A Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane with MCM-41 Silica Nanoparticles for Brackish Water Purification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of MCM-41 NPs
2.3. Preparation of PSU Support Layer Sheets
2.4. Preparation of Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane
2.5. TFN Membrane Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
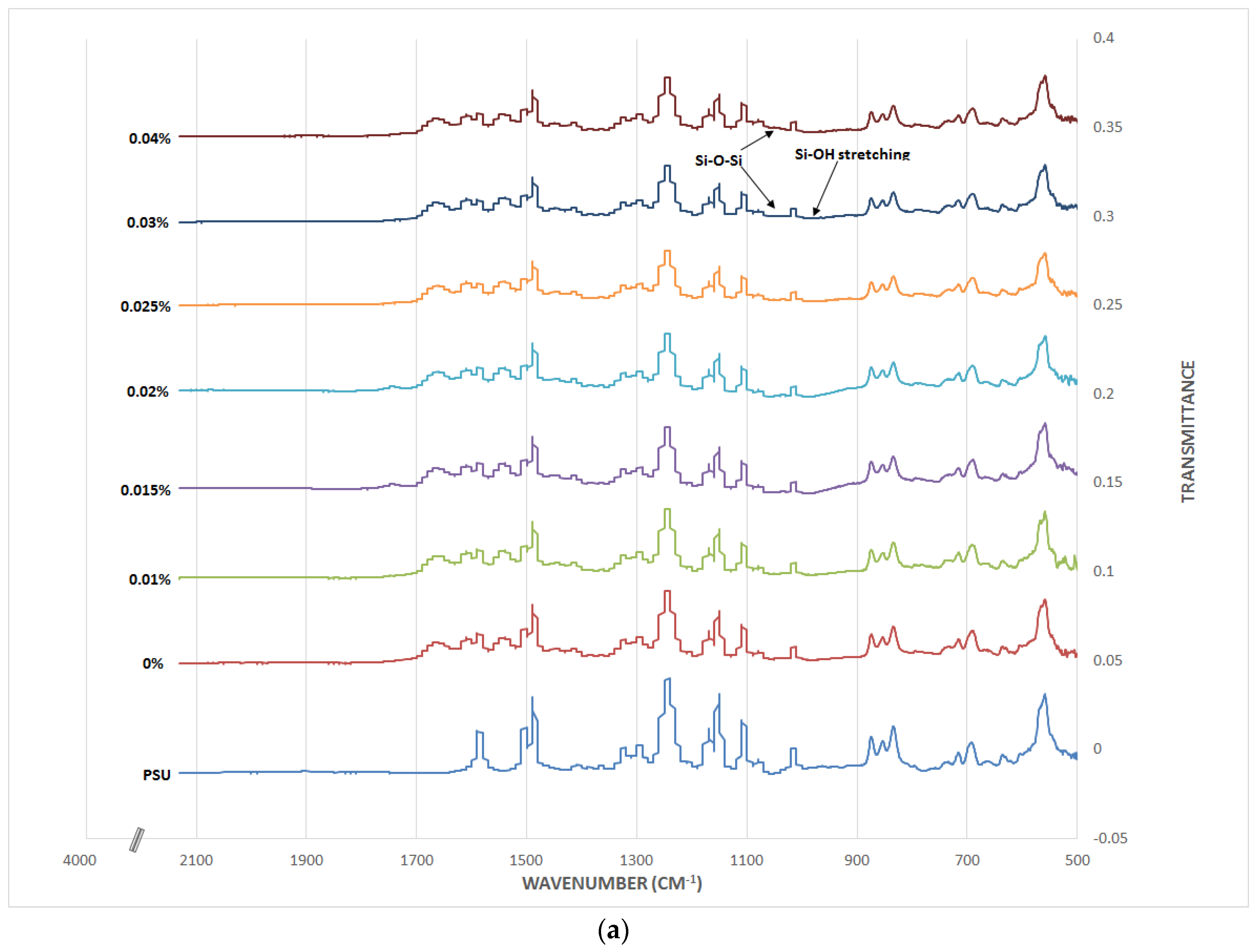
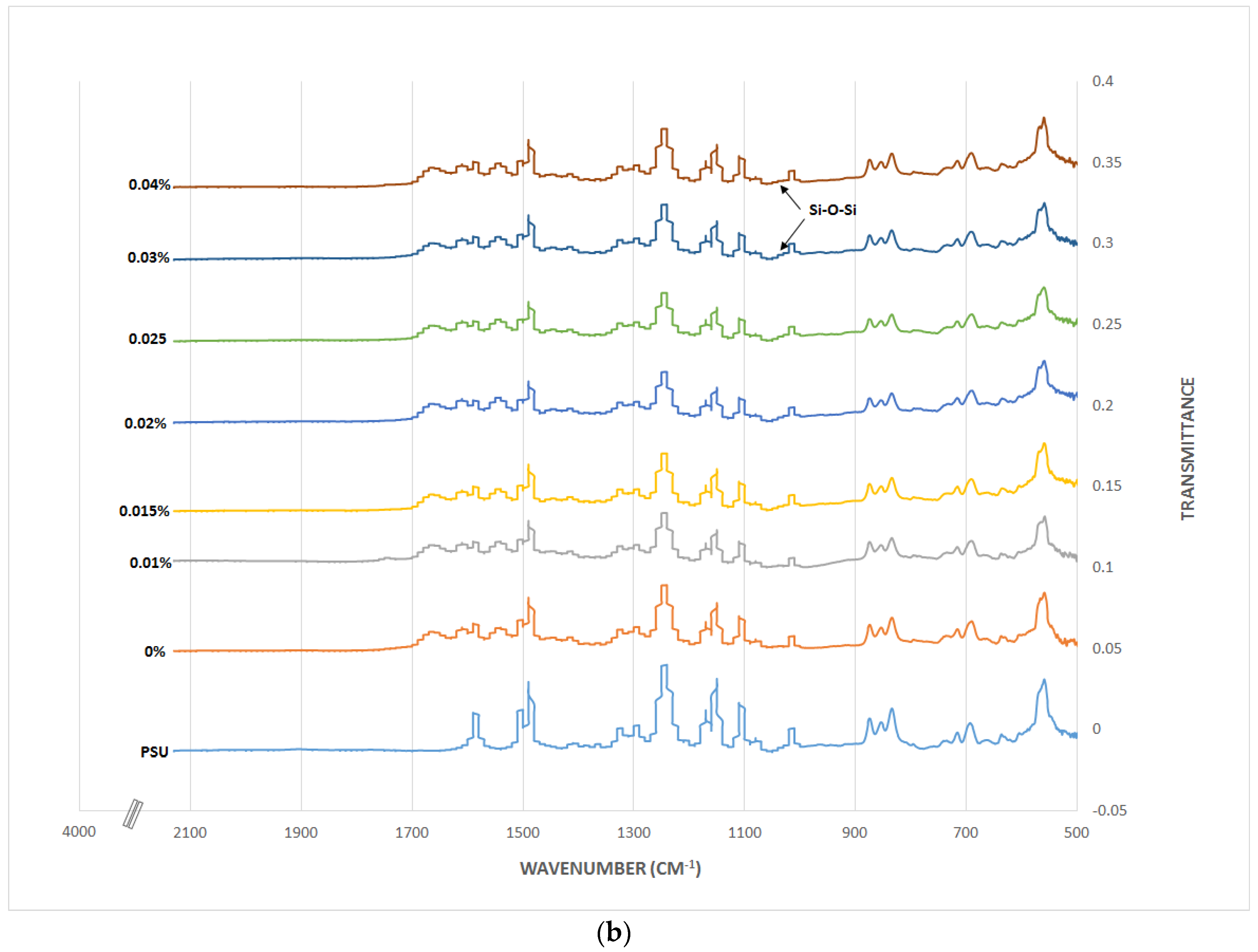
3.1. Characterizations of MCM-41 NPs
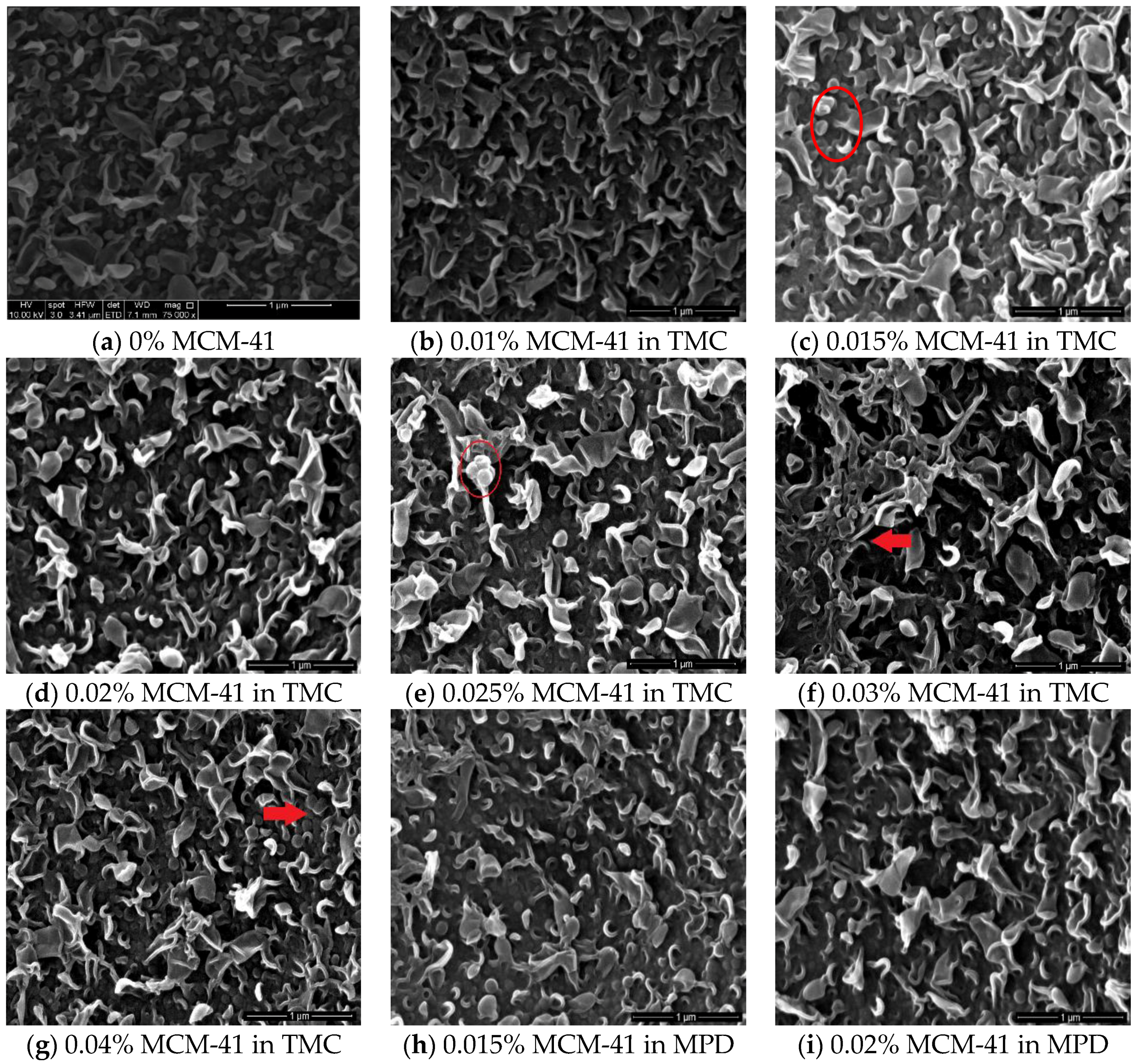
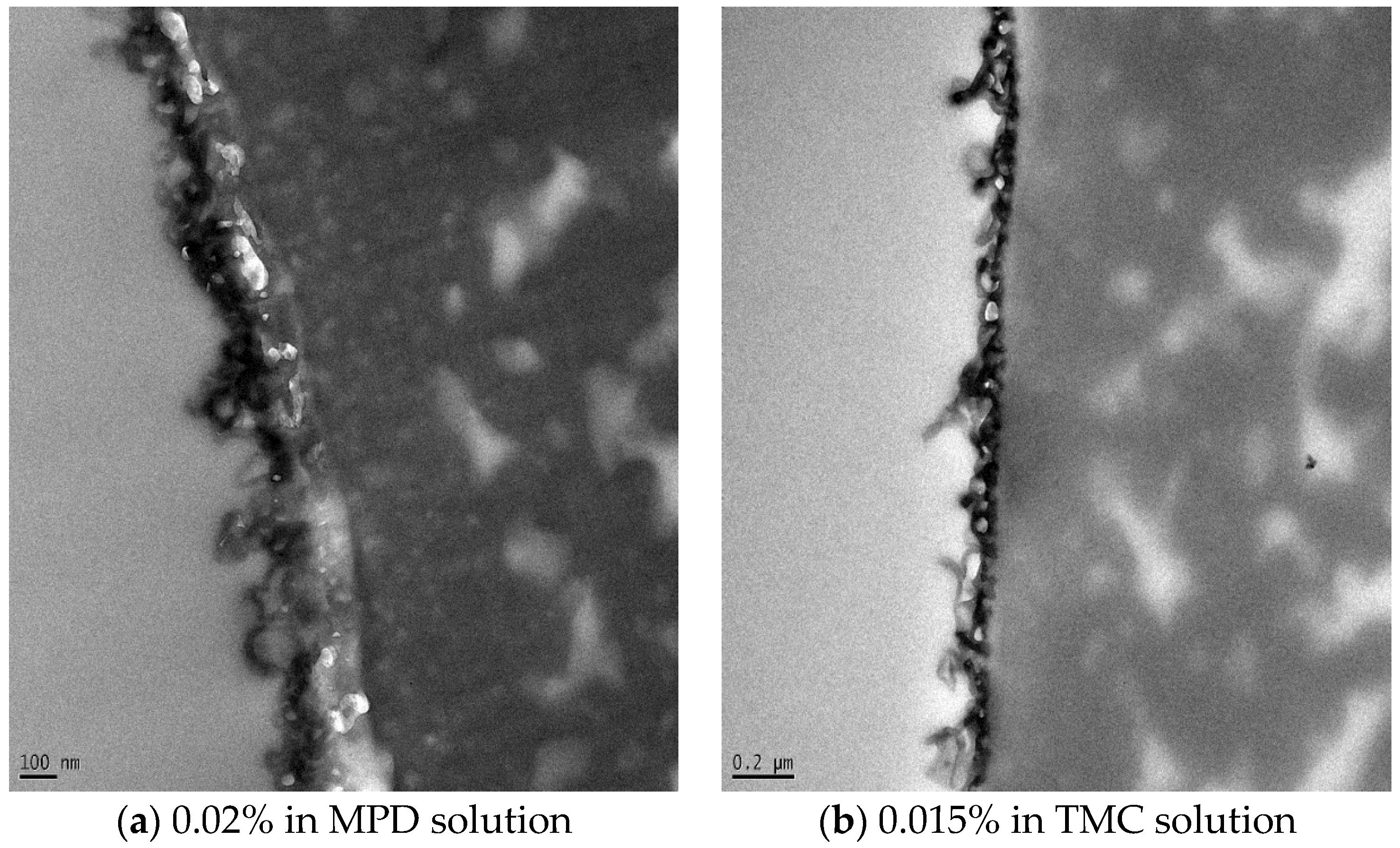
3.2. TFN Membrane Characterizations
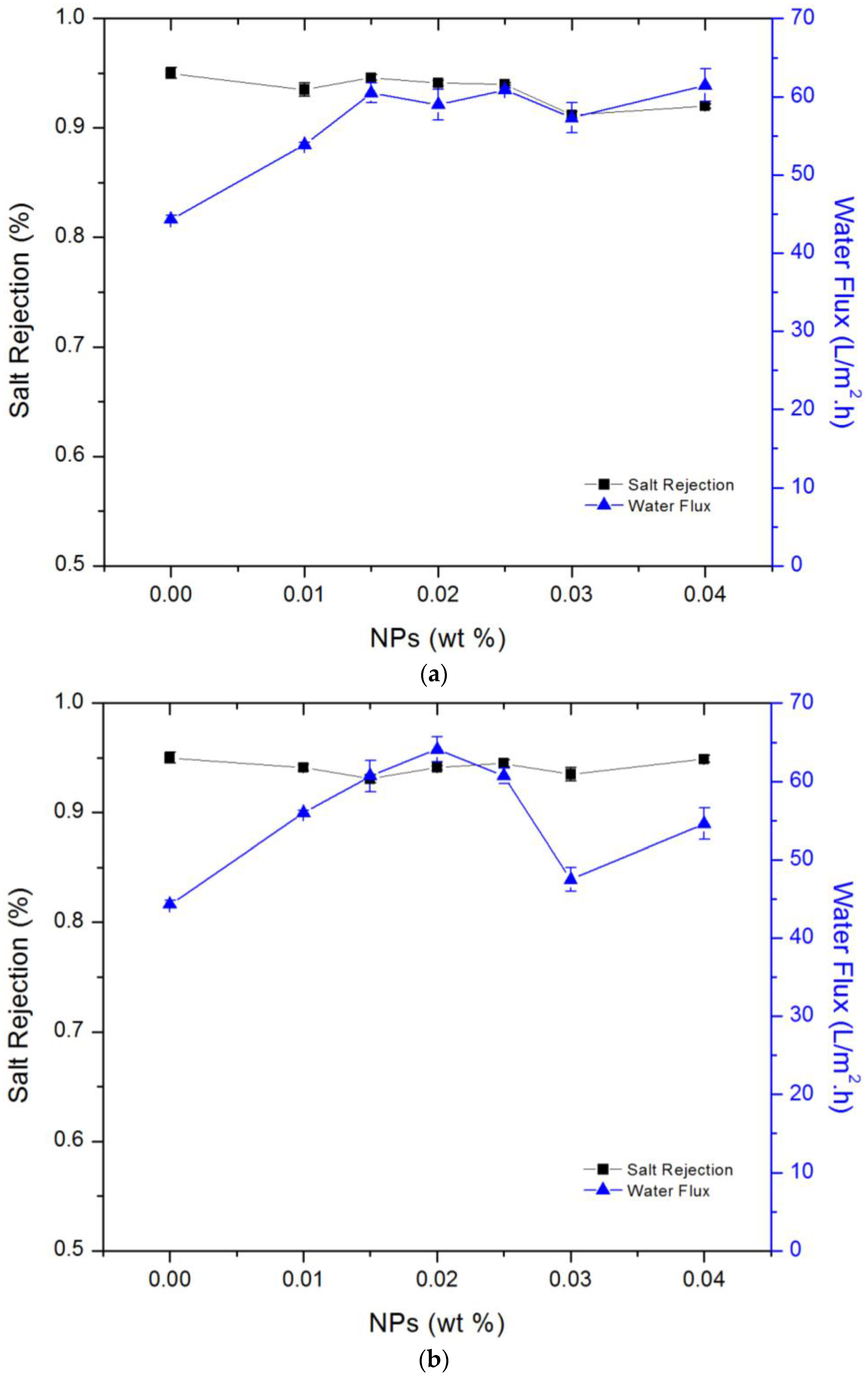
3.3. Membrane Salt Rejection and Water Flux
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of sea water desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, D.L.; Yip, N.Y.; Gilron, J.; Elimelech, M. Seawater desalination for agriculture by integrated forward and reverse osmosis: Improved product water quality for potentially less energy. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettouney, H.M.; El-Dessouky, H.T.; Faibish, R.S.; Gowin, P.J. Evaluating the economics of desalination. Chem. Eng. Prog. 2002, 98, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C. Distillation vs. membrane filtration: Overview of process evolutions in seawater desalination. Desalination 2002, 143, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, J.E. Interfacially Synthesized Reverse Osmosis Membrane. U.S. Patent 4,277,344, 7 July 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.J. Composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 83, 81–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yu, Q.; Deng, B. Preparation and characterization of polyamide thin-film composite membrane (PA-TFC) based on plasma-modified polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Kim, E.; Yang, J.; Deng, B. Fabrication of a novel thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane containing MCM-41 silica nanoparticles (NPs) for water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E.; Meng, D.; Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and superhydrophilic surfaces and materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9804–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, A. Flotation; McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C.; Ho, W.S.W. High-flux reverse osmosis membranes in corporate with NaY zeolite nanoparticles for brackish water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, M.L.; Ghosh, A.K.; Jawor, A.; Huang, X.; Hou, W.; Yang, Y.; Hoek, E. Influence of zeolite crystalsize on zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10139–10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.L.; Shintani, T.; Tsuru, T. Pre-seeding assisted synthesis of a high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposite membrane for water purification. New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qu, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Role of NaA zeolites in the interfacial polymerization process towards a polyamide nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8203–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qu, X.; Ji, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Hou, L. Acid and multivalent ion resistance of thin film nanocomposite RO membranes loaded with silicalite-1 nanozeolites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11343–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Qu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.H.; Chen, H.L.; Gao, C.J. Preparation and characterization of surface-modified zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes for desalination. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 34, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A.; Chikuni, M.; Kojima, E.; Kitamura, A.; Shimohigoshi, M.; Watanabe, T. Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces. Nature 1997, 388, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadzadeh, D.; Lau, W.J.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Rahbari-Sisakht, M. Synthesis and characterization of thin film nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane with hydrophilic nanocomposite support to reduce internal concentration polarization. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadaa, M.; Inouea, Y.; Akihitoa, G.; Nodab, I.; Torikaia, T.; Wataria, T.; Hotokebuchi, T. Apatite-forming ability of titanium compound nanotube thin films formed on a titanium metal plate in a simulated body fluid. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emadzadeha, D.; Laua, W.J.; Matsuura, T.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. The potential of thin film nanocomposite membrane in reducing organic fouling in forward osmosis process. Desalination 2014, 348, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettey, K.E.; Yee, M.Q.; Lee, D. Photocatalytic and conductive MWCNT/TiO2 nanocomposite thin films. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G. Metal-organic framework composite membranes: Synthesis and separation applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 232–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Optimizing polyamide thin film composite membrane covalently bonded with modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lee, N.; Oh, H.; Hwang, J.; Kim, S. Preparation and characterization of silica/polyamide-imide nanocomposite thin films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiraferri, A.; Kang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P.; Elimelech, M. Highly hydrophilic thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes functionalized with surface-tailored nanoparticles. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5044–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadav, G.L.; Singh, P.S. Synthesis of novel silica-polyamide nanocomposite membrane with enhanced properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Luo, Z.; Pang, W.; Fan, Y.; Chen, X.; Cui, F.Z. Dilute solution routes to various controllable morphologies of MCM-41 silica with a basic medium. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hexane Safety Data Sheet, version 5.6; Product No. 139386; Sigma-Aldrich: St. Louis, MO, USA, 23 May 2016.
- Hexane Safety Data Sheet; Cat No. AC326920000; Fisher Scientific: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2 April 2014.
- Isooctane Safety Data Sheet, version 5.1; Product No. IRMM442; Sigma-Aldrich: St. Louis, MO, USA, 3 November 2015.
- Isooctane Safety Data Sheet, version 1.5; Product No. 1116963; Chevron Phillips: The Woodlands, TX, USA, 17 May 2016.
- Viart, N.; Niznansky, D.; Rehspringer, J.L. Structural evolution of a formamide modified sol—Spectroscopic study. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wei, X.; Zhu, B. High flux positively charged nanofiltration membranes prepared by UV-initiated graft polymerization of methacrylatoethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DMC) onto polysulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboush, B.J.A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Arafat, H.A.; Narbaitz, R.M. Preparation of thin-film-composite polyamide membranes for desalination using novel hydrophilic surface modifying macromolecules. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.P.; Min, B.R. Polyamidethin-film nanofiltration nanoparticles. Desalination 2008, 219, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, H.A.; Chae, S.-R.; Lin, S.; Wiesner, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of a carbon nanotube/polymer nanocomposite membrane for water treatment. Desalination 2011, 272, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhu, G.; Deng, B. Graphene oxide (GO) enhanced polyamide (PA) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for water purification. Desalination 2016, 379, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Improving the performance of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by incorporation of modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.-H.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Yan, Y.; Subramani, A.; Huang, X.; Hurwitz, G.; Ghosh, A.K.; Jawor, A. Interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposites: A new concept for reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 294, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Isooctane | Hexane |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point (°C) | 99 | 69 |
| Flash Point (°C) | −12 | −26 |
| Evaporation Rate | 1 | 15.8 |
| Vapor Pressure (mmHg) | 88 (at 37.80 °C) | 256 (at 37.70 °C) |
| Vapor Density (Air = 1) | 3.94 | 2.97 |
| Relative Density (g/cm3) | 0.690 | 0.659 |
| Health Hazard | Less | Higher |
| Nanofiller | Optimum Loading (wt %) | Water Permeability (L/m2·h·kPa) | NaCl Rejection % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | 0.02 | 0.0310 | 94.1 ± 0.2 | This work |
| Graphene oxide | 0.015 | 0.0287 | 93.8 ± 0.6 | [37] |
| Multi wall nanotubes | 0.1 | 0.0175 | ~90 | [38] |
| Zeolite | 0.4 | 0.0137 | 93.9 ± 0.3 | [39] |
| Silica | 0.6 | 0.0087 | 95.1 | [25] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadhom, M.; Yin, J.; Deng, B. A Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane with MCM-41 Silica Nanoparticles for Brackish Water Purification. Membranes 2016, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6040050
Kadhom M, Yin J, Deng B. A Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane with MCM-41 Silica Nanoparticles for Brackish Water Purification. Membranes. 2016; 6(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadhom, Mohammed, Jun Yin, and Baolin Deng. 2016. "A Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane with MCM-41 Silica Nanoparticles for Brackish Water Purification" Membranes 6, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6040050
APA StyleKadhom, M., Yin, J., & Deng, B. (2016). A Thin Film Nanocomposite Membrane with MCM-41 Silica Nanoparticles for Brackish Water Purification. Membranes, 6(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6040050







