Analytical and Finite Element Modeling of Nanomembranes for Miniaturized, Continuous Hemodialysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Silicon Nanomembranes
2.2. Analytical Model
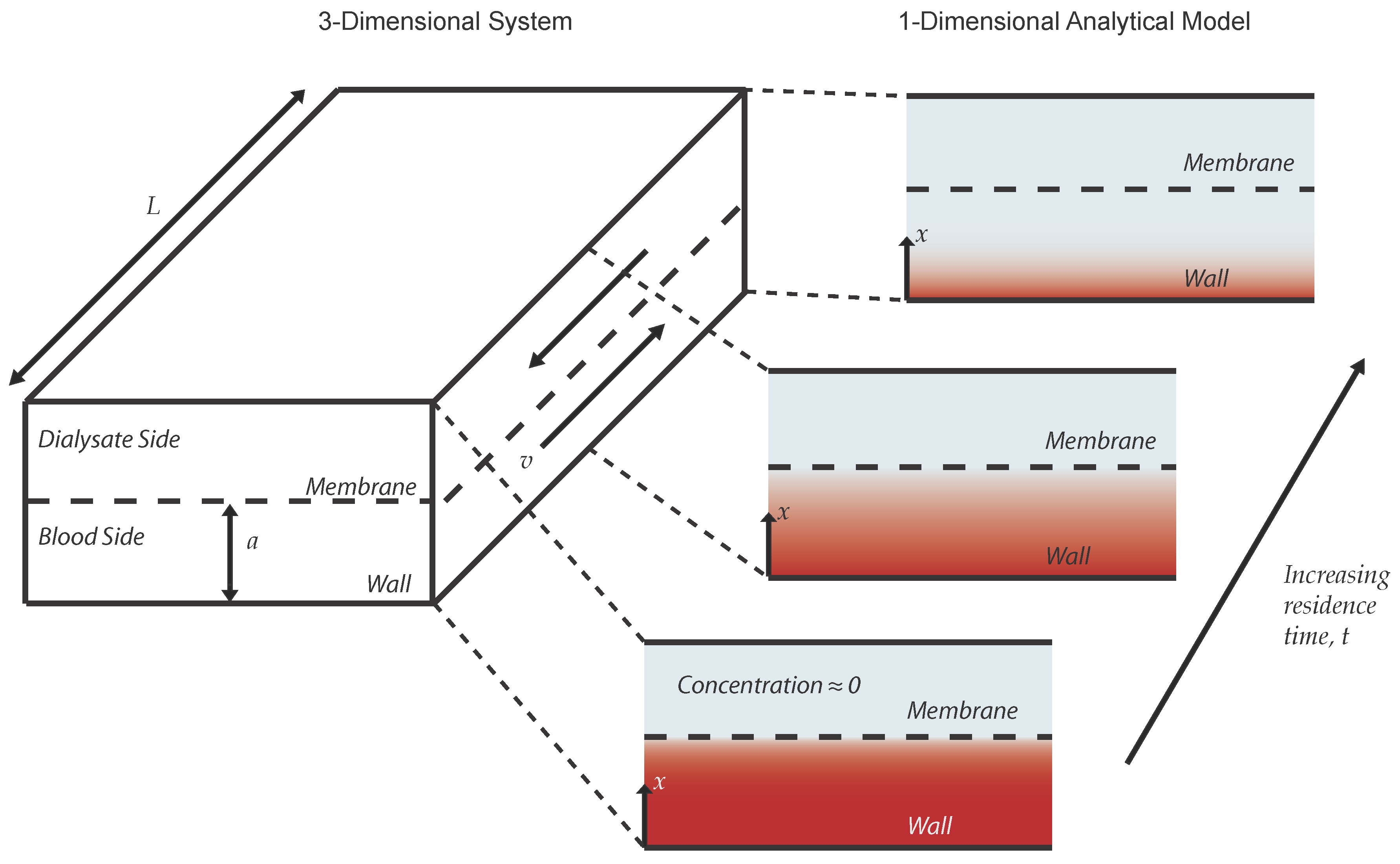
2.3. Experimental System and the Finite Element Model
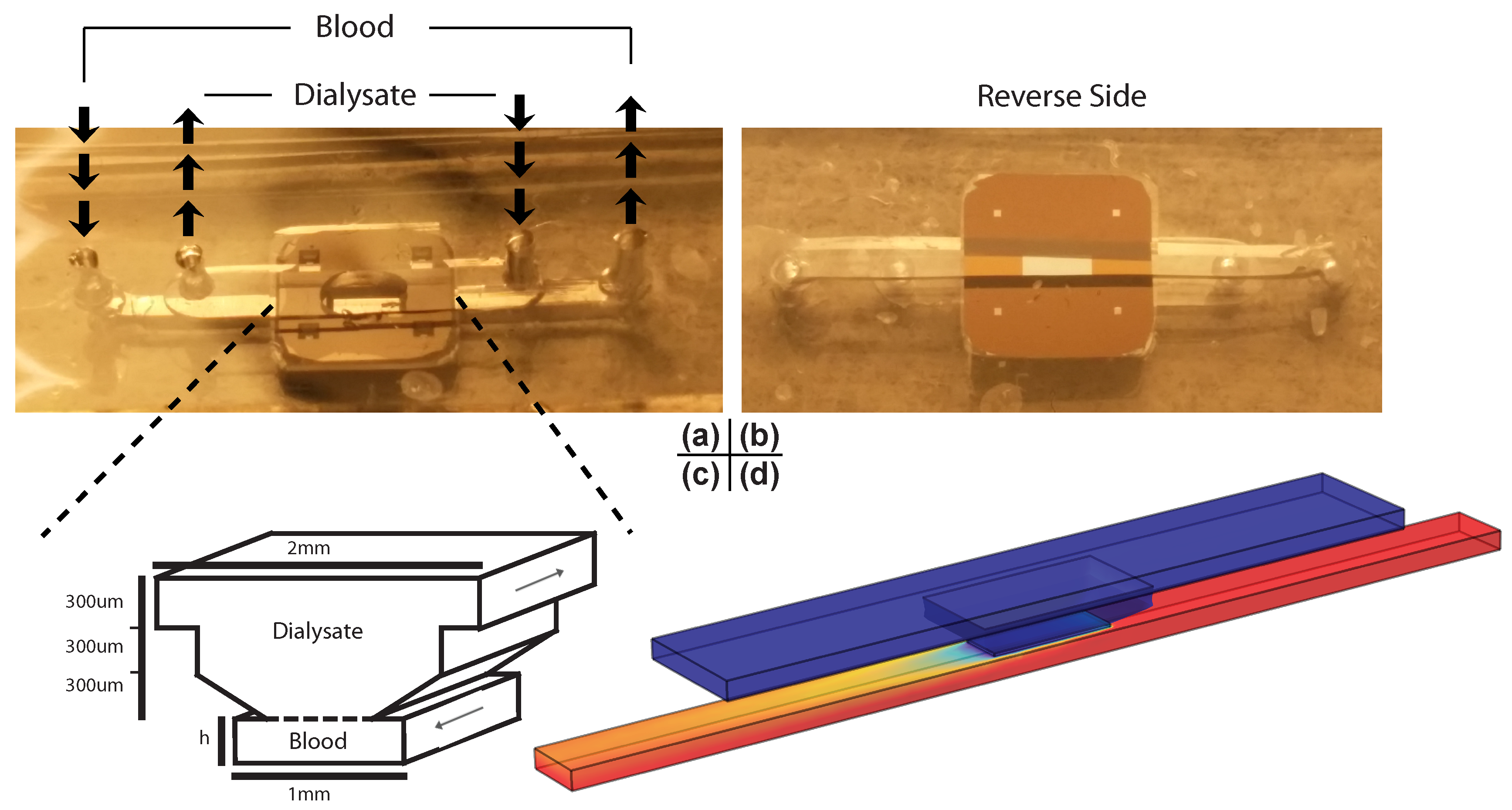
2.4. Prediction of Dialyzer Adequacy
2.5. Design Selection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of Models
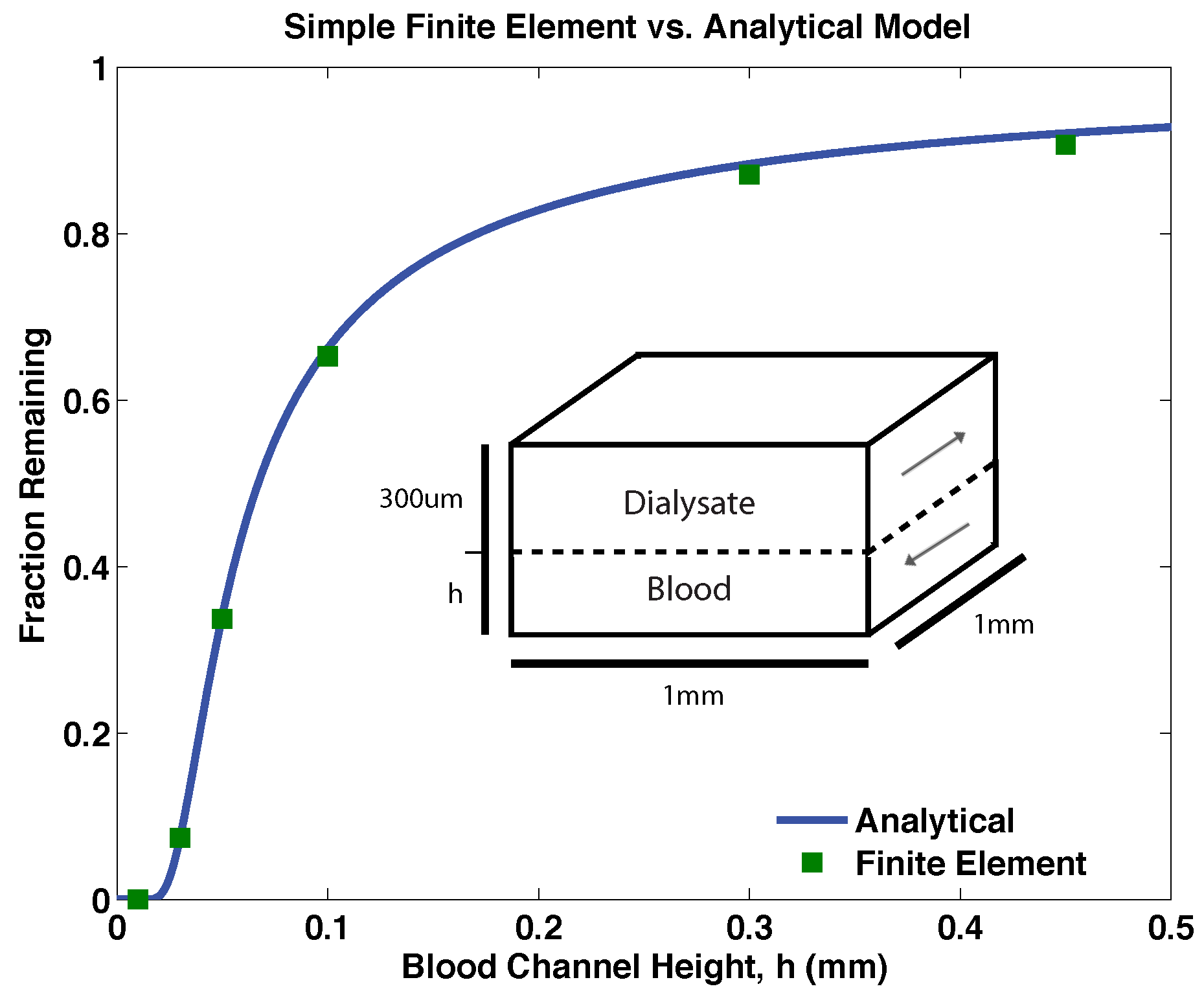
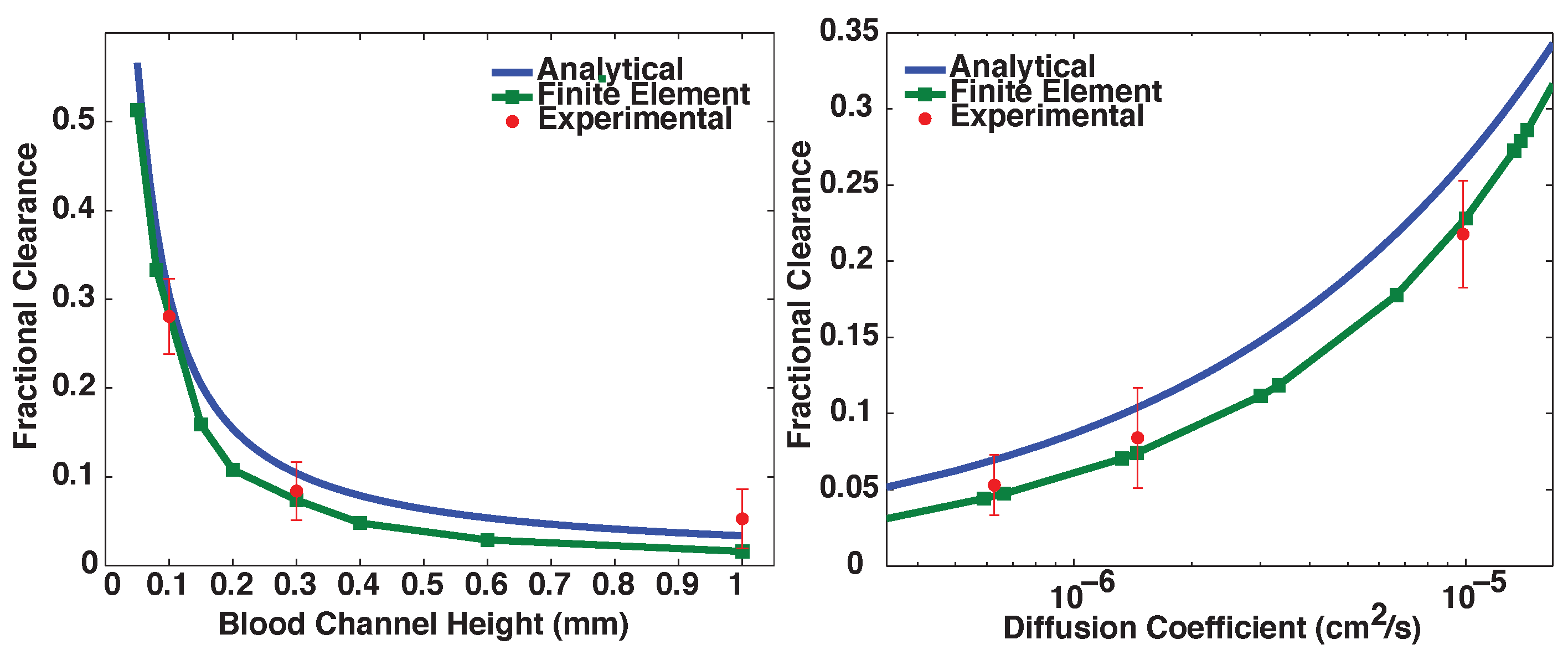
3.2. Proof-of-Principle Design
| Plasma Solute | (mmol/h) | Physiological Concentration (mM) | Target Clearance (L/h) | Steady-State Concentration (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] | ||||
| Creatinine | [19] | [18] | ||
| -microglobulin | [20] | [21] | ||
| Albumin | [22] | [18] |
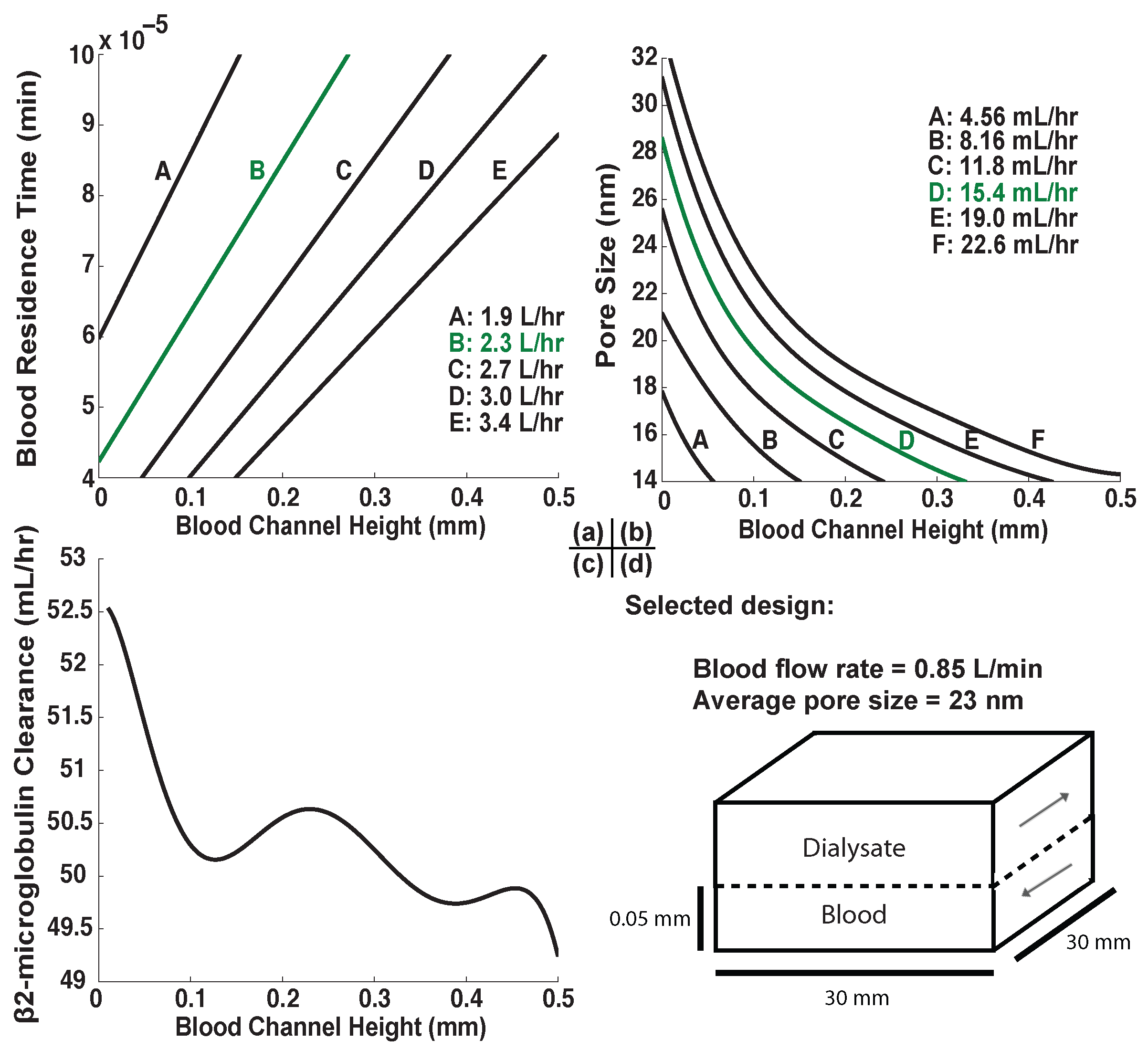
3.3. Finite Element Models of Practical Designs
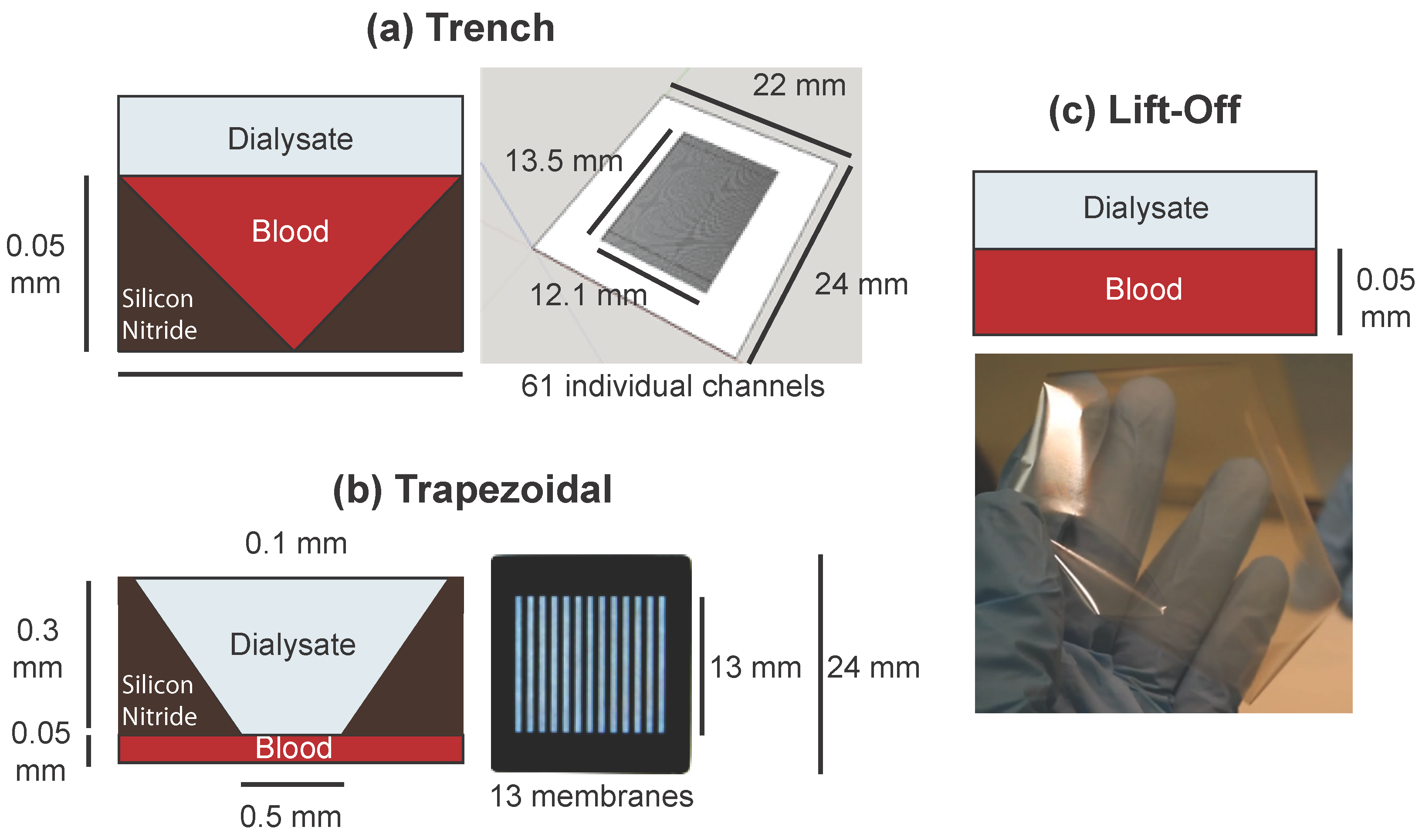
| Plasma Solute | Physiological | Trapezoidal | Trench | Lift-off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea | 24 | |||
| Creatinine | ||||
| -microglobulin | ||||
| Albumin |
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Renal Data System 2014 Annual Data Report: End Stage Renal Disease. In National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014.
- Fleming, G. Renal replacement therapy review: Past, present and future. Organogenesis 2011, 7, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Ikizler, T. Hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhondt, A.; Vanholder, R.; van Biesen, W.; Lameire, N. The removal of uremic toxins. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2000, 76, S47–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleyer, A.J.; Russell, G.B.; Satko, S.G. Sudden and cardiac death rates in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, R.N.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Murray, T.; Collins, A.J. Long interdialytic interval and mortality among patients receiving hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FHN Trial Group; Chertow, G.M.; Levin, N.W.; Beck, G.J.; Depner, T.A.; Eggers, P.W.; Gassman, J.J.; Gorodetskaya, I.; Greene, T.; James, S.; et al. In-center hemodialysis six times per week versus three times per week. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Weinhandl, E.D.; Liu, J.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Arneson, T.J.; Collins, A.J. Survival in daily home hemodialysis and matched thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Renal Data System 2013 Annual Data Report: End Stage Renal Disease, Chapter 3: Hospitalization. In National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013.
- Armignacco, P.; Lorenzin, A.; Neri, M.; Nalesso, F.; Garzotto, F.; Ronco, C. Wearable devices for blood purification: Principles, miniaturization, and technical challenges. Semin. Dial. 2015, 28, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.G.; Khire, T.S.; Lyubarskaya, Y.L.; Smith, K.J.; Desormeaux, J.P.; Taylor, J.G.; Gaborski, T.R.; Shestopalov, A.A.; Striemer, C.C.; McGrath, J.L. Ultrathin silicon membranes for wearable dialysis. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013, 20, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striemer, C.C.; Gaborski, T.R.; McGrath, J.L.; Fauchet, P.M. Charge- and size-based separation of macromolecules using ultrathin silicon membranes. Nature 2007, 445, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.; Clark, A.J.; Fang, D.; Gaborski, T.; Striemer, C.; Fauchet, P.; McGrath, J. An experimental and theoretical analysis of molecular separations by diffusion through ultrathin nanoporous membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DesOrmeaux, J.; Winans, J.; Wayson, S.; Gaborski, T.; Khire, T.; Striemer, C.; McGrath, J. Nanoporous silicon nitride membranes fabricated from porous nanocrystalline silicon templates. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10798–10805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Chan, C.; Khire, T.; Marsh, G.; Clark, A.J.; Waugh, R.; McGrath, J. Highly permeable silicon membranes for shear free chemotaxis and rapid cell labeling. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.; Carter, R.; McNabb, K.; DesOrmeaux, J.; Striemer, C.; Winans, J.; Gaborski, T. Lift-off of large-scale ultrathin nanomembranes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopot, F.; Kotyk, P.; Bláha, J.; Válek, A. Analysis of the urea generation rate and the protein catabolic rate in hemodialyzed patients. Artif. Organs 1995, 19, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Master Surgeon Reference Tables. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6dVDRW1Ss (accessed on 3 December 2015).
- Medscape: Creatinine. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6dVDhenk2 (accessed on 3 December 2015).
- Karlsson, F.A.; Wibell, L.; Evrin, P.E. beta 2-Microglobulin in clinical medicine. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 1980, 154, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.J.; Flye, M.; Javadpour, N. Serum beta 2 microglobulin levels in patients with testicular cancer. Urology 1980, 16, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medscape: Hypoalbuminemia. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6dVDpwKJ7 (accessed on 3 December 2015).
- Liabeuf, S.; Drueke, T.B.; Massy, Z.A. Protein-bound uremic toxins: New insight from clinical studies. Toxins 2011, 3, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumtaz, A.; Anees, M.; Bilal, M.; Ibrahim, M. Beta-2 microglobulin levels in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2010, 21, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liabeuf, S.; Barreto, D.V.; Barreto, F.C.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Schepers, E.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A.; European Uraemic Toxin Work Group. Free p-cresylsulphate is a predictor of mortality in patients at different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2010, 25, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, J.M.; Pandeya, S.; Humen, D.P.; Krivitski, N.; Lindsay, R.M. Arteriovenous fistula-associated high-output cardiac failure: A review of mechanisms. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, e17–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, N.A.; Okkels, F.; Bruus, H. Reexamination of Hagen-Poiseuille flow: Shape dependence of the hydraulic resistance in microchannels. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2005, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivitski, N.M.; Kislukhin, V.V.; Snyder, J.W.; MacGibbon, D.R.; Kuznetsova, O.A.; Reasons, A.M.; Depner, T.A. In vivo measurement of hemodialyzer fiber bundle volume: Theory and validation. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burgin, T.; Johnson, D.; Chung, H.; Clark, A.; McGrath, J. Analytical and Finite Element Modeling of Nanomembranes for Miniaturized, Continuous Hemodialysis. Membranes 2016, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6010006
Burgin T, Johnson D, Chung H, Clark A, McGrath J. Analytical and Finite Element Modeling of Nanomembranes for Miniaturized, Continuous Hemodialysis. Membranes. 2016; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurgin, Tucker, Dean Johnson, Henry Chung, Alfred Clark, and James McGrath. 2016. "Analytical and Finite Element Modeling of Nanomembranes for Miniaturized, Continuous Hemodialysis" Membranes 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6010006
APA StyleBurgin, T., Johnson, D., Chung, H., Clark, A., & McGrath, J. (2016). Analytical and Finite Element Modeling of Nanomembranes for Miniaturized, Continuous Hemodialysis. Membranes, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes6010006







