Antifouling Properties of PES Membranes by Blending with ZnO Nanoparticles and NMP–Acetone Mixture as Solvent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.3.2. Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) Analysis
2.3.3. Viscosity Analysis
2.3.4. Porosity and Pore Size Determination
2.3.5. Contact Angle Measurements
2.4. Membrane Performance Evaluation
2.4.1. HA Feed Solution Preparation and Characterization
2.4.2. Membrane Permeation Test and Fouling Analysis for Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Variation of Membrane
3.2. Pore Size and Porosity
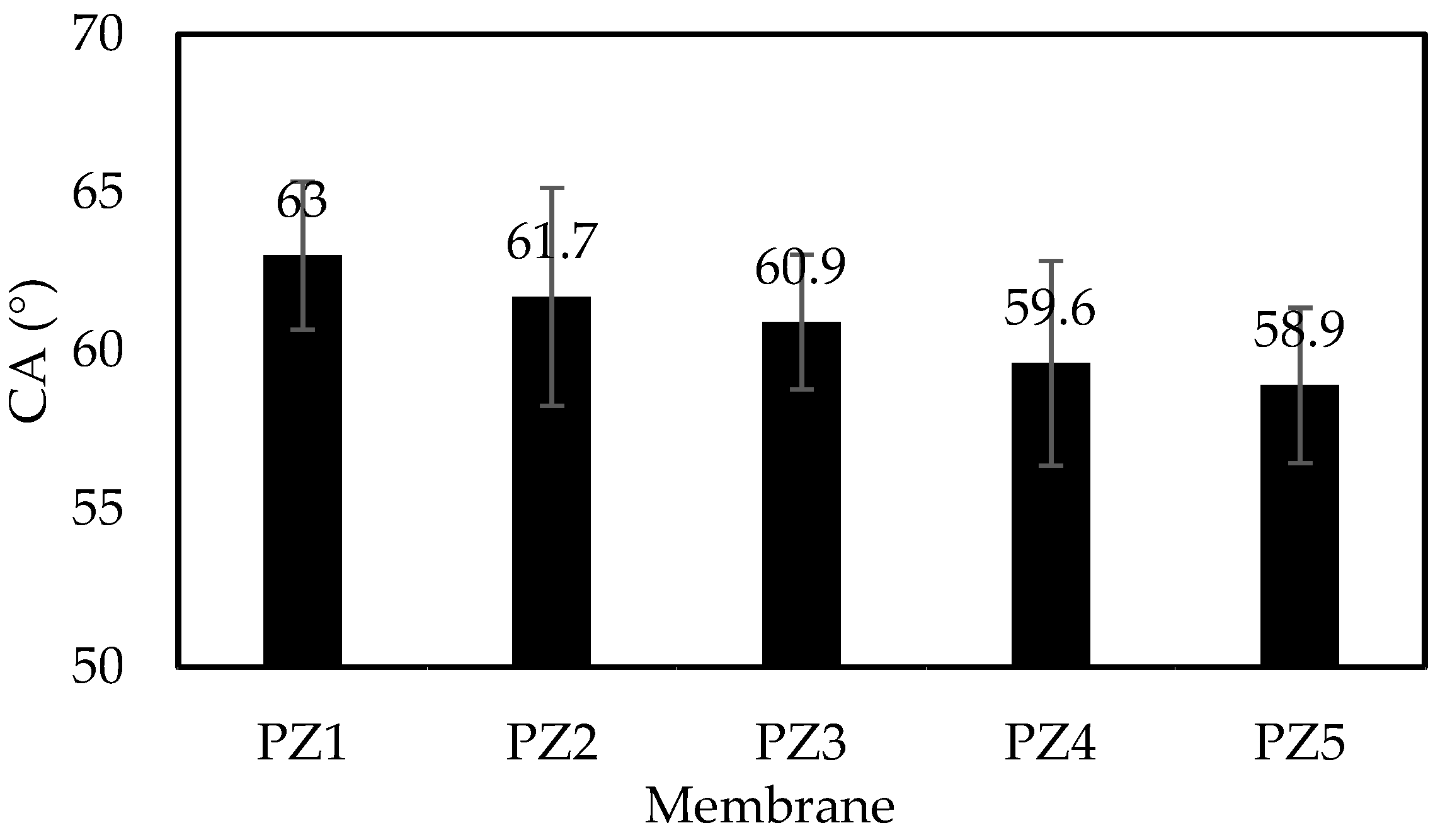
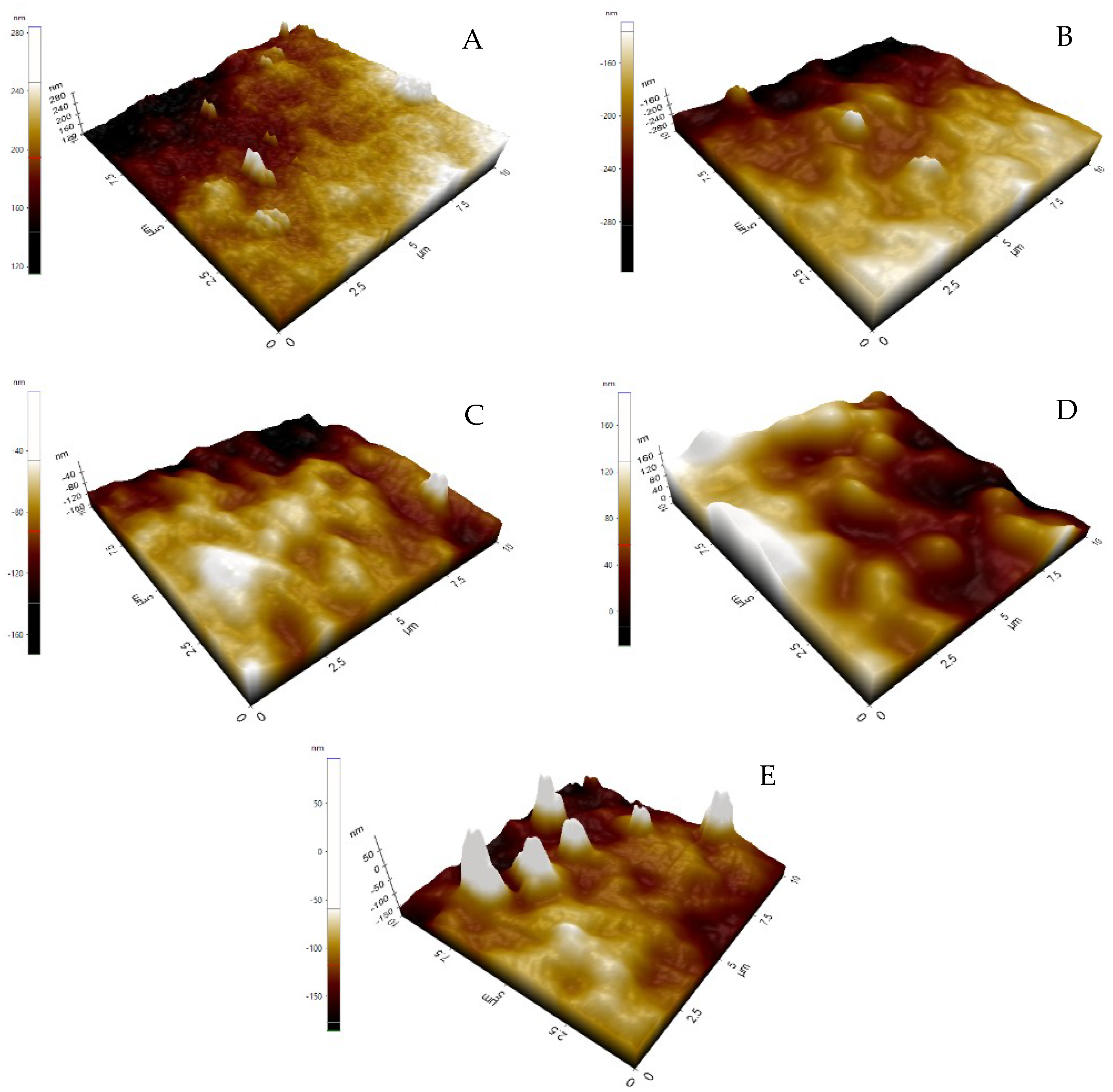
3.3. Contact Angle and Surface Roughness
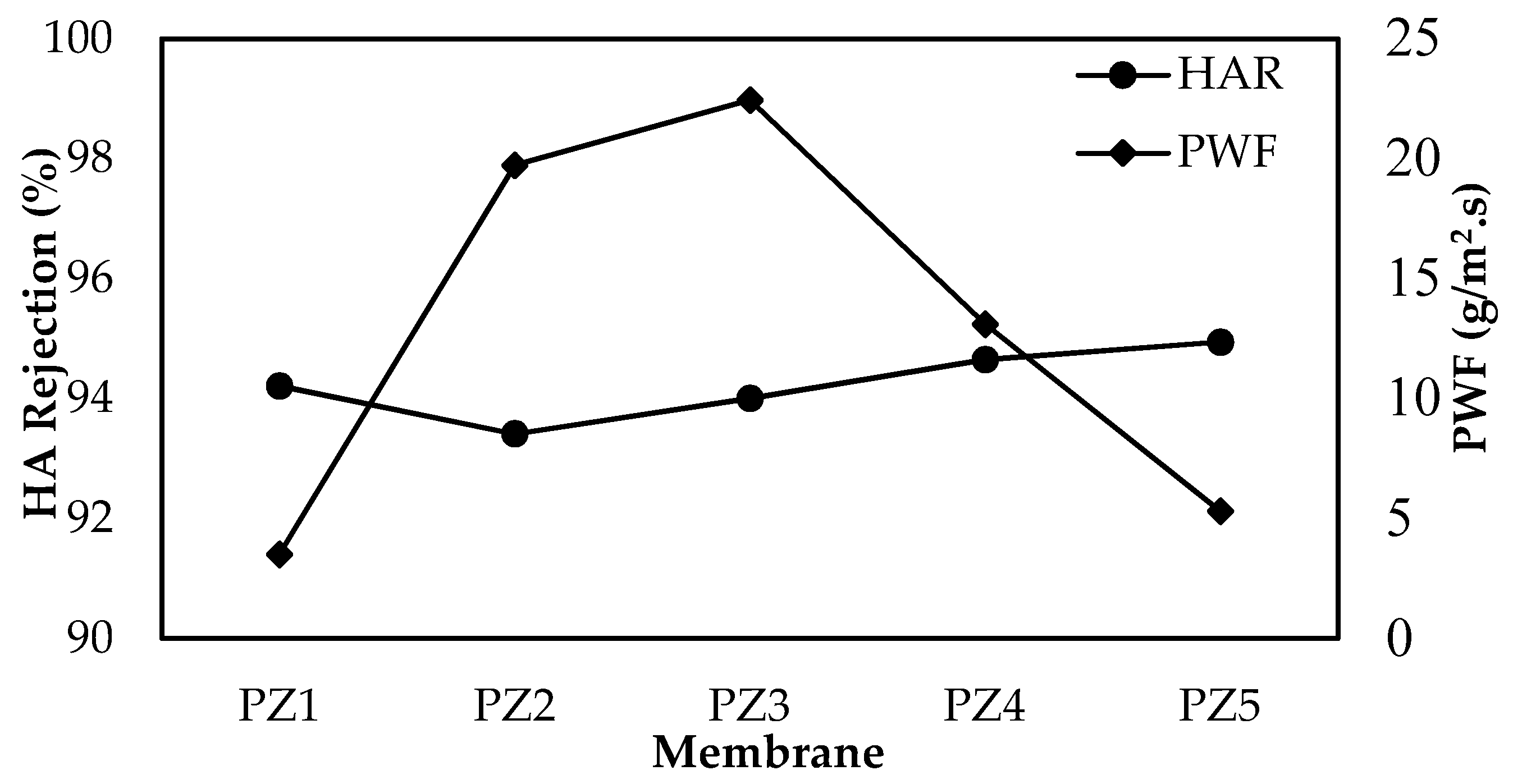
3.4. Performance Evaluation of the Membrane
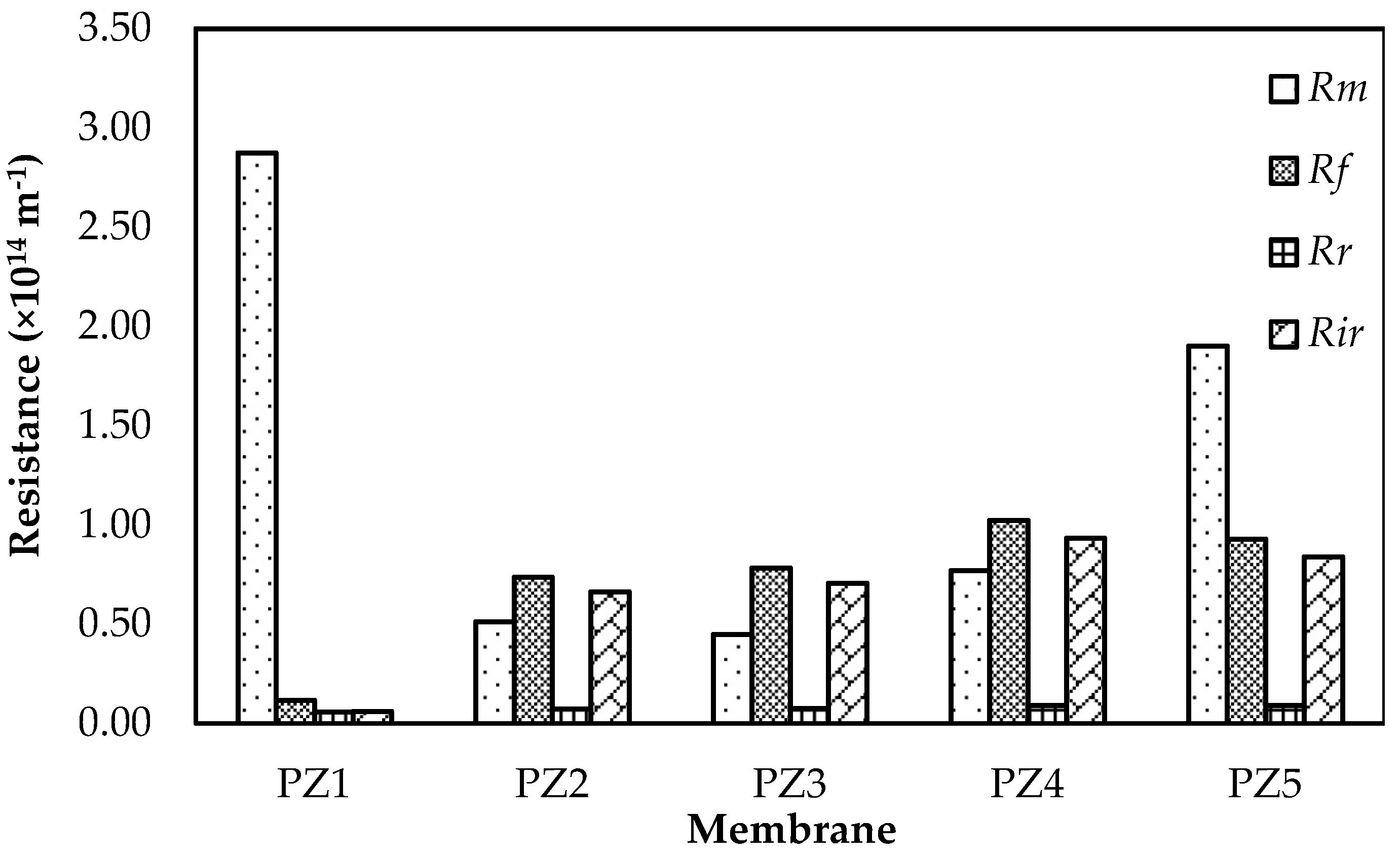
3.5. Fouling Evaluation of Membrane
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daufin, G.; Escudier, J.P.; Carrère, H.; Bérot, S.; Fillaudeau, L.; Decloux, M. Recent and Emerging Applications of Membrane Processes in the Food and Dairy Industry. Food Biprod. Process. 2001, 79, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takht Ravanchi, M.; Kaghazchi, T.; Kargari, A. Application of membrane separation processes in petrochemical industry: A review. Desalination 2009, 235, 199–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Mai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Vankelecom, I. Ion exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Wu, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, K. Micro-structured alumina hollow fibre membranes—Potential applications in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2.1 Billion People Lack Safe Drinking Water at Home, More Than Twice as Many Lack Safe Sanitation. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/detail/12-07-2017-2-1-billion people-lack-safe-drinking-water-at-home-more-than-twice-as-many-lack-safe-sanitation (accessed on 27 October 2018).
- About the Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 22 November 2018).
- Nasrollahi, N.; Vatanpour, V.; Aber, S.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Preparation and characterization of a novel polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membrane modified with a CuO/ZnO nanocomposite to improve permeability and antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Sotto, A.; Luis, P.; Benea, L.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Kim, J. A new outlook on membrane enhancement with nanoparticles: The alternative of ZnO. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.; Lee, H.S.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.; McGrath, J.; Paul, D.R. Water Purification by Membranes: The Role of Polymer Science. J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1685–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi Gohari, R.; Halakoo, E.; Nazri, N.A.M.; Lau, W.J.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Improving performance and antifouling capability of PES UF membranes via blending with highly hydrophilic hydrous manganese dioxide nanoparticles. Desalination 2014, 335, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodar, R.A.; You, S.J.; Chou, H.H. Study the self cleaning, antibacterial and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 entrapped PVDF membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, C.P.; Cathie Lee, W.P.; Ahmad, A.L.; Mohammad, A.W. Polysulfone membranes blended with ZnO nanoparticles for reducing fouling by oleic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Park, H.; Choi, H.; Choi, H. Carbon nanotube blended polyethersulfone membranes for fouling control in water treatment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. Anti-fouling and anti-bacterial polyethersulfone membranes quaternized from the additive of poly(2-dimethylamino ethyl methacrylate) grafted SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 15566–15574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotto, A.; Boromand, A.; Zhang, R.; Luis, P.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Kim, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Effect of nanoparticle aggregation at low concentrations of TiO2 on the hydrophilicity, morphology, and fouling resistance of PES–TiO2 membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Hou, L.A. Fabrication of GO modified PVDF membrane for dissolved organic matter removal: Removal mechanism and antifouling property. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.; Ghaemi, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Daraei, P.; Astinchap, B.; Zinadini, S.; Razavizadeh, S.H. Nano-ZnO embedded mixed matrix polyethersulfone (PES) membrane: Influence of nanofiller shape on characterization and fouling resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipheko, T.D.; Matabola, K.P.; Kotlhao, K.; Moutloali, R.M.; Klink, M. Fabrication and Assessment of ZnO Modified Polyethersulfone Membranes for Fouling Reduction of Bovine Serum Albumin. Inter. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 3587019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Jahanshahi, M.; Rajaeian, B.; Rahimnejad, M. TiO2 entrapped nano-composite PVDF/SPES membranes: Preparation, characterization, antifouling and antibacterial properties. Desalination 2011, 278, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.H.; Kim, I.C.; Tak, T.M. Preparation and characterization of fouling-resistant TiO2 self-assembled nanocomposite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 275, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Taheri, A.H. Effect of Casting Solution on Morphology and Performance of PVDF Microfiltration Membranes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.C.; Lee, K.H.; Tak, T.M. Preparation and characterization of integrally skinned uncharged polyetherimide asymmetric nanofiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 183, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, L.; García-Payo, M.C.; Khayet, M. Effects of mixed solvents on the structural morphology and membrane distillation performance of PVDF-HFP hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Idris, A.; Hussain, A.; Yusof, Z.A.M.; Saad Khan, M. Influence of Co-Solvent Concentration on the Properties of Dope Solution and Performance of Polyethersulfone Membranes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Xiao, C. Morphology changes of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane under different phase separation mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Shi, B.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Preparation and properties of microporous membrane from poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-tetrafluoroethylene) for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 237, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Ultrafilter Membranes and Ultrafiltration. ACS 1936, 18, 373–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Bian, X.; Lu, X.; Shi, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Hou, Z.; Fan, K. Preparation and characterization of ZnO/polyethersulfone (PES) hybrid membranes. Desalination 2012, 293, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Vatanpour, V.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Zarrabi, H. Improvement in flux and antifouling properties of PVC ultrafiltration membranes by incorporation of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, H.; Wenten, I.G. Polysulfone membranes for CO2/CH4 separation: State of the art. IOSR J. Eng. 2012, 2, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.-S. Fundamentals of semi-crystalline poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane formation and its prospects for biofuel (ethanol and acetone) separation via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teow, Y.H.; Seng, O.; Ahmad, A.L.; Lim, J.K. Mixed-Matrix Membrane for Humic Acid Removal: Influence of Different Types of TiO2 on Membrane Morphology and Performance. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2012, 3, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Vuong, F.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Nijmeijer, K.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. Hydraulically irreversible fouling on ceramic MF/UF membranes: Comparison of fouling indices, foulant composition and irreversible pore narrowing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufidou, K.; Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J. A study of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by humic acids and flux recovery by backwashing: Experiments and modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 266, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Lin, A.Y.C.; Chandana, P.S.; Tsai, C.Y. Effects of mass retention of dissolved organic matter and membrane pore size on membrane fouling and flux decline. Water Res. 2009, 43, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, W.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Improving permeability and antifouling performance of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of ZnO-DMF dispersion containing nano-ZnO and polyvinylpyrrolidone. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 478, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanti, P.T.P.; Noviyani, A.M.; Kurnia, M.F.; Rahayu, D.A.; Nisa, A.Z. Modified Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membrane for Humic Acid Removal During Peat Water Treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 288, 012118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Rostami, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Jalilian, E. Preparation of antibiofouling polyethersulfone mixed matrix NF membrane using photocatalytic activity of ZnO/MWCNTs nanocomposite. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.T.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohammad, A.W.; Benamor, A.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N. Development of polysulfone-nanohybrid membranes using ZnO-GO composite for enhanced antifouling and antibacterial control. Desalination 2017, 402, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Membrane | PES Weight Percent (wt%) | NMP: Acetone Ratio of Solvent | ZnO Weight Percent (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PZ1 | 18 | 1:0.05 | 0 |
| PZ2 | 18 | 1:0.05 | 0.5 |
| PZ3 | 18 | 1:0.05 | 1.0 |
| PZ4 | 18 | 1:0.05 | 1.5 |
| PZ5 | 18 | 1:0.05 | 2.0 |
| Membrane | Porosity (%) | Mean Pore Size (nm) | Viscosity (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PZ1 | 37.29 ± 2.86 | 6.80 ± 1.45 | 920 ± 10 |
| PZ2 | 42.87 ± 1.24 | 14.01 ± 3.45 | 950 ± 5 |
| PZ3 | 47.34 ± 3.24 | 13.96 ± 5.78 | 990 ± 10 |
| PZ4 | 43.73 ± 6.32 | 11.26 ± 3.42 | 1160 ± 15 |
| PZ5 | 41.87 ± 2.34 | 7.38 ± 2.52 | 1290 ± 10 |
| Membrane | Ra (nm) | Rq (nm) | Rz (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PZ1 | 23.73 ± 3.25 | 29.36 ± 3.43 | 165.37 ± 4.47 |
| PZ2 | 24.28 ± 6.15 | 29.98 ± 8.53 | 184.88 ± 4.32 |
| PZ3 | 24.74 ± 6.75 | 30.63 ± 7.21 | 182.55 ± 4.31 |
| PZ4 | 25.96 ± 3.22 | 36.98 ± 2.64 | 210.17 ± 6.53 |
| PZ5 | 25.78 ± 5.20 | 31.77 ± 2.98 | 278.09 ± 2.41 |
| Membrane | JWF (g/m2·s) | JHA (g/m2·s) | JWF2 (g/m2·s) | FRR (%) | RFR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PZ1 | 3.51 | 3.37 | 3.44 | 97.93 | 3.94 |
| PZ2 | 19.72 | 8.08 | 8.59 | 43.55 | 59.03 |
| PZ3 | 22.44 | 8.19 | 8.72 | 38.89 | 63.52 |
| PZ4 | 13.09 | 5.62 | 5.92 | 45.24 | 57.06 |
| PZ5 | 5.30 | 3.56 | 3.68 | 69.38 | 32.83 |
| Casting Conditions and Membrane Characteristics | Nasrollahi et al. (2018) [8] | Zinadini et al. (2017) [41] | Chung et al. (2017) [42] | Rabiee et al. (2015) [32] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | PES | PES | PSF | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | PES |
| Polymer dosage (wt%) | 18 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 18 |
| Solvent | DMAc | DMAc | NMP | NMP | NMP and Acetone (0.05 mass ratio of NMP to acetone in a mixed solvent) |
| Additive and dosage | PVP (2 wt%) and Copper oxide (CuO) | PVP (1 wt%) and MWCNTs | GO | Polyethylene glycol (PEG 6 kDa); 4 wt% | - |
| ZnO dosage (wt%) | 0.1, 0.2, 0.5 and 1.0 a | 0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 b | 0.1, 0.3 and 0.6 c | 0.3, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 | 0.5, 0.1, 1.5 and 2.0 |
| Contact angle (°) | 66.5 (0.2 wt% CuO/ZnO) | 57.2 (0.5 wt% ZnO/MWCNTs) | 40 (0.6 wt% ZnO/GO) | 54.5 (3 wt% ZnO) | 60.9 (0.1 wt% ZnO) |
| Foulant | Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA), (500 mg/L) | Powder milk (8000 ppm) | Humic acid (10 ppm) | BSA (500 ppm) | Humic acid (50 mg/L) |
| Rejection (%) | 99 (0.2 wt% CuO-ZnO) | 95 (0.5 wt% ZnO/MWCNTs) d | 99 (0.6 wt% ZnO/GO) | 97.5 (3 wt% ZnO) | 94 (0.1 wt% ZnO) |
| Pure water flux | 679 kg/m2·h (0.2 wt% CuO-ZnO) | 16.7 kg/m2·h (0.5 wt% ZnO/MWCNTs) | 5.11 kg/m2·h·bar (0.6 wt% ZnO/GO) | 401.9 kg/m2·h (3 wt% ZnO) | 80 kg/m2·h (0.1 wt% ZnO) |
| Flux recovery ratio | 50.1 (0.2 wt% CuO-ZnO) | 88.6 (0.5 wt% ZnO/MWCNTs) | 99 (0.6 wt% ZnO/GO) | 91.8 (3 wt% ZnO) | 38.89 (0.1 wt% ZnO) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, A.L.; Sugumaran, J.; Shoparwe, N.F. Antifouling Properties of PES Membranes by Blending with ZnO Nanoparticles and NMP–Acetone Mixture as Solvent. Membranes 2018, 8, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040131
Ahmad AL, Sugumaran J, Shoparwe NF. Antifouling Properties of PES Membranes by Blending with ZnO Nanoparticles and NMP–Acetone Mixture as Solvent. Membranes. 2018; 8(4):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040131
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Abdul Latif, Jayasree Sugumaran, and Noor Fazliani Shoparwe. 2018. "Antifouling Properties of PES Membranes by Blending with ZnO Nanoparticles and NMP–Acetone Mixture as Solvent" Membranes 8, no. 4: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040131
APA StyleAhmad, A. L., Sugumaran, J., & Shoparwe, N. F. (2018). Antifouling Properties of PES Membranes by Blending with ZnO Nanoparticles and NMP–Acetone Mixture as Solvent. Membranes, 8(4), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040131






