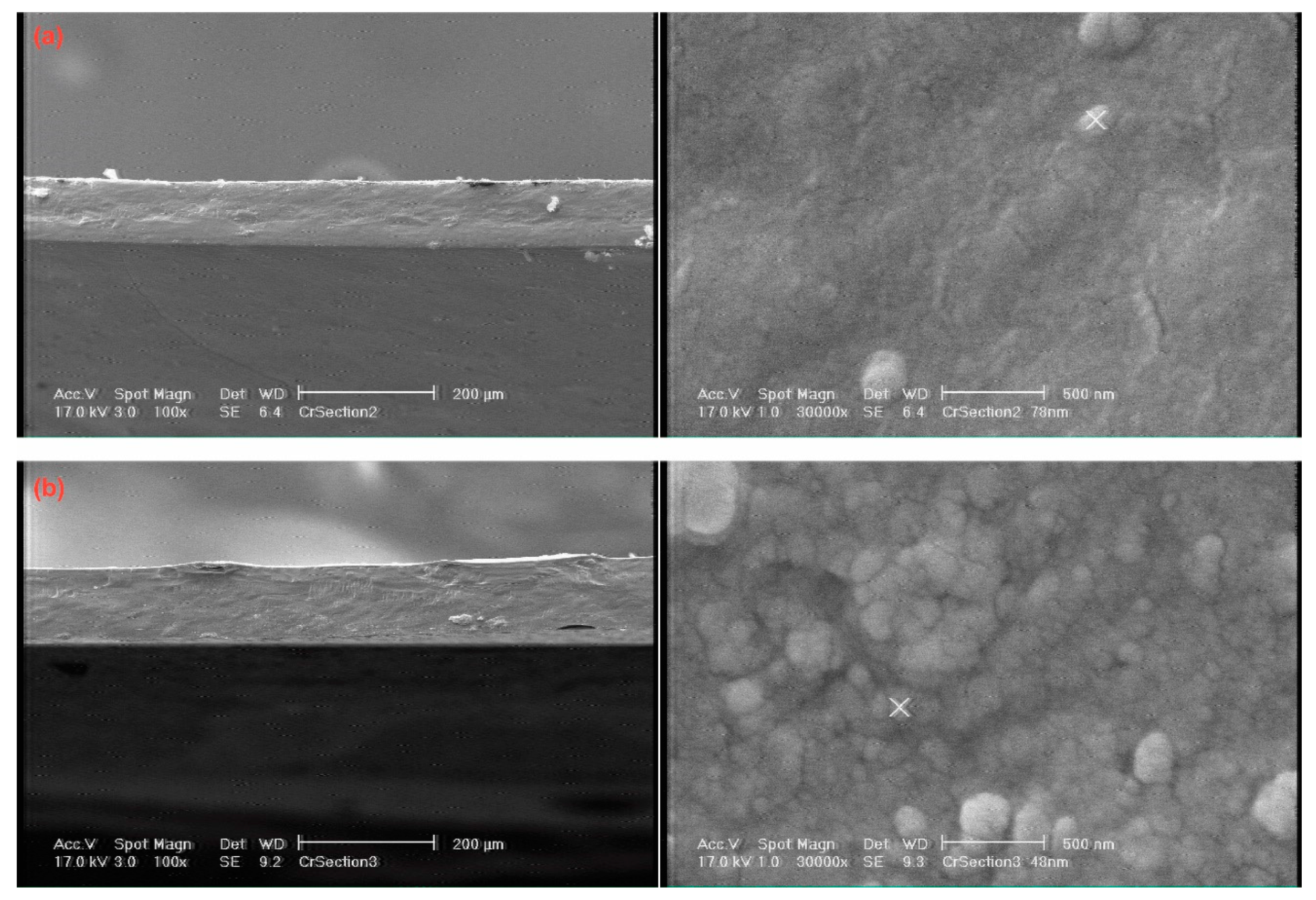
3.1. Chemical and Physical Characterization
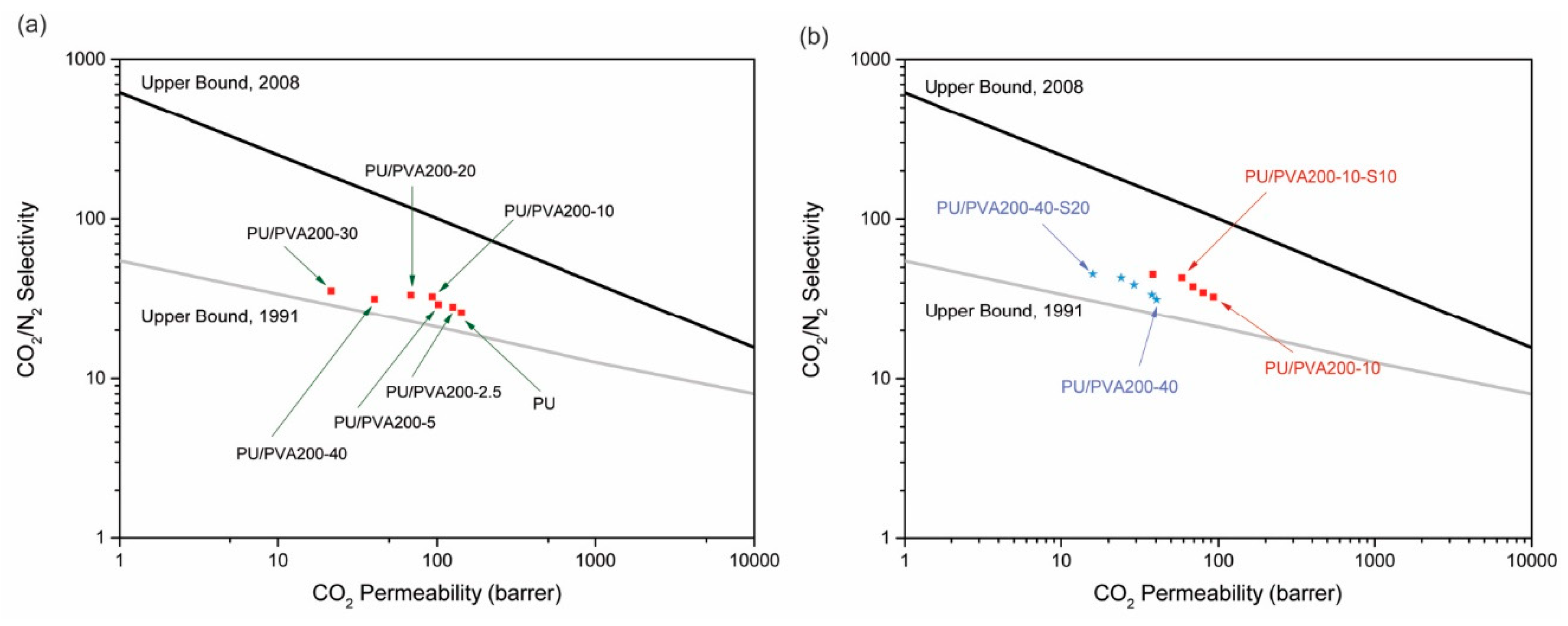
3.2. Gas Separation Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castarlenas, S.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Gas separation with mixed matrix membranes obtained from MOF UiO-66-graphite oxide hybrids. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghaei, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Ghalei, B.; Shahrooz, M. The role of compatibility between polymeric matrix and silane coupling agents on the performance of mixed matrix membranes: Polyethersulfone/MCM-41. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghami, S.; Sadeghi, M.; Mehrabani-Zeinabad, A. Recognition of polymer-particle interfacial morphology in mixed matrix membranes through ideal permeation predictive models. Polym. Test. 2017, 63, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghami, S.; Sadeghi, M.; Mehrabani-Zeinabad, A.; Zarabadi, M.; Ghalei, B. The Role of Interfacial Morphology in the Gas Transport Behavior of Nanocomposite Membranes: A Mathematical Modeling Approach. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 11022–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Xia, Y.; Li, J. ZIF-8/PDMS mixed matrix membranes for propane/nitrogen mixture separation: Experimental result and permeation model validation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Abiad, M.G.; Auras, R. The Influence of Cu3(BTC)2 metal organic framework on the permeability and perm-selectivity of PLLA-MOF mixed matrix membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, V.; Sadeghi, M.; Fakhar, A.; Khanbabaei, G.; Ismail, A.F. Gas separation properties of polyurethane/poly(ether-block-amide) (PU/PEBA) blend membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 185, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, P.S.O.; De Sales, J.A.; Silva, G.G.; Windmöller, D.; Machado, J.C. Effect of blend composition on microstructure, morphology, and gas permeability in PU/PMMA blends. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-R.; Xu, Q.-W.; Gu, S.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Dong, Z.-Q.; Wang, J.; Shao, H.-T.; Wang, X.-S. Oxygen enrichment across blend membranes of bipyridine and ethyl cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Hori, N.; Takahashi, M. Microscopic phase separation and long-time relaxation behavior in three-component heterogeneous blend systems. Langmuir 1996, 12, 5563–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghami, S.; Mehrabani-Zeinabad, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Mathematical modeling of temperature and pressure effects on permeability, diffusivity and solubility in polymeric and mixed matrix membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 205, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, B.; Pournaghshband Isfahani, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Vakili, E.; Jalili, A. Polyurethane-mesoporous silica gas separation membranes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Isfahani, A.P.; Muchtar, A.; Sakurai, K.; Shrestha, B.B.; Qin, D.; Yamaguchi, D.; Sivaniah, E.; Ghalei, B. Pebax/ionic liquid modified graphene oxide mixed matrix membranes for enhanced CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Wakimoto, K.; Gibbons, A.H.; Isfahani, A.P.; Kusuda, H.; Sivaniah, E.; Ghalei, B. Enhanced PIM-1 membrane gas separation selectivity through efficient dispersion of functionalized POSS fillers. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 539, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R. Control of Phase Structure in Polymer Blends. In Functional Polymers; Bergbreiter, D.E., Martin, C.R., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Demeuse, M.T. 1-Introduction to high temperature polymer blends. In High Temperature Polymer Blends; DeMeuse, M.T., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston/Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, G.; Visakh, P.M. 1-Polymer blends: State of art. In Recent Developments in Polymer Macro, Micro and Nano Blends; Visakh, P.M., Markovic, G., Pasquini, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston/Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiee, H.; Ghadimi, A.; Abbasi, S.; Mohammadi, T. CO2 separation performance of poly(ether-b-amide6)/PTMEG blended membranes: Permeation and sorption properties. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 98, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, L.G.; Freeman, B.D.; Spontak, R.J.; Morisato, A.; Pinnau, I. Gas Permeability and Phase Morphology of Poly(1-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne)/Poly(1-phenyl-1-propyne) Blends. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 4766–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, H.A.; Mukhtar, H.; Murugesan, T.; Nasir, R.; Mohshim, D.F.; Mushtaq, A. Recent applications of polymer blends in gas separation membranes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, S.; Liu, Y. Covalently bonded zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and polymers with enhanced compatibility in thin film nanocomposite membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Challenges and opportunities for mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4610–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, A.P.; Ghalei, B.; Wakimoto, K.; Bagheri, R.; Sivaniah, E.; Sadeghi, M. Plasticization resistant crosslinked polyurethane gas separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17431–17439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirouni, I.; Sadeghi, M.; Pakizeh, M. Separation of C3H8 and C2H6 from CH4 in polyurethane–zeolite 4Å and ZSM-5 mixed matrix membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, B.; Semsarzadeh, M.-A. A Novel Nano Structured Blend Membrane for Gas Separation. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 249–250, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, W.Y.; Jeong, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S. Gas Permeable Membranes Composed of Carboxylated Poly(vinyl chloride) and Polyurethane. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 1999, 20, 672–676. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-J.; Sea, B.; Youm, K.-H.; Lee, K.-H. Morphology and carbon dioxide transport properties of polyurethane blend membranes. Desalination 2006, 193, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semsarzadeh, M.A.; Ghalei, B. Characterization and gas permeability of polyurethane and polyvinyl acetate blend membranes with polyethylene oxide–polypropylene oxide block copolymer. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Arabi Shamsabadi, A.; Ronasi, A.; Isfahani, A.P.; Dinari, M.; Soroush, M. Engineering the dispersion of nanoparticles in polyurethane membranes to control membrane physical and transport properties. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 192, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, B.; Asghari, M. Effects of ZnO Nanoparticle on the Gas Separation Performance of Polyurethane Mixed Matrix Membrane. Membranes 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Semsarzadeh, M.A.; Barikani, M.; Chenar, M.P. Gas separation properties of polyether-based polyurethane–silica nanocomposite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 376, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, H.; Sadeghi, M.; Afarani, H.T.; Bagheri, R. Polyurethane/Poly (vinyl alcohol) Blend Membranes for Gas Separation. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, Z.; Moheb, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Alibouri, M. Titanate nanotubes–incorporated poly(vinyl alcohol) mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation separation of water-isopropanol mixtures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 145, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaghshband Isfahani, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Wakimoto, K.; Shrestha, B.B.; Bagheri, R.; Sivaniah, E.; Ghalei, B. Pentiptycene-based polyurethane with enhanced mechanical properties and CO2-plasticization resistance for thin film gas separation membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17366–17374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isfahani, A.P.; Ghalei, B.; Bagheri, R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kitagawa, H.; Sivaniah, E.; Sadeghi, M. Polyurethane gas separation membranes with ethereal bonds in the hard segments. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Talakesh, M.M.; Ghalei, B.; Shafiei, M. Preparation, characterization and gas permeation properties of a polycaprolactone based polyurethane-silica nanocomposite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohagheghian, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Chenar, M.P.; Naghsh, M. Gas separation properties of polyvinylchloride (PVC)-silica nanocomposite membrane. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Semsarzadeh, M.A.; Moadel, H. Enhancement of the gas separation properties of polybenzimidazole (PBI) membrane by incorporation of silica nano particles. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 331, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, A.P.; Sadeghi, M.; Dehaghani, A.H.S.; Aravand, M.A. Enhancement of the gas separation properties of polyurethane membrane by epoxy nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 44, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Sadeghi, M. Separation performance of poly(urethane-urea) membranes in the separation of C2 and C3 hydrocarbons from methane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


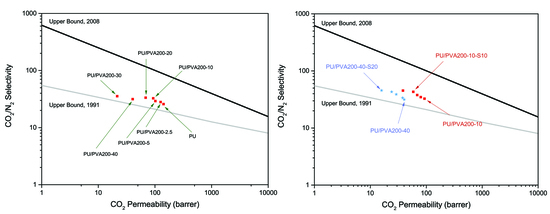
| Membrane | Permeability (Barrer) | Selectivity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | O2 | N2 | CH4 | CO2/N2 | CO2/CH4 | O2/N2 | |
| PU | 142.0 ± 7.0 | 15.3 ± 0.8 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 20.1 ± 1 | 25.8 ± 1.3 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | 2.8 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–2.5 | 126.0 ± 6.2 | 12.5 ± 0.6 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 16.5 ± 0.9 | 28.0 ± 1.4 | 7.6 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–5 | 102.0 ± 5.1 | 10.1 ± 0.5 | 3.5 ± 01 | 12.7 ± 0.6 | 29.1 ± 1.5 | 8.0 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–10 | 93.2 ± 4.5 | 8.3 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 9.8 ± 0.5 | 32.6 ± 1.7 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–20 | 68.7 ± 3.5 | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 33.4 ± 1.6 | 11.1 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.2 |
| PU/PVA200–30 | 21.6 ± 1.0 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 35.4 ± 1.8 | 11.2 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.2 |
| PU/PVA200–40 | 40.5 ± 2.0 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 7.4 ± 0.3 | 31.4 ± 1.5 | 8.8 ± 0.5 | 3.0 ± 0.1 |
| Membrane | Silica wt % | Permeability (Barrer) | Selectivity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | O2 | N2 | CH4 | CO2/N2 | CO2/CH4 | O2/N2 | ||
| PU/PVA200–10 | 0 | 93.2 ± 4.5 | 8.3 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 9.8 ± 0.5 | 32.6 ± 1.5 | 9.5 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–10-S2.5 | 2.5 | 79.9 ± 4.0 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.3 | 34.7 ± 1.6 | 11.6 ± 0.6 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–10-S5 | 5 | 69.1 ± 3.5 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 37.8 ± 1.7 | 12.8 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–10-S10 | 10 | 58.8 ± 3.0 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 42.9 ± 2 | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.2 |
| PU/PVA200–10-S20 | 20 | 38.3 ± 1.9 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 0.85 ± 0.0 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 45.1 ± 2.1 | 15.2 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.2 |
| PU/PVA200–40 | 0 | 40.5 ± 2.0 | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 31.4 ± 1.6 | 8.6 ± 0.4 | 3.0 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–40-S2.5 | 2.5 | 37.8 ± 1.9 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 33.8 ± 1.7 | 10.3 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–40-S5 | 5 | 29.1 ± 1.5 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.0 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 33.8 ± 1.7 | 11.0 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–40-S10 | 10 | 24.1 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 42.9 ± 2.1 | 11.5 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.1 |
| PU/PVA200–40-S20 | 20 | 15.9 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 45.4 ± 2.2 | 14.0 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 0.2 |
| Sample | CO2/N2 (50/50 vol %) | CO2/CH4 (50/50 vol %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permeability (Barrer) | CO2/N2 Selectivity | Permeability | CO2/CH4 Selectivity | |||
| CO2 | N2 | CO2 | CH4 | |||
| PU | 105.0 | 5.4 | 19.5 | 92.6 | 18.2 | 5.1 |
| PU/PVA200–10-S20 | 30.1 | 0.8 | 38.0 | 24.8 | 2.2 | 11.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shirvani, H.; Maghami, S.; Pournaghshband Isfahani, A.; Sadeghi, M. Influence of Blend Composition and Silica Nanoparticles on the Morphology and Gas Separation Performance of PU/PVA Blend Membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070082
Shirvani H, Maghami S, Pournaghshband Isfahani A, Sadeghi M. Influence of Blend Composition and Silica Nanoparticles on the Morphology and Gas Separation Performance of PU/PVA Blend Membranes. Membranes. 2019; 9(7):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070082
Chicago/Turabian StyleShirvani, Hemmat, Saeid Maghami, Ali Pournaghshband Isfahani, and Morteza Sadeghi. 2019. "Influence of Blend Composition and Silica Nanoparticles on the Morphology and Gas Separation Performance of PU/PVA Blend Membranes" Membranes 9, no. 7: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070082
APA StyleShirvani, H., Maghami, S., Pournaghshband Isfahani, A., & Sadeghi, M. (2019). Influence of Blend Composition and Silica Nanoparticles on the Morphology and Gas Separation Performance of PU/PVA Blend Membranes. Membranes, 9(7), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070082