Role of Cation Structure in CO2 Separation by Ionic Liquid/Sulfonated Polyimide Composite Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
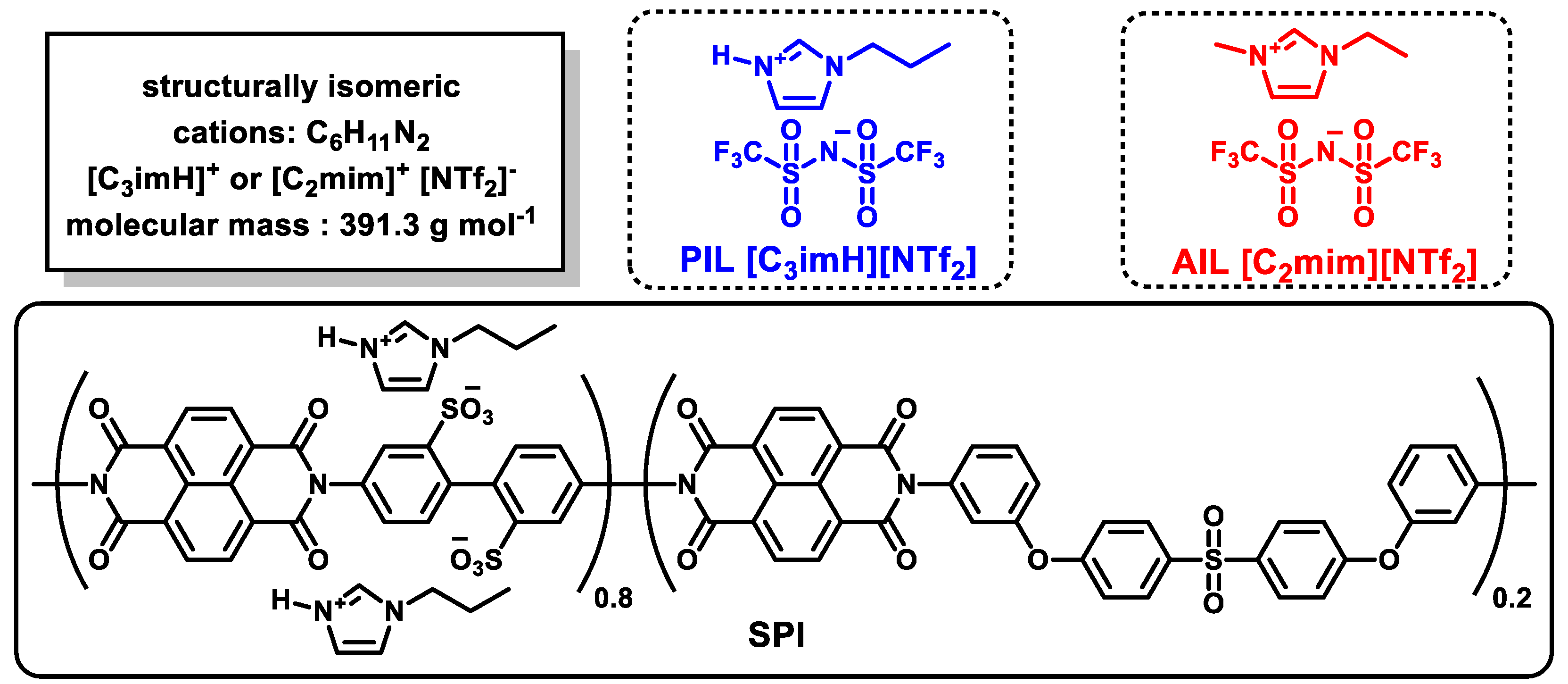
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Protic Ionic Liquid, Sulfonated Polyimide, and Composite Membranes
2.3. Gas Permeability Measurement
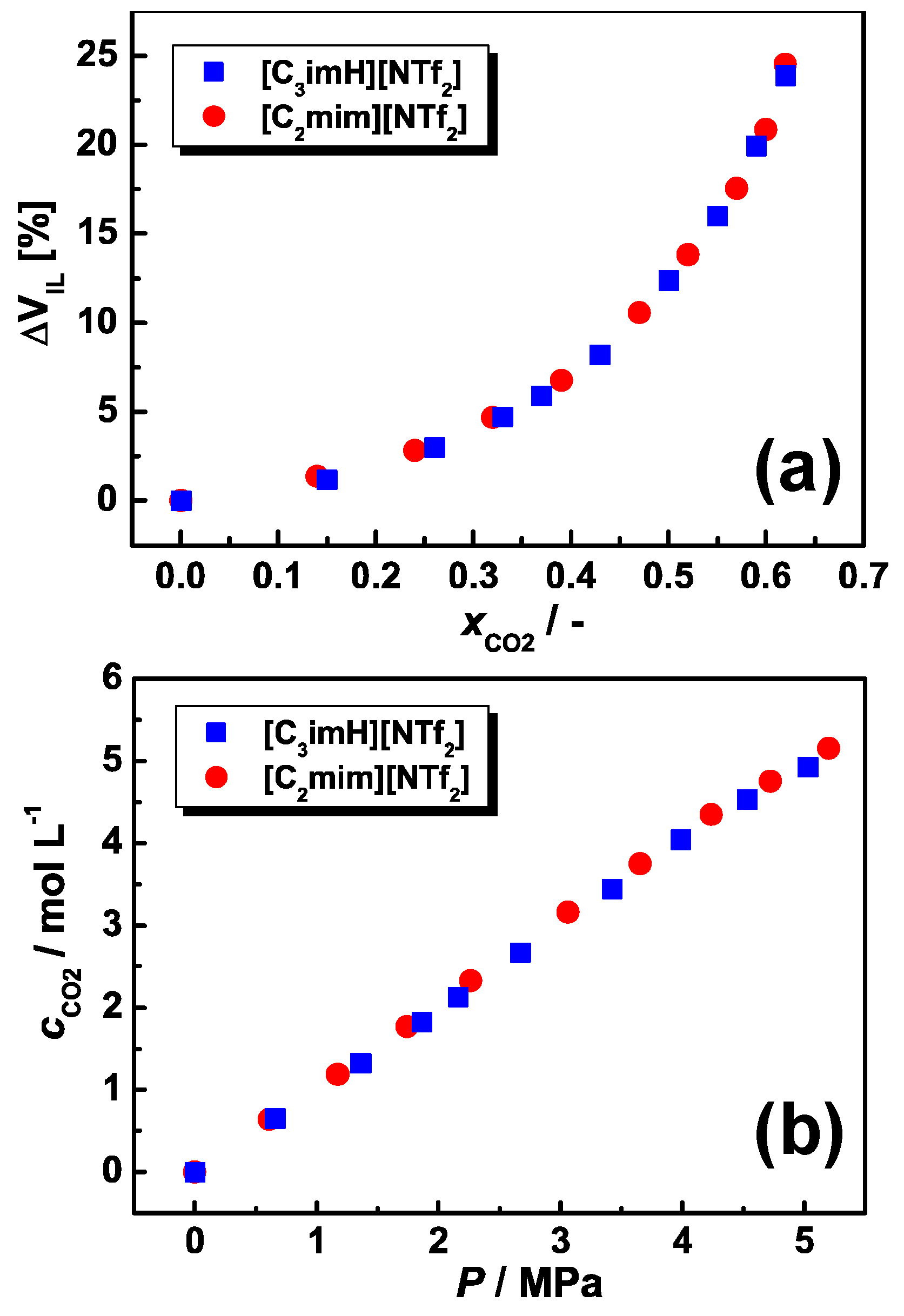
2.4. Volume Expansion and CO2 Solubility Measurements for the Ionic Liquids
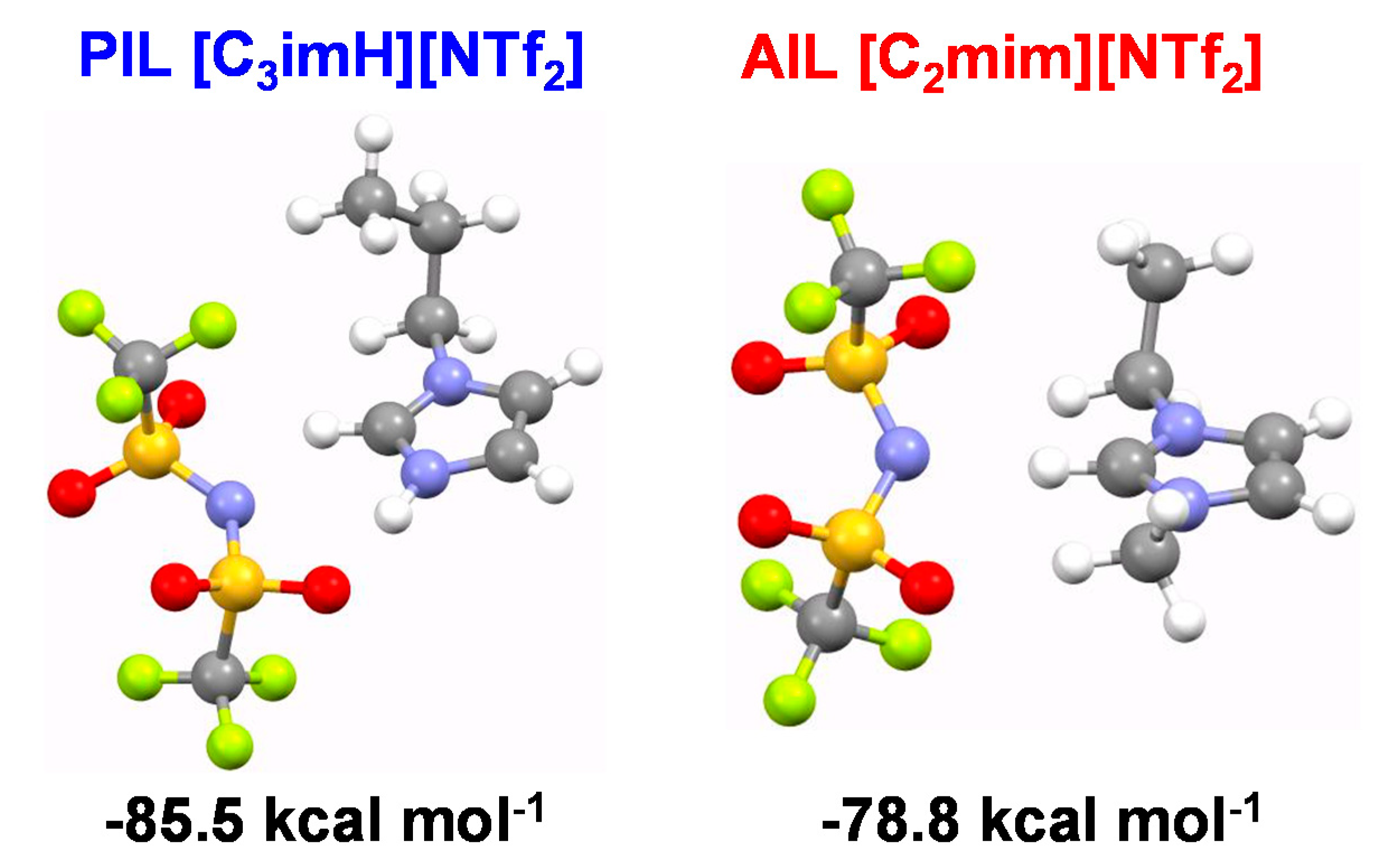
2.5. Ab Initio Calculation
2.6. Other Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
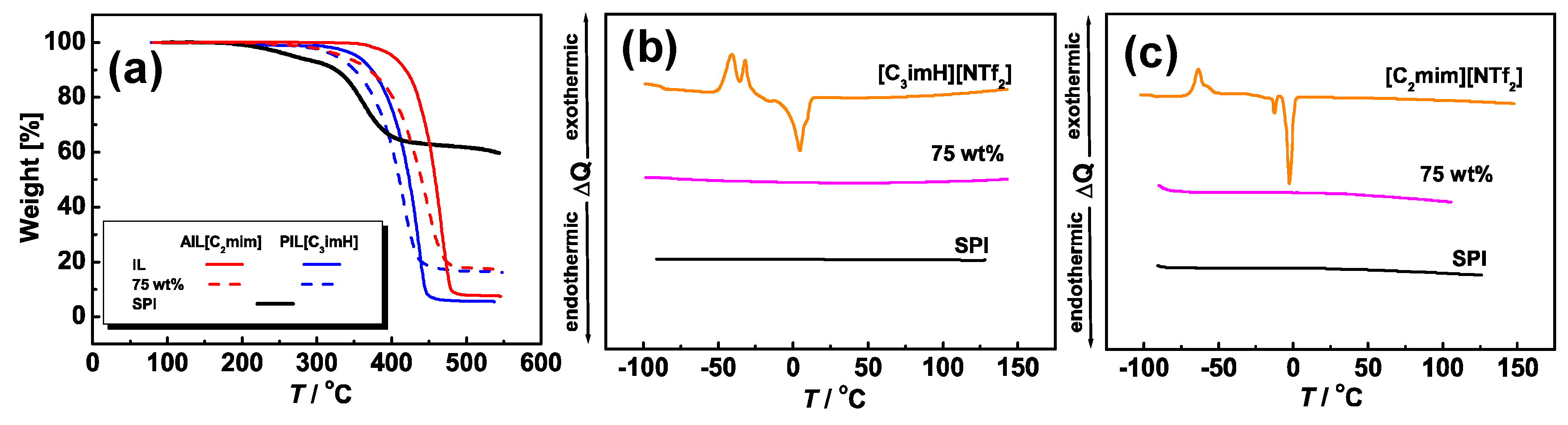
3.1. Thermal Analyses
3.2. Gas Permeability Measurement
3.3. CO2 Absorption Behavior
3.4. Plasticization Effect by IL
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angell, C.A.; Ansari, Y.; Zhao, Z. Ionic liquids: Past, present and future. Faraday Discuss. 2012, 154, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. Green solvents for the future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L. Combination of ionic liquids with membrane technology: A new approach for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Herzog, A.; Benson, S.M.; Hidy, G.M.; Gunter, W.D.; Penkala, S.J.; White, C.M. Separation and capture of CO2 from large stationary sources and sequestration in geological formations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 53, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadas, F.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. Review on the use of Ionic Liquids (ILs) as alternative fluids for CO2 capture and natural gas sweetening. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5817–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas Anjum, M.; de Clippel, F.; Didden, J.; Laeeq Khan, A.; Couck, S.; Baron, G.V.; Denayer, J.F.M.; Sels, B.F.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Polyimide mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separations using carbon–silica nanocomposite fillers. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, E. Membrane processes and postcombustion carbon dioxide capture: Challenges and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.T.; Allinson, G.W.; Wiley, D.E. Reducing the cost of CO2 capture from flue gases using membrane technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, M.B.; Lindbråthen, A. CO2 capture from natural gas fired power plants by using membrane technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 7668–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredesen, R.; Jordal, K.; Bolland, O. High-temperature membranes in power generation with CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Process. 2004, 43, 1129–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Cussler, E.L.; Lodge, T.P. ABA-triblock copolymer ion gels for CO2 separation applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ogawa, A.; Kanno, M.; Nakamoto, H.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M. Nonhumidified intermediate temperature fuel cells using protic ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9764–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Nakamura, S.; Honda, Y.; Kinugawa, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Watanabe, M. Effects of polymer structure on properties of sulfonated polyimide/protic ionic liquid composite membranes for nonhumidified fuel cell applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Yasuda, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Yoshida, A.; Li, X.; Hashimoto, K.; Nagai, K.; Shibayama, M.; Watanabe, M. Sulfonated polyimide/ionic liquid composite membranes for CO2 separation: Transport properties in relation to their nanostructures. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 7112–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, E.; Thomas, M.L.; Hashimoto, K.; Tsuzuki, S.; Ito, A.; Watanabe, M. Application of protic ionic liquids to CO2 separation in a sulfonated polyimide-derived ion gel membrane. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belieres, J.P.; Angell, C.A. Protic ionic liquids: Preparation, characterization, and proton free energy level representation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4926–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, M.S.; Kinoshita, H.; Yasuda, T.; Susan, M.A.; Watanabe, M. Physicochemical properties determined by DeltapKa for protic ionic liquids based on an organic super-strong base with various Bronsted acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, M.S.; Hoque, M.; Yasuda, T.; Tsuzuki, S.; Ueno, K.; Watanabe, M. Key factor governing the physicochemical properties and extent of proton transfer in protic ionic liquids: DeltapKa or chemical structure? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, M.; Amin, S.A.; Yarger, J.L.; Davidowski, S.K.; Angell, C.A. Proton transfer and ionicity: An 15N NMR study of pyridine Base protonation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, H.; Watanabe, M. Bronsted acid-base ionic liquids for fuel cell electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2007, 24, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision, A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, C.; Plesset, M.S. Note on an approximation treatment for Many-Electron systems. Phys. Rev. 1934, 46, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head-Gordon, M.; Pople, J.A.; Frisch, M.J. MP2 energy evaluation by direct methods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1988, 153, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransil, B.J. Studies in molecular structure. IV. Potential curve for the interaction of two helium atoms in Single-Configuration LCAO MO SCF approximation. J. Chem. Phys. 1961, 34, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan, M.A.B.H.; Kaneko, T.; Noda, A.; Watanabe, M. Ion gels prepared by in situ radical polymerization of vinyl monomers in an ionic liquid and their characterization as polymer electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4976–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Ryan, J.J.; Spontak, R.J.; Deng, L. Nafion/IL hybrid membranes with tuned nanostructure for enhanced CO2 separation: Effects of ionic liquid and water vapor. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Yasuda, T.; Ma, X.; Watanabe, M. Sulfonated polyimide/ionic liquid composite membranes for carbon dioxide separation. Polym. J. 2017, 49, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, S.N.V.K.; Mellein, B.R.; Saurer, E.M.; Brennecke, J.F. High-Pressure phase behavior of carbon dioxide with imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 20355–20365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, S.; Tokuda, H.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M. Magnitude and directionality of interaction in ion pairs of ionic liquids: Relationship with ionic conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 16474–16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bai, L.; Han, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Functionalized ionic liquid membranes for CO2 separation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12671–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayashi, E.; Hashimoto, K.; L. Thomas, M.; Tsuzuki, S.; Watanabe, M. Role of Cation Structure in CO2 Separation by Ionic Liquid/Sulfonated Polyimide Composite Membrane. Membranes 2019, 9, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070081
Hayashi E, Hashimoto K, L. Thomas M, Tsuzuki S, Watanabe M. Role of Cation Structure in CO2 Separation by Ionic Liquid/Sulfonated Polyimide Composite Membrane. Membranes. 2019; 9(7):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070081
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayashi, Eri, Kei Hashimoto, Morgan L. Thomas, Seiji Tsuzuki, and Masayoshi Watanabe. 2019. "Role of Cation Structure in CO2 Separation by Ionic Liquid/Sulfonated Polyimide Composite Membrane" Membranes 9, no. 7: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070081
APA StyleHayashi, E., Hashimoto, K., L. Thomas, M., Tsuzuki, S., & Watanabe, M. (2019). Role of Cation Structure in CO2 Separation by Ionic Liquid/Sulfonated Polyimide Composite Membrane. Membranes, 9(7), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070081




