Characterization of Polyethylene-Graft-Sulfonated Polyarylsulfone Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
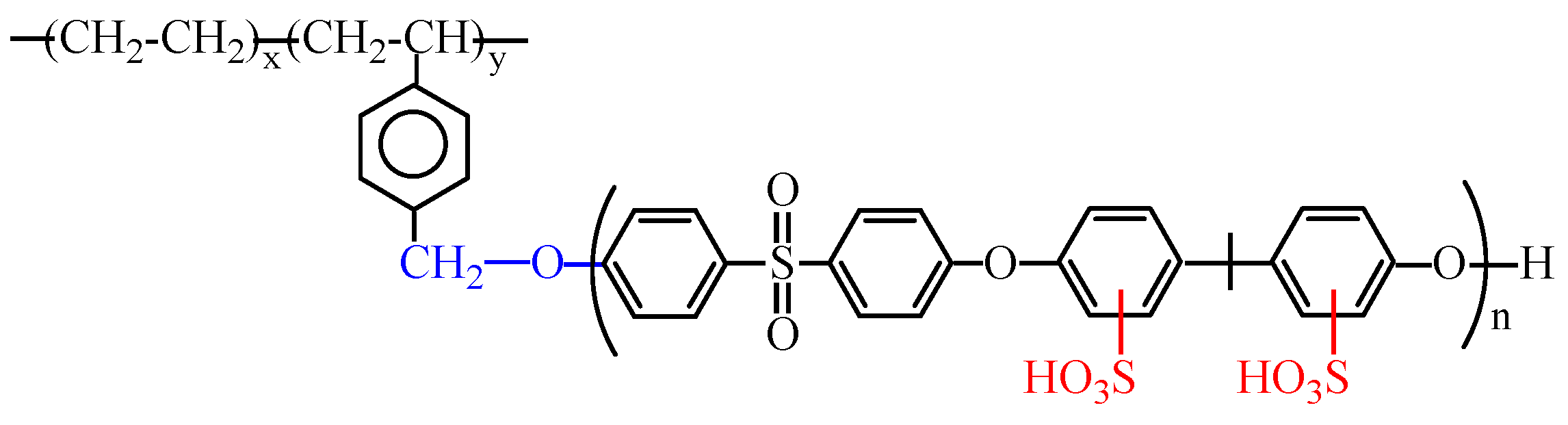
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology of PE-g-s-PAES PEMs
| Sample | No. of s-PAES Per PE | s-PAES (vol %/wt %) | IEC (mmol/g) | Hydration Number (λ) | Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Young’s Modulus (Mpa] | Elongation at Break (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s-PAE | PE-g-s-PAES | |||||||
| A-1 | 4.6 | 25/30 | 3.67 | 1.10 | 11 | 22 ± 5 | 870 ± 100 | 20.8 ± 0.3 |
| A-2 | 7.7 | 35/42 | 3.43 | 1.44 | 12 | 29 ± 5 | 1150 ± 100 | 10.8 ± 0.3 |
| A-3 | 9.4 | 40/47 | 3.45 | 1.62 | 12 | 33 ± 5 | 1290 ± 100 | 7.2 ± 0.3 |
| A-4 | 14.5 | 51/57 | 3.39 | 1.93 | 13 | 35 ± 5 | 1480 ± 100 | 5.7 ± 0.3 |
| BPSH30 | – | – | 1.3 | 1.3 | 10 | – | – | – |
| BPSH40 | – | – | 1.7 | 1.7 | 13 | – | – | – |
| Nafion117 | – | – | 0.91 | 0.91 | 15 | 14 ± 2 | 120 ± 10 | 208 ± 13 |

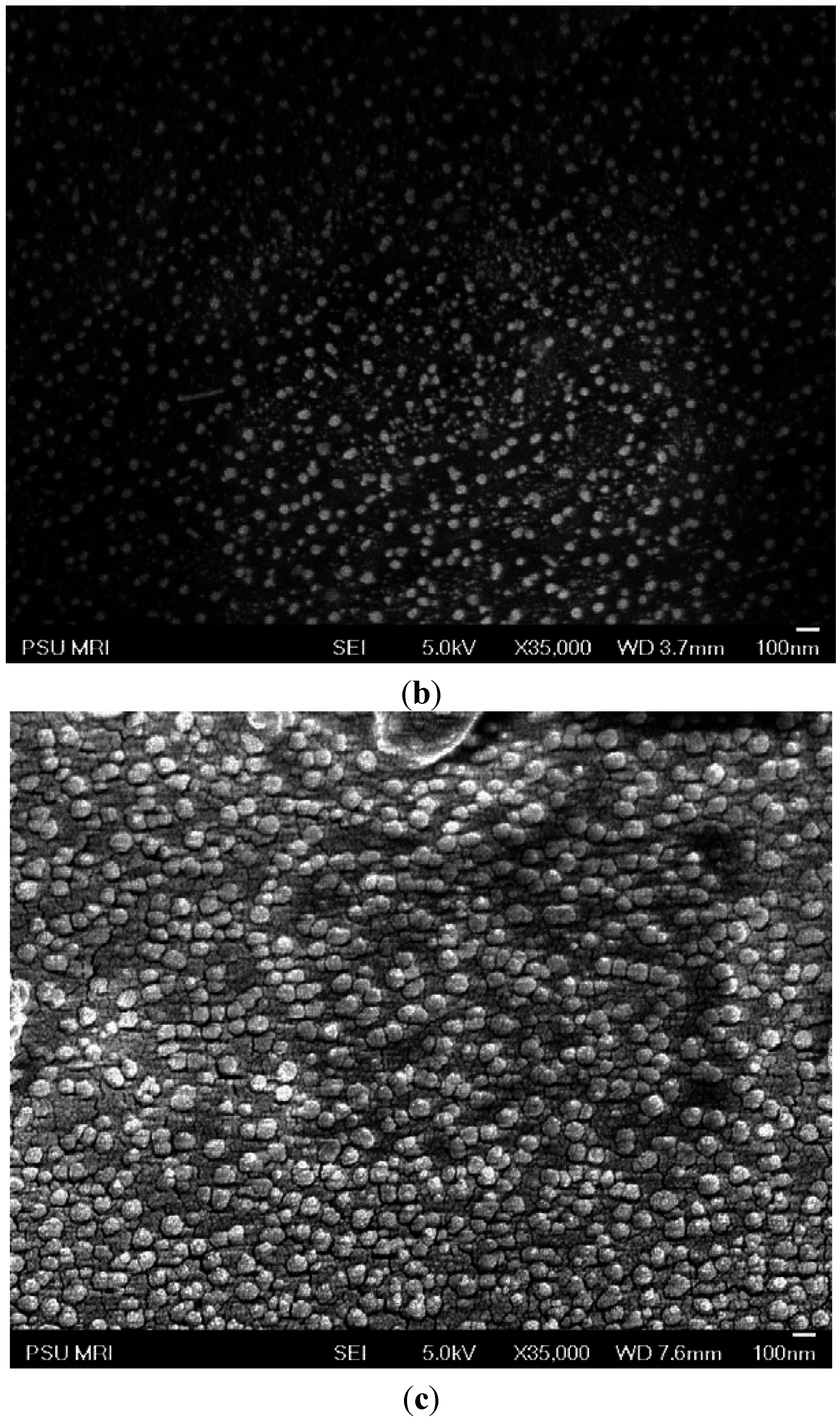
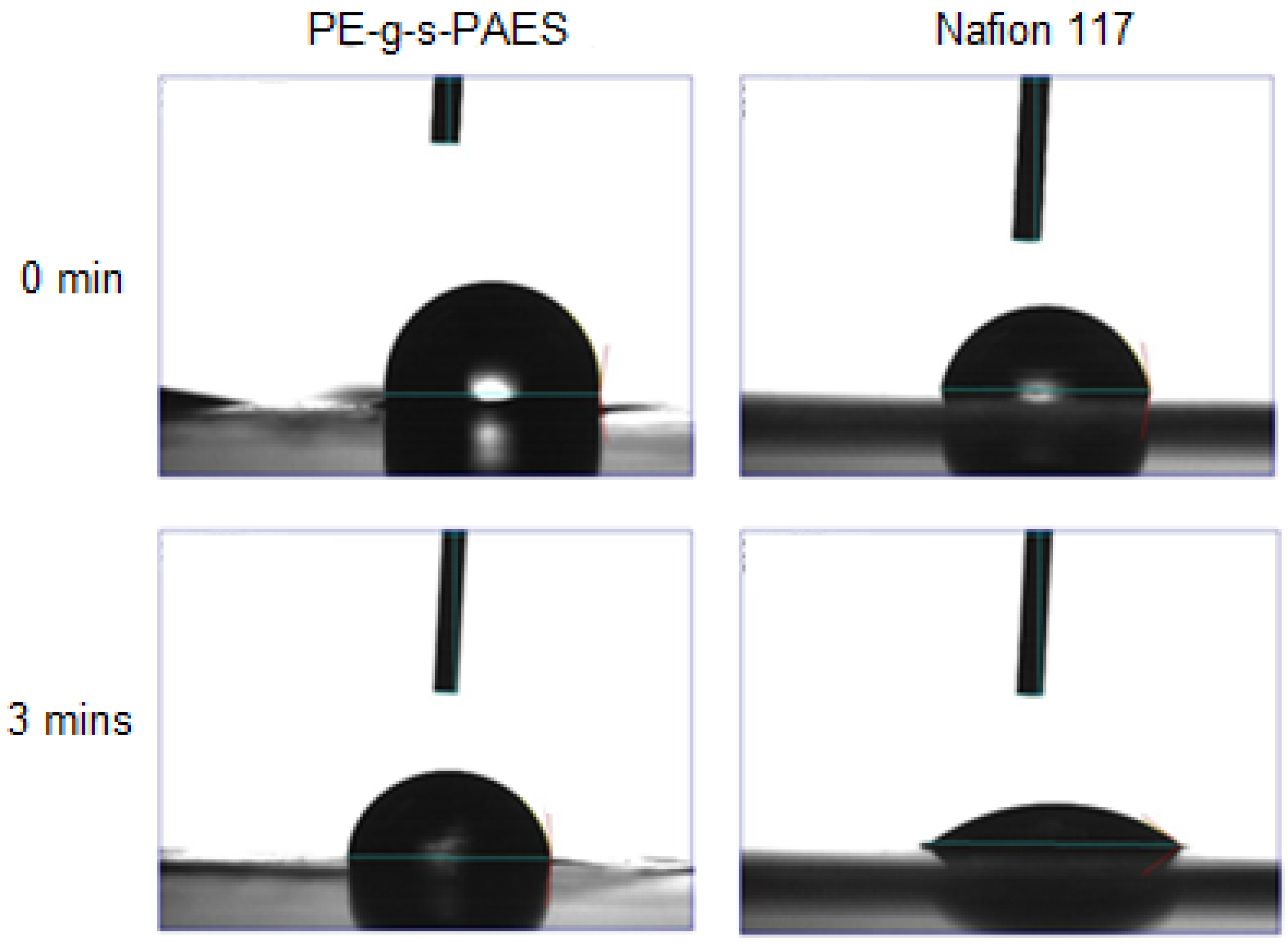
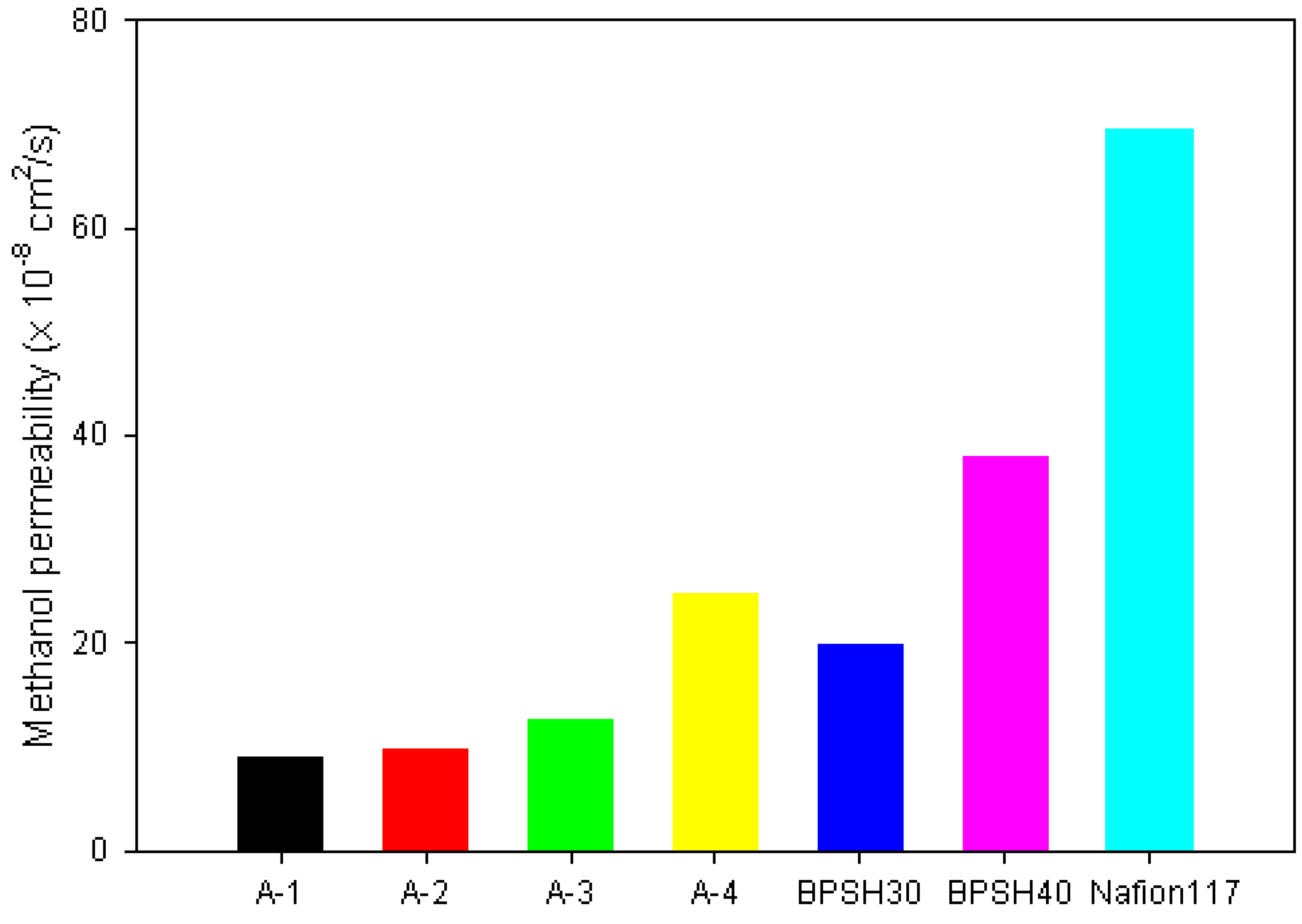
2.2. Methanol Permeability and Selectivity of PE-g-s-PAES PEMs
| Sample | In-Plane Conductivity (mS/cm) | Through-Plane Conductivity (mS/cm) | Methanol Permeability (×10−8 cm2/s) | Selectivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-1 | 30 | 34 | 9.02 | 3.77 |
| A-2 | 42 | 57 | 9.87 | 5.78 |
| A-3 | 63 | 85 | 12.7 | 6.69 |
| A-4 | 85 | 131 | 24.9 | 5.26 |
| BPSH30 | 30 | – | 20 | 1.5 |
| BPSH40 | 75 | – | 38 | 1.97 |
| Nafion 117 | 77 | 81 | 69.7 | 1.16 |
2.3. Chemical Stability of PE-g-s-PAES PEMs
| Sample | IEC (mmol/g) | Residual Weight % after Fenton Test for 1 h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80 °C | 95 °C | ||
| PE-co-p-MS | – | 100 | 100 |
| PE-co-p-MS-Br | – | 100 | 100 |
| PE-g-PAES | – | 100 | 100 |
| PE-g-s-PAES, A-1 (30 wt %) | 1.1 | 100 | 99.6 |
| PE-g-s-PAES, A-3 (47 wt %) | 1.62 | 98.7 | 96.9 |
| PE-g-s-PAES, A-4 (56 wt %) | 1.93 | 97.5 | 95.2 |
| Nafion 117 | 0.91 | 96.4 | 93.7 |
| X30Y8 | 1.62 | 40 | – |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Membrane Characterization
3.3. Methanol Permeability

3.4. Electrochemical Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- James, L.; Andrew, D. Fuel Cell Systems Explained, 2nd ed.; Johns Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Apanel, G.; Johnson, E. Direct methanol fuel cells—Ready to go commercial? Fuel Cells Bull. 2004, 2004, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Army lab awards MTI Micro DMFC contract. Fuel Cells Bull. 2004, 2004, 9–10.
- Suominen., A.; Tuominen, A. Analyzing the direct methanol fuel cell technology in portable applications by a historical and bibliometric analysis. J. Bus. Chem. 2010, 7, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarudin, S.K.; Achmad, F.; Daud, W.R.W. Overview on the application of direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) for portable electronic devices. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 6902–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Springer, T.E.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Gottesfeld, S. Methanol transport through nation membranes. electro-osmotic drag effects on potential step measurements. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, A.; Barragán, V.M. A review of the state-of-the-art of the methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 1999, 84, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.K.; Thombre, S.B. Barriers to commercialization of passive direct methanol fuel cells: A review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 6000–6007. [Google Scholar]
- Curtin, D.E.; Lousenberg, R.D.; Henry, T.J.; Tangeman, P.C.; Tisack, M.E. Advanced materials for improved PEMFC performance and life. J. Power Sources 2004, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubner, G.; Roduner, E. EPR investigation of HO/radical initiated degradation reactions of sulfonated aromatics as model compounds for fuel cell proton conducting membranes. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, H.; Lindén, L.Å.; Rabek, J.F. Photo-oxidative degradation of poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) in the presence of concentrated hydroxy peroxide: The role of hydroxy (HO.) and hydroperoxy (HO2.) radicals. Polymer Degrad. Stab. 1995, 47, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.C.H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pianca, M.; Barchiesi, E.; Esposto, G.; Radice, S. End groups in fluoropolymers. J. Fluor. Chem. 1999, 95, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, W.H.; Lee, H.K. Physical and electrochemical properties of Nafion/polypyrrole composite membrane for DMFC. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chalkova, E.; Lee, J.K.; Fedkin, M.V.; Komarneni, S.; Lvov, S.N. Composite membranes with sulfonic and phosphonic functionalized inorganics for reduced relative humidity PEM fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, B690–B697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, Y.S.; Jung, B. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated polyimide membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 220, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Wainright, J.S.; Savinell, R.F.; Litt, M. A direct methanol fuel cell using acid-doped polybenzimidazole as polymer electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1996, 26, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.; Hong, Y.T.; Kim, S.C. Phase separation and morphology control of polymer blend membranes of sulfonated and nonsulfonated polysulfones for direct methanol fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. Compositional effect on the properties of sulfonated and nonsulfonated polymer blend membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.H.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, S.-Y. Nanoscale phase separation of sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)/poly(ether sulfone) semi-IPNs for DMFC membrane applications. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5244–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.K.; Shin, C.; Kim, S.C. Polymer blend membranes of sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, X.; Lvov, S.N.; Chung, T.C.M. Synthesis of polyethylene-based proton exchange membranes containing PE backbone and sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) side chains for fuel cell applications. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickner, M.A.; Fujimoto, C.H.; Cornelius, C.J. Transport in sulfonated poly(phenylene)s: Proton conductivity, permeability, and the state of water. Polymer 2006, 47, 4238–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Wang, F.; Hickner, M.; McCartney, S.; Hong, Y.T.; Harrison, W.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; McGrath, J.E. Effect of acidification treatment and morphological stability of sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymer proton-exchange membranes for fuel-cell use above 100 °C. J. Polymer Sci. Part B 2003, 41, 2816–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Hickner, M.A.; Dong, L.; Pivovar, B.S.; McGrath, J.E. Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymer proton exchange membranes: Composition and morphology effects on the methanol permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Jung, B. Proton conductivities and methanol permeabilities of membranes made from partially sulfonated polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 207, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivovar, B.S.; Wang, Y.; Cussler, E.L. Pervaporation membranes in direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 154, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletzky, P.; Bauer, R.; Lahnsteiner, J.; Pouresmael, B. Immobilisation of iron ions on nafion® and its applicability to the photo-fenton method. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, A.; Silva, R.F.; de Francesco, M.; Giorgi, L. Nafion degradation in PEFCs from end plate iron contamination. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, H.J.H. LXXIII—Oxidation of tartaric acid in presence of iron. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1894, 65, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.J.; Paulus, U.A.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. The oxygen reduction reaction on a Pt/carbon fuel cell catalyst in the presence of chloride anions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 508, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, B.; Yoda, T.; Miyatake, K.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. Proton-conductive aromatic ionomers containing highly sulfonated blocks for high-temperature-operable fuel cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Du, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Okamoto, K.-I. Sulfonated polyimides with flexible aliphatic side chains for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikashige, Y.; Chikyu, Y.; Miyatake, K.; Watanabe, M. Poly(arylene ether) ionomers containing sulfofluorenyl groups for fuel cell applications. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7121–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.K.; Zhang, G.; Nam, C.; Chung, T.C.M. Characterization of Polyethylene-Graft-Sulfonated Polyarylsulfone Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes 2015, 5, 875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040875
Kim HK, Zhang G, Nam C, Chung TCM. Characterization of Polyethylene-Graft-Sulfonated Polyarylsulfone Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes. 2015; 5(4):875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040875
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyung Kyu, Gang Zhang, Changwoo Nam, and T.C. Mike Chung. 2015. "Characterization of Polyethylene-Graft-Sulfonated Polyarylsulfone Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Applications" Membranes 5, no. 4: 875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040875
APA StyleKim, H. K., Zhang, G., Nam, C., & Chung, T. C. M. (2015). Characterization of Polyethylene-Graft-Sulfonated Polyarylsulfone Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Applications. Membranes, 5(4), 875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040875






